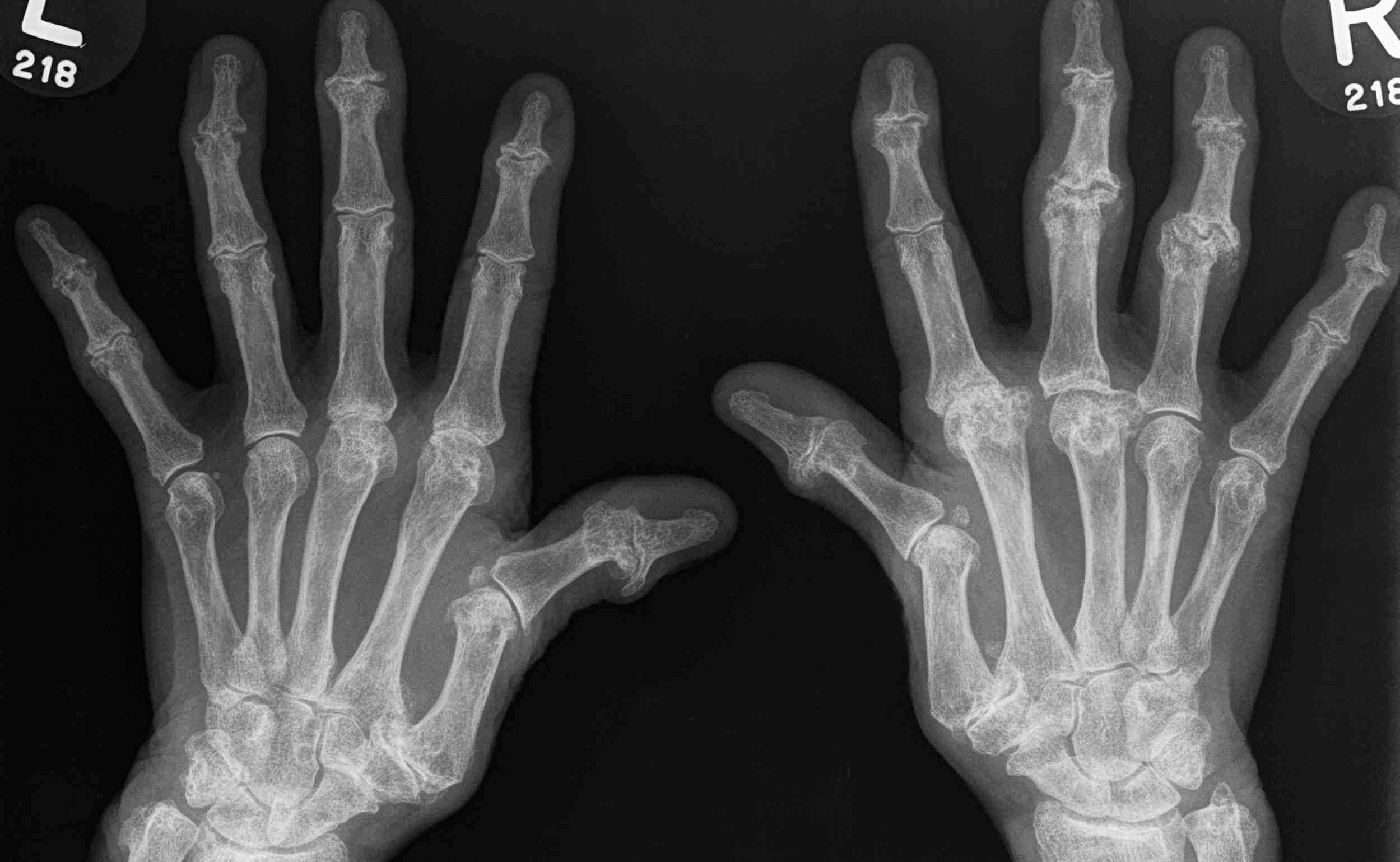
Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostic Criteria
1987 American College of Rheumatology
Need 4/7 (MAX RANS)
1. Morning Stiffness
2. Arthritis of 3 areas > 6/52
3. Xray changes
4. Rh factor
5. Arthritis of Hand > 6/52
6. Nodules
7. Symmetric Arthritis > 6/52
Types of Surgery
5 basic Groups
1. Synovectomy / Capsulorrhaphy
2. Tenosynovectomy
3. Tendon surgery & soft tissue balancing
4. Arthroplasty
5. Arthrodesis
General Principles
Replace all MCPJs
Fuse IF/MF PIPJs
Replace RF/LF PIPJs
Fuse DIPJs
Correct wrist deformity at same time or risk recurrence
Caput Ulnae Syndrome
Components
- volar subluxation of ulnar carpus
- supination of carpus on wrist
- apparent dorsal subluxation of distal ulna
Nalebuff Classification MCPJ
Stage I - Synovitis
- medical Rx and splinting
- synovectomy
Stage II - Synovitis + Ulna deviation
- medical treatment and splinting
- synovectomy + soft tissue reconstruction
Stage III - Moderate joint destruction
- volar subluxation and ulnar drift
- soft tissue reconstruction possible
- arthroplasty gives more reliable results
Stage IV - Advanced joint destruction
- fixed joint deformities
- arthroplasty with soft tissue releases
Causes of MCPJ Deformity
Ulna Drift / Ulna Dislocation
1. Physiological
- gravity
- lateral pinch pressure
2. Anatomic
- shape of MC heads
- collateral ligament length & orientation
- intrinsics to LF asymmetric (hypothenars strong)
3. Pathological
- joint / capsule instability due to bony erosions
- collateral ligament stretching due to synovitis
- ulna/volar dislocation flexor tendons due to stretching pulleys
- ulna dislocation extensor tendons due to stretching sagittal bands
- intrinsic contracture
- radial deviation of wrist (Landsmere) redirecting line of pull of tendons
- volar / ulna carpal subluxation
Nalebuff Classification Thumb
Note: Type II now removed as Nalebuff later said doesn't exist
Type I - Boutonniere
- the commonest
- MCPJ flexion, IPJ hyperextension
Type II - Boutonniere & Swan Neck
Type III - Swan Neck
- second most common
- deformity is at CMC / Dorsal & radial subluxation
- hyperextension MPJ / flexion IPJ
Type IV - Gamekeepers
Type V - Stretched Volar Plate MCPJ
Type VI - Arthritis Mutilans
Swan Neck
Causes
DIPJ
- terminal extensor tendon rupture or attenuated
- entrapped FDP
PIPJ
- volar capsule stretching / FDS rupture
- contracted central extenor slip
MCPJ
- intrinsic tightness
- extrinsic weakness / MCPJ subluxation and subluxation extensor apparatus
Management
Flexible
- FDS tenodesis / Lateral band transfer
- DIPJ arthrodesis (mallet)
Intrinsic tightness
- above +
- intrinsic release
Fixed deformity
- PIPJ dorsal release
- then above
Arthrosis
- arthrodesis (20/30/40/50)
- arthroplasty (LF / RF)
Boutonniere Finger
Problem
- rupture of central slip
Solution
- flexible - Matev's central slips reconstruction
- radial lateral band to central slip
- ulna lateral band to radial lateral band insertion