Position
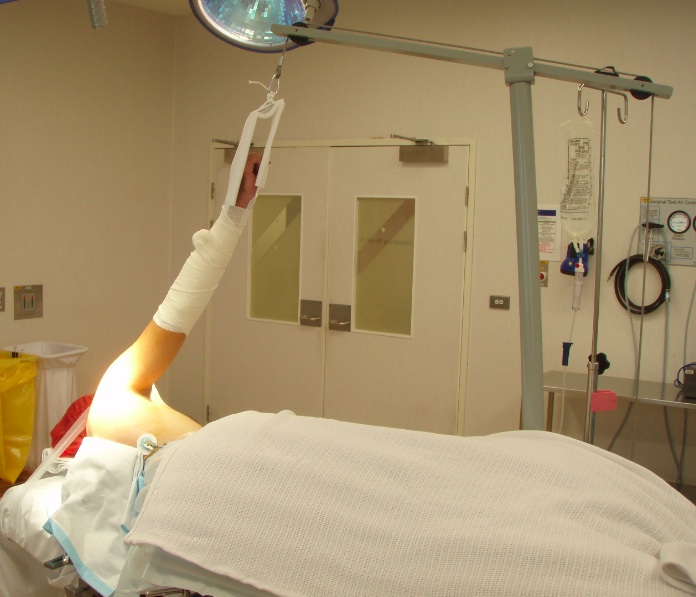
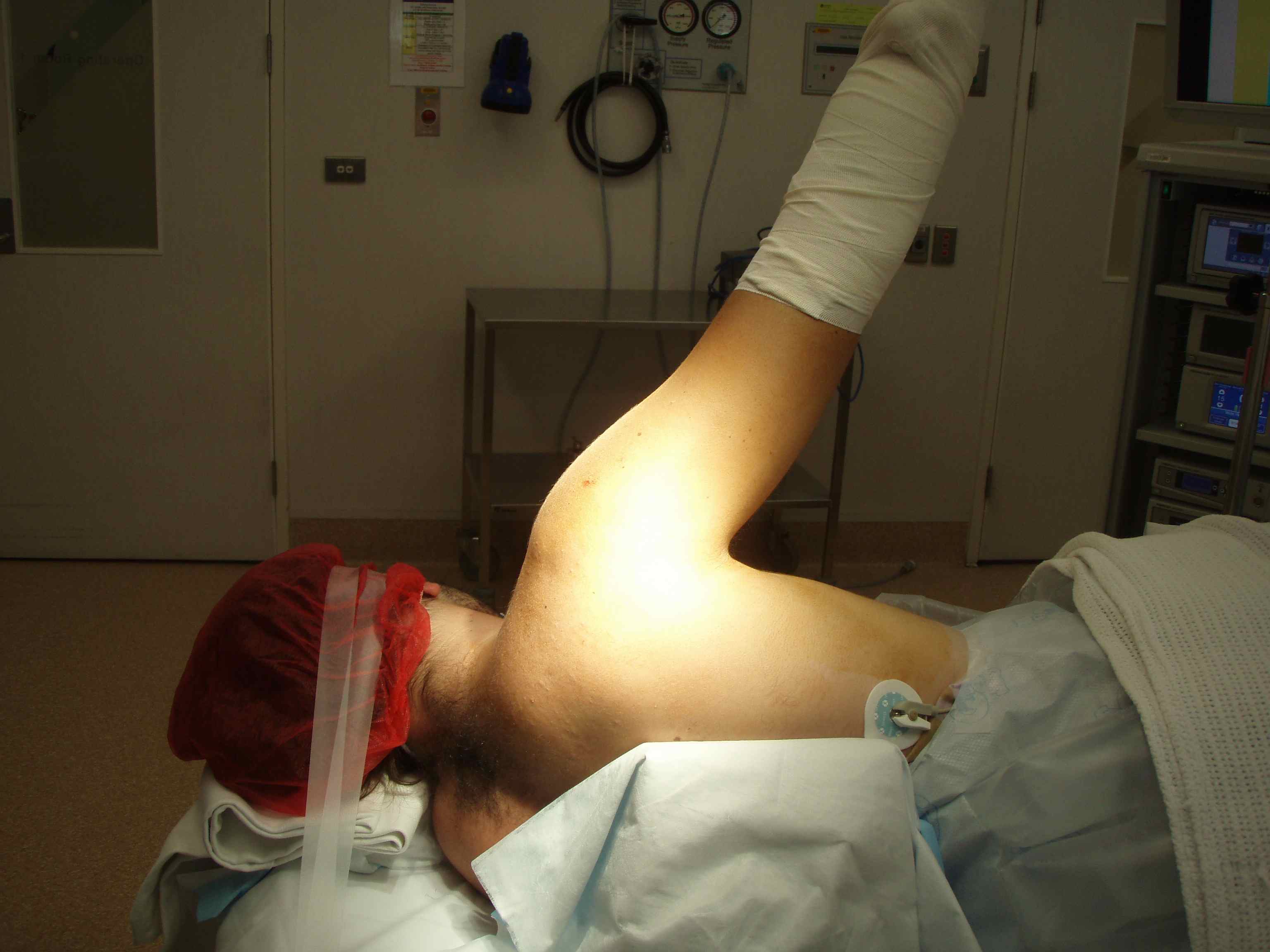
1. Lateral decubitus
- stabilise patient with beanbag or lateral rests
- apply skin traction to forearm
- place traction pole at foot of table opposite surgeon
- suspend arm with 10 lb weight
- abduction 60°
- forward flexion of 20°
- tilt top shoulder posteriorly 30° so that glenoid is parallel wwith bed
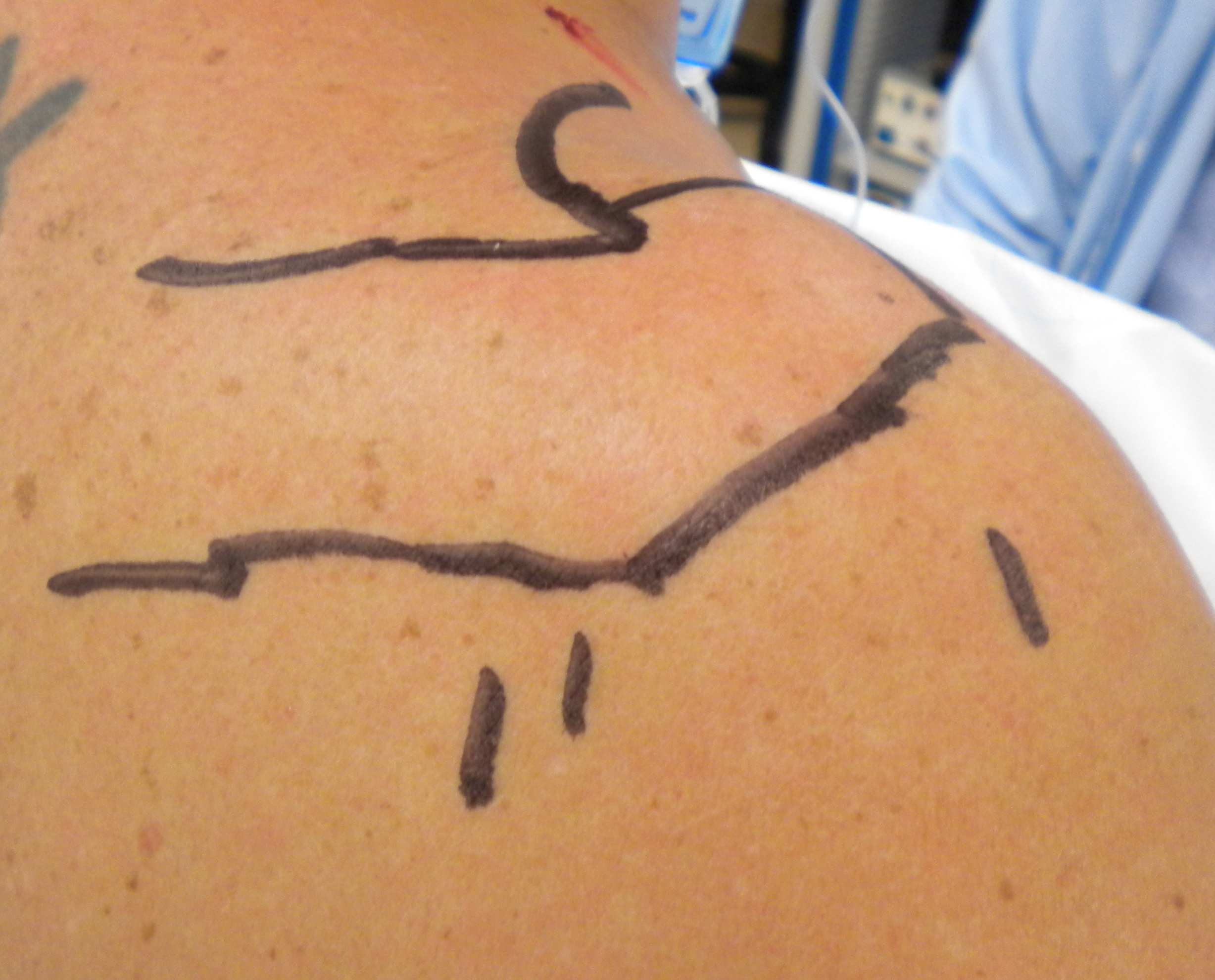
- mark bony landmark
- prep & free drape
2. Beachchair
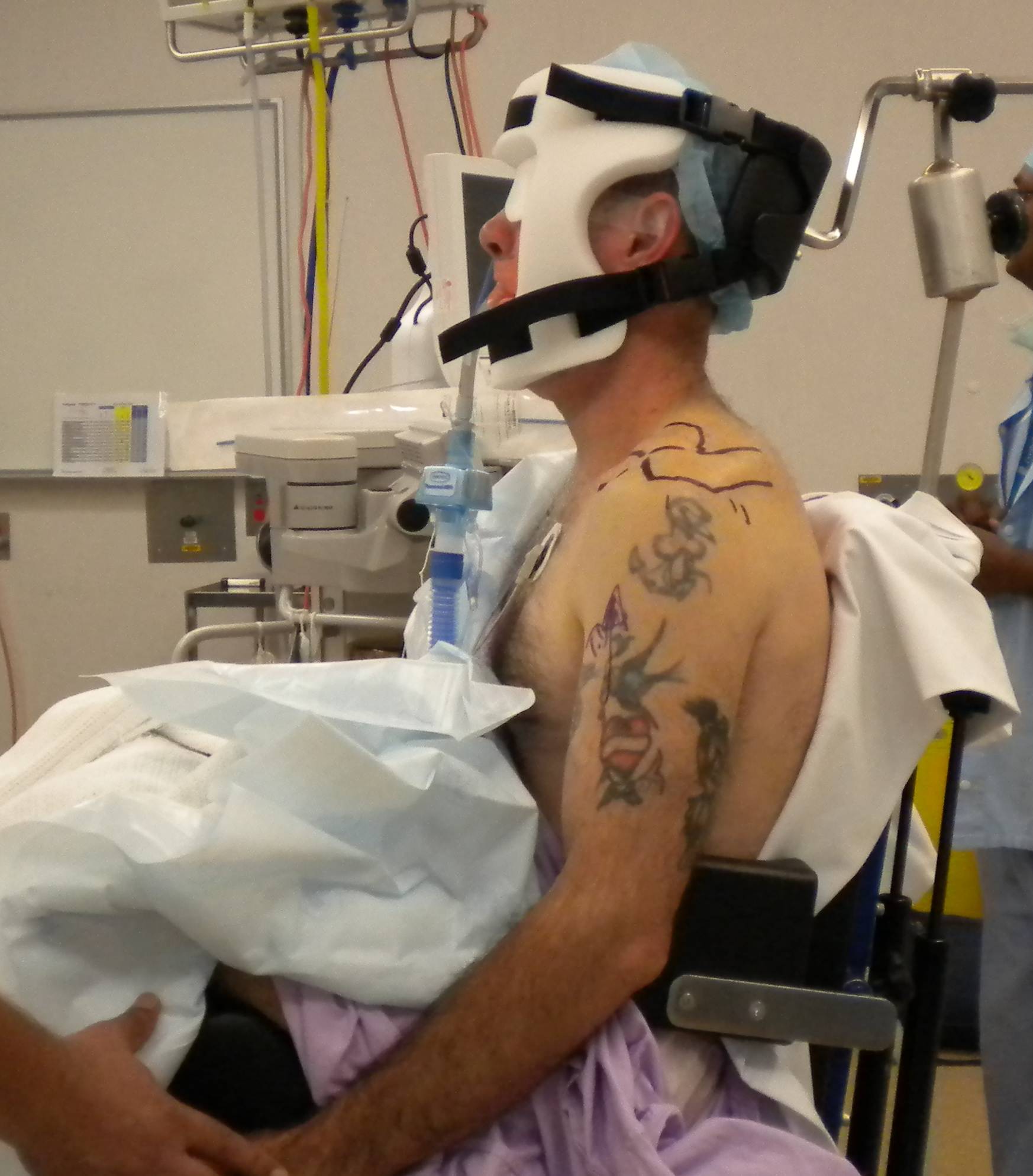
A. Beachchair table
- pillow under thighs
- arm draped free
- access to posterior shoulder
- head secured to Mayfield head ring
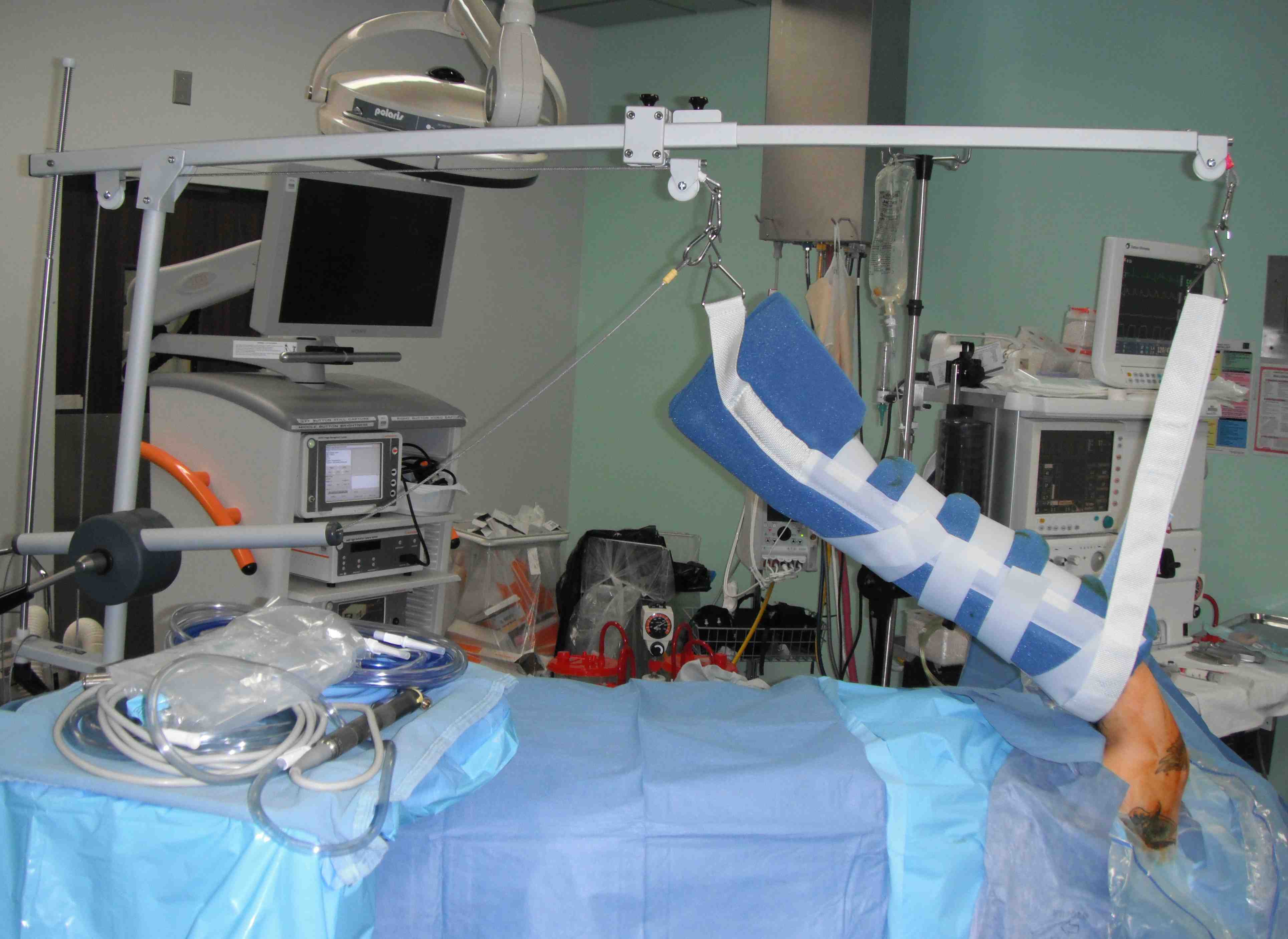
B. Spyder / Tmax
- holds head secure
- good access to posterior shoulder
- hydraulic arm holder elminates need for assistant to hold arm
Portals
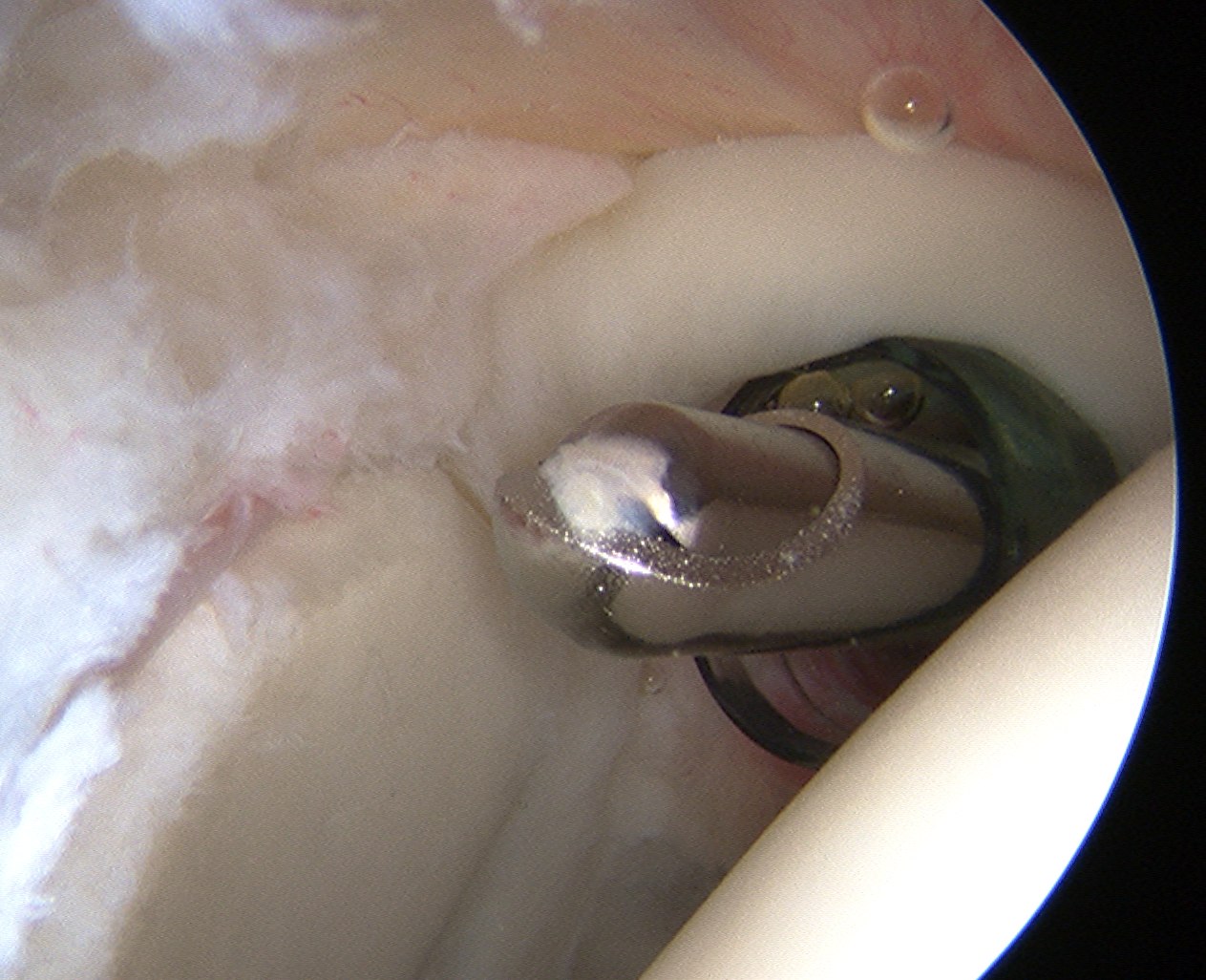
Posterior Portal
Main portal for arthroscopy
A. Soft spot
- identify posterolateral acromion
- 2 cm medial & 2 cm inferior
- through deltoid
- between infraspinatous and T minor
Make stab wound at post portal
- introduce cannula & trocar
- tip towards coracoid process
- distract shoulder joint whilst inserting
- introduce arthroscope
B. Variation
- if mainly performing subacromial / rotator cuff
- move portal lateral and superior
- 1 cm inferior and 1 cm medial to posterolateral acromion
- aims scope over cuff tear which is usually lateral
- increases distance from cuff vertically
- can view larger area
Additional portals
Anterior Glenohumeral Portals
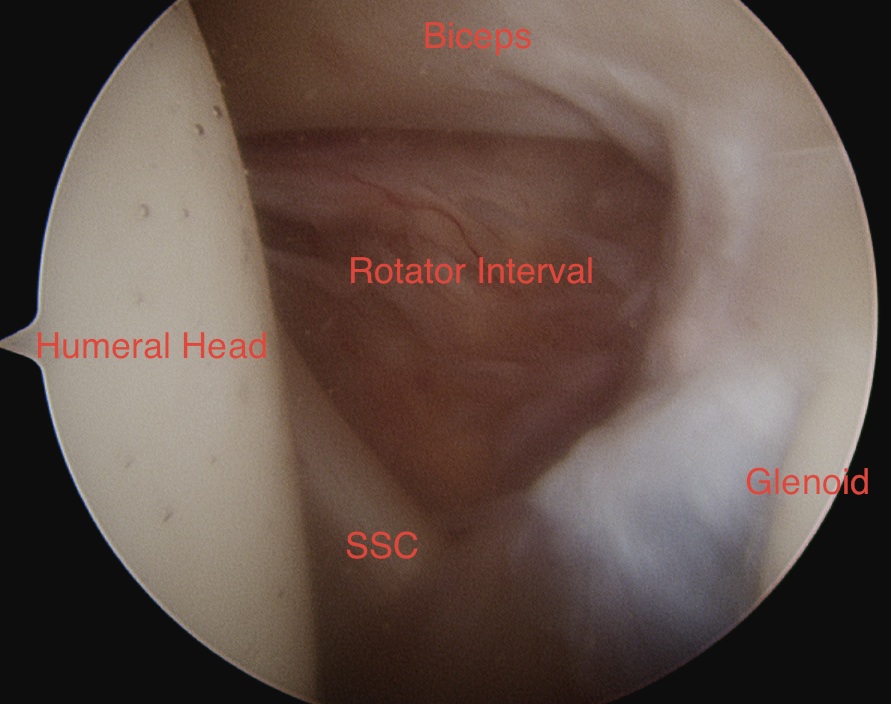
Rotator Interval
- biceps, glenoid & humeral head form a triangle with subscapularis in the base
- place anterior portals in this triangle above subscapularis, lateral to coracoid
A. Retrograde method
- direct scope into rotator interval
- advance until rests against anterior capsule at superior edge subscapularis
- light transilluminates skin at site of portal
- ensure lateral to coracoid
- remove scope from sheath
- insert Wissinger rod / switching stick through sheath
- make stab incision
- advance rod
- insert cannula over stick
- use portal for probe & instruments
B. Direct / anterograde
- insert 19 gauge spinal needle
- always lateral to coracoid
- pass into rotator interval
- stab incision / switching stick / cannula
Anteroinferior portal
- just above SSC
- angle to get to anterior labrum / bankart repair
- 3 - 6 o'clock
Anterosuperior portal
- high in rotator interval
- in angle between humeral head and biceps
- working portal for suture exchange in stabilisation surgery
- good angle for anchor insertion for SLAP repair
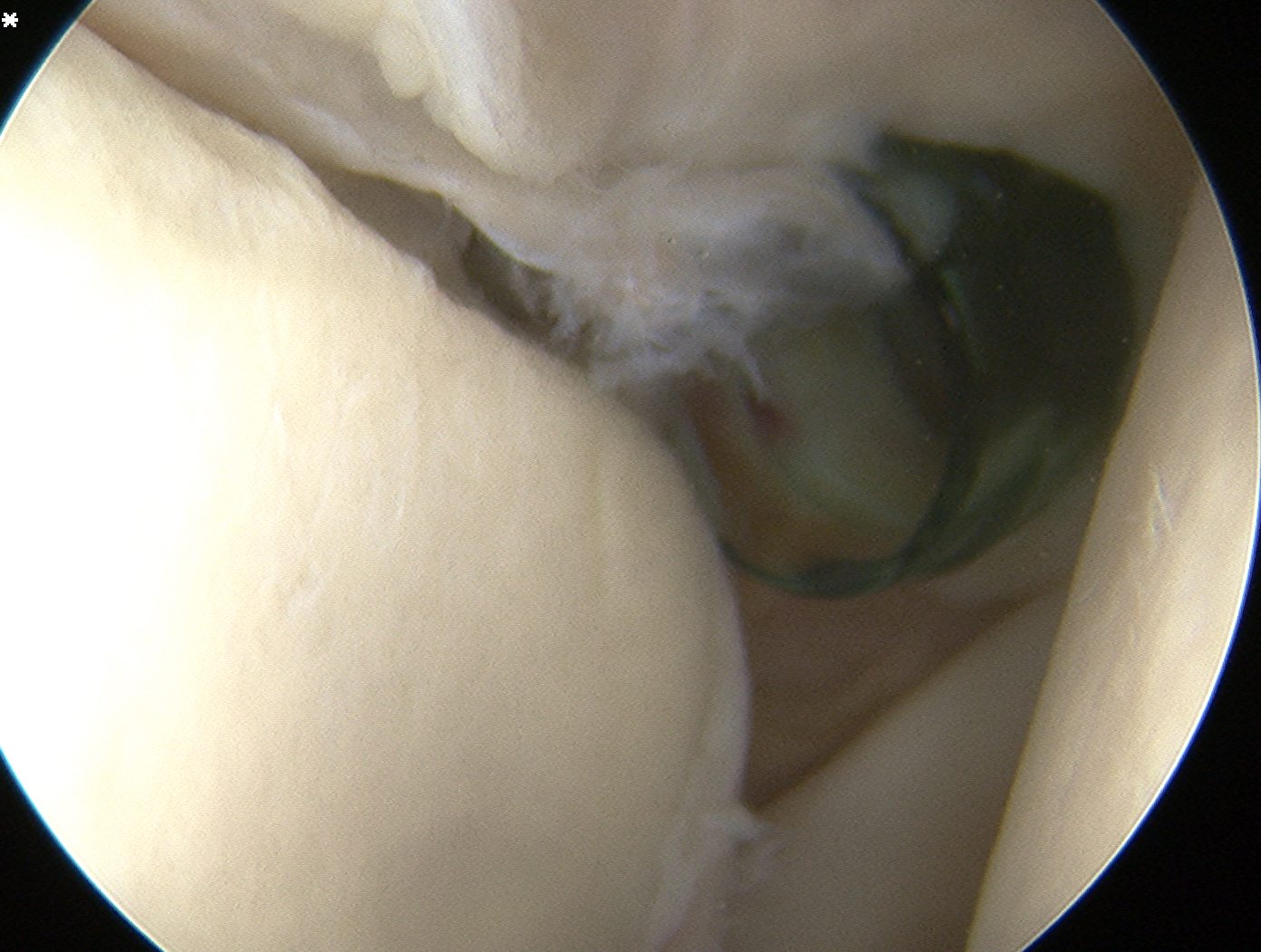
Posterior Portal
Technique
- insert switching stitch through camera cannula
- insert camera through anterior cannula
- pass cannula over switching stick
Uses
- inspect / probe / repair posterior portal
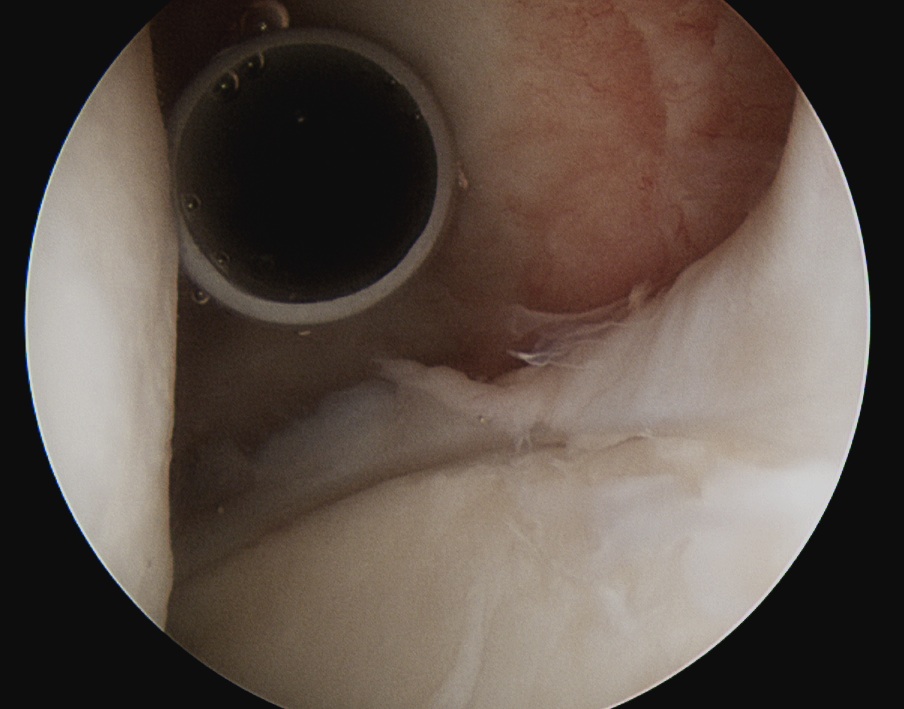
Posterolateral portal
For posterior labral tears
- inferior and lateral to posterior portal
- allows placement of the inferior anchor
Posterior Subacromial Portal
Redirect posterior cannular with blunt trochar
- remove camers
- direct it superiorly immediately below acromion once through deltoid
- sweep trochar laterally to break adhesions
Lateral Subacromial portal
Working portal
- for subacromial decompression / ACJ resection / RC surgery
- 2 - 3 cm lateral to lateral acromion
- 1 - 2 cm posterior to anterior acromion
- usually in line midportion / posterior border of clavicle
- insert needle
- should be above cuff, below acromion
- parallel to acromion
Anterosuperiorlateral Portal / Port of Wilminton
Indication
- SLAP
- passes through supraspinatous
- anterolateral border acromion
- can place more posteriorly to access posterior aspect of SLAP
- in this case will pass through infraspinatous
Superior portal Neviaser / Superomedial portal
Indication
- access posterior SLAP / decompress suprascapular nerve
- pass through RC / supraspinatous
- 1 cm medial to acromion
- 1 cm posterior to clavicle
Fluid
A. Pressure pump
- usually 40 - 50 mmHg
- can temporarily increase if required
B. Adrenaline in bags
- 1 mg in each 3L bag
Examination of GHJ
Systematic Approach
A. Glenoid medial / Humeral head lateral
- arthritis / chondral damage
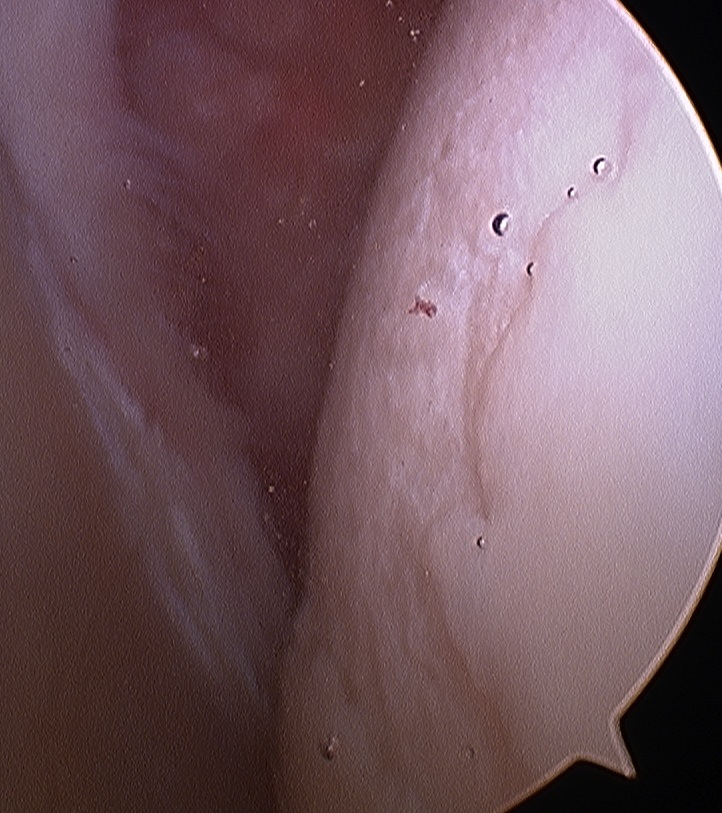
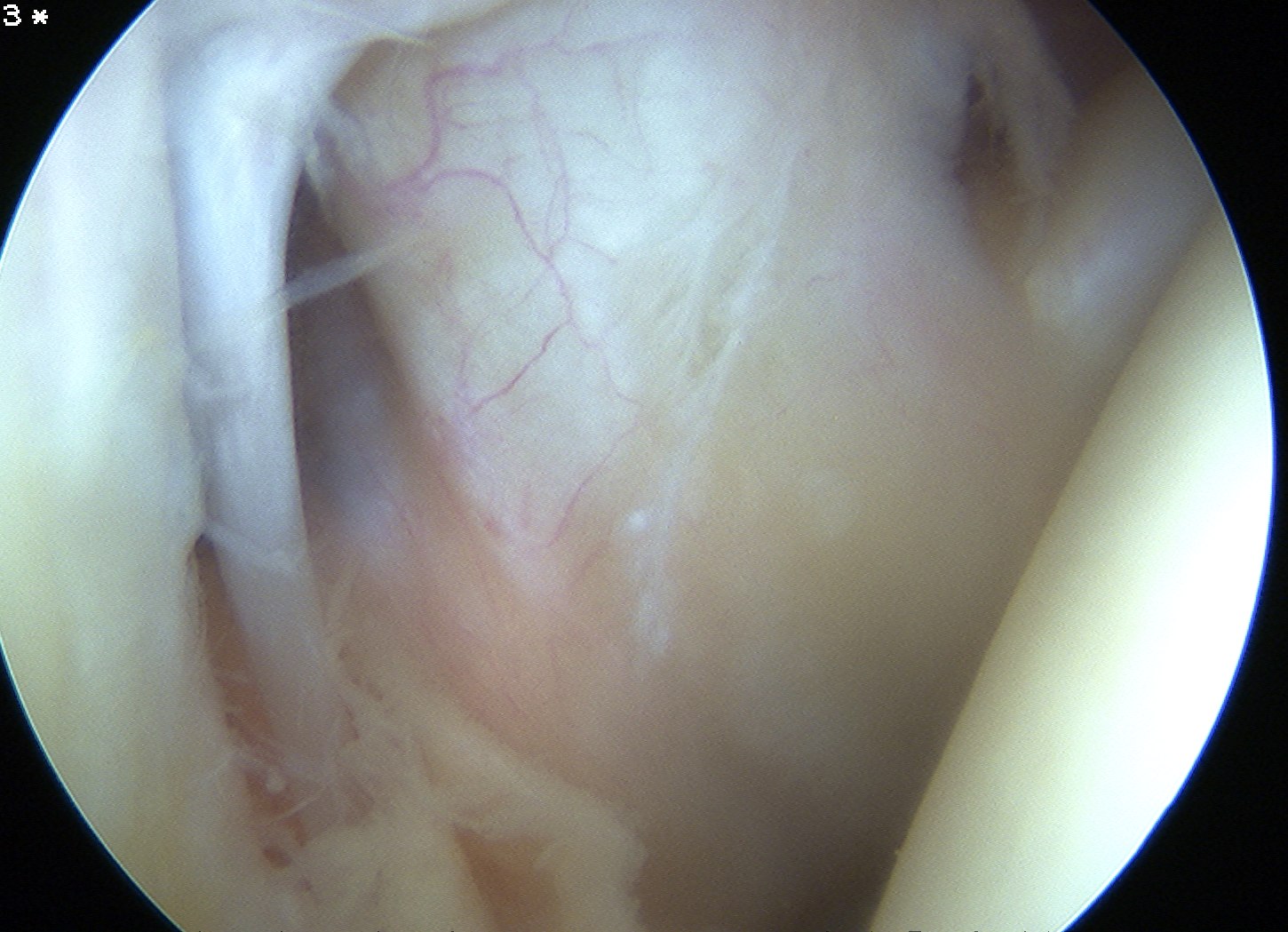
B. Biceps
- careful examination / probing of insertion
- examination of intra-articular portion for degeneration
- pull extra-articular portion into joint to confirm gliding well
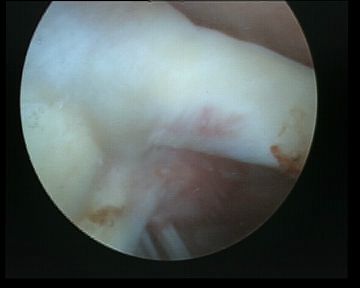
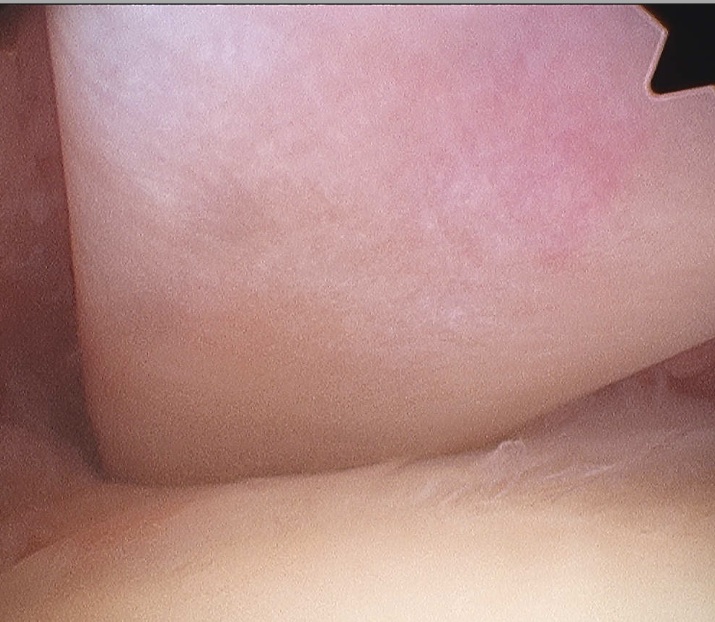
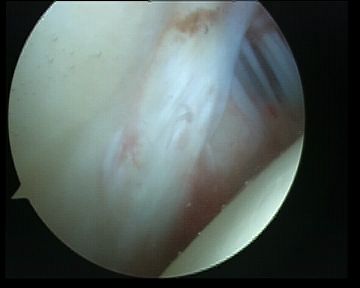
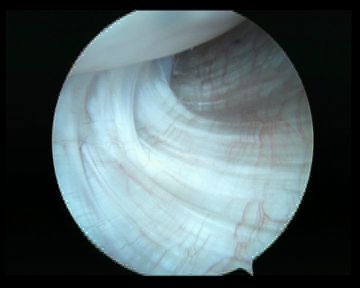
C. Labrum
- 360o examination
- anterior / inferior / posterior
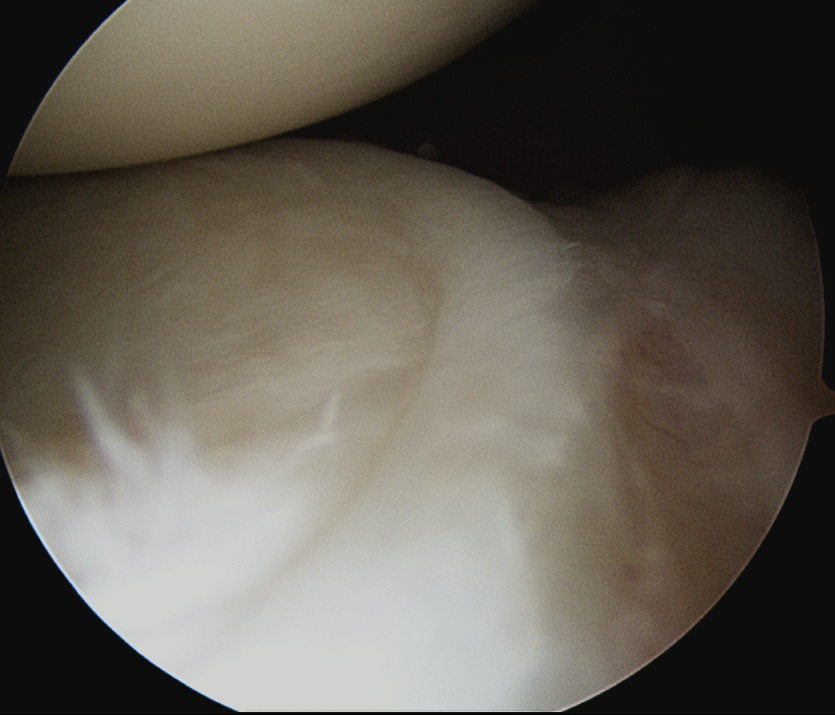
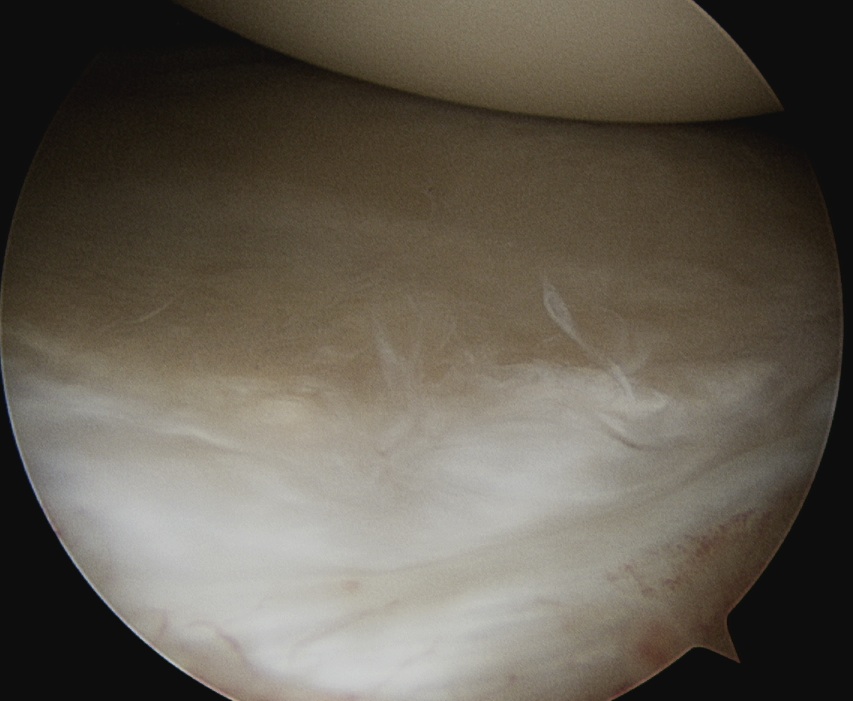
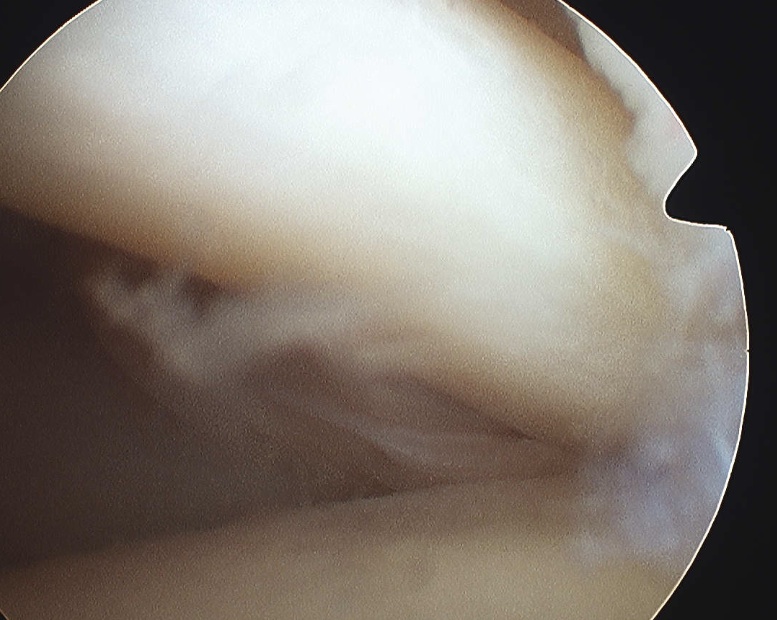
D. Glenohumeral ligaments
Superior
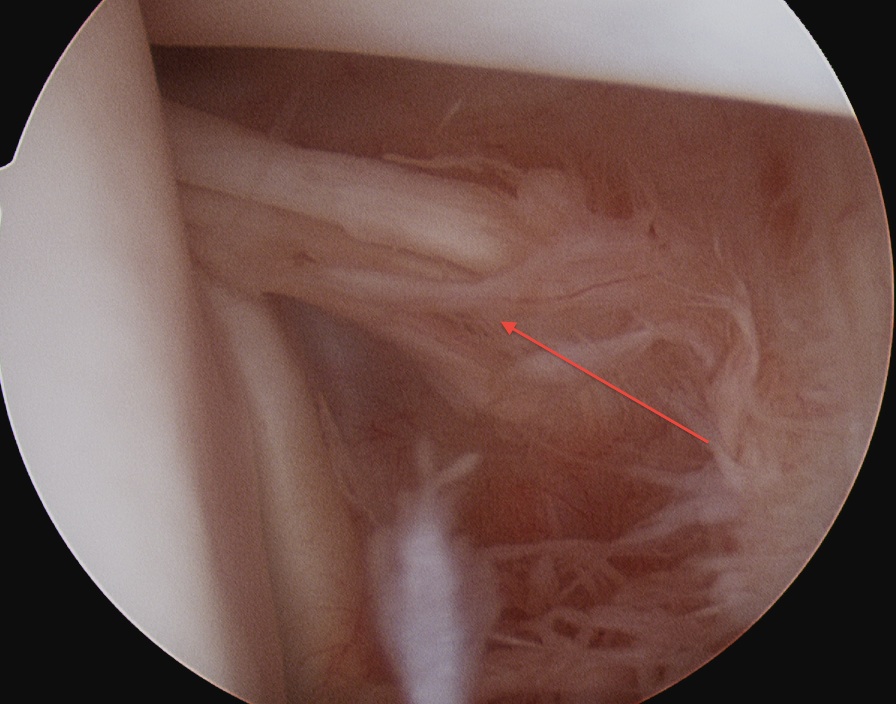
Middle
- crosses subscapularis vertically
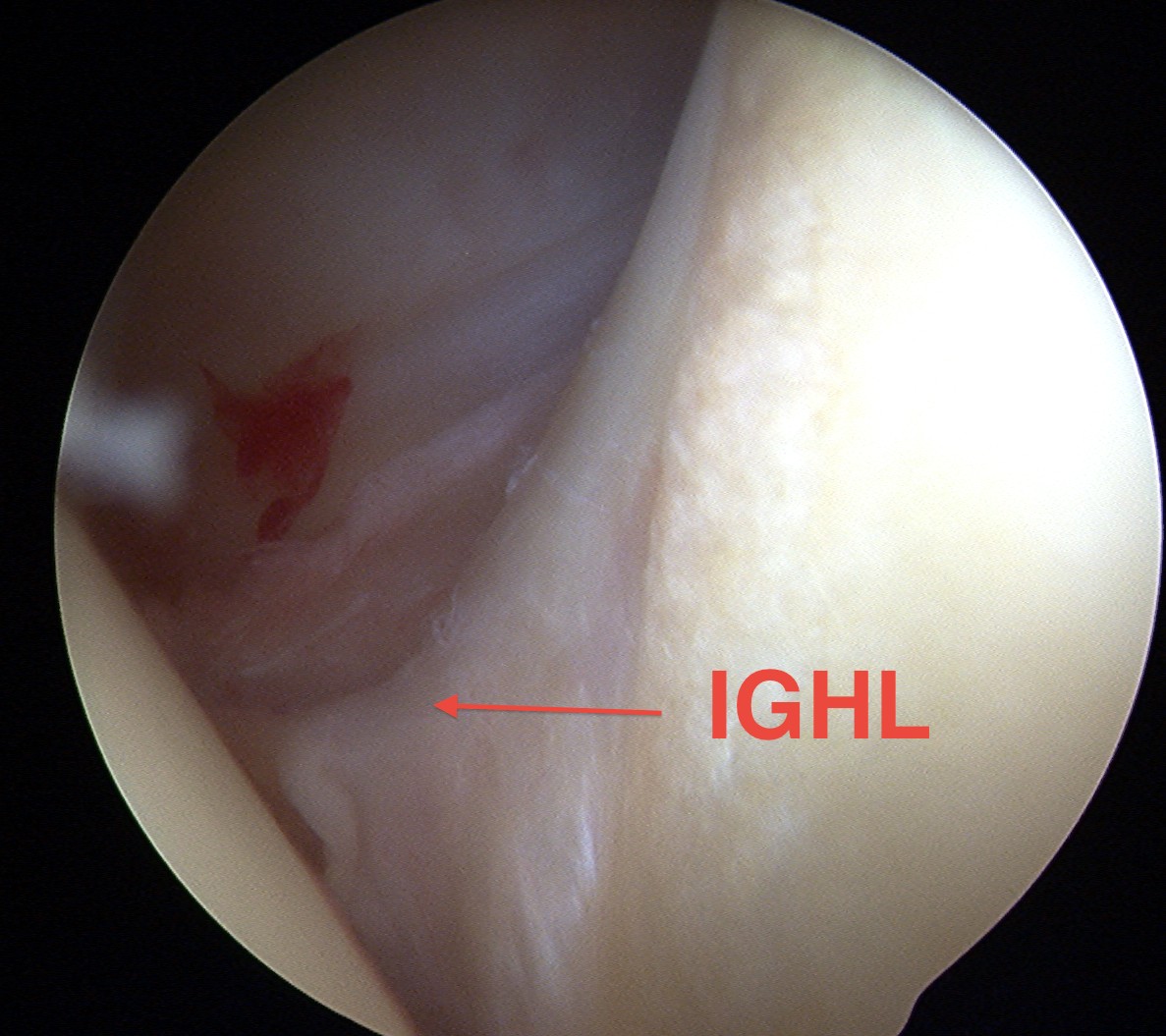
Inferior / anterior aspect of IGHL
- attachment to labrum between 3 and 6 o'clock
- look down into inferior recess
- see attachment to inferior humerus
- exclude HAGL / exclude loose body
E. Rotator Cuff
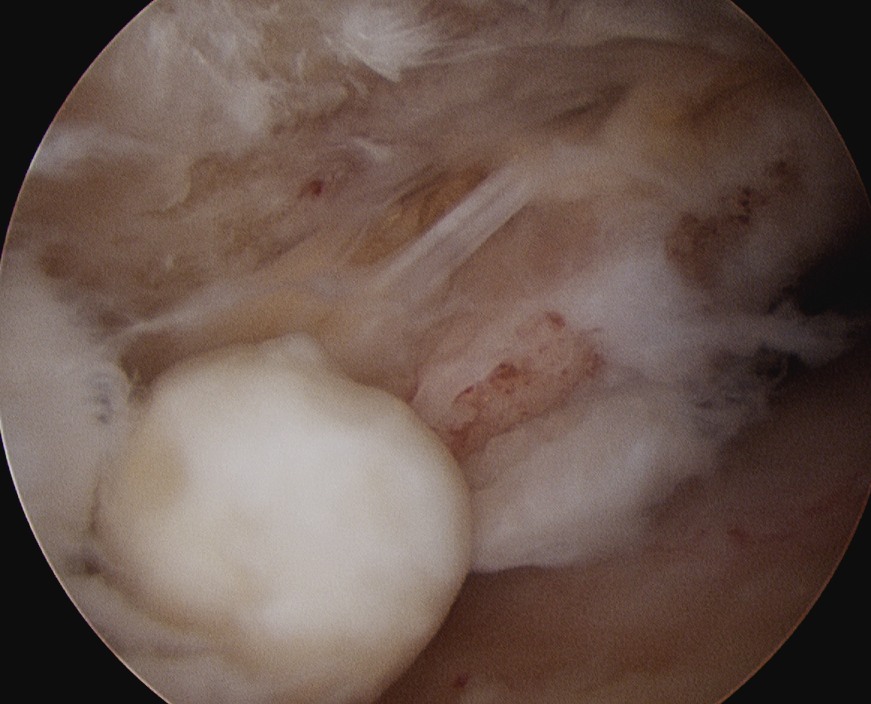
Subscapularis
- examine insertion
- ER the humerus
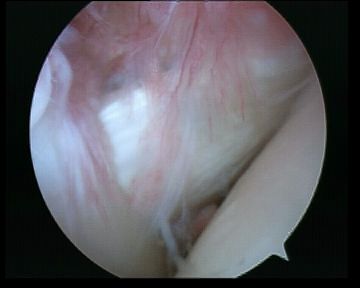
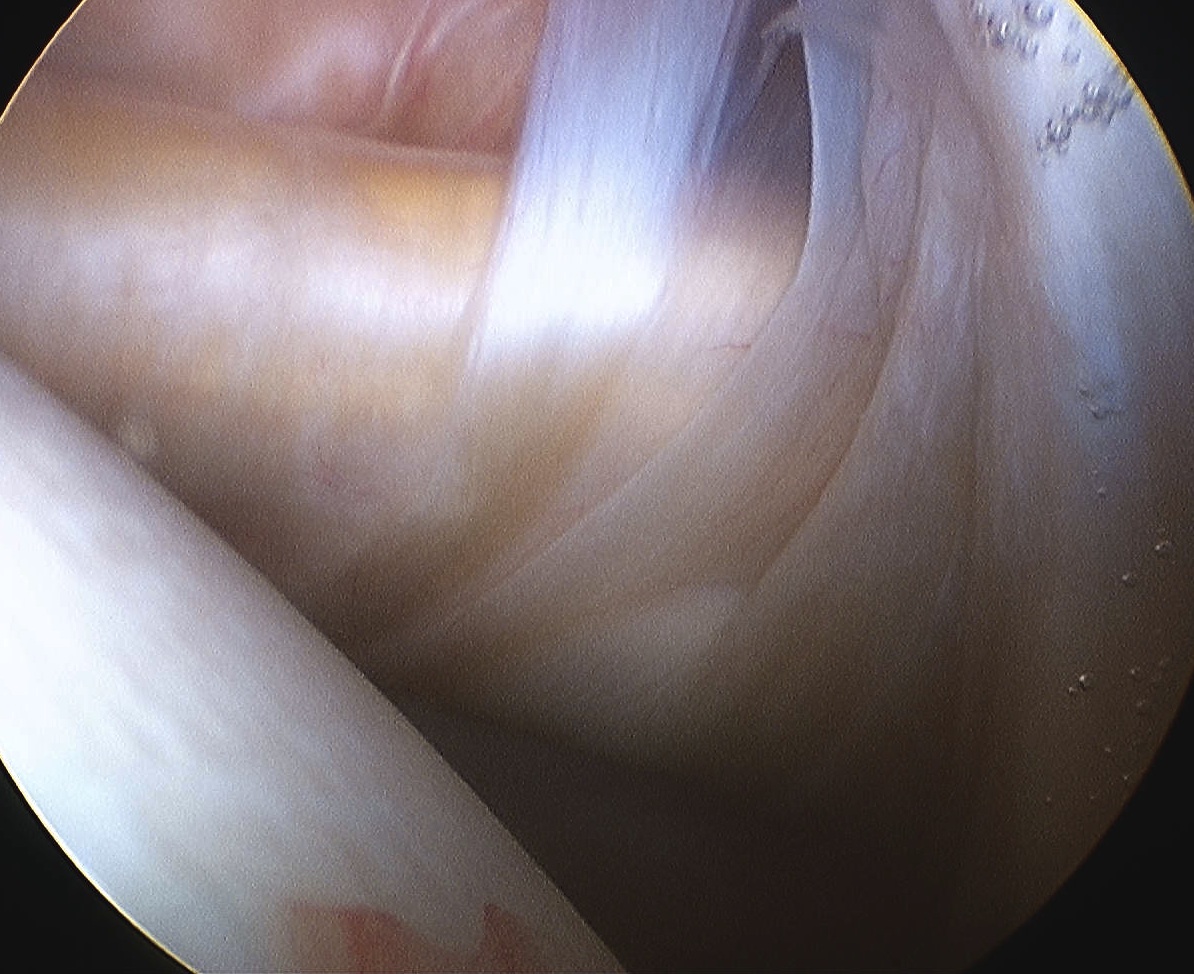
Supraspinatous
- examine underside and insertion
- abduct and ER
- should be no gap between cartilage and insertion
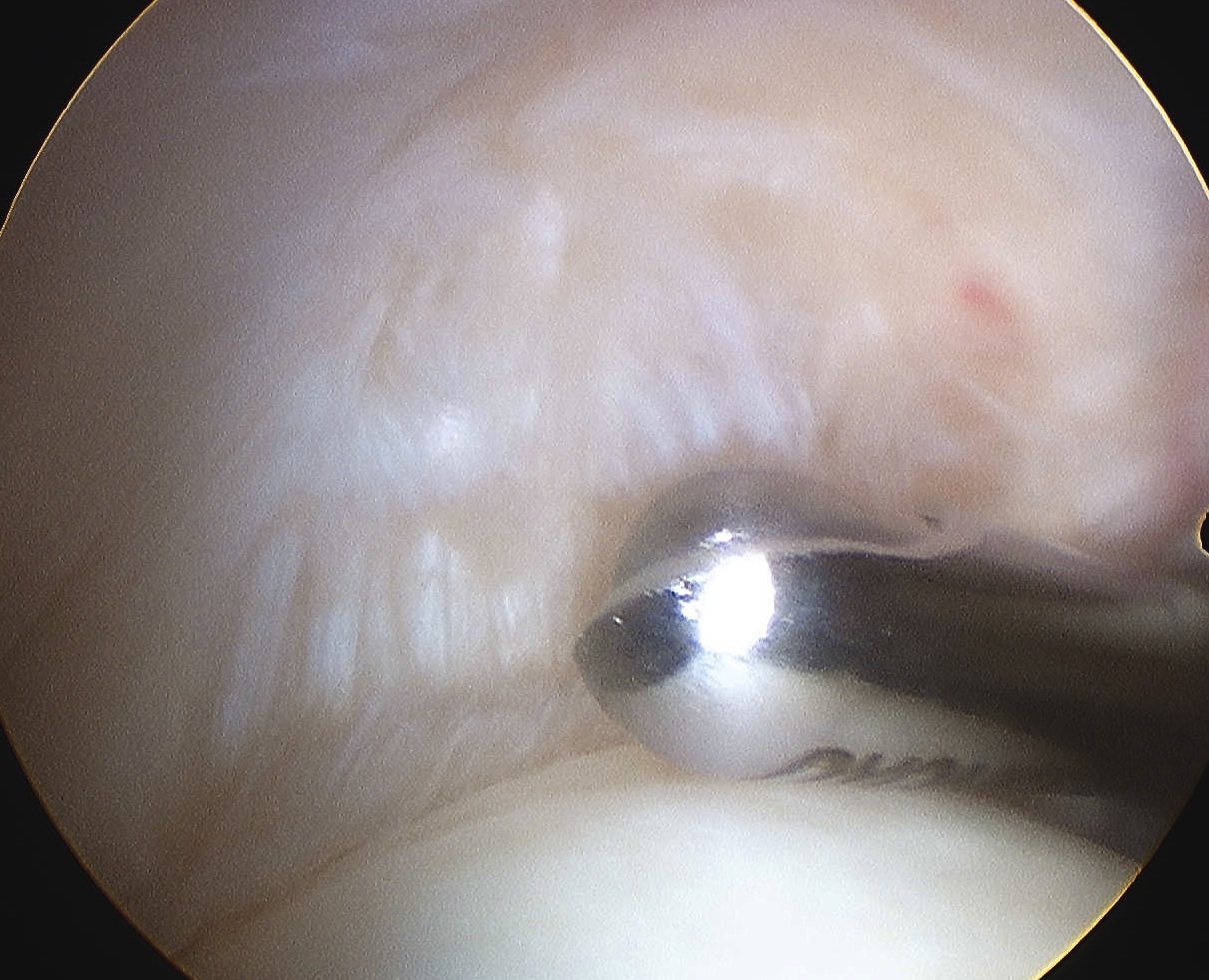
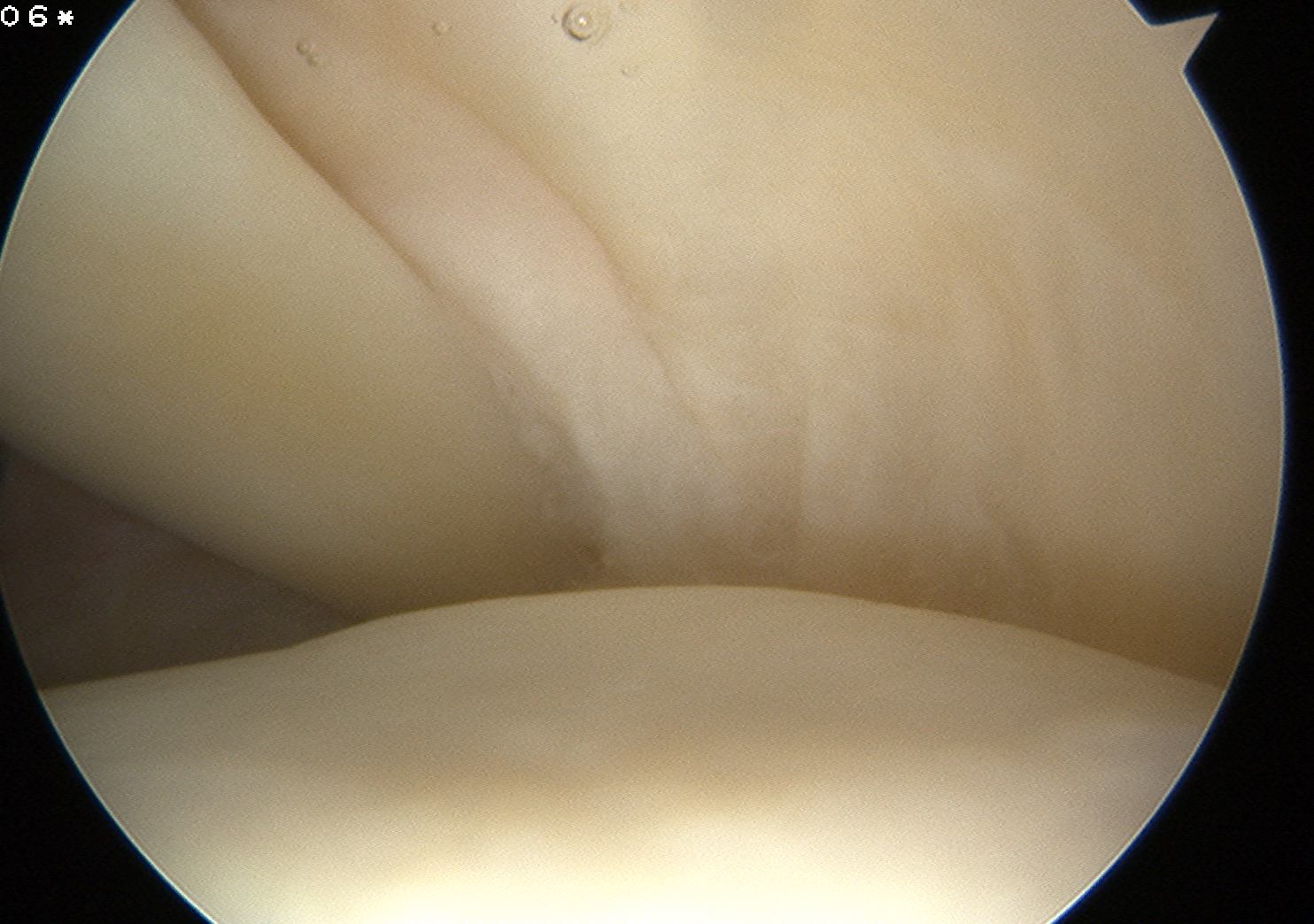
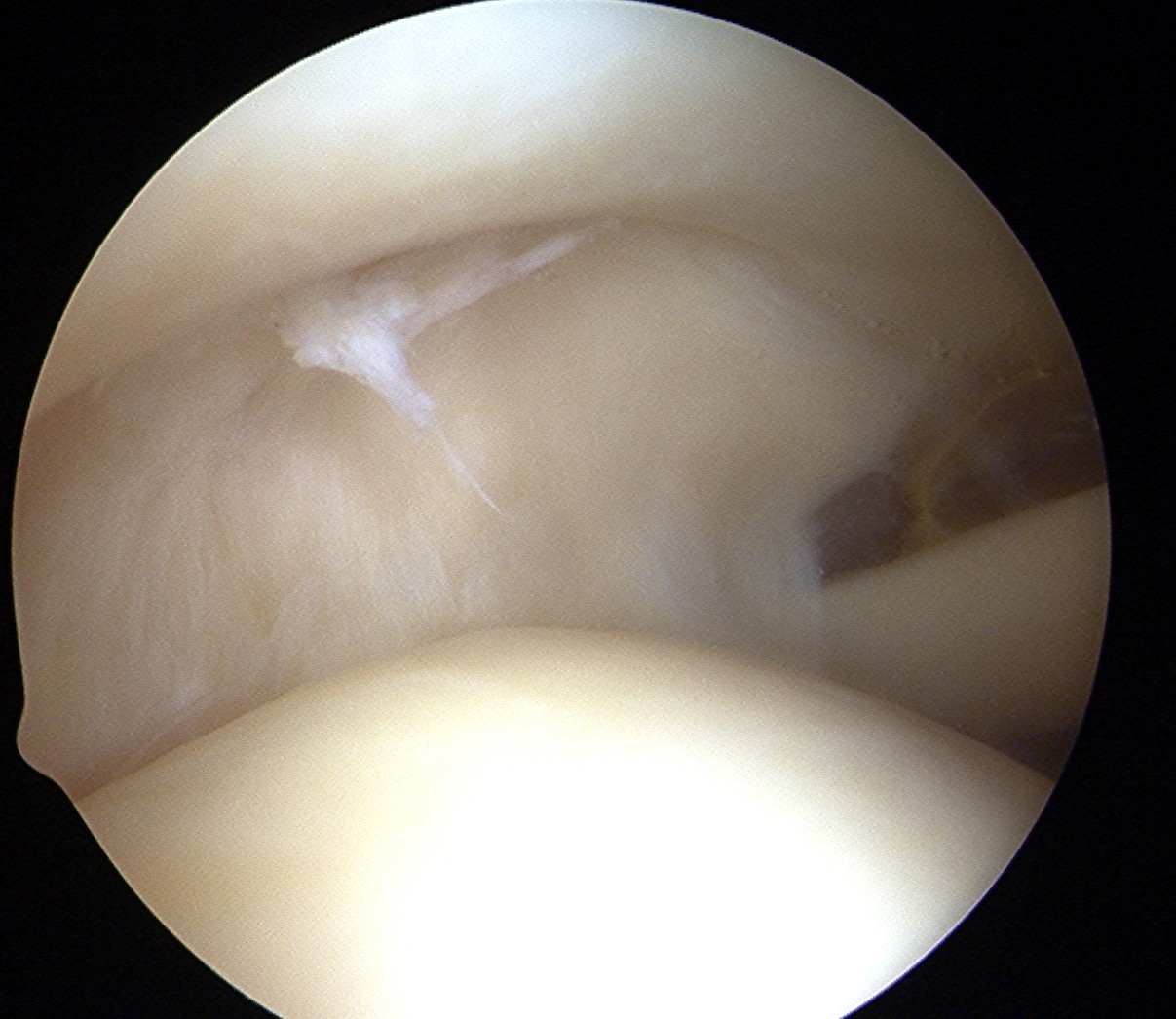
Infraspinatous
- insertion at posterior humerus next to bare area
- Hill Sach's lesion (has cartilage each side c.f. bare area)
Neurological Complications
Uncommon (0.1%)
1. Posterior Portal
- if placed inferiorly can damage AXN below Teres minor
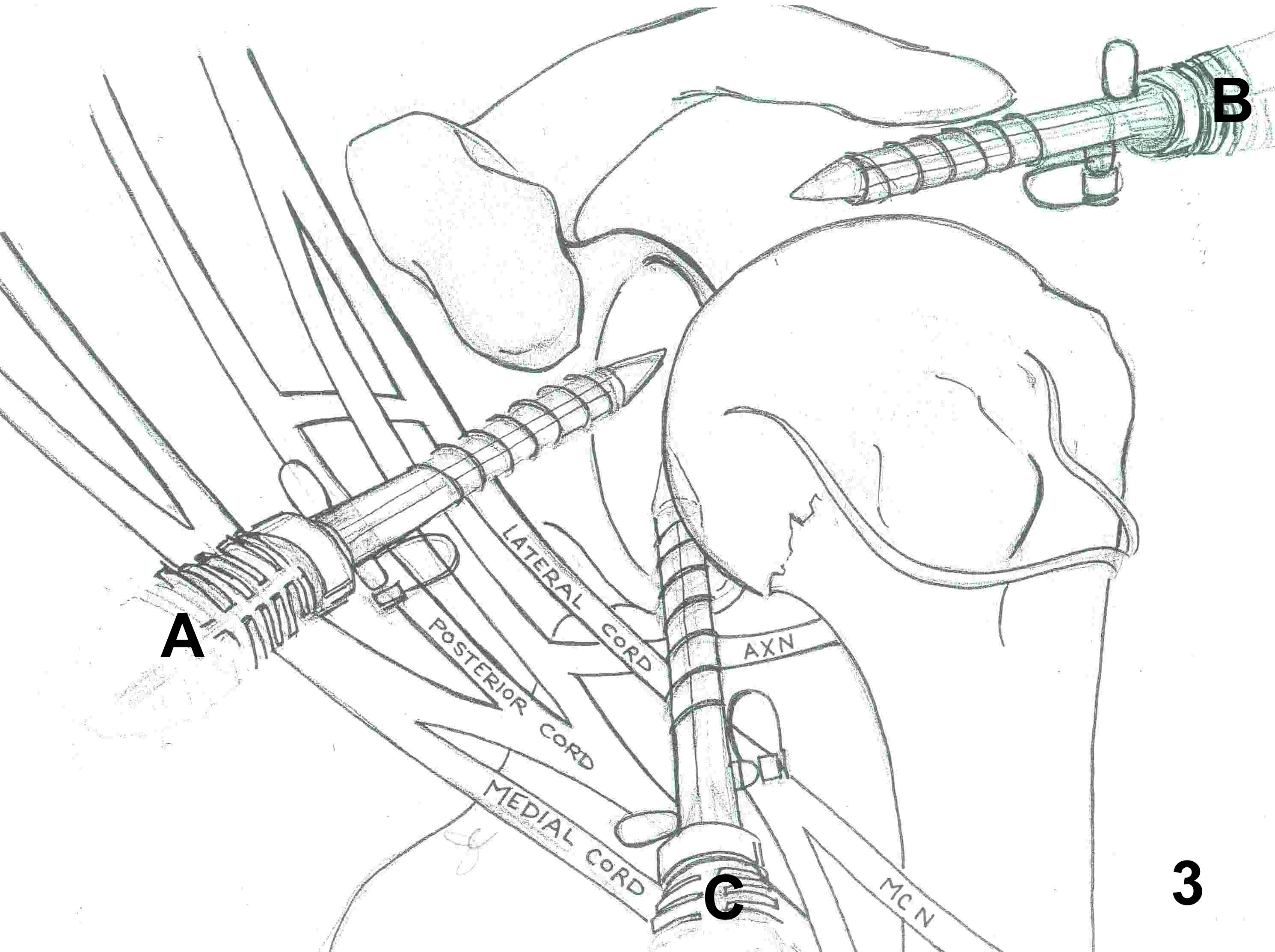
2. Anterior Portal
- damages MCN if medial to coracoid
- brachial plexus & axillary artery
