Definition
Present with pain but not instability
Types
Traumatic
Degenerative
Different treatment algorithms for each
History
Ulna side wrist pain
- may be worse with rotation
- opening doors and jars
History of trauma
Examination
Local tenderness DRUJ
Supinate / pronate
- pain
- click
Forcibly ulna deviate and pronate wrist
- grinds carpus against TFCC
- generates pain
Check for DRUJ instability / Piano Key
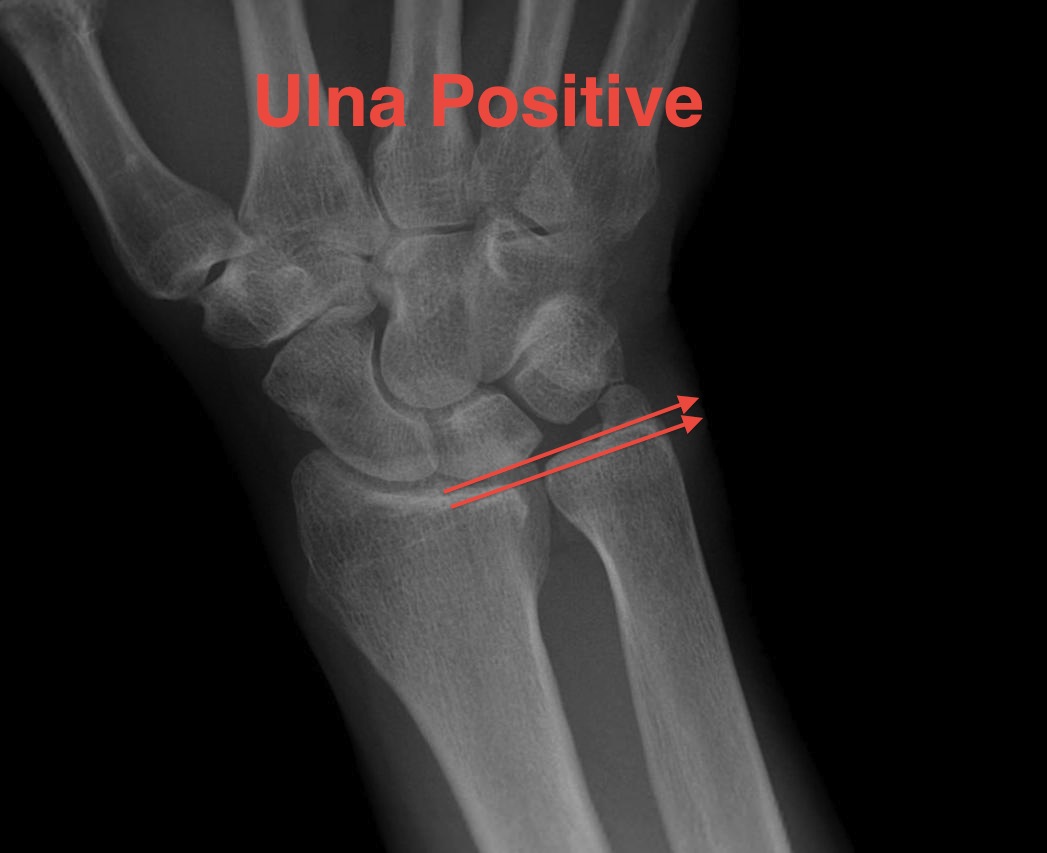
Ulna variance
Position
Xray in neutral supination / pronation
Variance is not static
- Pronation increases ulnar variance
- Supination decreases variance
- May be up to 3 mm
Measurement
Transverse line of lunate fossa
Transverse line of ulna head
Variation
Population is on average 1 mm ulna plus
- wide variation
- 1/4 wrists are ulna negative
Importance
Neutral variance
- Takes < 20% of load
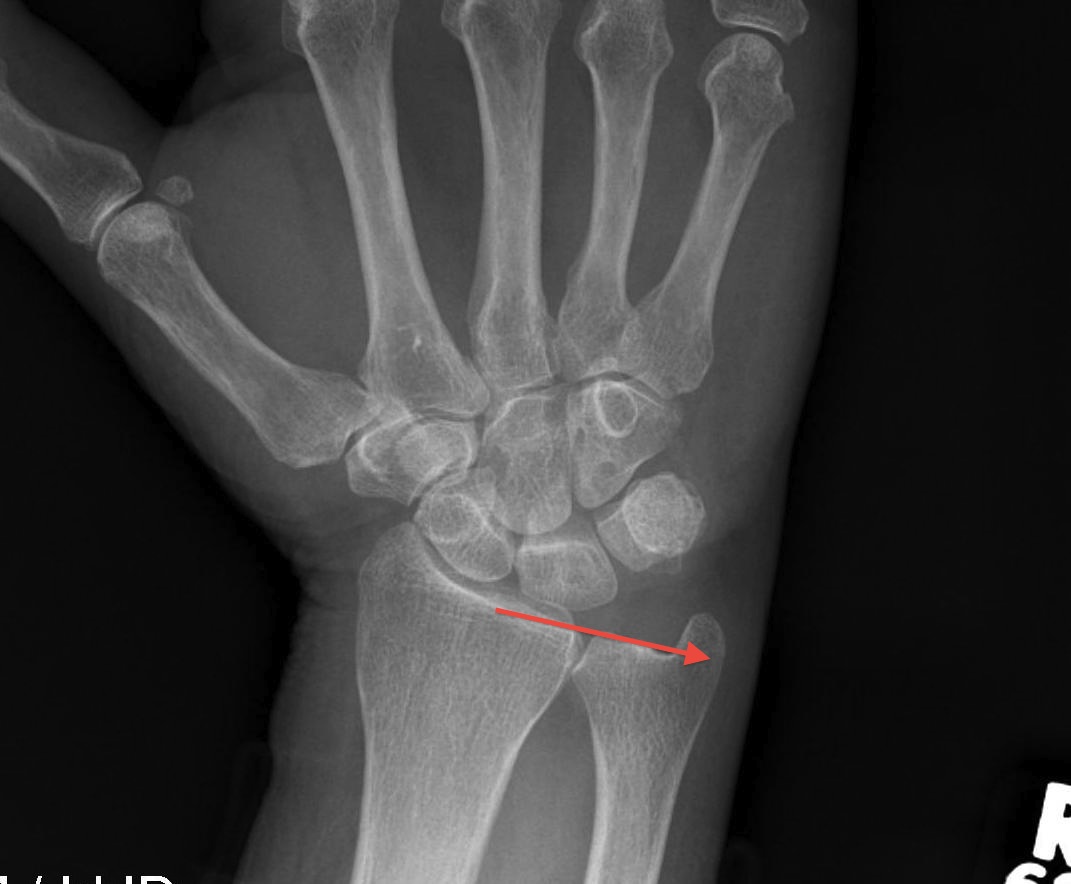
2.5mm Ulnar negative
- 4.3% of load
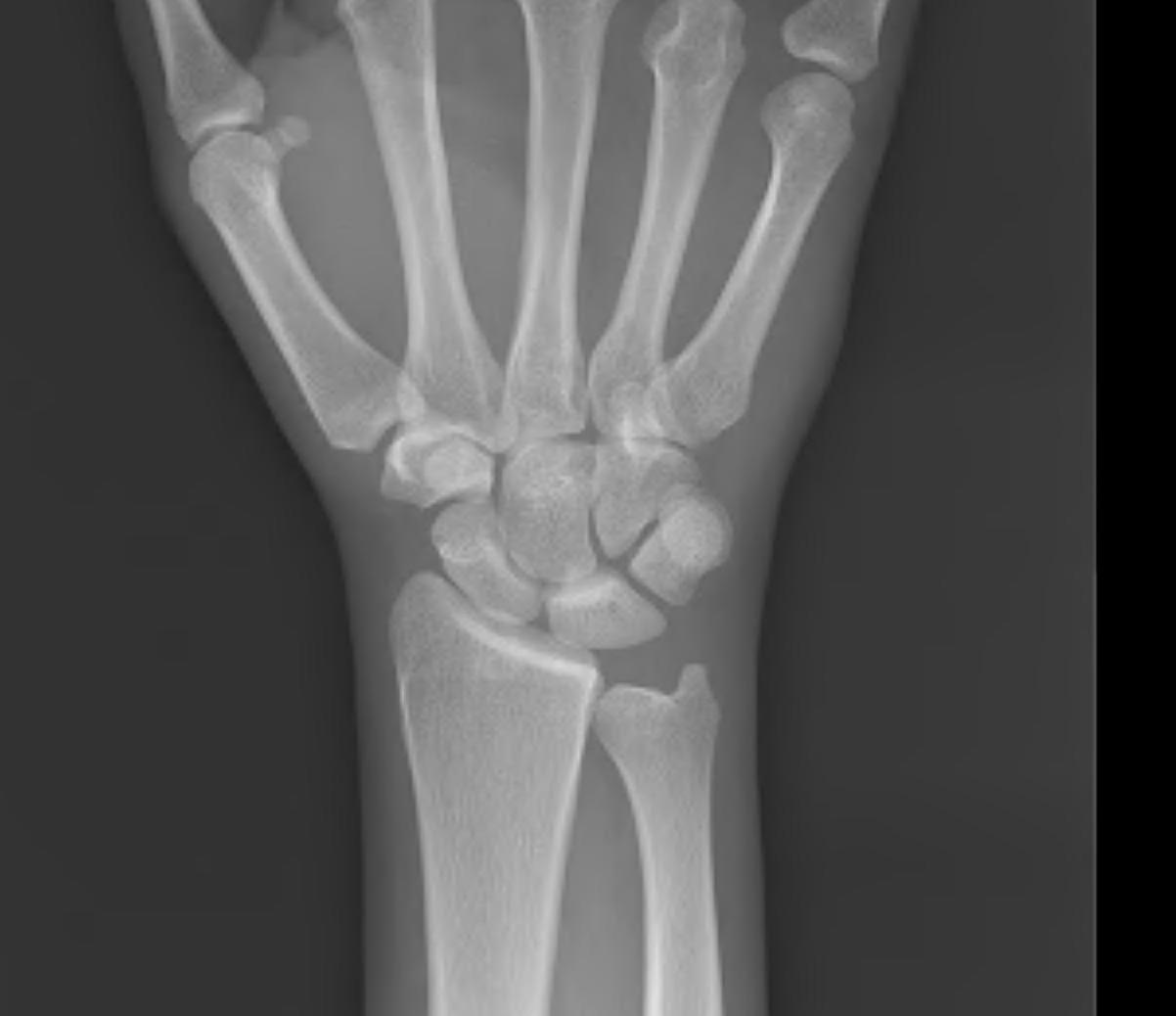
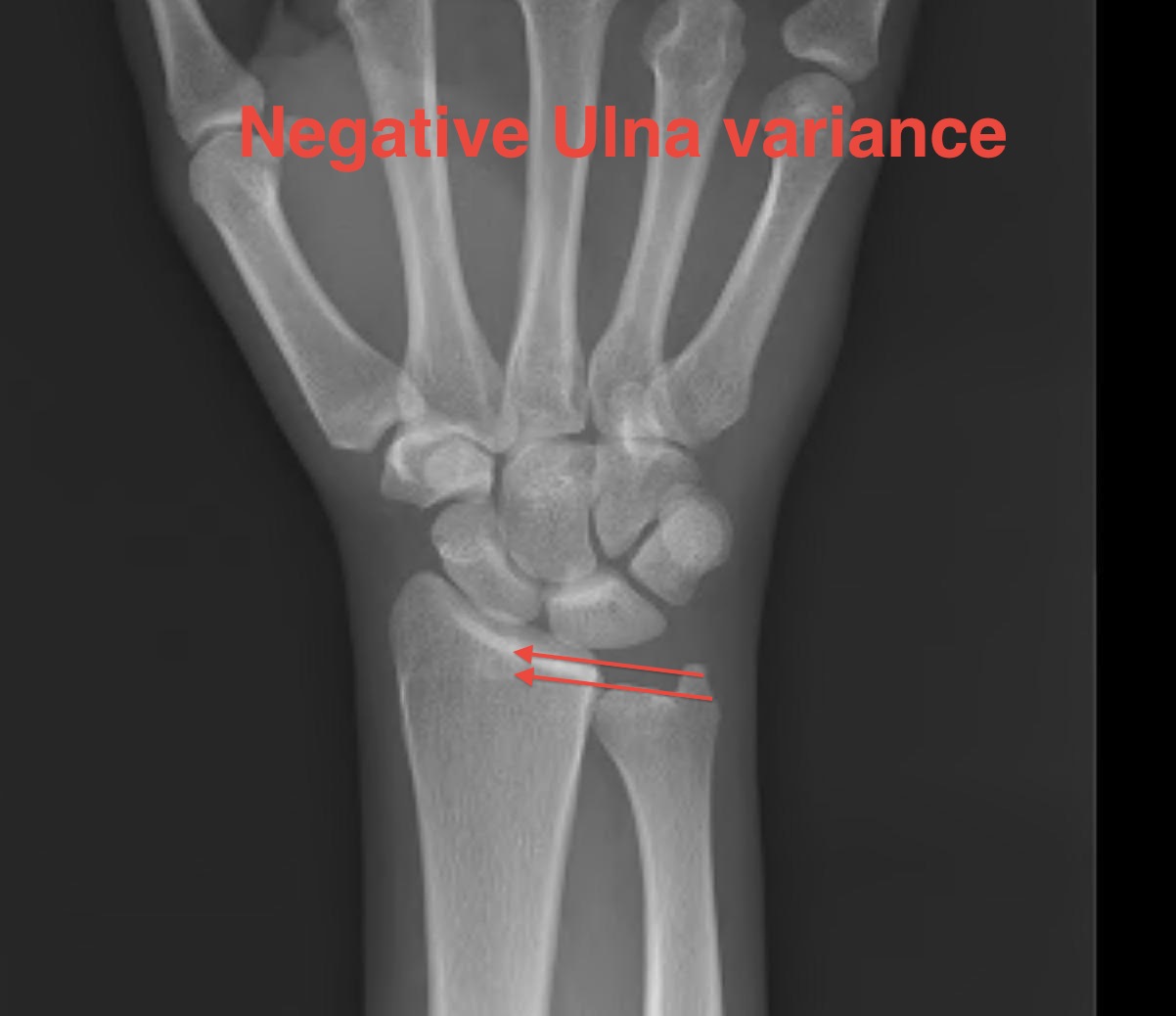
2.5mm Ulnar positive
- 42% of load
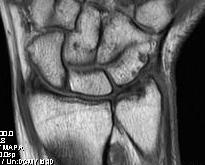
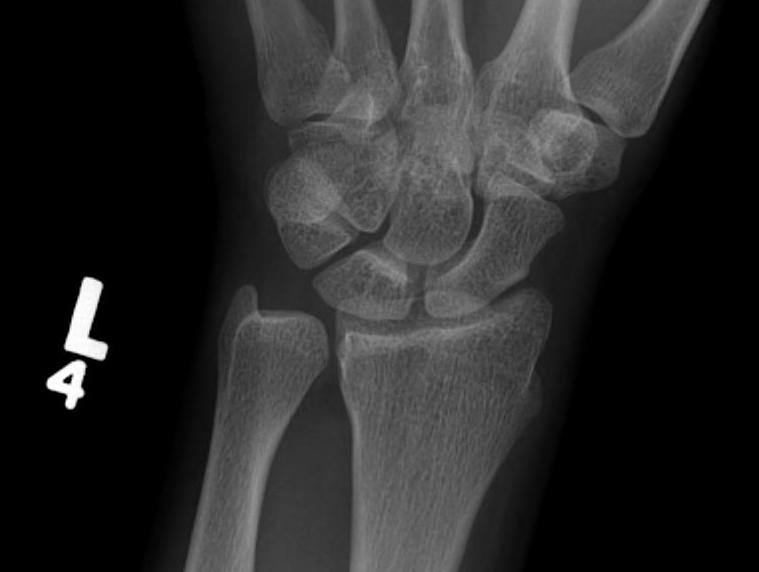
Xray
Ulna Variance
Evidence ulnocarpal abutment / arthritis
MRI
Look for discontinuity of TFCC
- radial / ulna / central / carpal

Wang et al, J Hand Surg Eur Vol
- 154 patients >20y with assymptomatic wrists had MRI performed
- 44% had full thickness tear
- Worse with age, 17% 20-29y; 77% if > 60y
Palmer Classification TFCC Lesions
Class 1 Traumatic
A. Central perforation
B. Ulnar avulsion
- With distal ulnar fracture
- Without distal ulnar fracture
C. Carpal / Distal avulsion
- ulno-carpal ligament injury
D. Radial avulsion (+/- sigmoid notch fracture)
Class 2 Degenerative
Central
A. TFCC wear
B. TFCC wear
+ lunate and/or ulnar chondromalacia
C. TFCC perforation
+ lunate and/or ulnar chondromalacia
D. TFCC perforation
+ lunate and/or ulnar chondromalacia
+ Luno-Triquetral ligament perforation
E. TFCC perforation
+ lunate and/or ulnar chondromalacia
+ Luno-Triquetral ligament perforation
+ ulnocarpal arthritis
Arthroscopy
Diagnose central tears
Trampoline test
- TFCC should bounce on probe
- if very soft, likely has a peripheral tear
Management
Concepts
- acute repair if DRUJ unstable
- delayed repair if continued symptoms and ulna / radial tear
- debridement of central tears + ulna shortening if ulna positive
- ulna shortening if ulnocarpal abutment / arthritis
Class 1 Traumatic
A. Ulna
Acute Injury
1. Stable DRUJ
- immobilise in neutral rotation
- need long arm cast
- surgical repair if continued symptoms / non healing
2. Unstable DRUJ
A. Obtain closed reduction / supination
- immobilise
B. Failure closed reduction
- open / arthroscopic TFCC repair to stabilise DRUJ
Operative repair
Indications
- acute instability
- continues pain / late presentation
Open
- good success as very vascular
- 5/6 approach / bed of EDM
- interval between EDM and ECU
- open capsule
- sutures in TFCC, pass through drill holes in base ulna styloid
- immobilise in cast
Arthroscopic
B. Radial
Commonest
- difficult to access / repair / very avascular
Open repair
- 5/6 approach
- drill holes through dorsal radius into ulna fossa
- use suture retriever
- stabilise with RU K wires if continued instability
C. Central
Site
- usually occur along avascular origin from radius
- usually 1-2mm from origin
- may be traumatic or degenerative
Neutral ulna variance
- Arthroscopic debridement
- 73% success complete pain relief
- Can take central 2/3 of disk without problems
Positive ulna variance
- do worse if debride disc alone
- consider combining with ulnar shortening as well
Class 2 Degenerative
Class 2A - C
Definition
- TFCC wear or perforation
- lunate and / or ulna chondromalacia
- lunate triquetral ligament intact
1. Positive ulna variance
Shorten ulna +/- arthroscopic debridement TFCC
Options
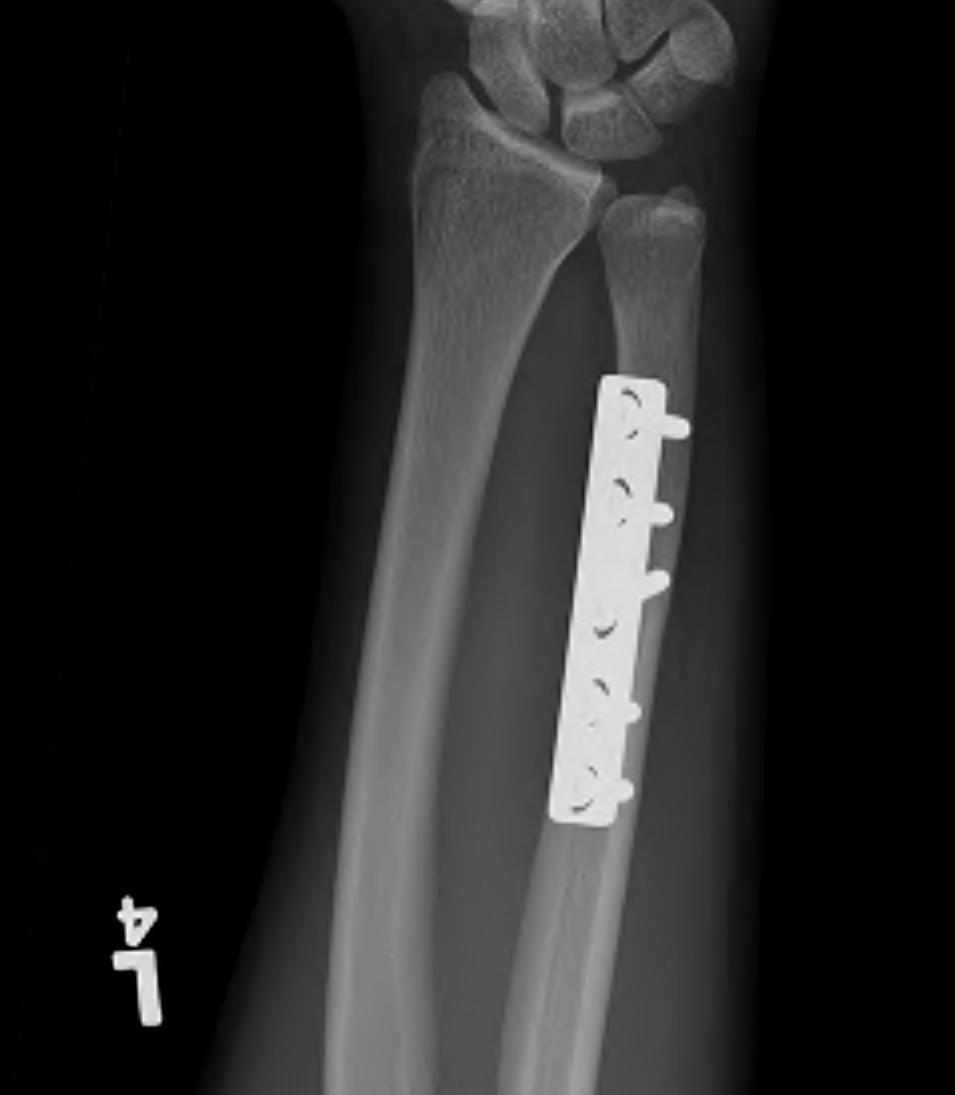
A. Ulnar shortening and plate fixation
- specific plates (Trimed)
- have advantage of rotational control throughout procedure
- midportion ulna, apply plate dorsal
- fix distally, sliding screw proximally
- oblique osteotomy through jig
- 5 or 8 mm
- shorten, lag screw through plate
- apply proximal screw
B. Wafer / Bower's hemiresection procedure
- open or arthroscopic
- remove 2-3 mm ulna head
- aim to make ulna negative
- not indicated if > 4mm ulna positive
- leave ulna styloid / TFCC intact
2. Ulna neutral
- arthroscopic debridement
- +/- ulna shortening
Class 2D
Definition
- Lunotriquetral ligament perforation
Options
- Arthroscopic debridement / ulna shortening
- LT fusion if unstable
Type 2E / Ulnocarpal Impaction Syndrome
Definition
- LT ligament perforated
- ulnocarpal abutment / arthritis
Associated with positive ulnar variance
- from repetitive loading
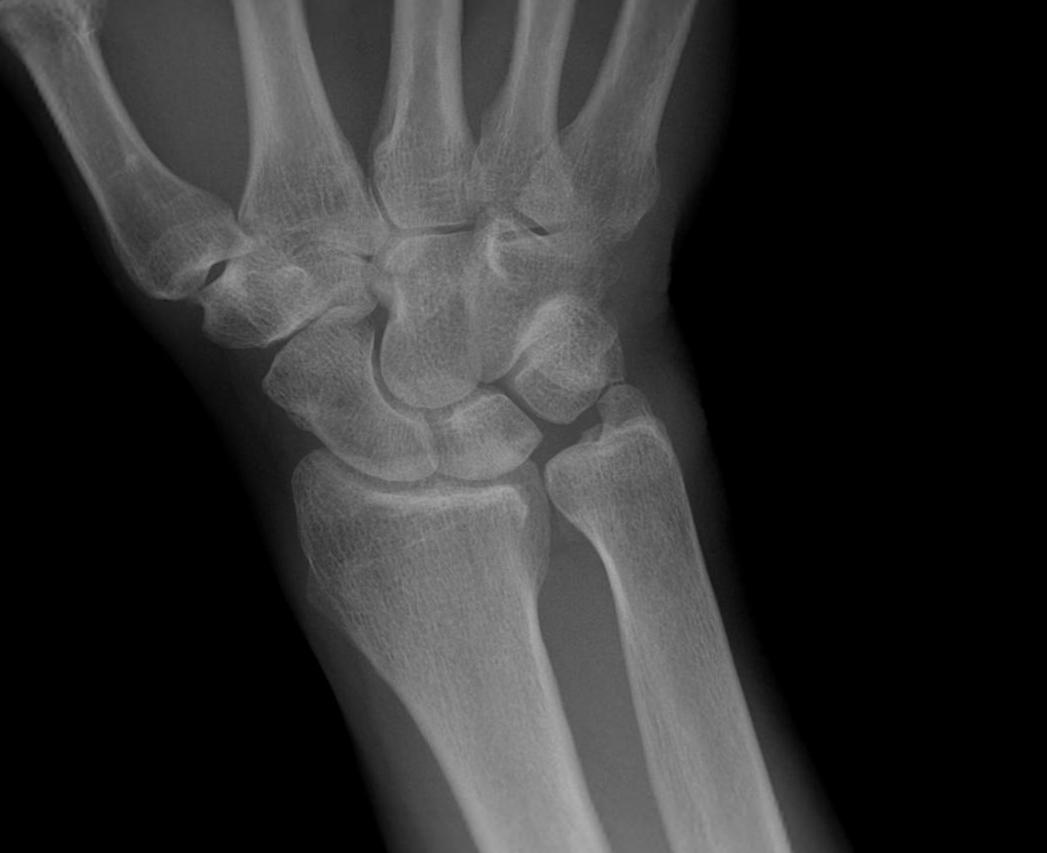
Options
1. Bower's ulna head hemiresection
- resect 2mm ulna head leaving ulna styloid
- +/- interposition of dorsal capsule
2. Darrach's
- excision of distal ulan
- +/- stabilisation with tendon transfer
3. Suave-Kapandji
- distal radioulna fusion