Definition
Instability in at least 2 planes
- postero-inferior
- antero-inferior
- antero-postero-inferior
Epidemiology
Recognised as a common problem
- often misdiagnosed
Most patients athletic
- average age 24 years (15 - 54 years)
Aetiology
1. Inherent ligament laxity > 50%
2. Repetitive overuse with capsular stretch
- microtrauma
3. Macro-trauma < 50%
Pathology
Collagen abnormality
Increased joint volume
- 2° enlarged inferior axillary capsular pouch
- patulous anterior and posterior
Often attenuated, broad rotator interval
History
Often bilateral
Instability of other joints
Feeling of shoulder "slipping down" while carrying heavy loads
- inferior instability
Often recurrent subluxation with minimal trauma
- sleeping
Shoulder pain
- fatigue
- impingement type pain with overhead activities
Examination
Ligamentous laxity 75%
Inferior instability
- Sulcus Sign +
Anterior instability
- anterior draw
- anterior load and shift
- anterior apprehension, positive Jobe's relocation
Posterior instability
- posterior draw
- posterior load and shift
- posterior apprehension / jerk test
Xray
Traction xray
- patient standing with 5-10 kg in each hand
- Shows inferior subluxation of head
DDx of Inferior displacement of head
Torn superior rotator cuff
Suprascapular nerve palsy
Deltoid atony eg CVA
Deltoid / axillary nerve palsy
Management
Non-operative
Mainstay of treatment
- operative results poor
Physiotherapy
Minimum 12/12
- initial shoulder strengthening
- strengthen 3 parts of deltoid, cuff & scapular stabilisers
- specific programme with rope & pulleys
- combined with education program
- ~ 90 % success
Operative
Principles
- never operate on voluntary dislocator
- MDI surgery less successful than surgery for unidirectional instability
- cannot perform isolated anterior surgery
- bristow procedures etc fail as capsule remains redundant
- anterior surgery may displace head posteriorly
MDI with traumatic anterior bankart
- new symptomatic instability on a background of ligamentous laxity / MDI
- MRA diagnosis of anterior bankart
- is reasonable to operate on patient with new traumatic anterior instability with labral tear
- issue is whether to combine with capsular shift
Options for MDI
1. Neer and Foster inferior capsular shift
2. Arthroscopic capsular plication
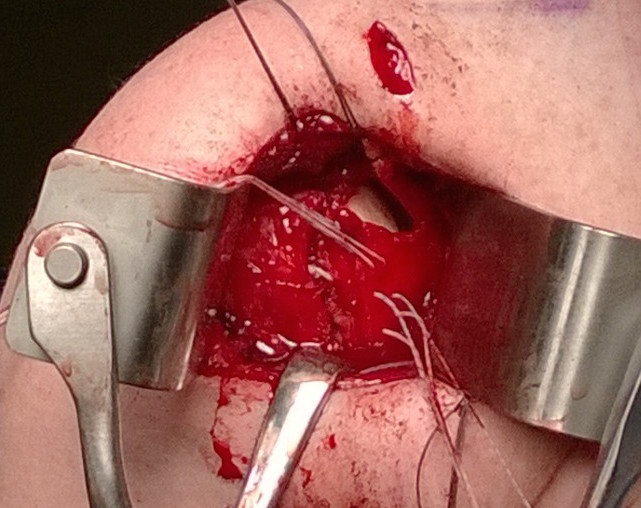
1. Open Inferior Capsular Shift ~ Neer & Foster 1980
Principle
- detach capsule from neck of humerus
- shift capsule superiorly to obliterate the inferior pouch
- decrease joint volume
Technique
EUA
- to confirm diagnosis
Deltopectoral Approach / Axillary fold
SSC
- must divide SSC separate to capsule
- need to leave capsule intact
- make horizontal incision in inferior border of SSC
- at muscular aspect
- insert curved artery forcep between SSC and capsule
- will exit at rotator interval
- insert medial stay sutures x 2 (use different colour to differentiate from capsular sutures)
- make vertical incision on artery forcep to avoid injury to capsule
T shape capsulotomy of capsule
- vertical component on humeral insertion
- transverse component to midpoint glenoid
- mark with pen first
- make vertical component on articular margin
- place inferior and superior stay sutures
- make horizontal incision
- creates superior and inferior capsular flaps
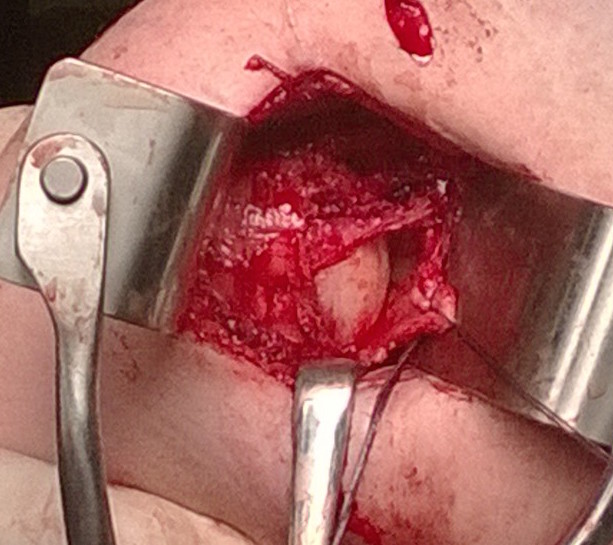
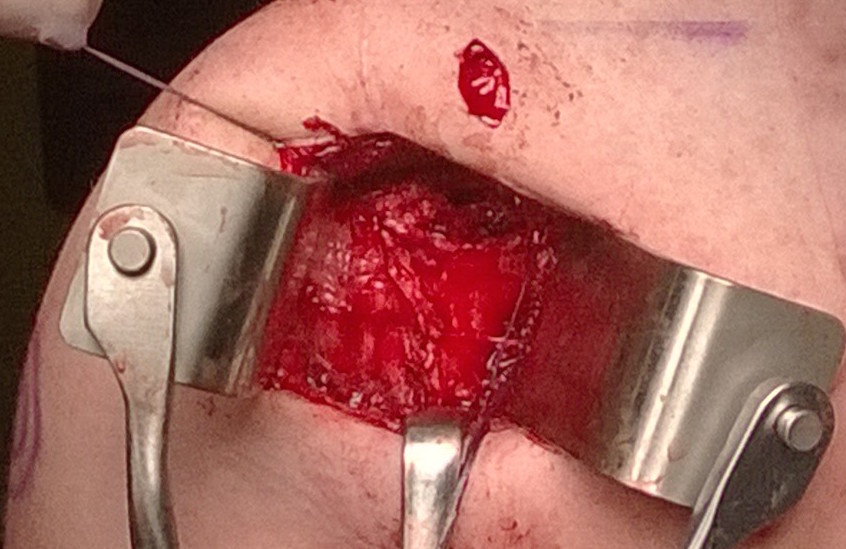
Inspect joint
- ensure no loose bodies
- repair bankart lesion if needed
Inferior capsular flap
- must sharp dissect capsule off inferiorly around humeral head
- protect AXN at all times
- do so by following articular margin around
- ER shoulder +++
- must get past 6 o'clock into posterior aspect
- check that traction on interior flap reduces inferior capsular pouch
Superior advancement inferior capsular flap
- tension on flap aimed at eliminating inferior pouch
- must reduce posterior capsular redundancy
- multiple 0 pull off stay sutures through flap and into remnant humeral tissue
- +/- anchors
- begin inferiorly, care with AXN
- cut and clip each sutures
- then tie all sutures togther at end
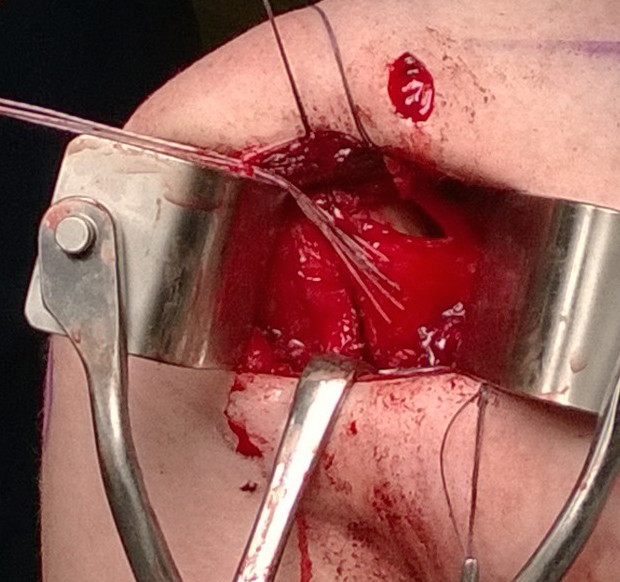
Check ER
- arm adducted, check ER 45o
- arm abducted to 90o, check ER 45o
Superior flap sutured down over inferior flap
- again multiple 0 pull off sutures
- tie
- check ER as above
Check not too tight
- can dislocated posteriorly
Closure of RI
- check ER as above
Subscapularis tendon brought over & reattached to normal location
- check ER as above
Post op
- Arm immobilised in sling 6/52
- No sport for 9/12
Results
Bigliani et al JBJS Am 2000
- 52 shoulders with open inferior capsular shift
- approach posterior or anterior depending on greatest instability
- 96% remained stable at average 61 months
- 60% excellent and 30% good results
- 70% athletes able to return to sport at same level
Ogilvie-Harris Br J Sports Med 2002
- contact athletes
- antero-inferior capsular shift in 37 with 3 recurrences (8%)
- posterior-inferior capsular shift in 16 with 2 recurrences (1 anterior / 1 posterior)(12%)
- 80% return to sport in antero-inferior capsular shift
- 75% return to sport in postero-inferior capsular shift
- only 17% return to sport if bilateral procedures
2. Arthroscopic
Technique
EUA
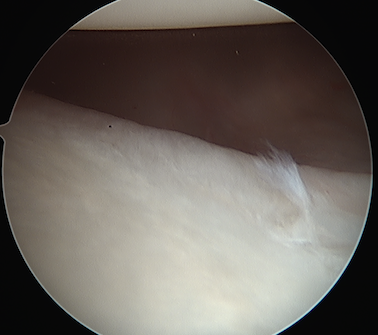
View via posterior and anterosuperior portal
- labrum is attached
- capsule very lax
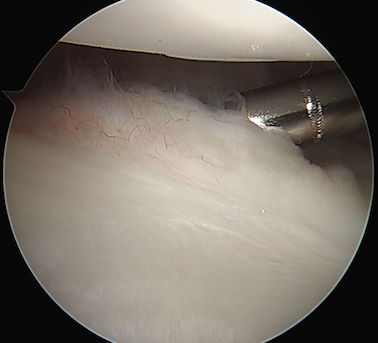
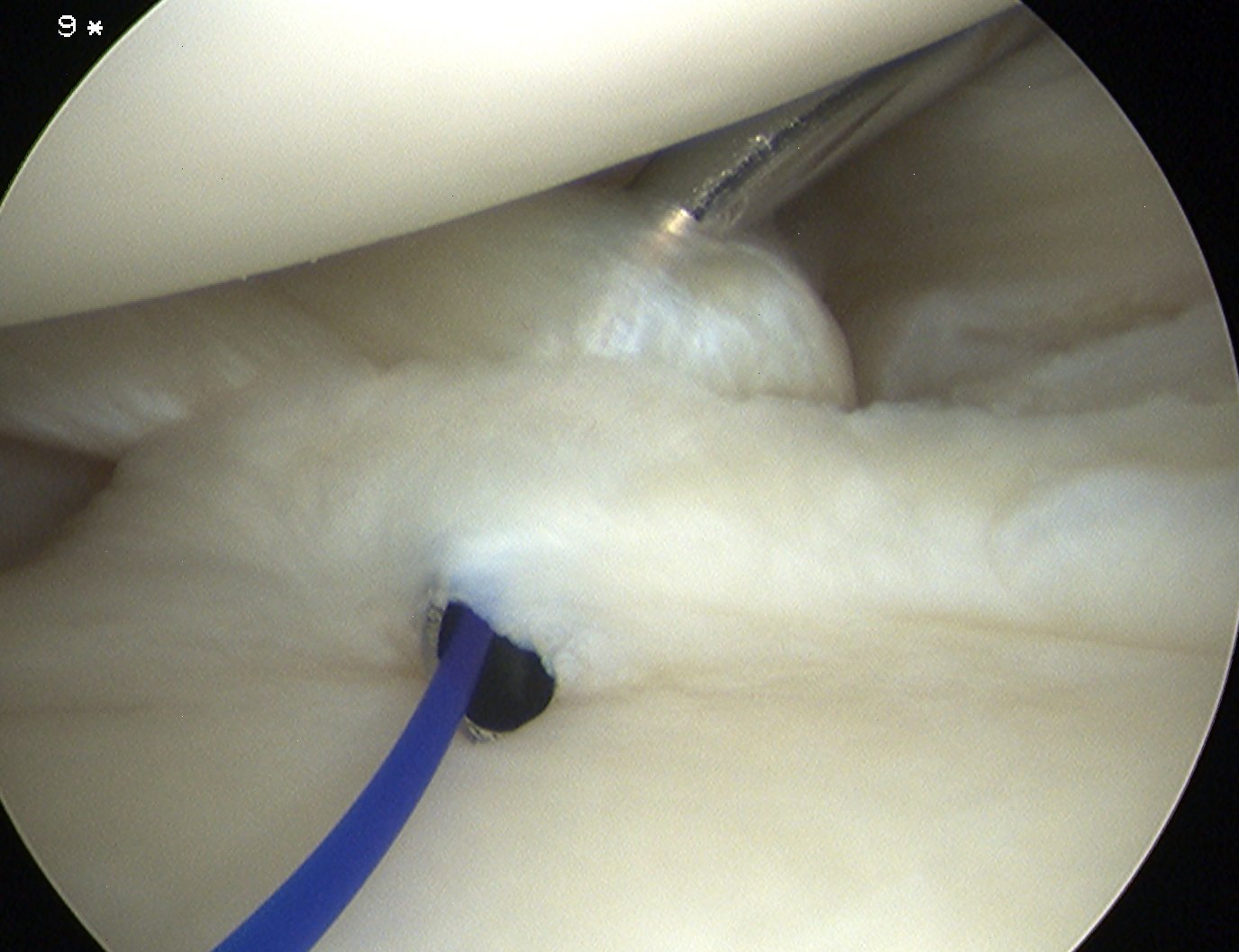
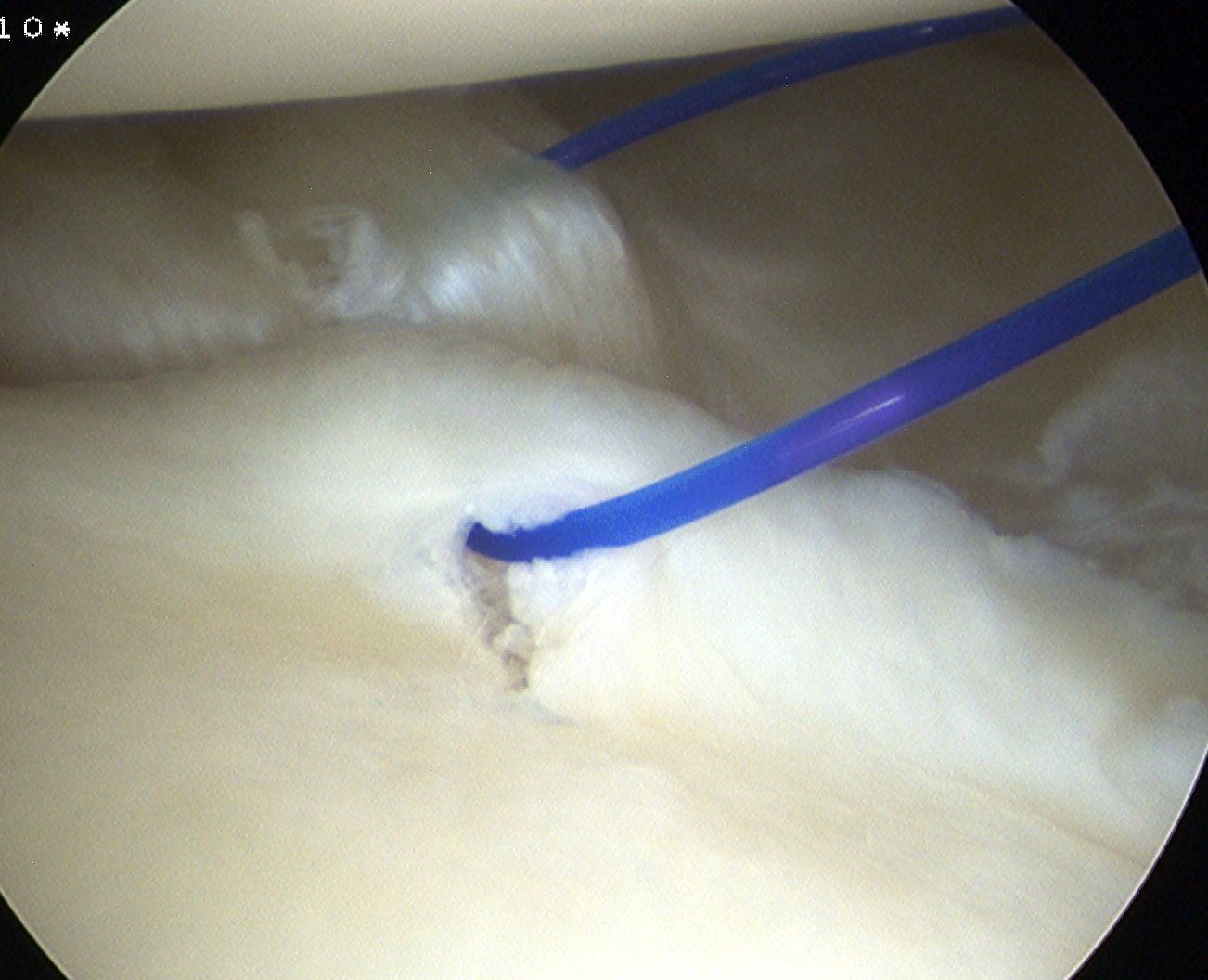
Anterior plication
- use shaver to create capsular stimulation
- don't remove or resect capsule
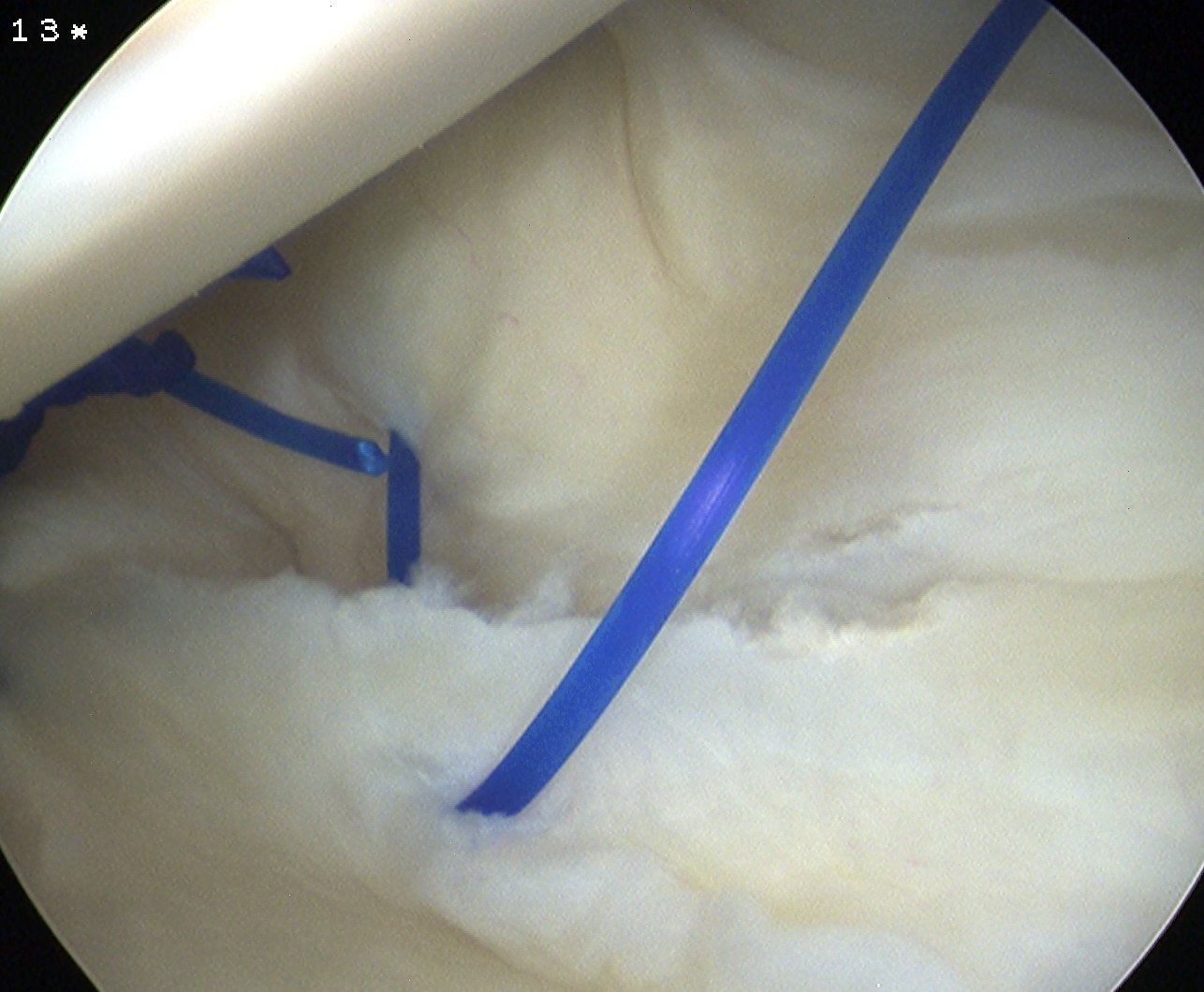
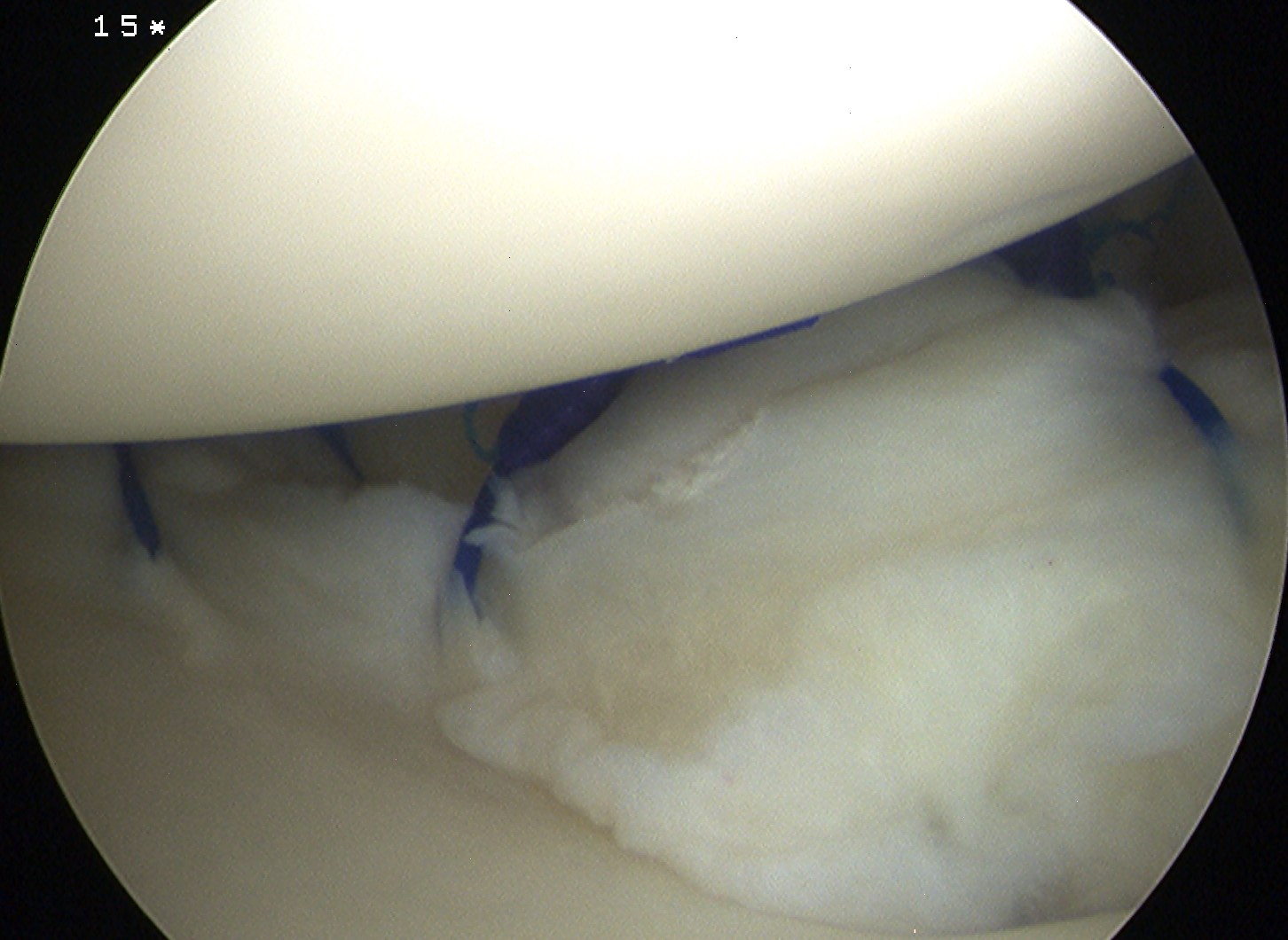
Option 1
- pass through capsule, then through labrum
- inferior suture first
- take bite of anterior inferior capsule with suture passer
- advance suture passer
- then pass separately through anterior labrum at a more superior level
- tie
- repeat x 2
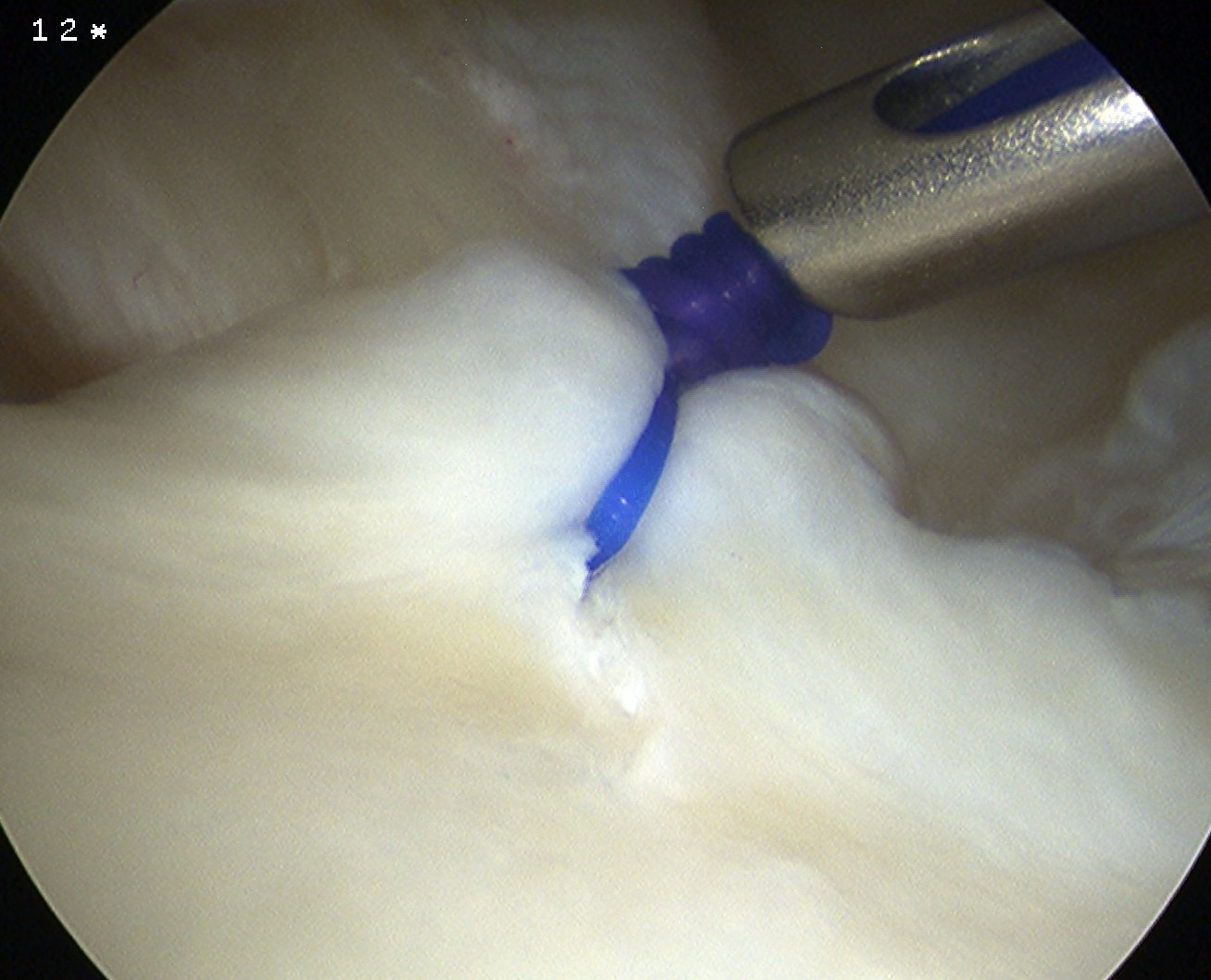
Option 2
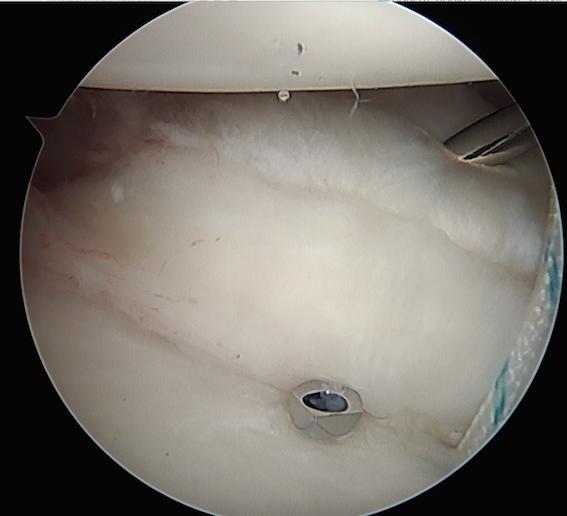
- anchor in glenoid
- pass stures throught capsule and labrum
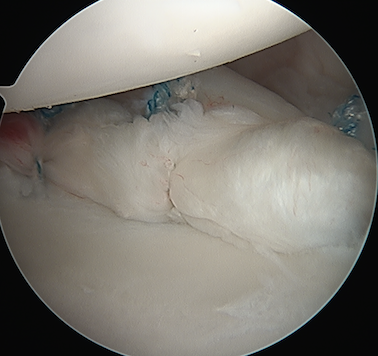
Posterior plication
- camera inserted via anterior portal
- insert posterior cannula
- repeat inferior posterior sutures x 3
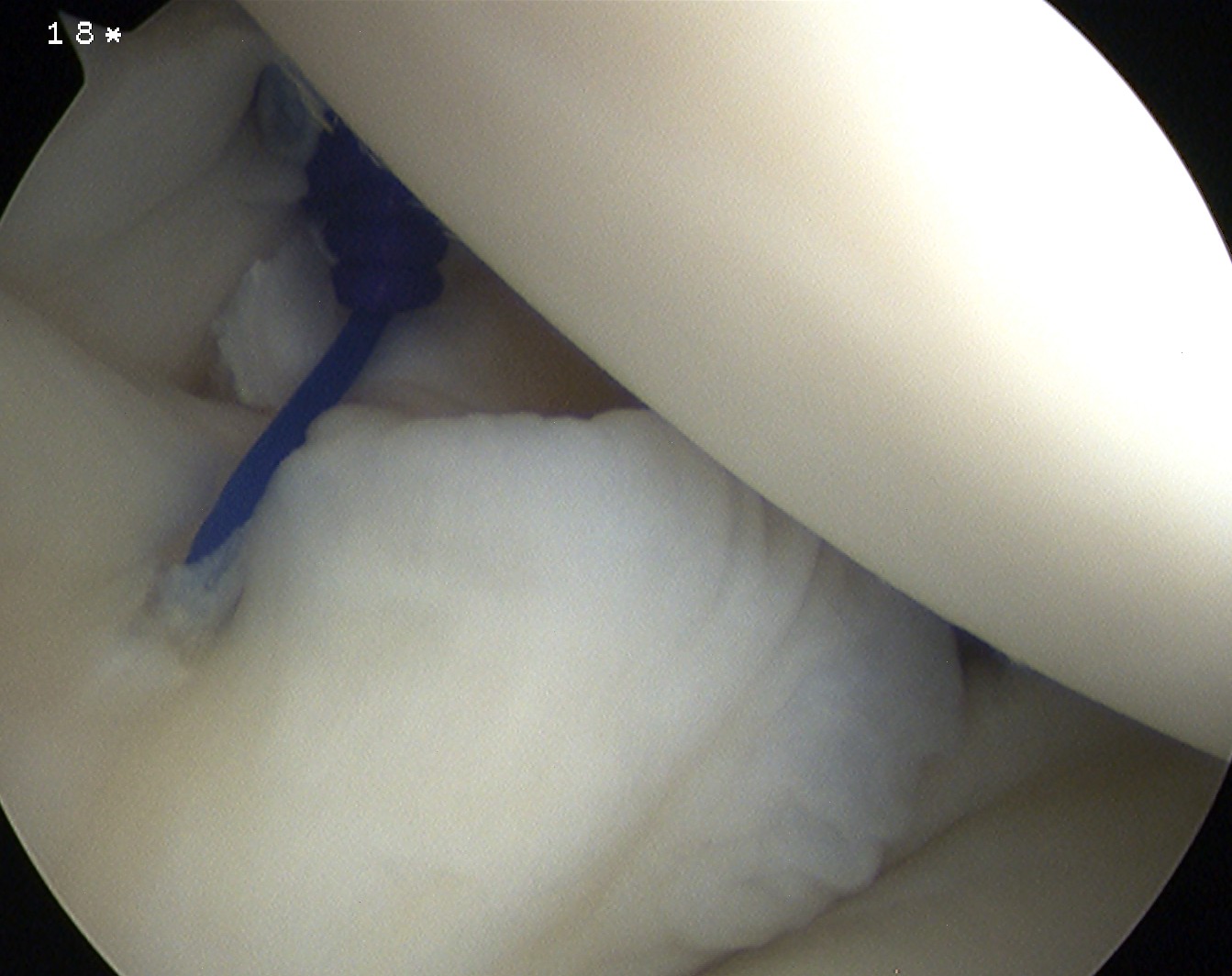
May suture rotator interval if needed
Results
Baker et al Am J Sports Med 2009
- 43 patients average age 19 years
- 86% return to sport
3. Thermal Capsular Shrinkage
Recognised as poor procedure
Results
Miniaci et al JBJS Am 2003
- 19 patients with MDI
- 9 recurrent instability
- 4 had parasthesia in AXN, one had deltoid weakness, all resolved
- worse results in posteroinferior compared with anteroinferior
