Definition
Benign, bone-forming neoplasm
- small nidus of neoplastic tissue
- surrounded by a wide zone of mature, reactive bone
Epidemiology
10% of benign bone tumours
Young people aged 5 - 25
Male:Female 3:1
Clinical
Night pain
Pain secondary to prostaglandin production
Relieved by aspirin / NSAIDS
Site
Femur and tibia (50%)
Posterior elements spine (10%)
Hands and feet
Cortical / Medullary
Extra-articular / Intra-articular
Natural history
Gradual resolution with time
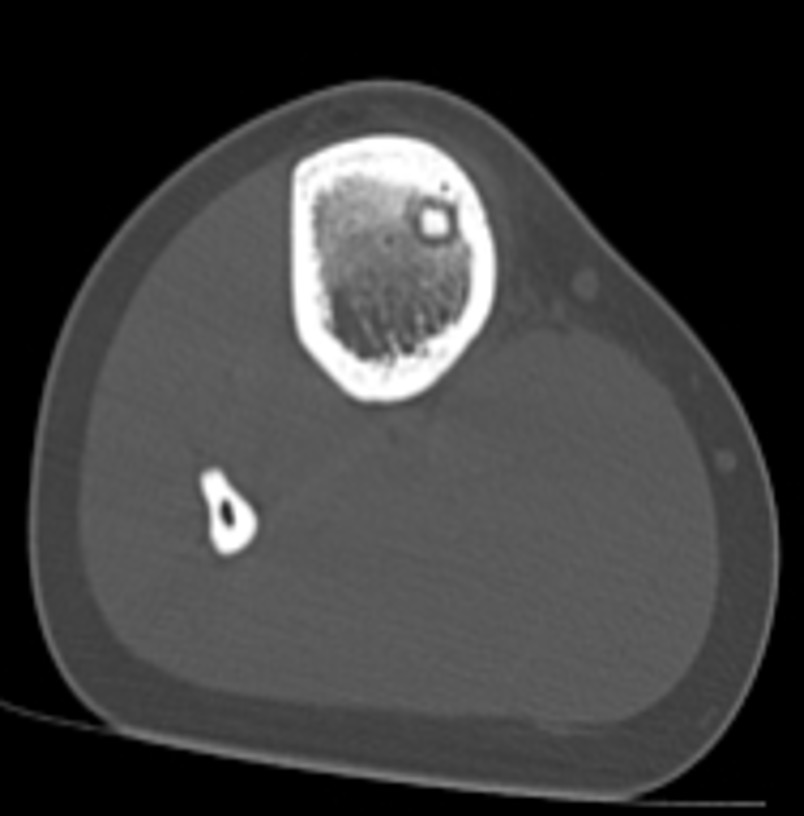
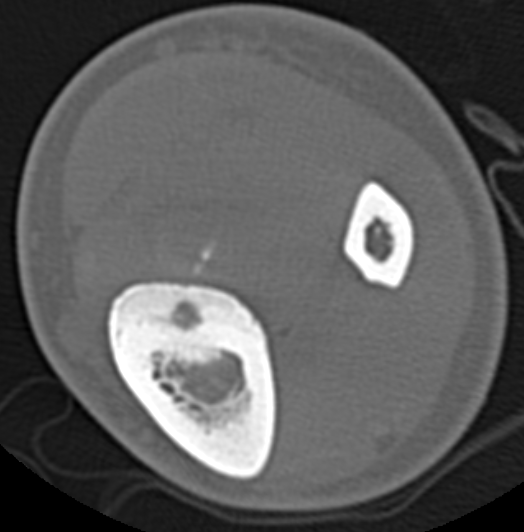
X-ray
Sclerotic bone
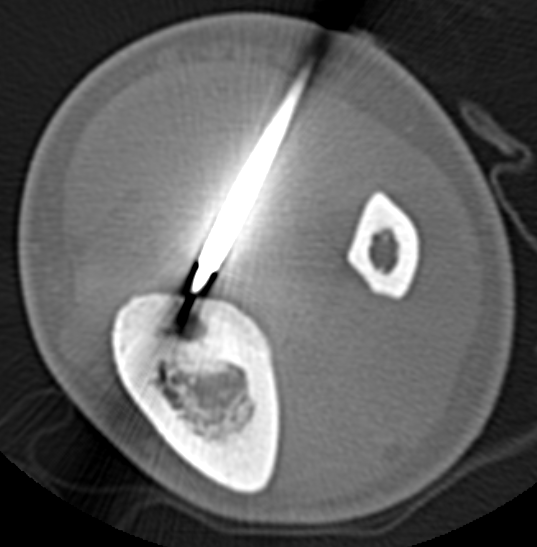
CT
Best investigation
- lucent nidus surrounded by dense bone
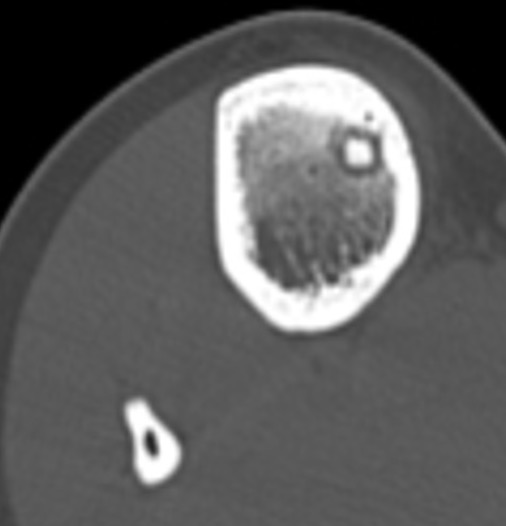
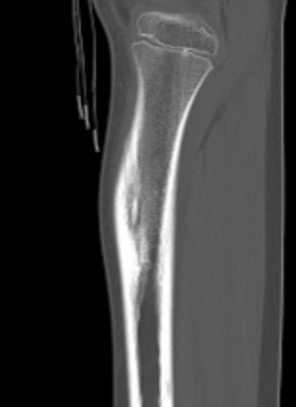
Osteoid osteoma tibia
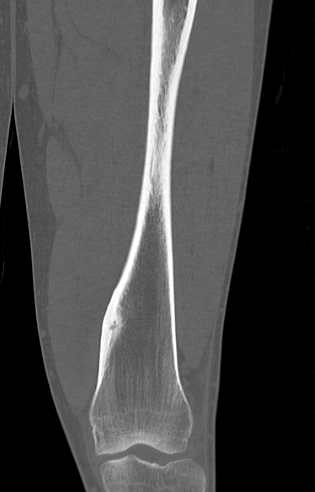
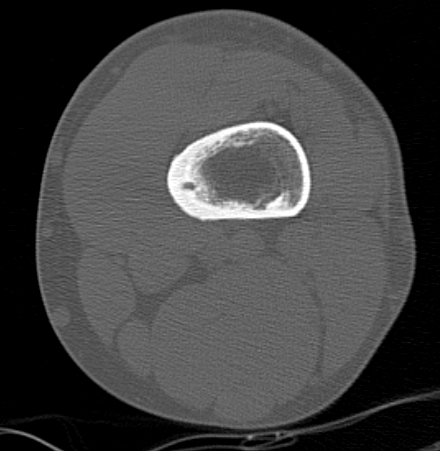
Osteoid osteoma femur
MRI
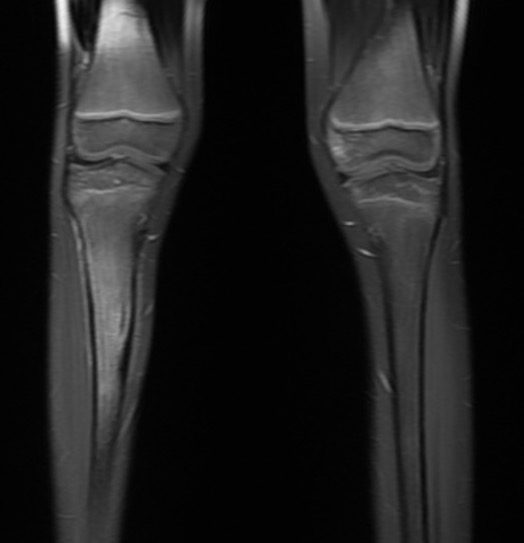
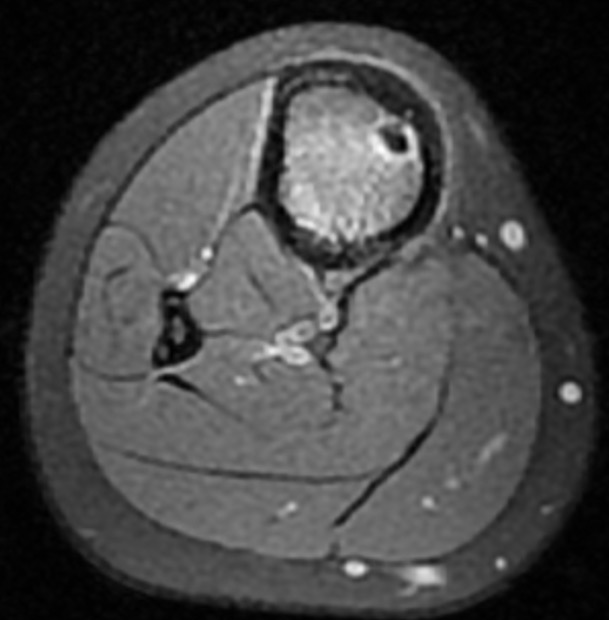
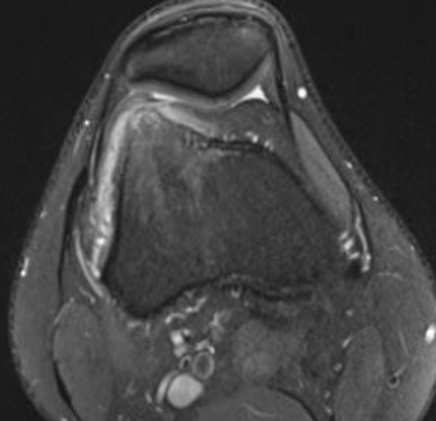
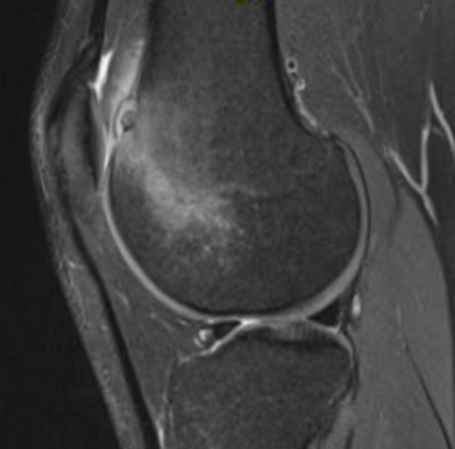
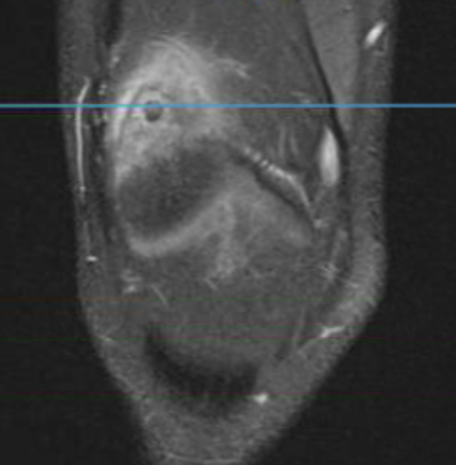
Pathology
Gross
Nidus
- < 1 cm diameter
- red - pink
- surrounded by sclerotic bone
Histology
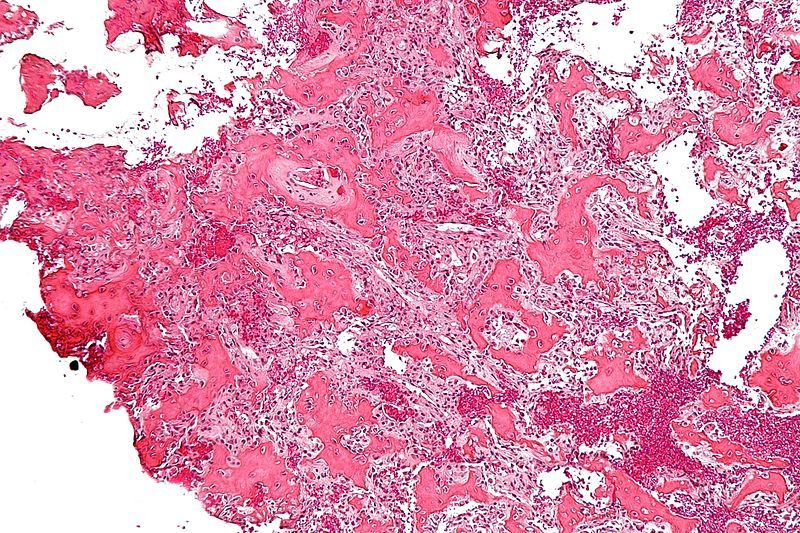
Nidus - highly vascularised osteoid
Rim - osteoblasts and thickened trabecular bone
Differential Diagnosis
Brodies abscess
Osteoblastoma - nidus > 1.5 cm
Stress fracture
Management
Options
Prolonged NSAIDS - can take years to resolve
Radiofrequency ablation
En-bloc excision / currettage
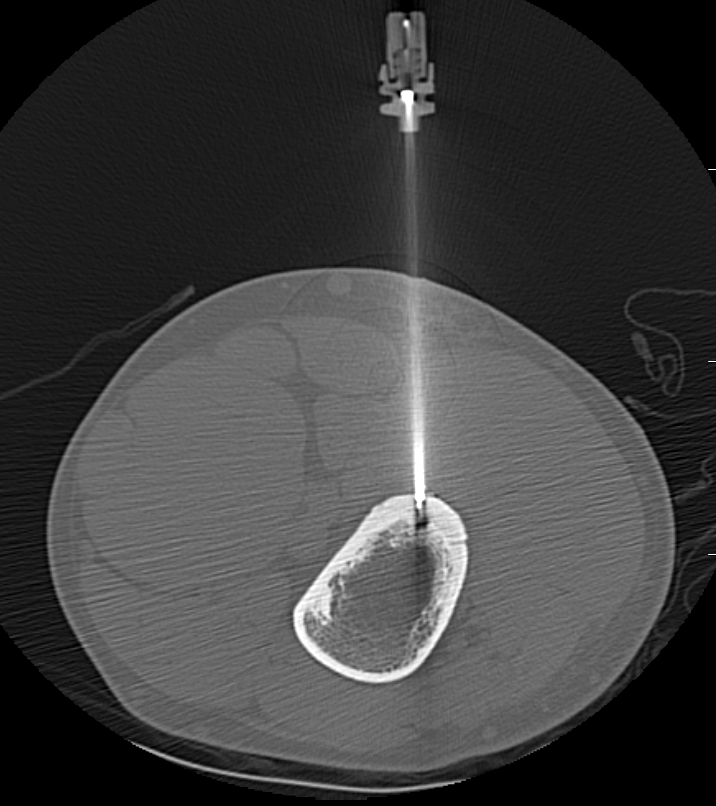
Radiofrequency Ablation
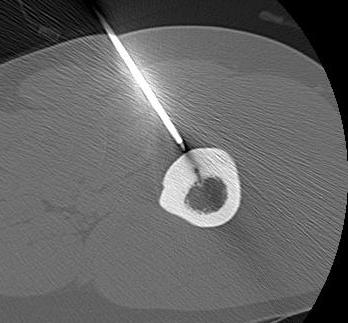
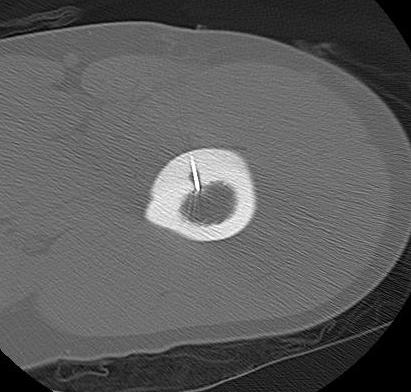

Concept
High frequency current
Thermal ablation
Technique
GA
- introduce electrode under CT
- tissue for histology
- radiofrequency
- increase temperature to 90o for 4 - 6 minutes
Complications
Neurovascular injury
- > 10 mm from NV bundles
Skin burns with osteoid osteoma of subcutaneous bones
Cartilage damage with intra-articular lesions
- avoid articular approach
- > 10 mm from cartilage surface
Results
Rosenthal et al Radiology 2003
- 126 RF ablation procedures with 2 year follow up
- primary procedure - success rate 91%
- repeat procedures - success rate 60%
- 69 patients operative excision - recurrence rate 9%, length of stay 5 days
- 33 patients RF ablation - recurrence rate 12%, same day discharge
Surgery
Issue
Can be difficult to identify
Tend to excise excessive bone
Fracture risk
Technique
Must completely remove nidus
Do not have to completely remove sclerotic bone
Intraoperative CT guidance
- direct incision over lesion
- shave cortex off with high speed burr to reactive bone
- scoop nidus out once hit hypervascular zone & sent for fresh frozen sections
- burr 2mm zone out
- can leave strong reactive bone behind
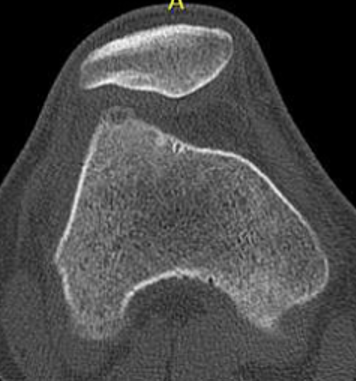
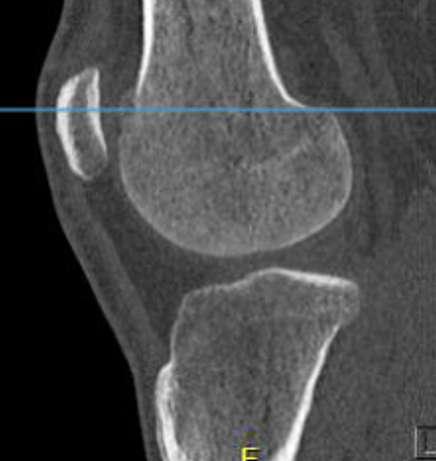
Intra-articular Osteoid osteoma
Issue
Risk cartilage damage from RF ablation
Options
Arthroscopic resection
Results
Ge et al Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2020
- systematic review of arthroscopic treatment of upper limb osteoid osteomas
- 32 cases in 19 articles involving shoulder / elbow / wrist
- no recurrence
- success rate 94%
- 2/24 (8%) in the elbow had incomplete resection
Ge et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2019
- systematic review of arthroscopic management of ankle osteoid osteomas
- 17 articles, 27 cases, most on talar neck
- success rate 95%, 2 recurrences
Spine Osteoid Osteoma
Symptoms
Back pain
Scoliosis + back pain
Location
Posterior elements
Options
RF ablation
Surgical excision
RF Ablation
Sangiorgio et al Eur Spine J 2023
- systematic review of RF ablation versus surgical excision in spine
- surgery treatment success 86%, recurrence 6%, complications 9%
- RF ablation treatment success 89%, recurrence 7%, complications 4%
Surgical excision
- 84 patients mean age 21
- 12% enbloc resection
- 82% intra-lesional resection
- 7% recurrence, all with intra-lesional resection
