Principles of Acetabular reconstruction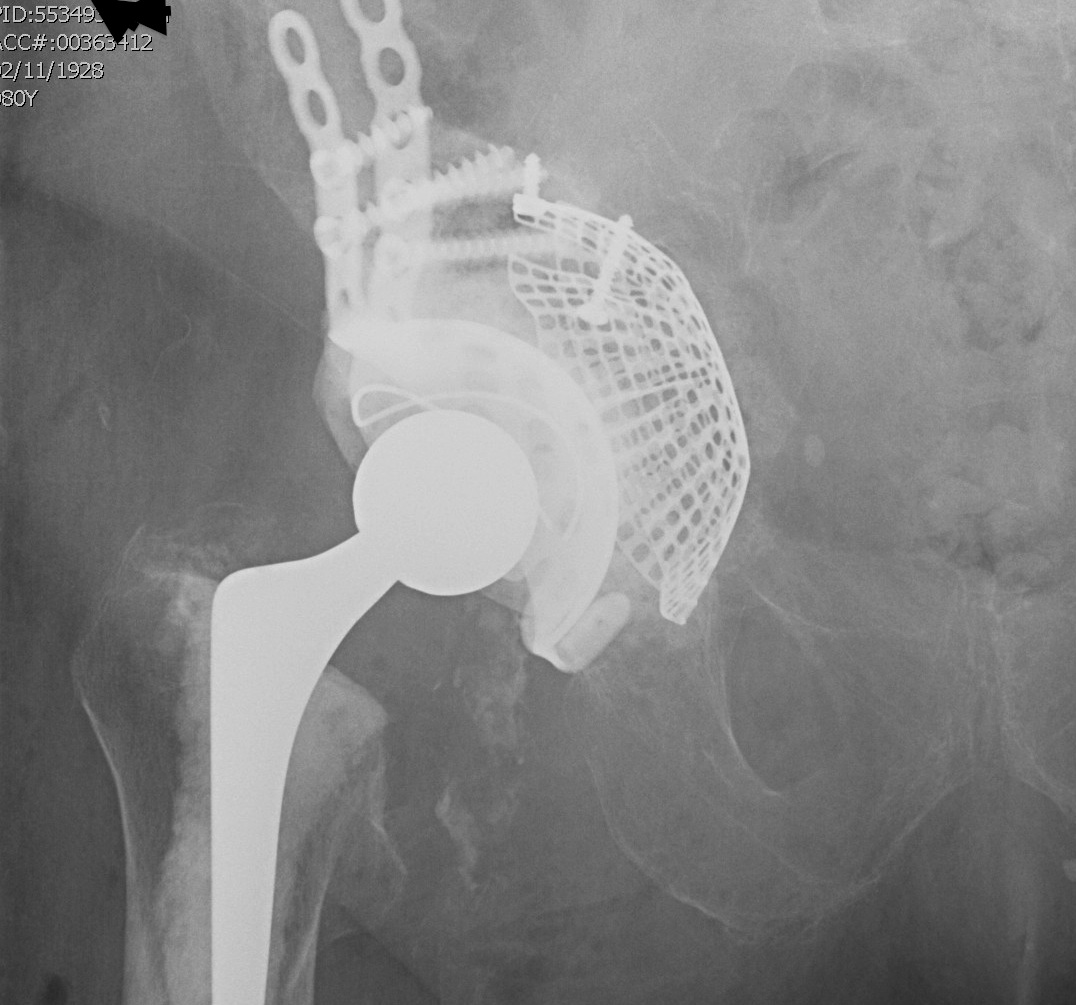
Restore centre of rotation
Restore acetabular integrity
Component containment
Secure fixation
Preoperatively planning
Know components in situ (esp if leaving femur)
Quantify and grade bone defects
Beware intrapelvic cement / cup (angiogram)
Basic Guidelines
> 50% host bone contact
- use press fit uncemented cup augmented with screws
< 50% host bone contact
- use metal augment in elderly to reconstruct defect
- use allograft augment in young to reconstruct defect
- press fit cup if able
- otherwise must use cage
Paprosky Type I, II A and B
I Rim intact
II A Mild superior migration / superior rim intact
II B < 30% superior rim missing
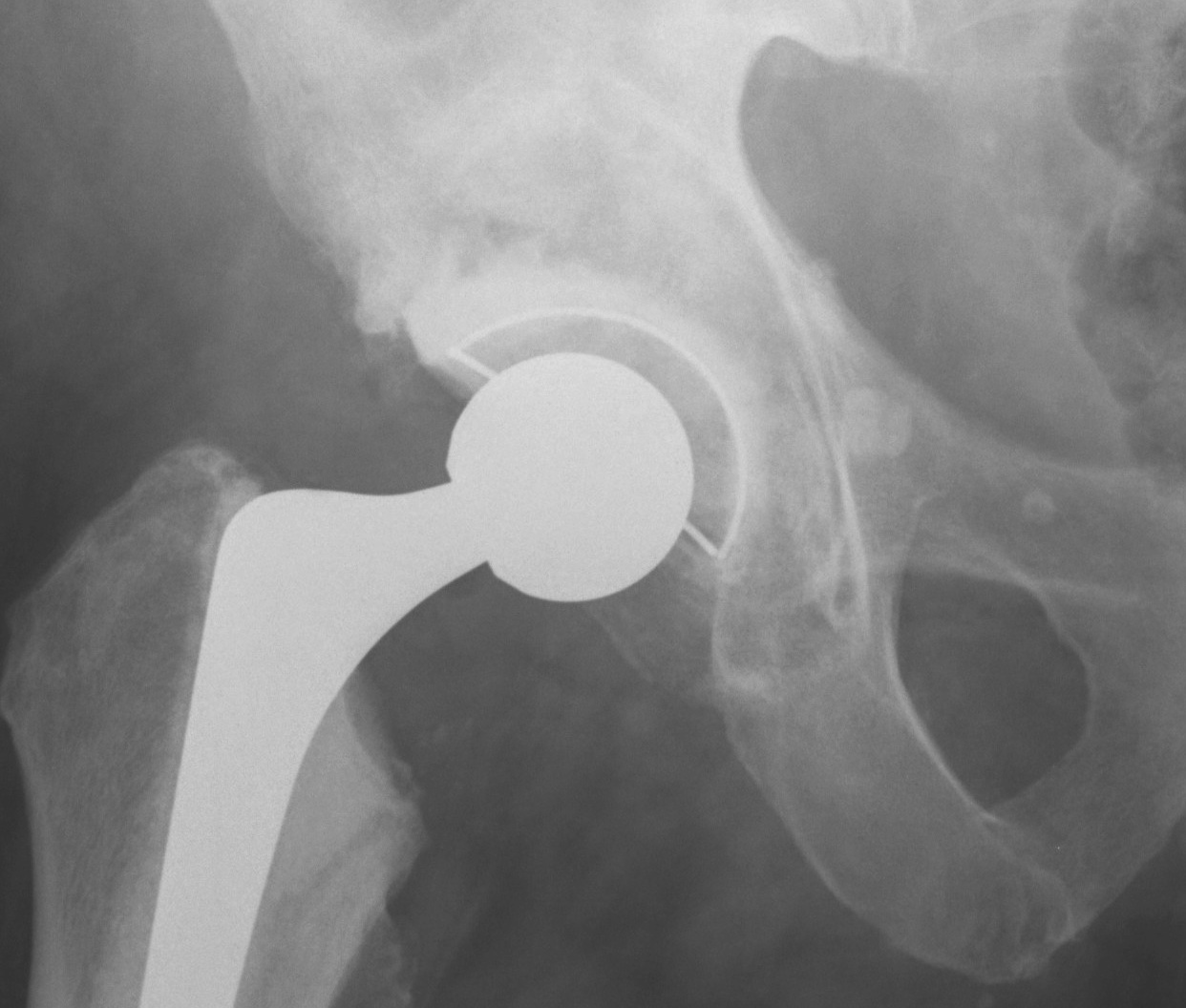
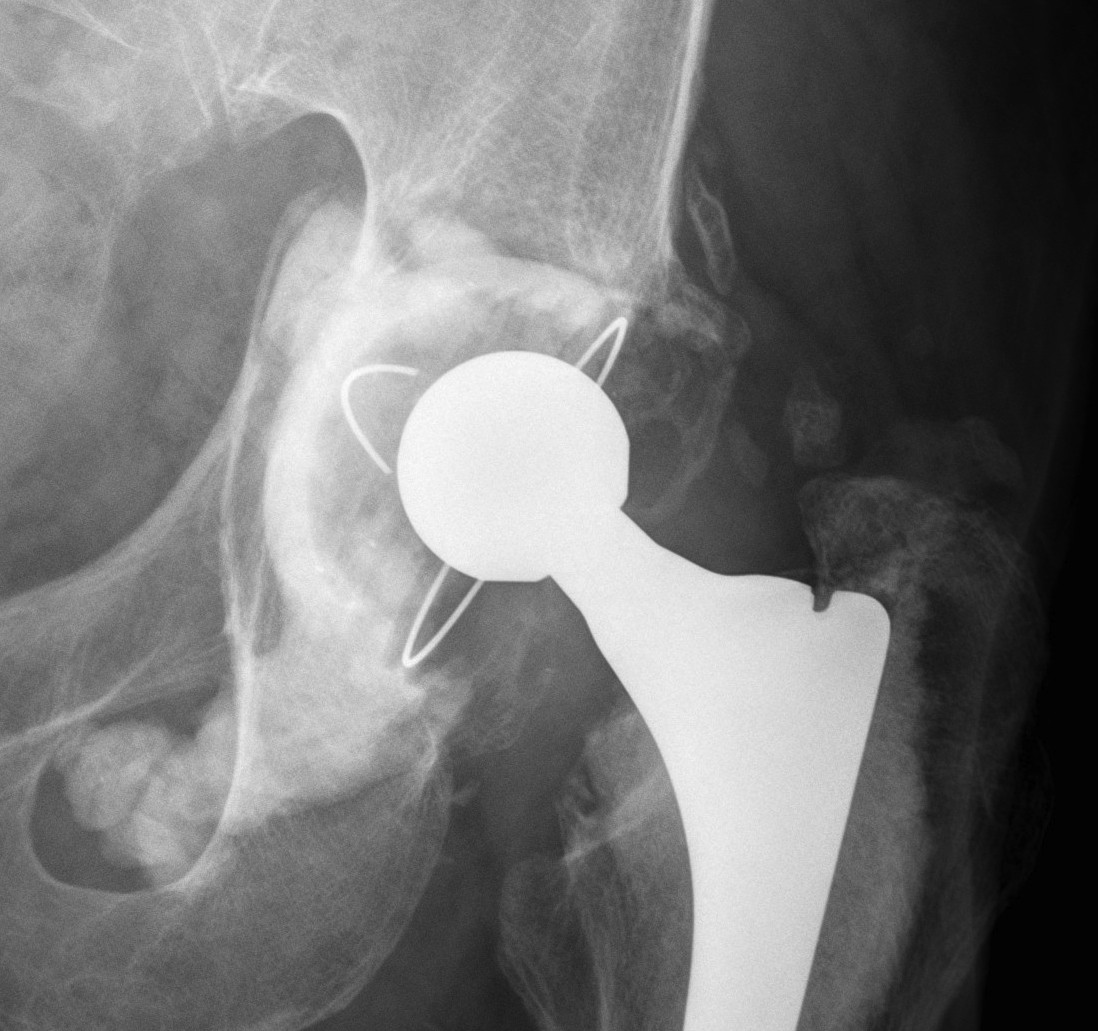
1. Uncemented Jumbo rim fit cup
Indications
- > 50% host bone available for ingrowth
- > 2/3 rim intact
Technique
- implant in usual position
- preferentially ream anteriorly
- preserve posterior column
- some uncovering superiorly allowed
- usually augment with screws
- +/- postoperatively NWB 6/52
Results
- 12-15 year survival between 81-96%
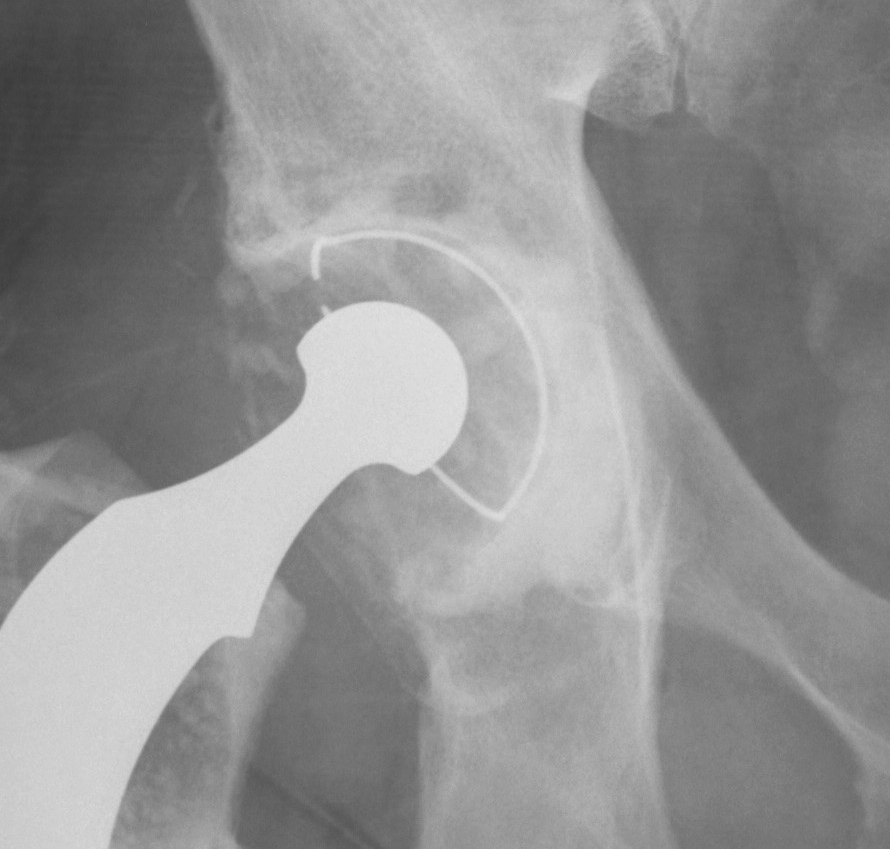
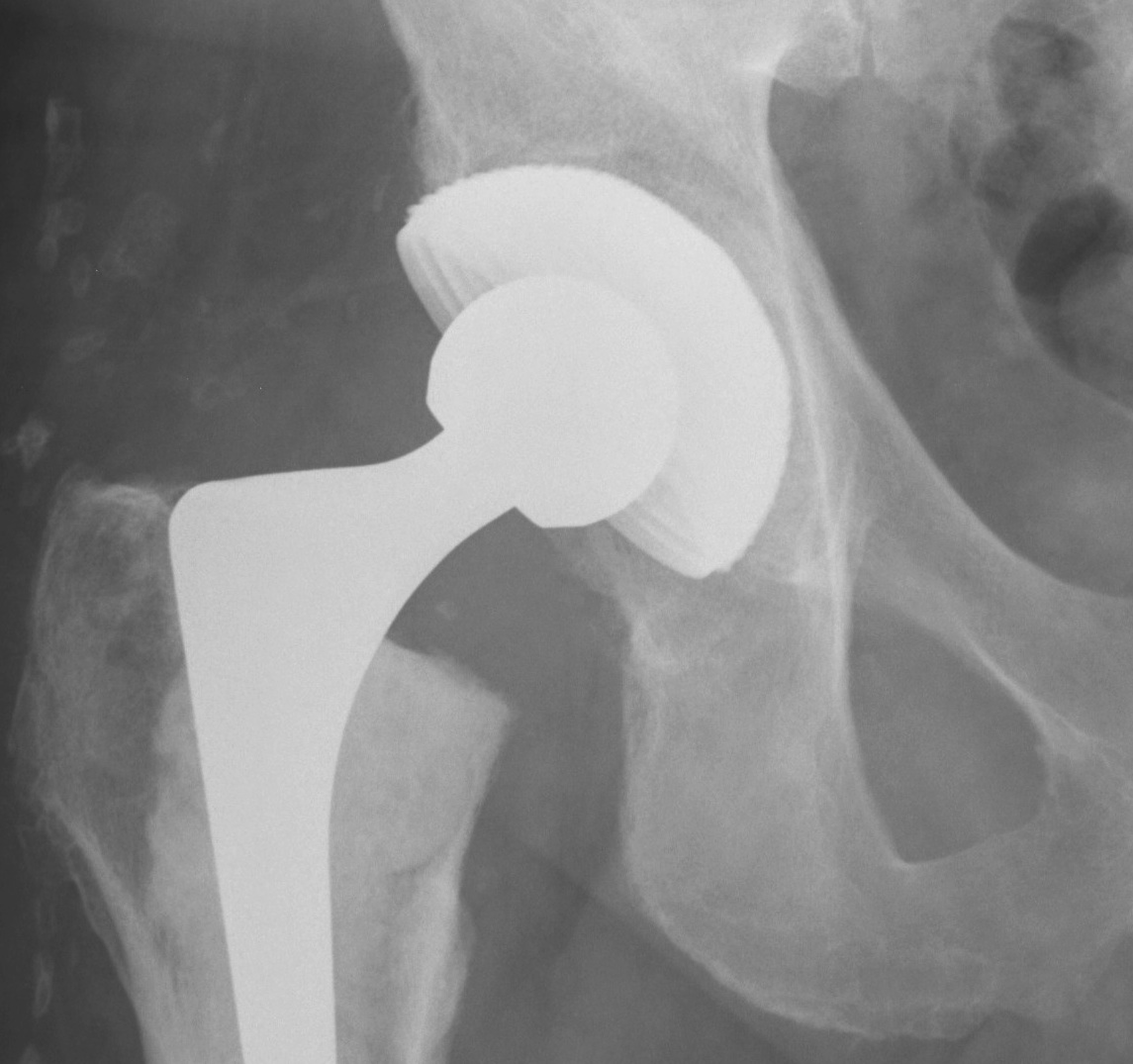
2. Impaction Bone Graft +/- Mesh + Cemented Cup
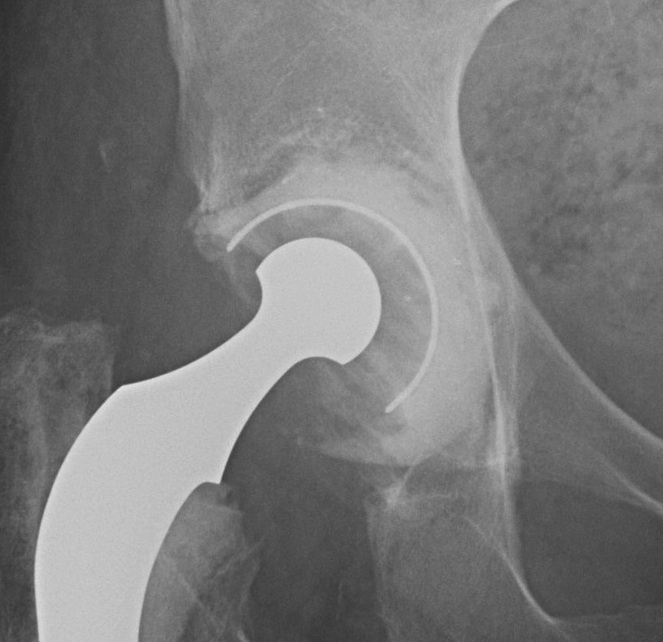
Type IIC
Type IIC: Medial wall deficiency but intact
Options
A. Particulate graft medially, jumbo cup
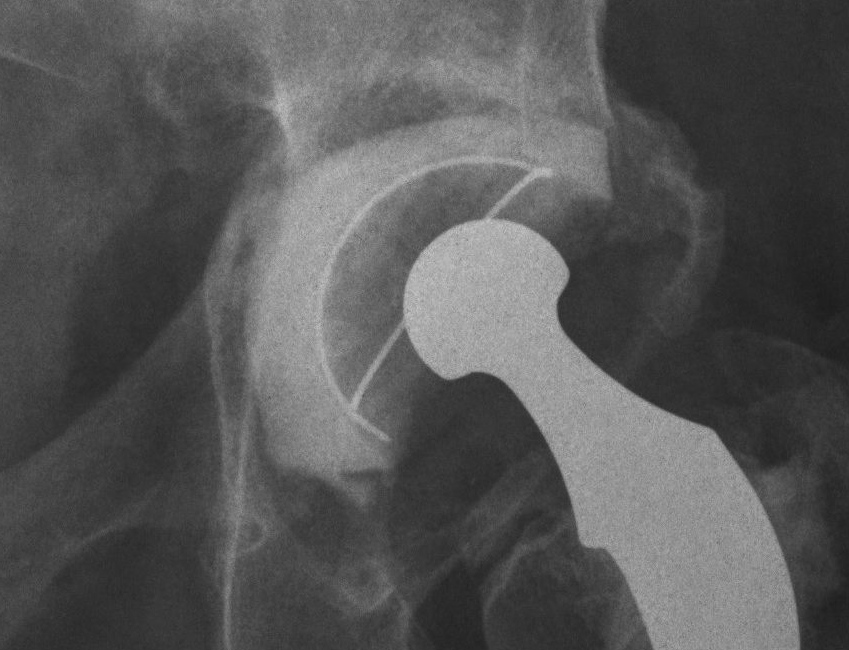
B. Impaction bone graft, cemented cup
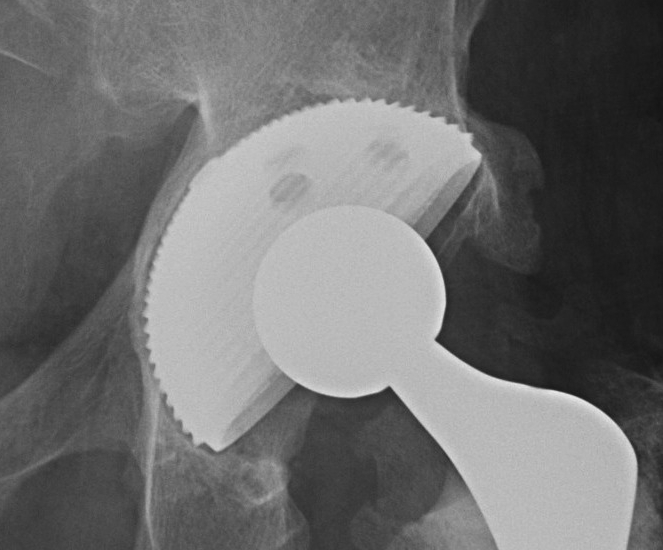
C. Cement +++
Indicated in elderly patients
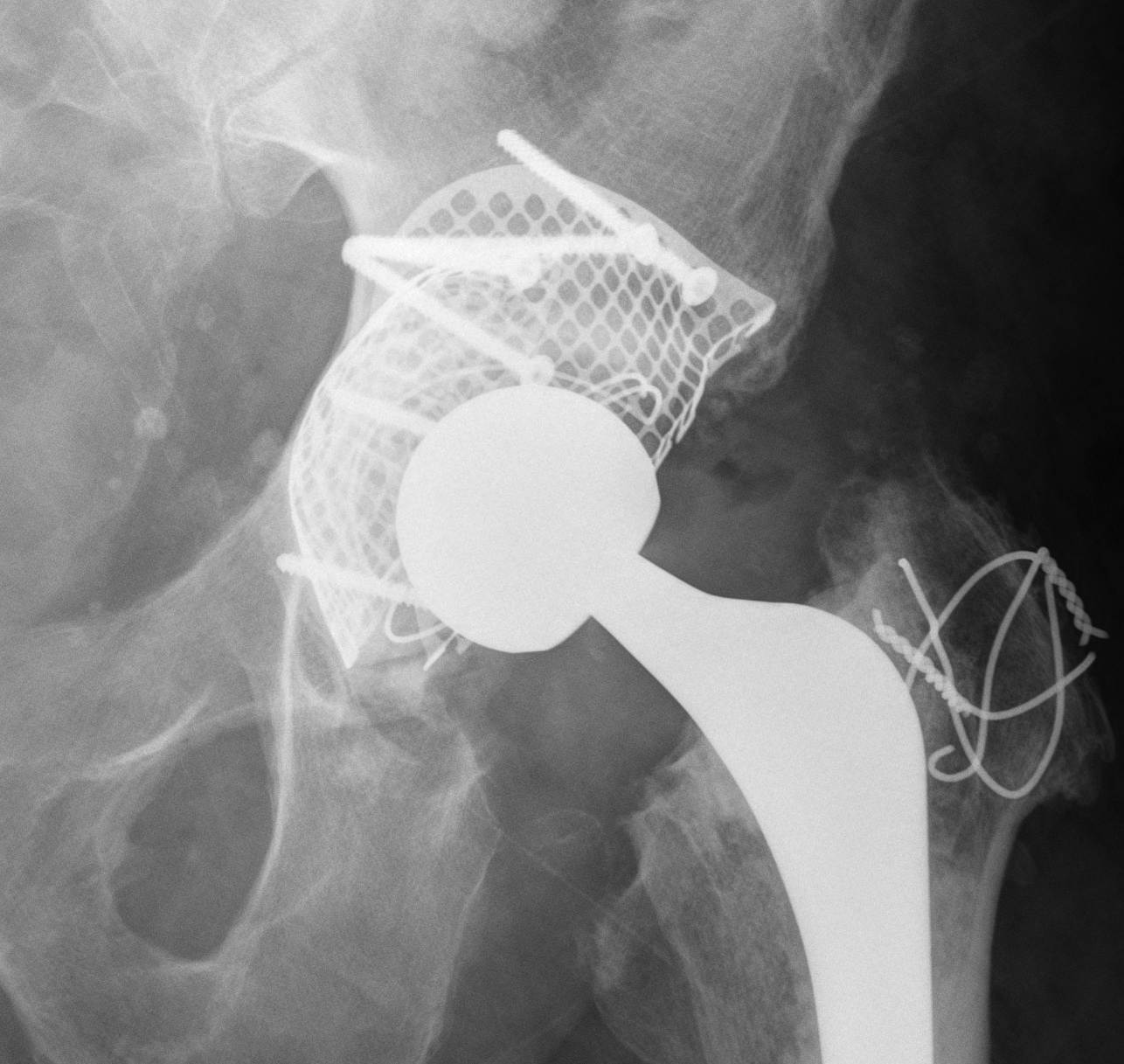
Segmental Medial Wall deficiency
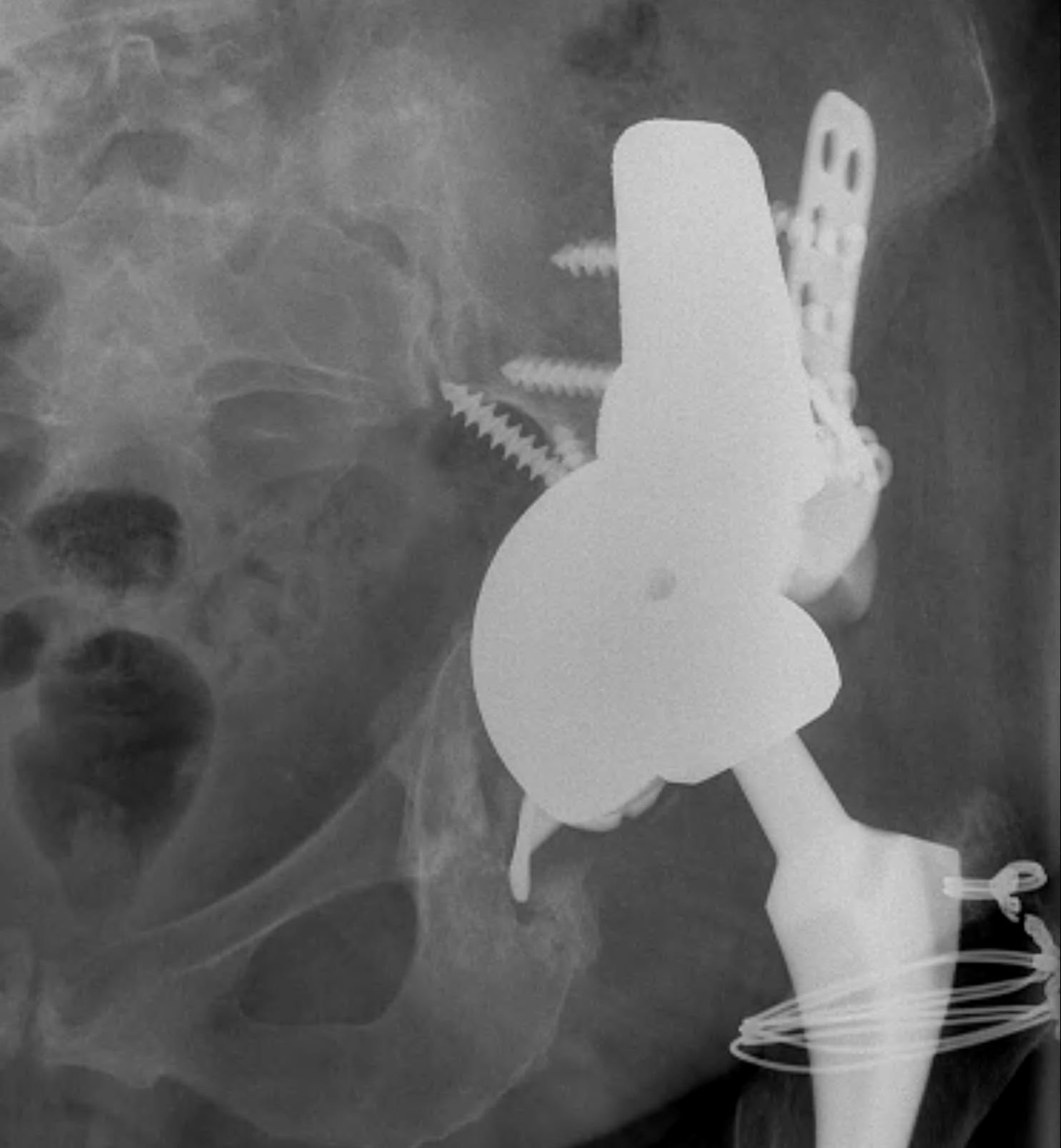
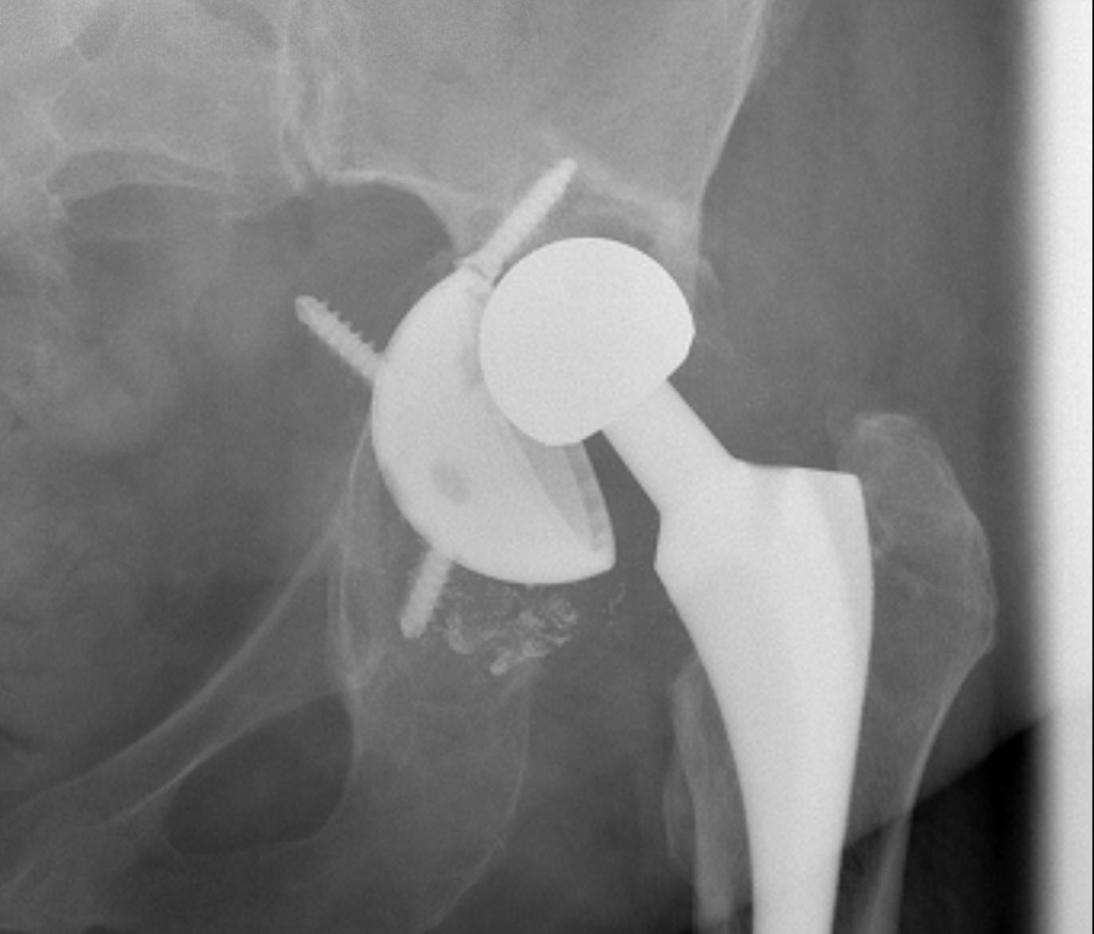
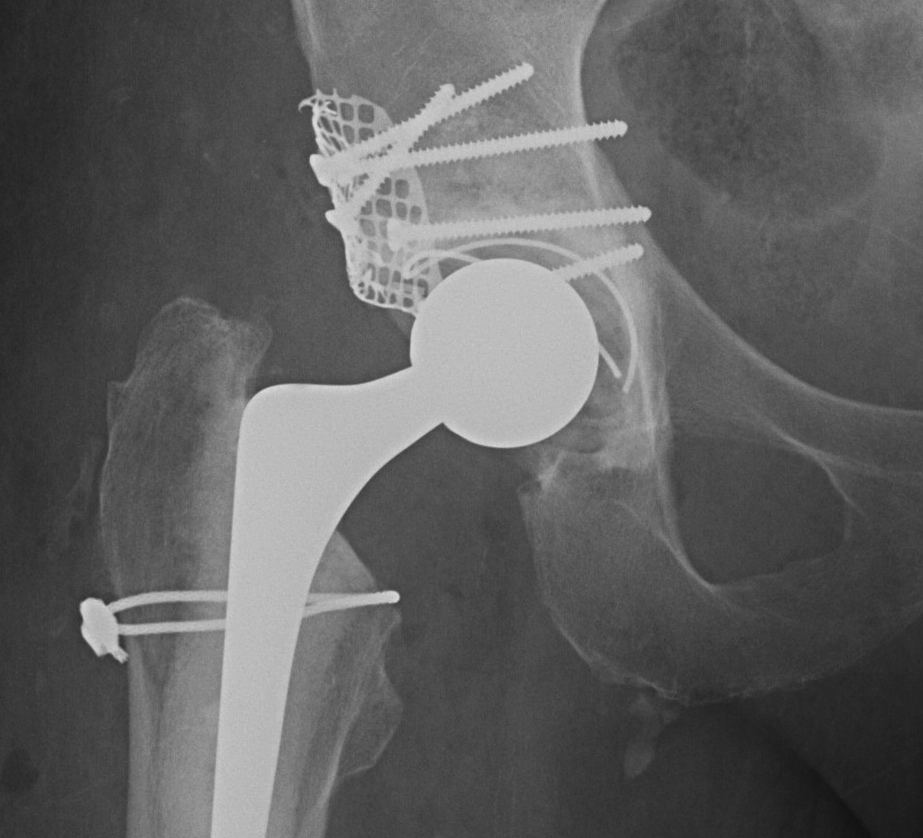
A. Allograft + Antiprotrusio Cages + Cemented Cup
Types
- Ganz / Muller / Burch Schneider
- variations on them
- hook or screws into ilium
- hook or screws onto ischium
- can have extension for screws onto pubis
B. Mesh + Impaction Bone grafting
Type IIIA defects
Type IIIA
- Rim < 50% missing, > 40% host bone contact
- want to reconstruct defect but don't need cage
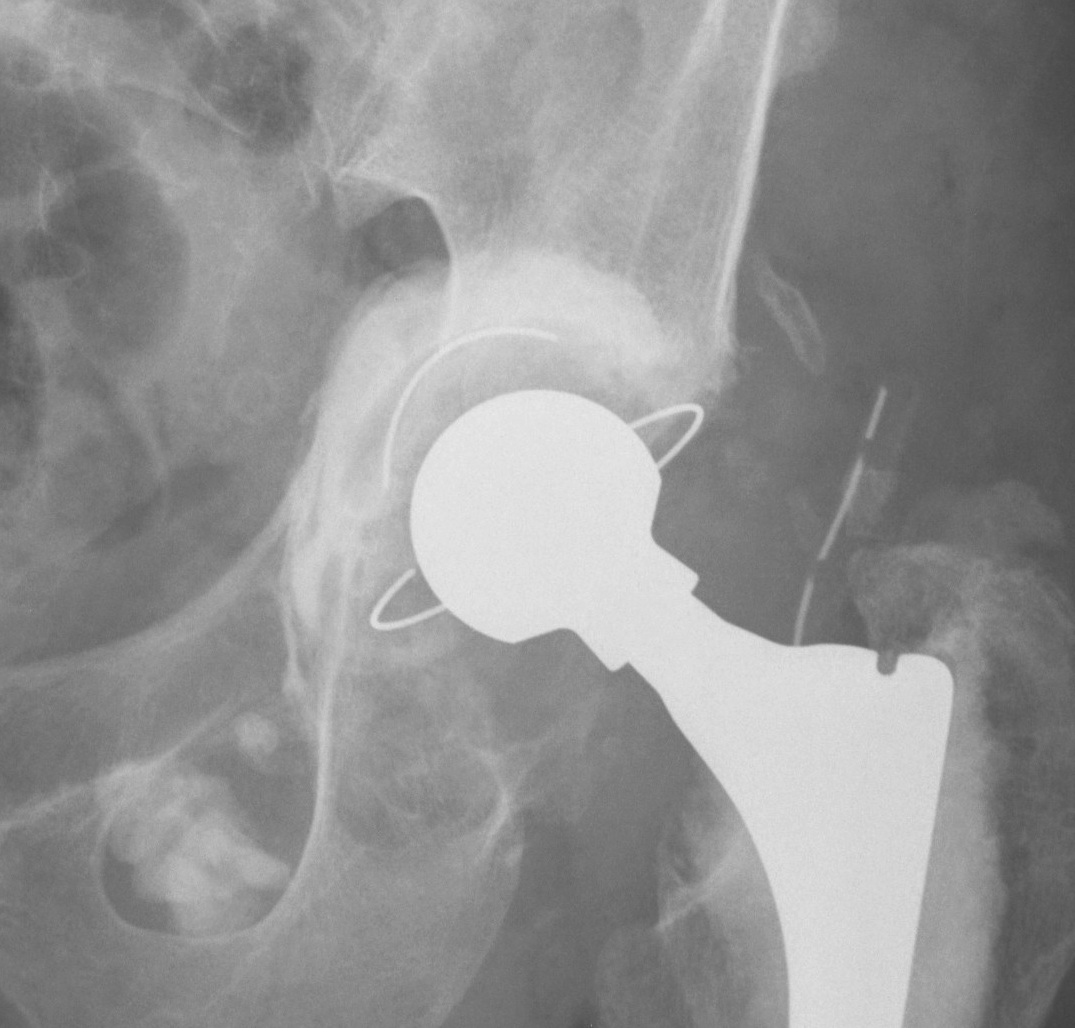
1. Uncemented rim fit cup / screws / Structural bone graft
Indications
- defect superolateral rim < 50% to support cup
- > 50% host bone contact
- allograft will not grow onto uncemented cup
- allograft to reconstuct defect
Technique
- femoral head allograft reconstruction (no 7 shape)
- fix with 6.5 mm screws
- tap first to prevent fracture
- ream into bone
2. Impaction bone graft +/- mesh + cemented cup
Technique
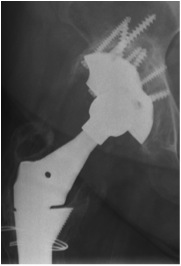
1. If required, convert uncontained defect into contained defect
- use titanium mesh fixed with screws
- acetabular rim or medial wall mesh (Stryker)
2. Impact morcellised cancellous bone graft
- tamps or reverse reaming
- progressively smaller impactors
- need 5 mm of bone graft
3. Insert prosthesis / Cemented poly liner
Results
- 85% 12 year survival
- 80% 15 year survival
Important Points
1. Rigorous technique important
2. Fresh frozen allograft
- does this perform better than irradiated BG
3. TWB 6 – 12/52
3. Trabecular metal components
New material made of element tantalum
1. Interconnecting porous material
- 80% porous
- allows 2-3 X bony ingrowth
2. Less stiff
- improved remodelling of BG underneath
3. High cancellous bone coefficient of friction
- excellent initial stability
- may need less than traditional 50% host bone contact
- may not need screws
Ream host bone for press fit cut
- trial then secure trabecular augment with screws
- press fit cup with cement between augment and cup
- screw augmentation of cup
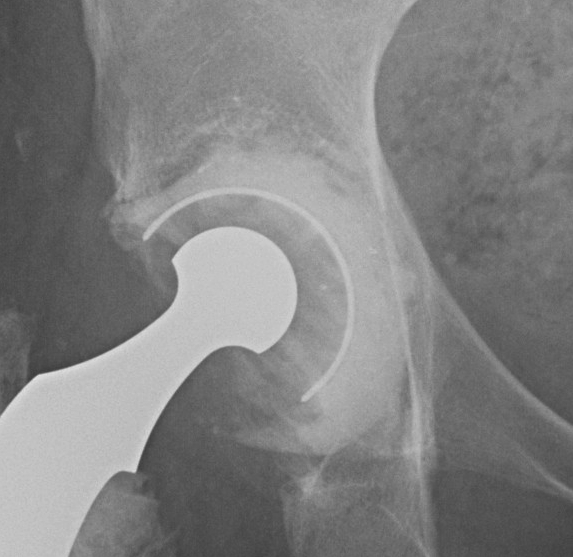
4. Bilobed uncemented acetabular components
Indications
- superolateral deficiency
- revision
- DDH cups
Problems
- can be difficult to get version right
Type IIIC
Type IIIC
- < 50% rim intact, < 40% contact
- must reconstruct for stability
- unable to use uncemented component
- use bone graft to reconstruct
- need cage for stability
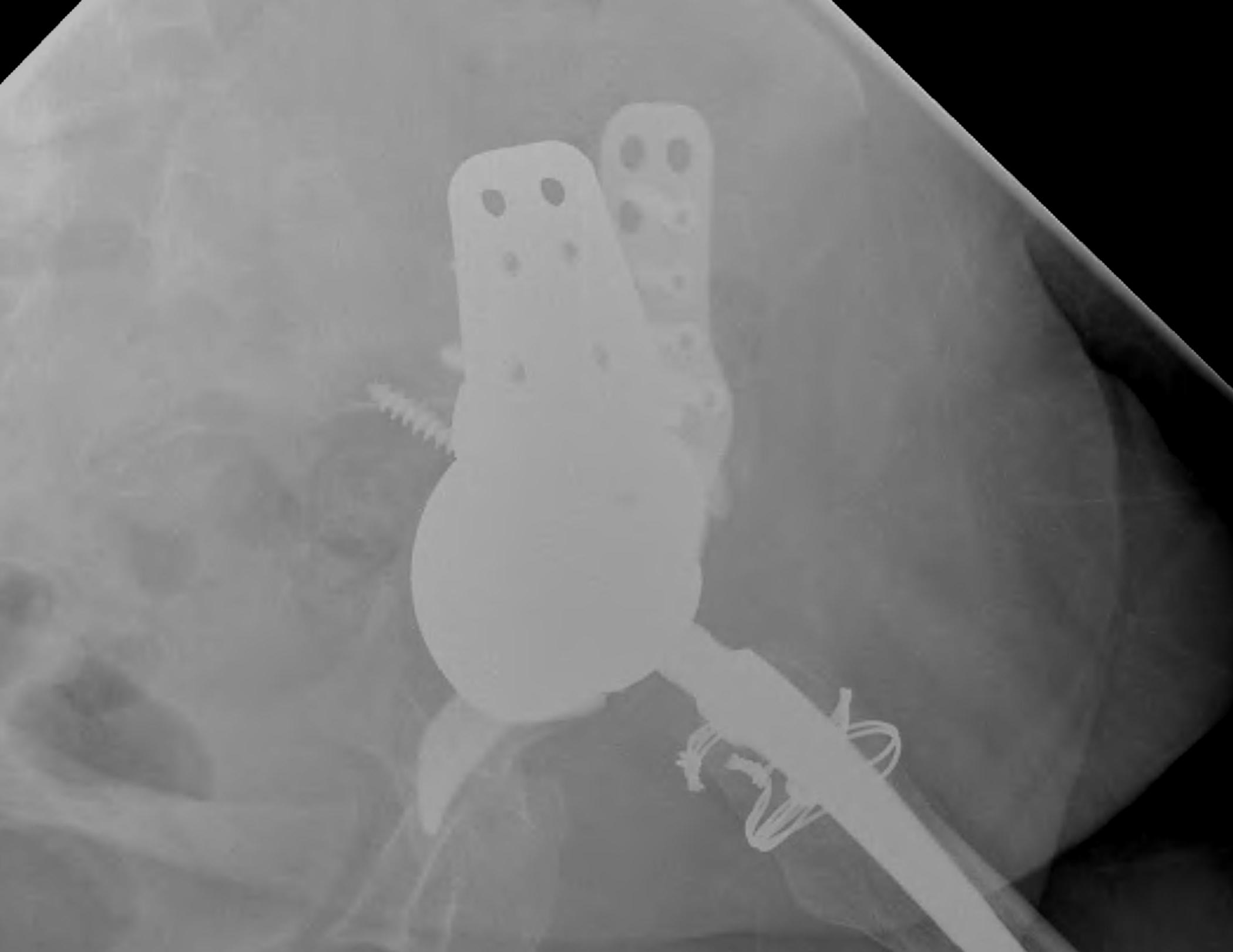
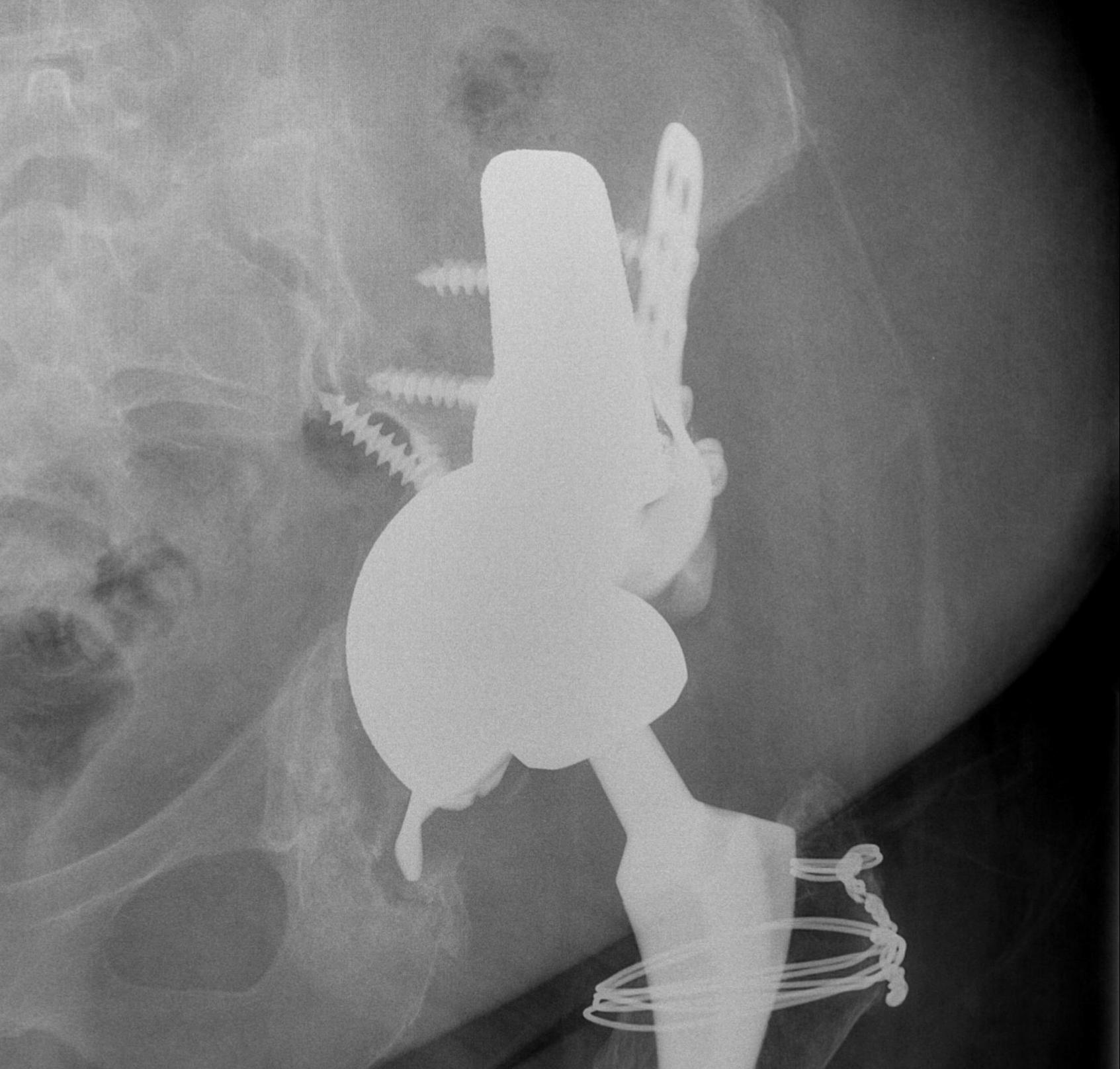
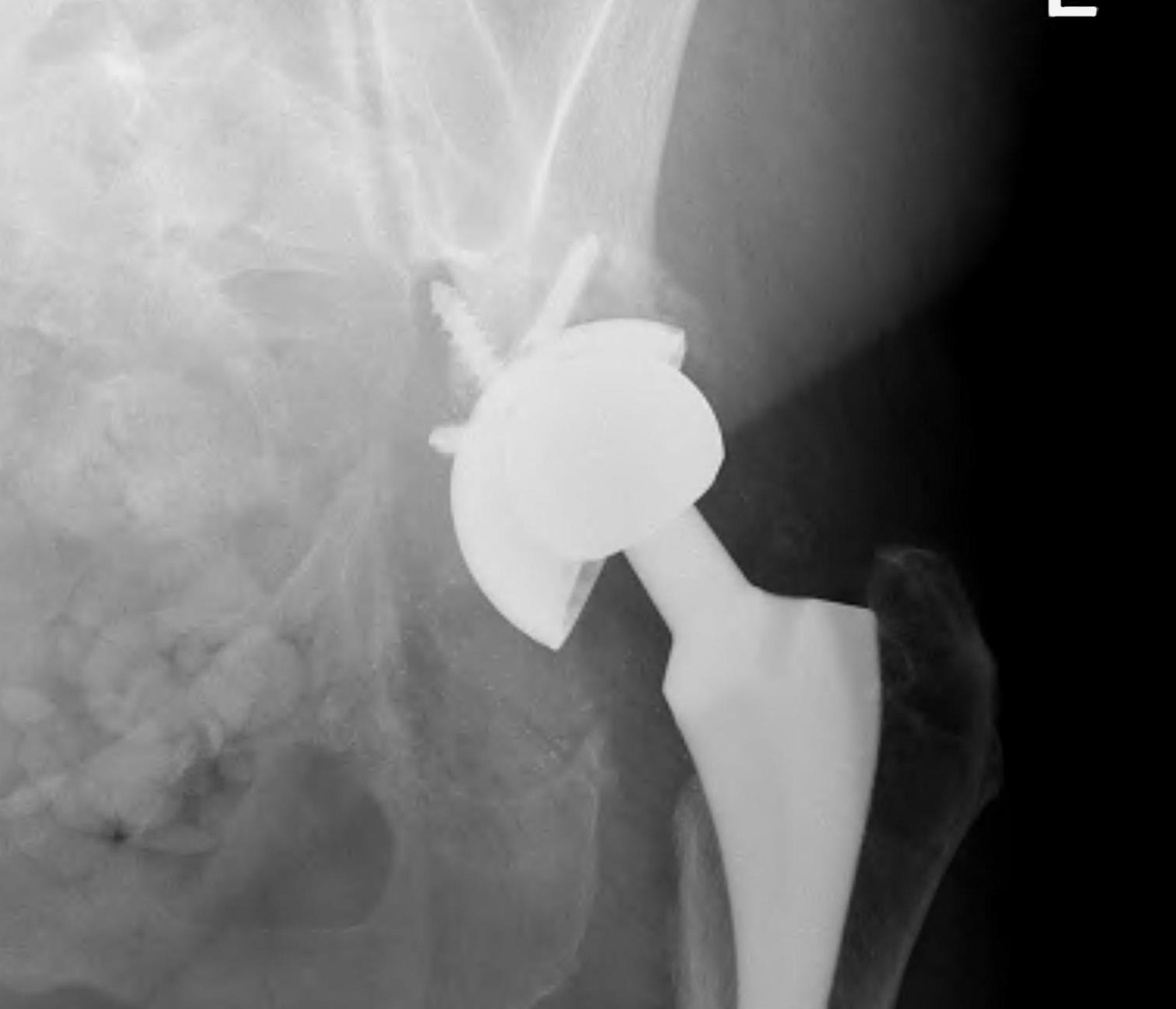
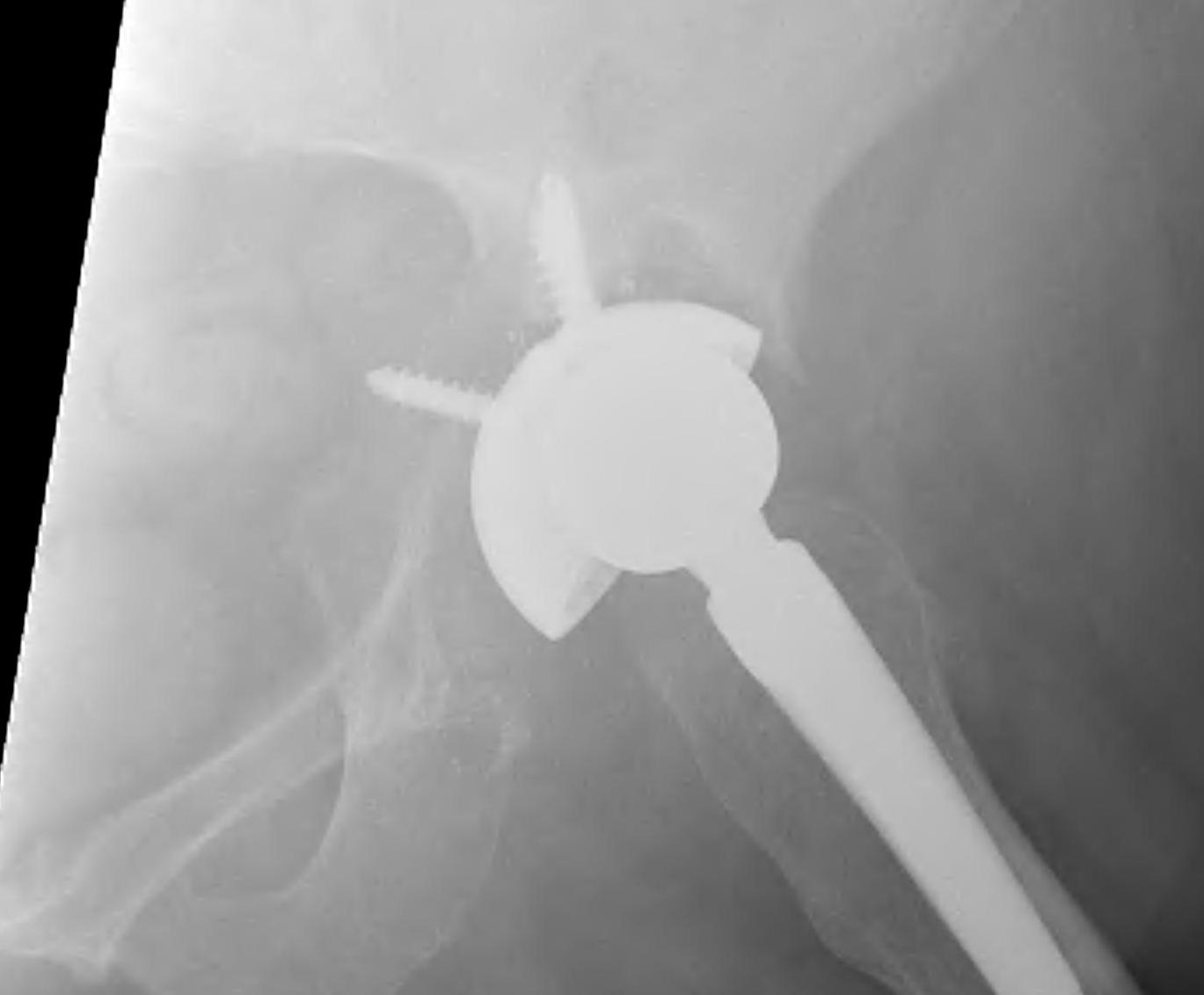
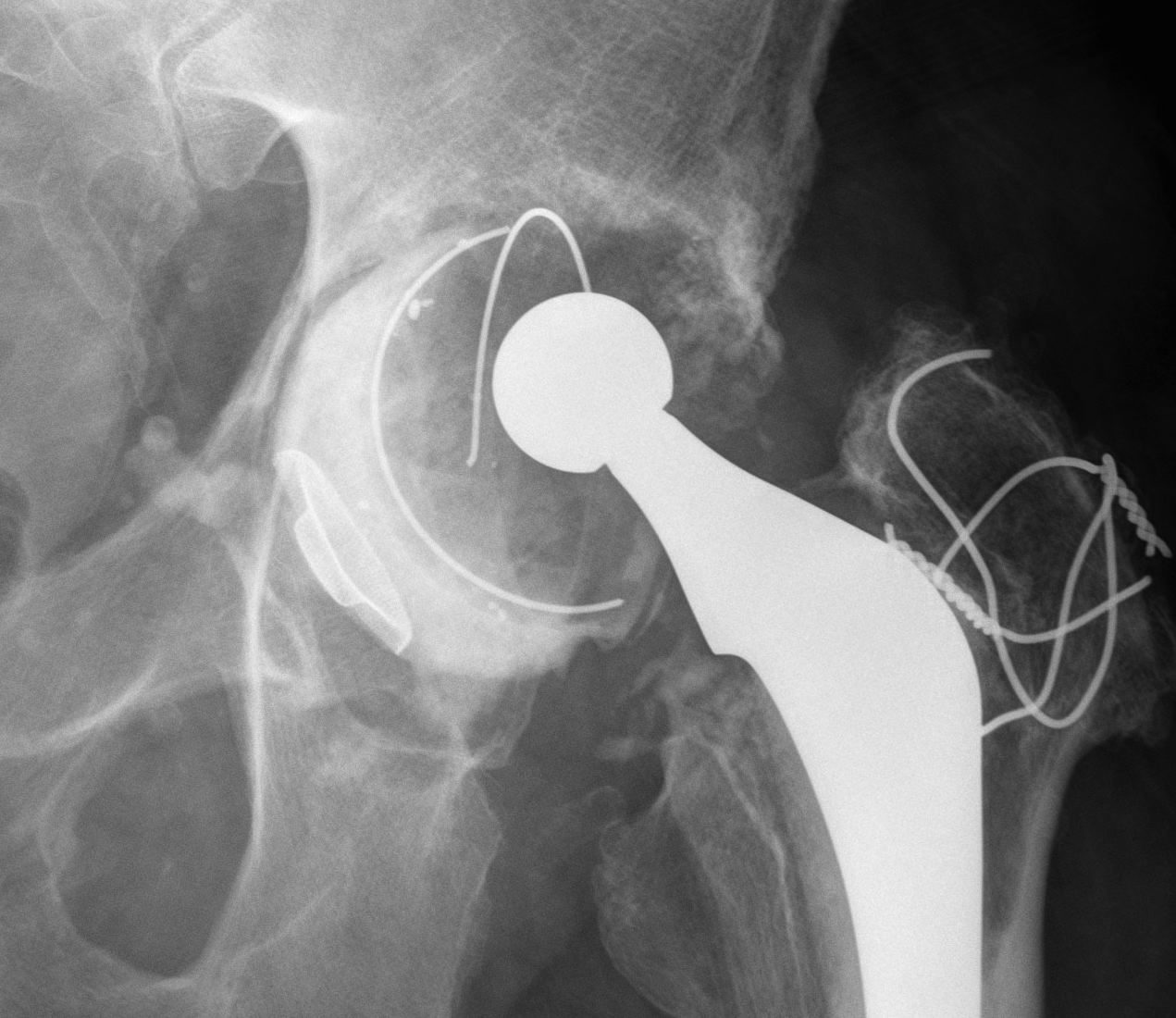
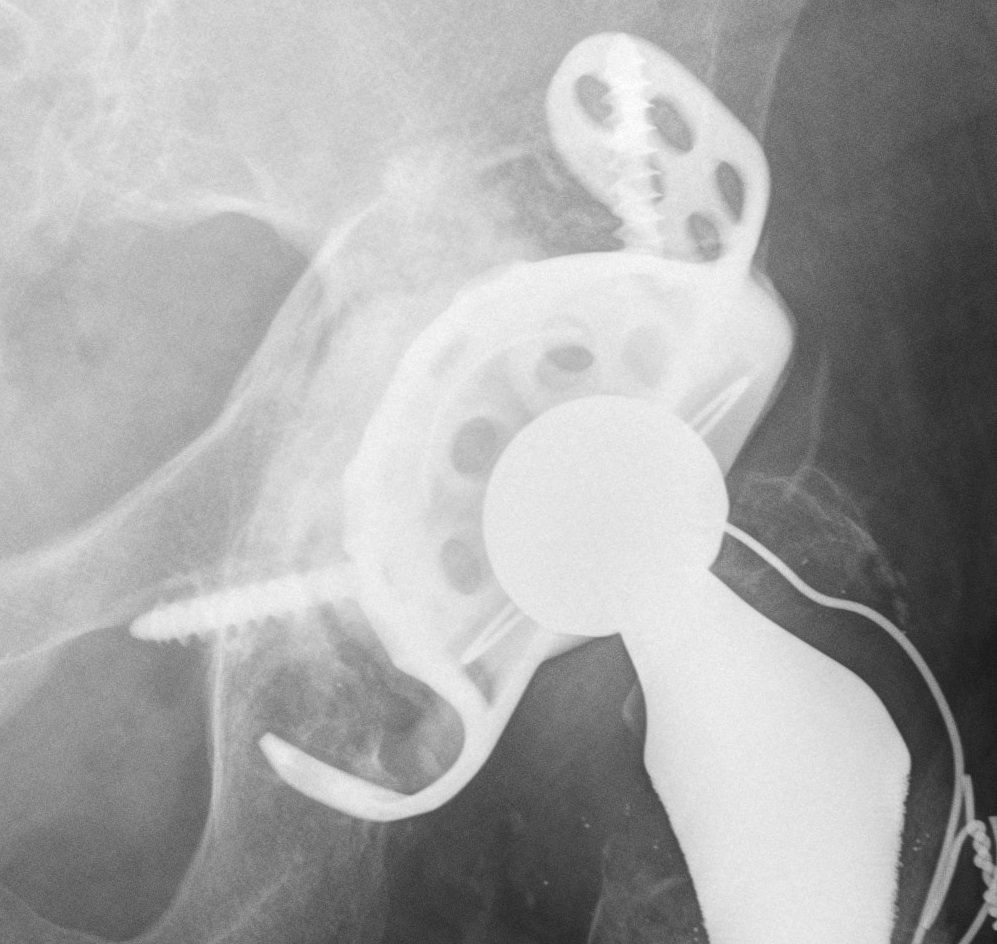
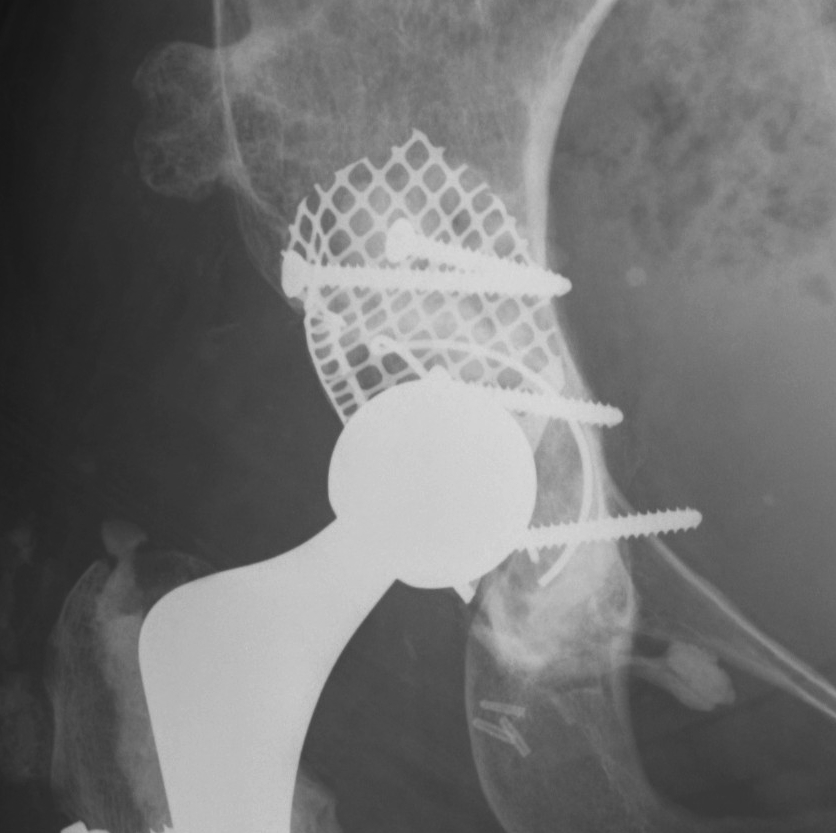
1. Structural Allograft + Cage
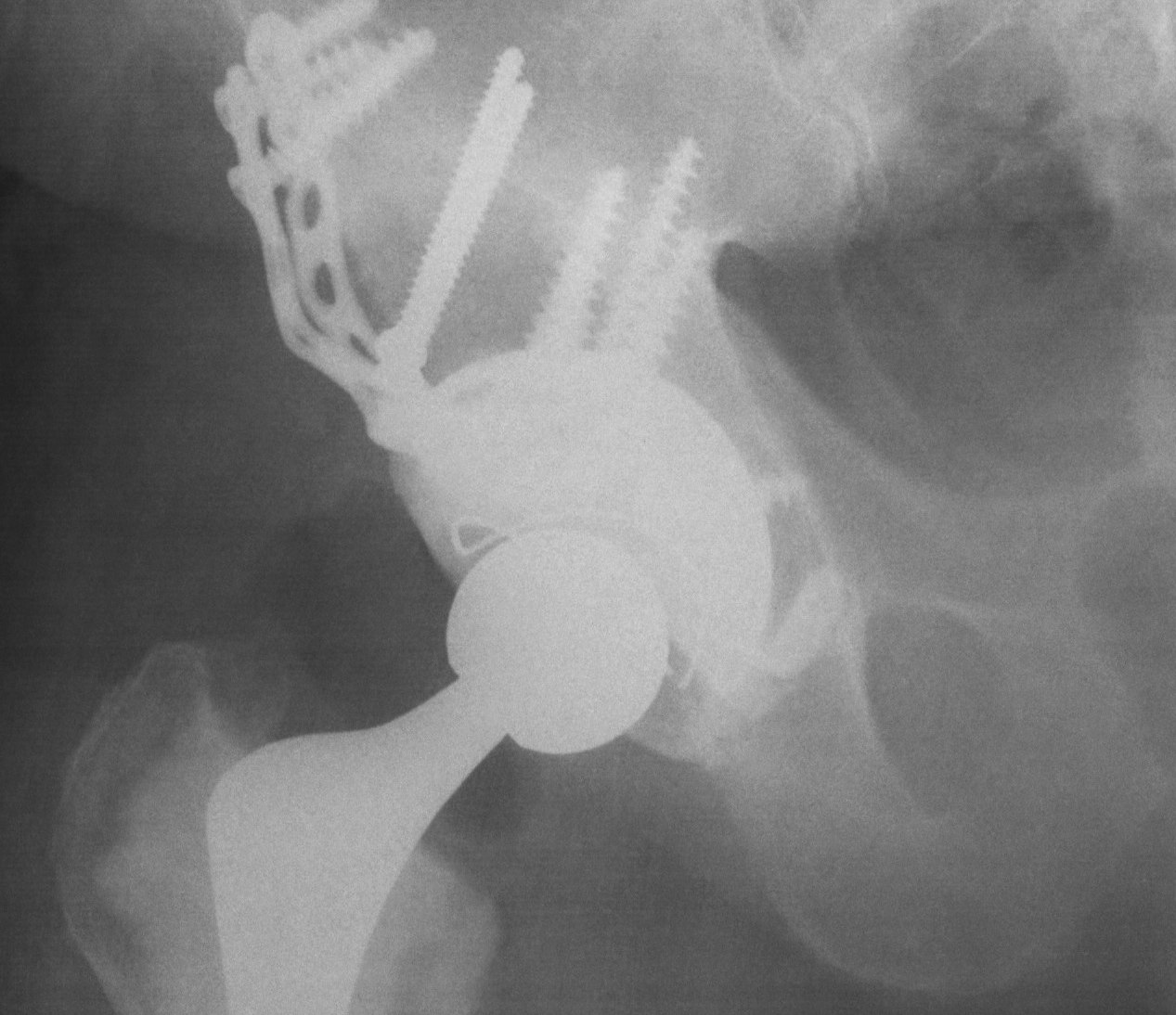
Indications
- when inadequate bone stock precludes the use of uncemented acetabular components
Theory
- cannot implant onto allograft
- graft under the cage
- secure with cage
- cement poly into it
Technique
- allograft reconstruction of rim with femoral head
- allograft particulate material in base
- secure cage to posterior column ilium and ischium
- 3 screws in each
- cement all poly cup into cage
Results
- 75% 10 – 15 year survival
Option: Custom-made triflange components
CT guided model of pelvis
- custom made acetabular cage
- fits defect exactly
- flanges perfectly designed and not malleable to improve strength
- HA coated
- cement poly cup into it
Indications
- massive defects
Results
- 90% 4.5 year survival in complicated patients
2. Impaction Bone Graft +/- Mesh + Cage + Cemented cup
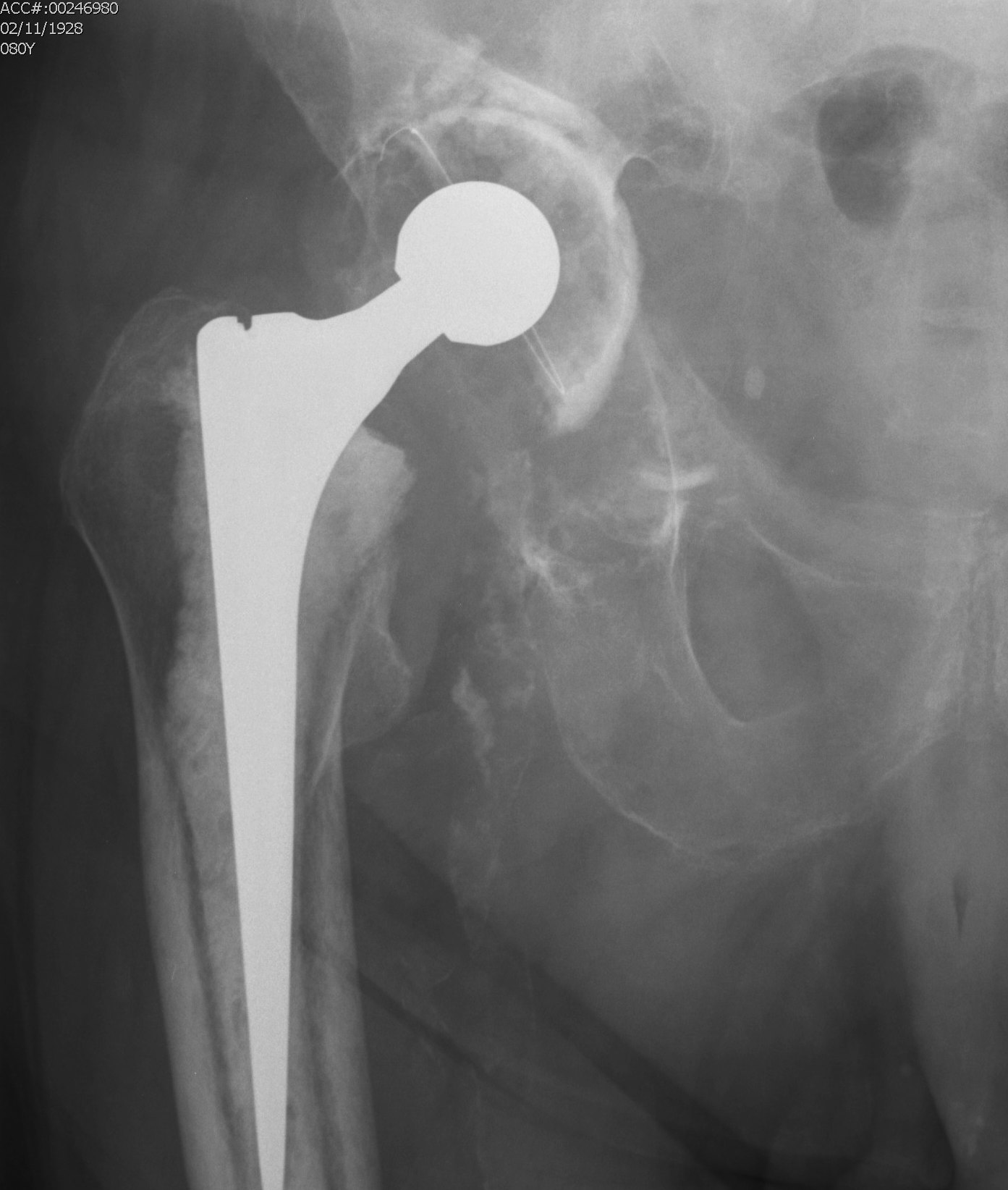

Pelvic discontinuity
1. Plate and bone graft posterior column
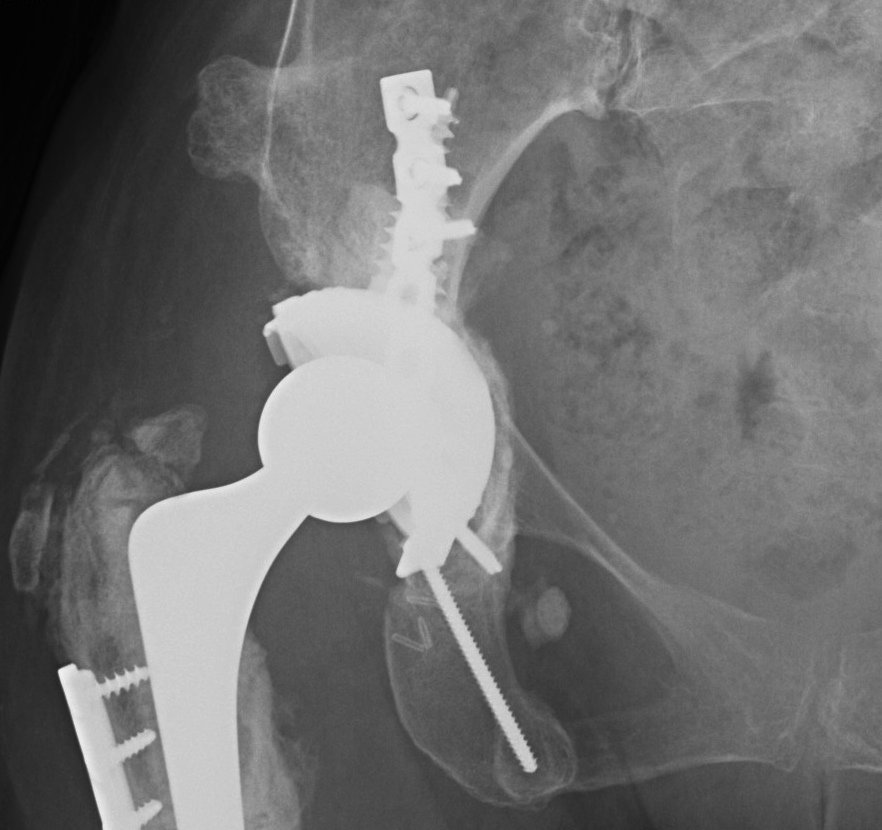
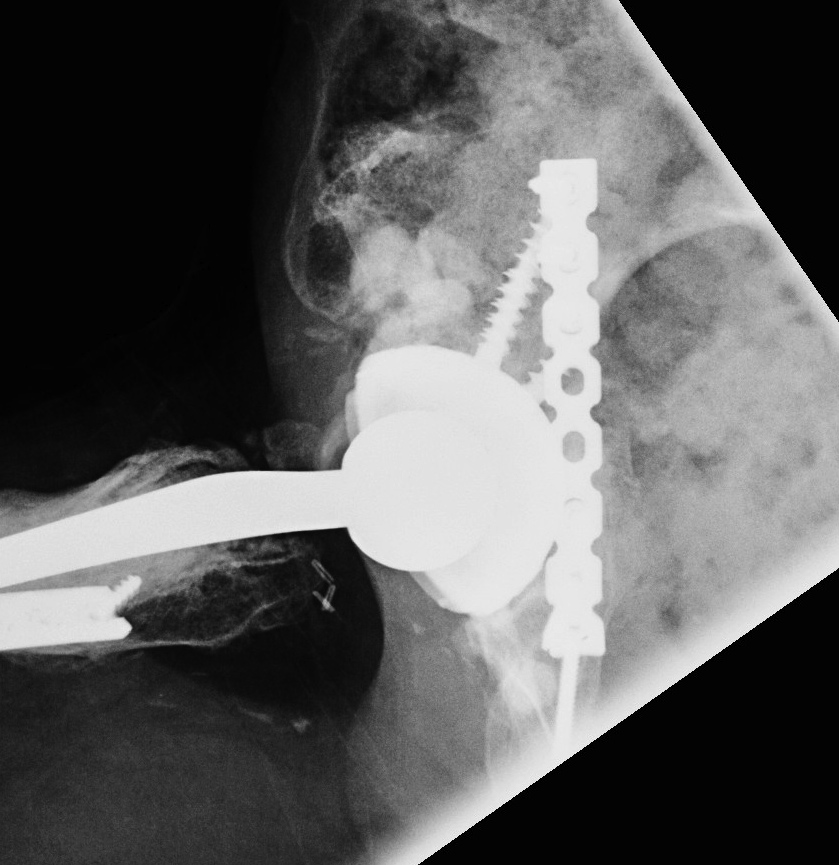
2. Plate + Cage reconstruction
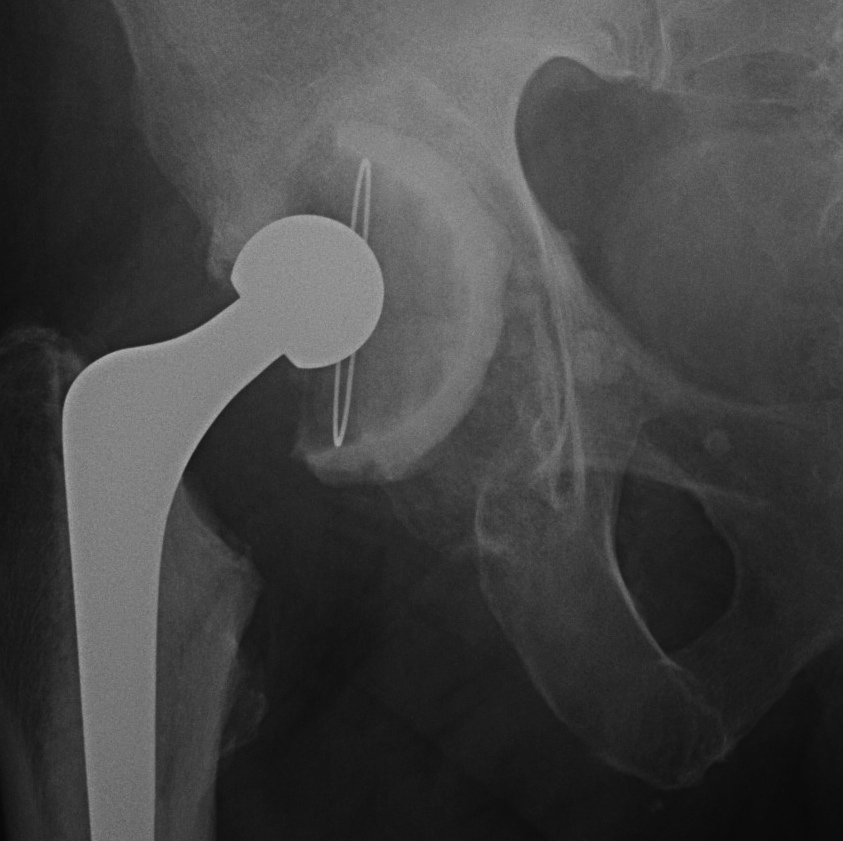
3. Cup Cage Reconstruction
Technique
- large tantalam cup inserted for reconstitution of discontinuity
- bone graft inserted
- cage, cement in cup