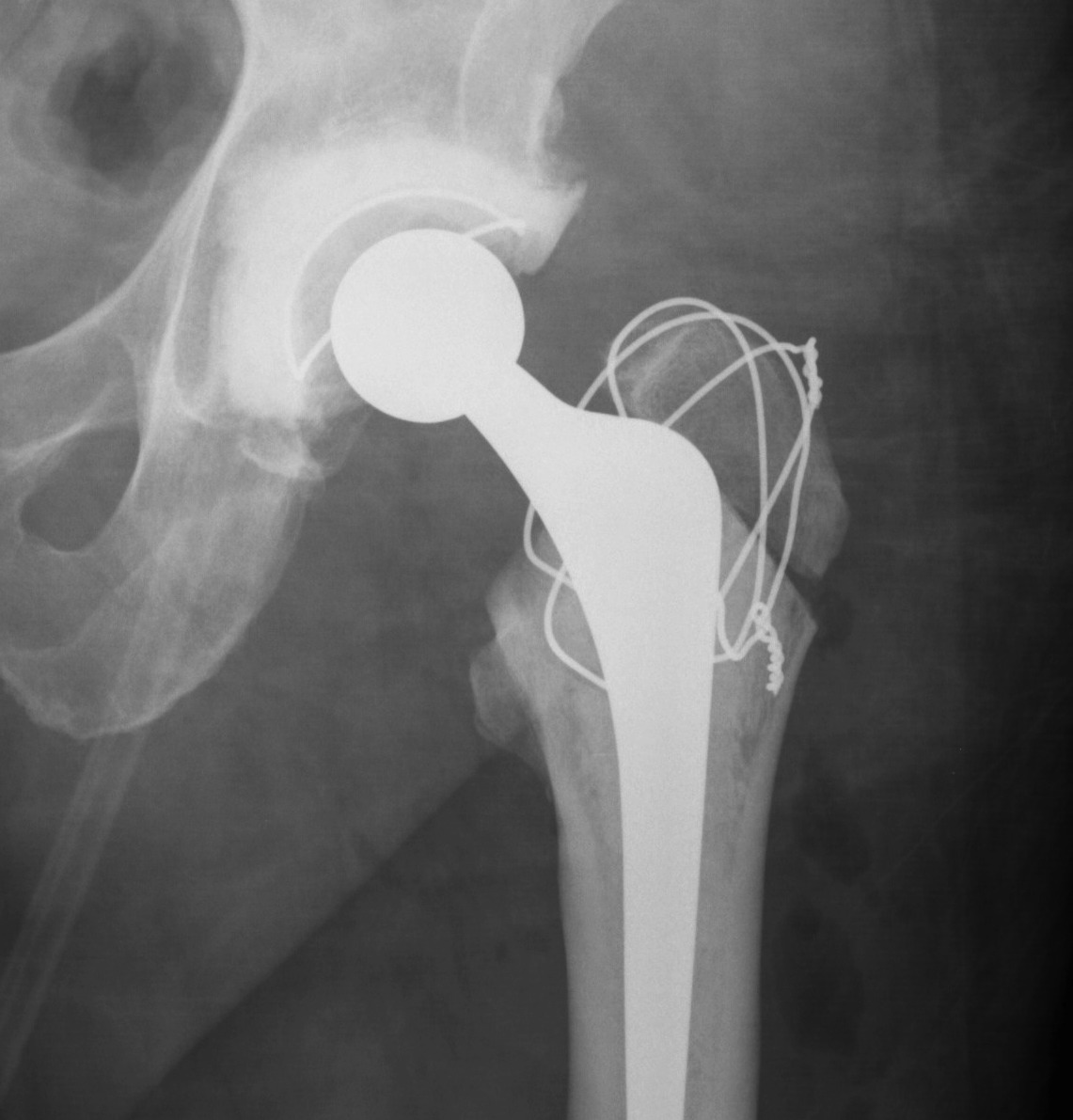
Types
1. Standard trochanteric osteotomy
2. Sliding trochanteric osteotomy
3. Extended trochanteric osteotomy
Standard Trochanteric osteotomy
Concept
- detach GT with only abductors attached
Indication
- increasing exposure to acetabulum in difficult cases
- retensioning abductors
Problem
- difficulty fixation / unstable
- most hip surgeons now use sliding osteotomy
Technique
- detach proximal attachment of vastus lateralis
- pass retractor deep to G medius / minimus and superficial to capsule
- saw osteotomy from lateral aspect of GT angled up towards retractor
- detach any short external rotators and reflect superiorly
Fixation
- 3 - 4 intraosseous wires
- claw plate
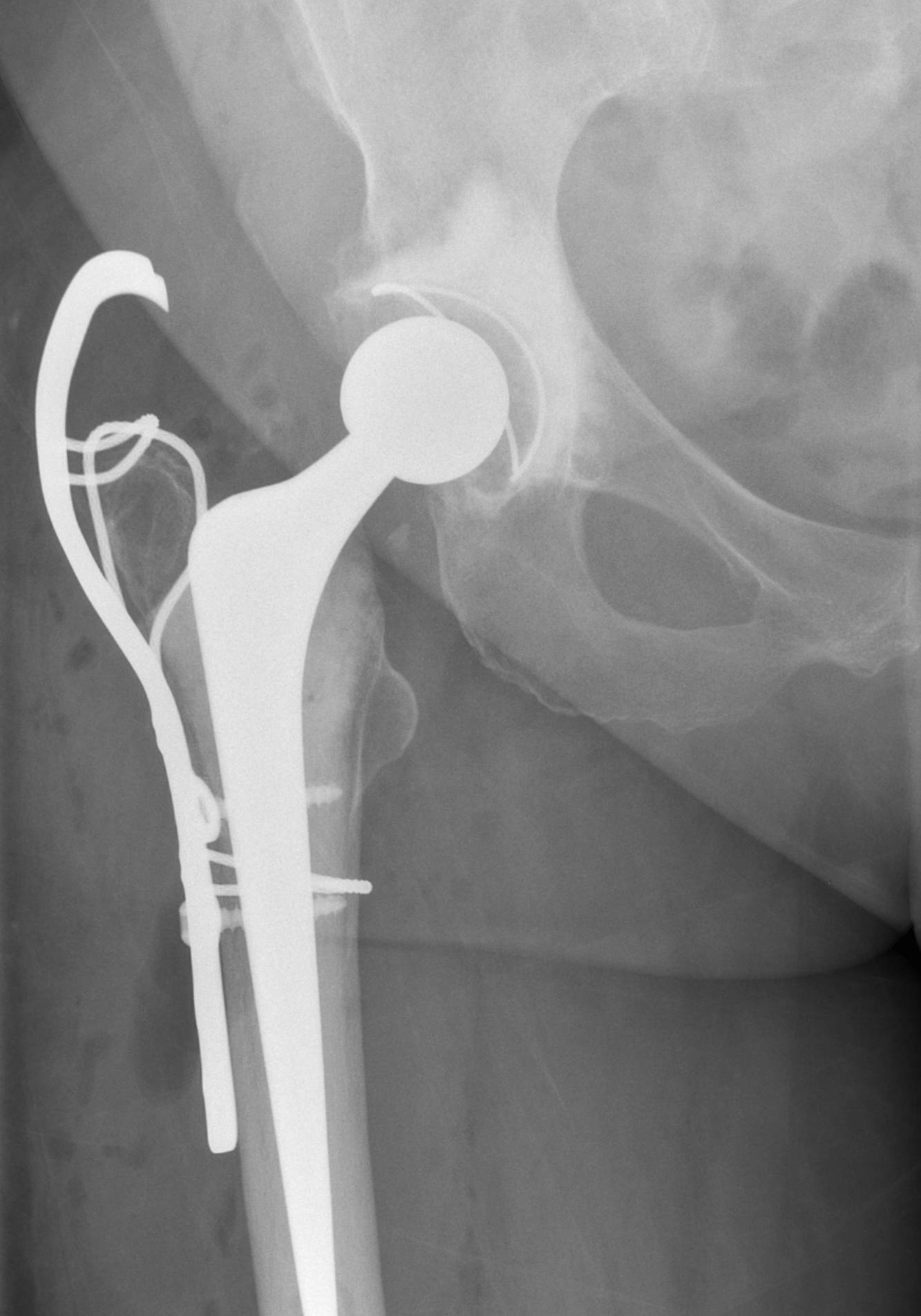
Modification / Chevron Osteotomy
- increased stability
- decreased non union
Complications
- non union
- migration
- wire breakage / painful hardware
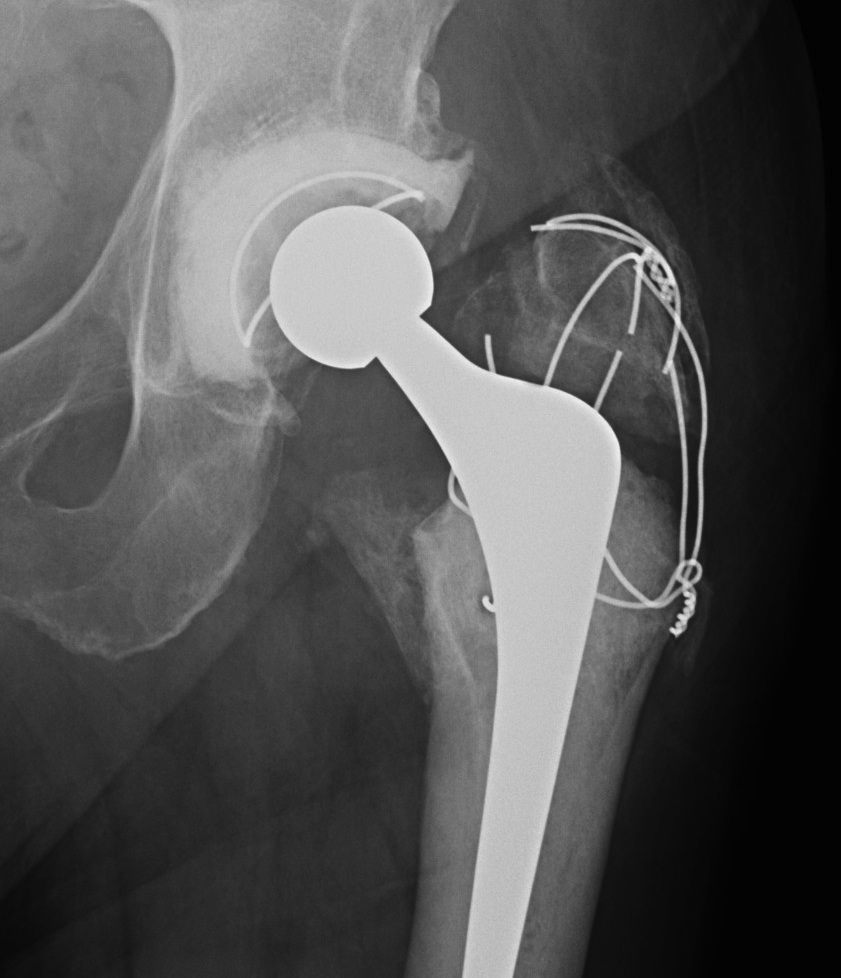
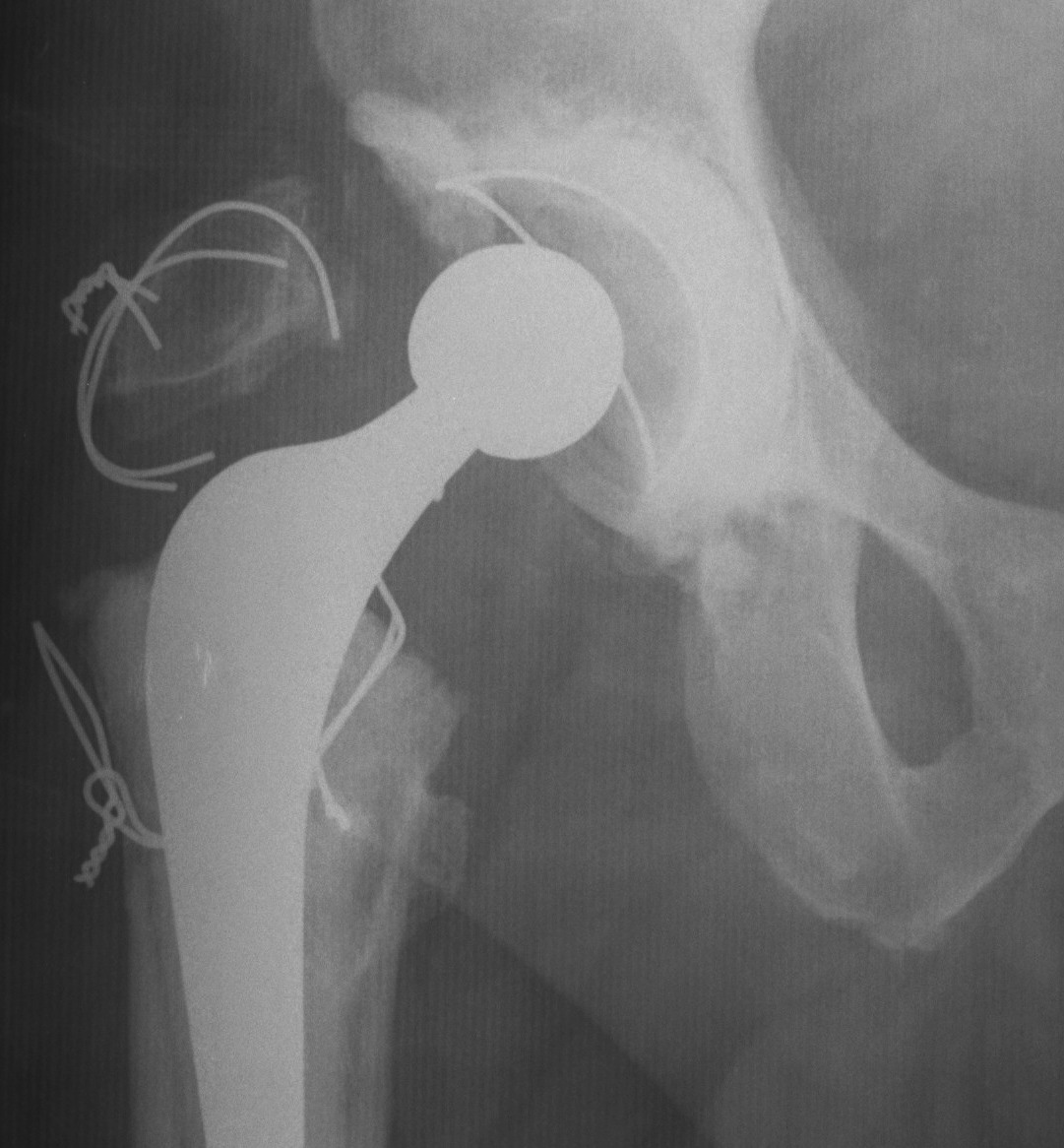
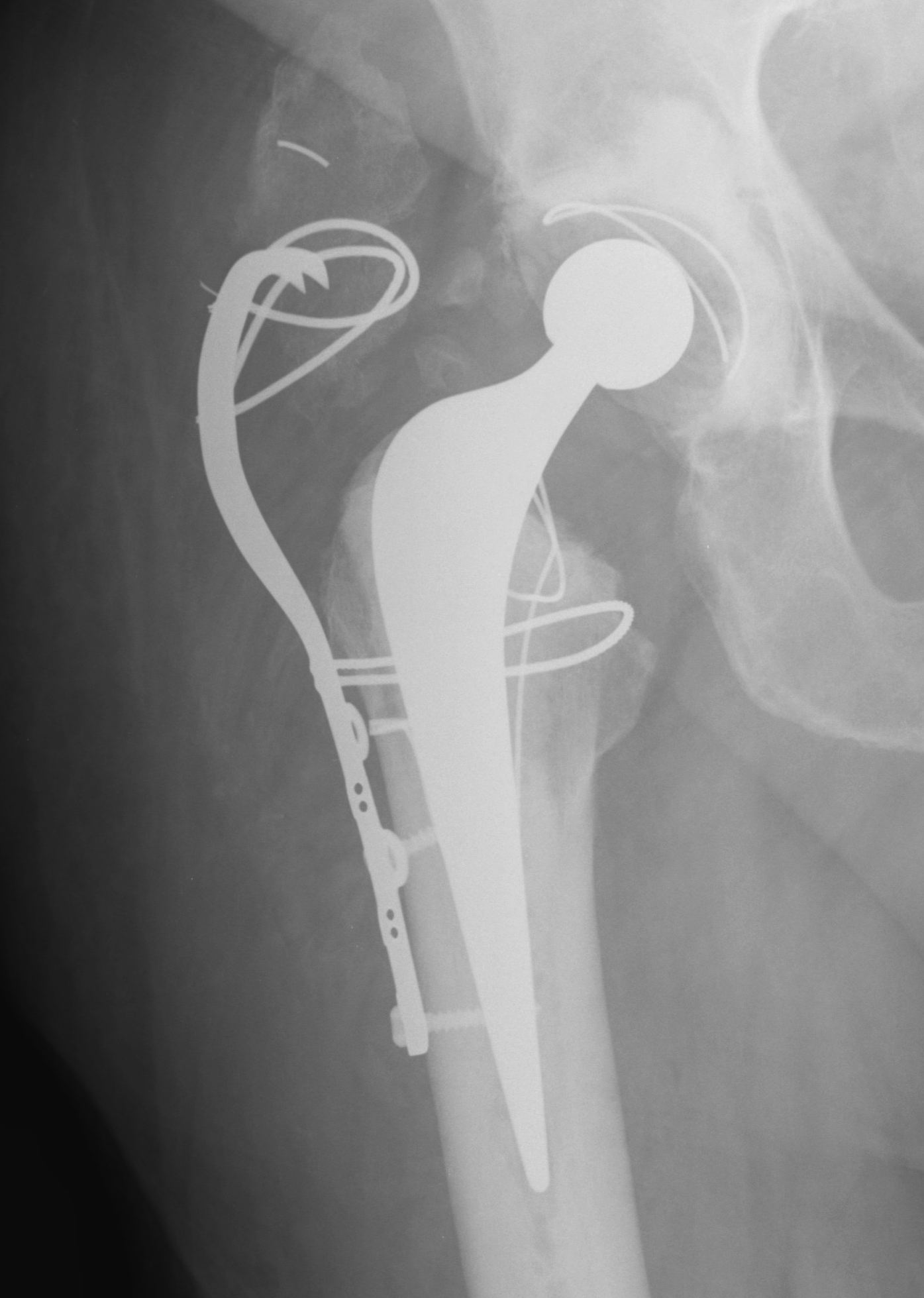
Trochanteric Slide
Concept
- PA osteotomy
- vastus lateralis and G medius left attached to fragment
- fragment retracted anteriorly
Advantage
- increased inherent stability
- vastus lateralis prevents proximal migration
Technique
- retractor superiorly deep to minimus and superior to capsule
- posterior elevation of vastus lateralis
- retractor under vastus lateralis insertion
- oscillating saw anterior to posterior
Fixation
- wires
- grip plate
Extended Trochanteric osteotomy
Concept
Osteotomy lateral 1/3 to 1/2 of trochanter & femur
- posterior to anterior longitudinal cut
- short distal transverse cut
- levers / hinges open anteriorly
- maintains anterior vasculature / muscle attachment
Indications
1. Aid exposure
2. Removal cement (especially infection)
3. Removal well fixed uncemented prosthesis
4. Removal cement plug / bone very poor / risk of perforation high
5. Abnormalities of the proximal femur
Contraindications / Relative
1. Impaction bone grafting
2. Cementing revision prosthesis
Technique ETO
Length
- measured from tip GT
- 2 – 15 cm long
- determined from preoperative template
- need to preserve diaphysis if using distal press fit uncemented stem
Timing
- usually after implant removal
- may not be possible
Site
- elevate vas lateralis forward
- expose linea aspera
- expose posterior femur
Osteotomy
- use drill holes to mark osteotomy
- drill both cortices
- thin oscillating saw
- cut down through anterior and posterior femur in line with GT
- through both cortices
- transverse cut distally through 1/3 diameter
- lever open
Fixation
- 3 x cerclage cables
- protect sciatic nerve / palpate / pass wires posterior to anterior
- submuscular
Results
98 – 100% union rate by 6/12