Most common locations
1. Femur
- femoral neck
- subtrochanteric / femoral shaft
- acetabular
- femoral shaft
- supracondylar
2. Humerus
- proximal humerus
- humeral shaft
3. Tibia
Femoral Neck pathological fracture / Major bone loss
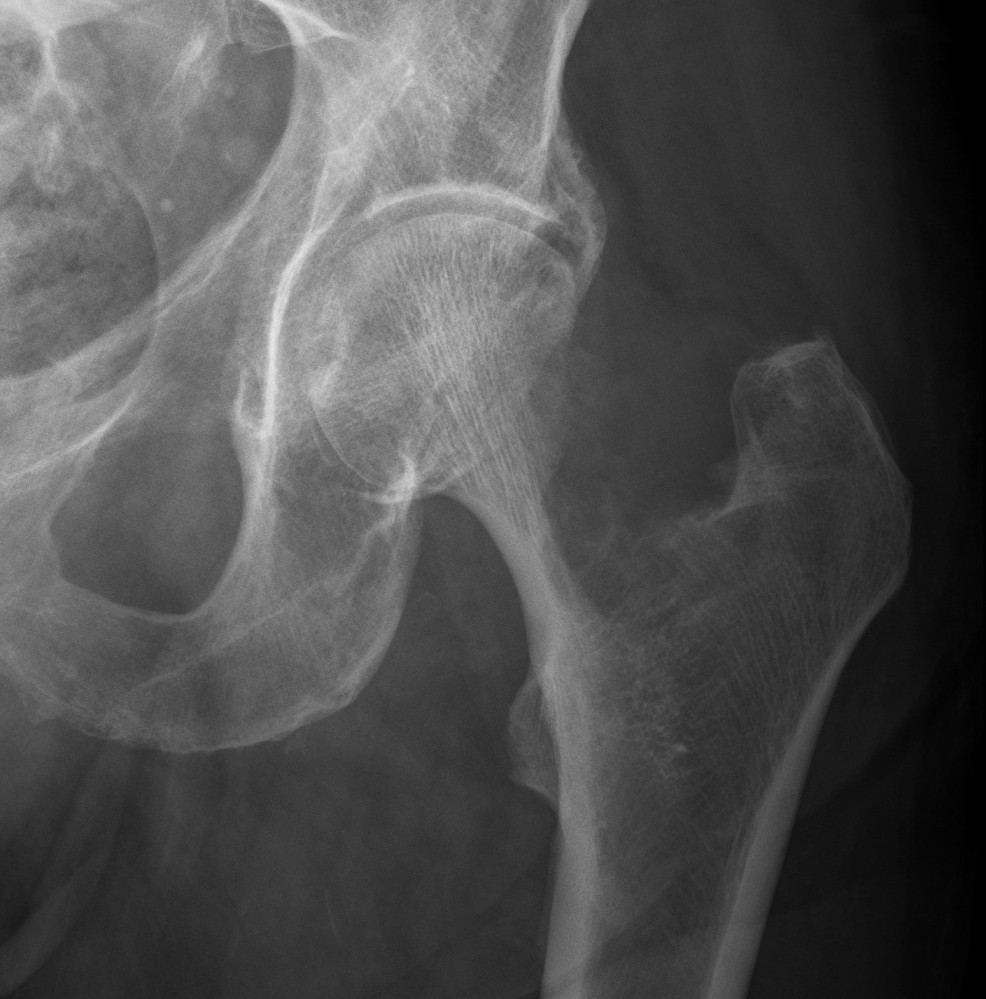
Issues
- fracture unlikely to heal
- hemi versus THA
- long versus short stems
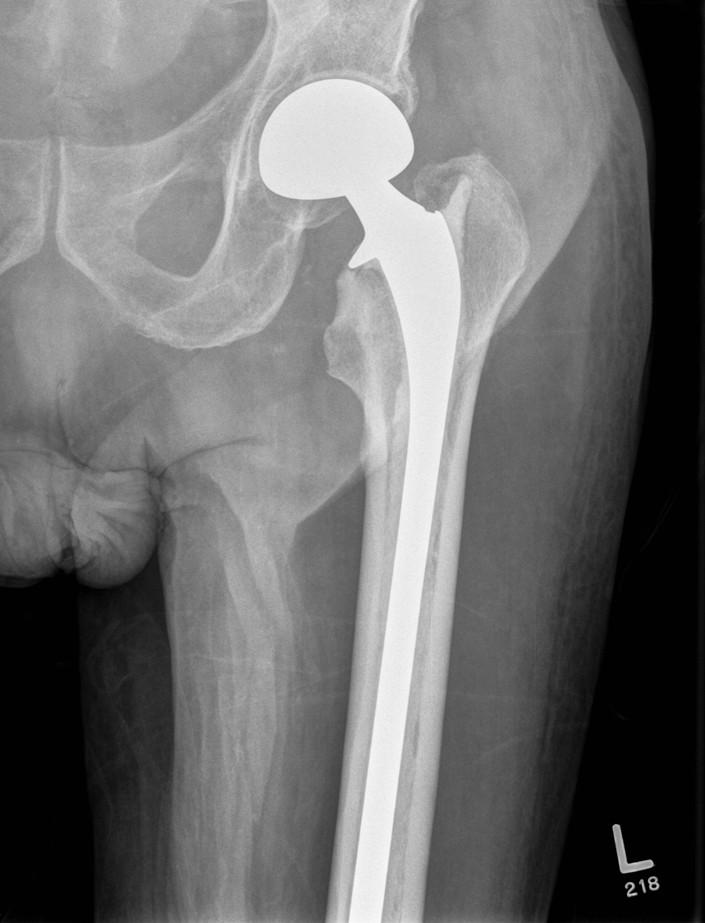
Hemi v THA
Consider life expectancy of patient
Varady et al J Arthroplasty 2019
- hemiarthroplasty versus total hip arthroplasty for pathological femoral neck fractures
- THA longer operative times
- no difference 30 day complication rate
Femoral stem length
- 203 patients with proximal femoral metastasis treated with arthroplasty
- no increased revision rate with short stems
- increased complications with long stems, especially cardiopulmonary complications
Femoral neck stabilization
Issues
- sufficient bone for fixation?
- determine if lesions further down femur (xray entire femur)
- consider augmentation with PMMA / cement
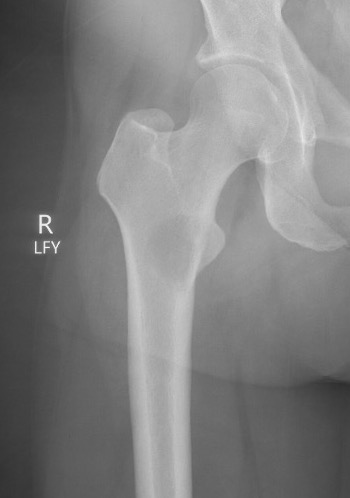
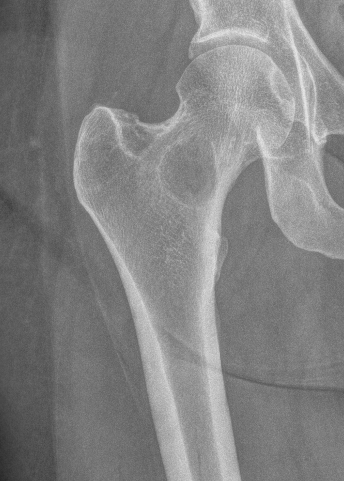
Plate versus IM nail
Meynard et al Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2020
- 309 cases proximal femoral metastasis
- plate versus IMN versus arthroplasty
- no difference in functional outcome
- increased complications with plating
Subtrochanteric / Femoral shaft metastasis
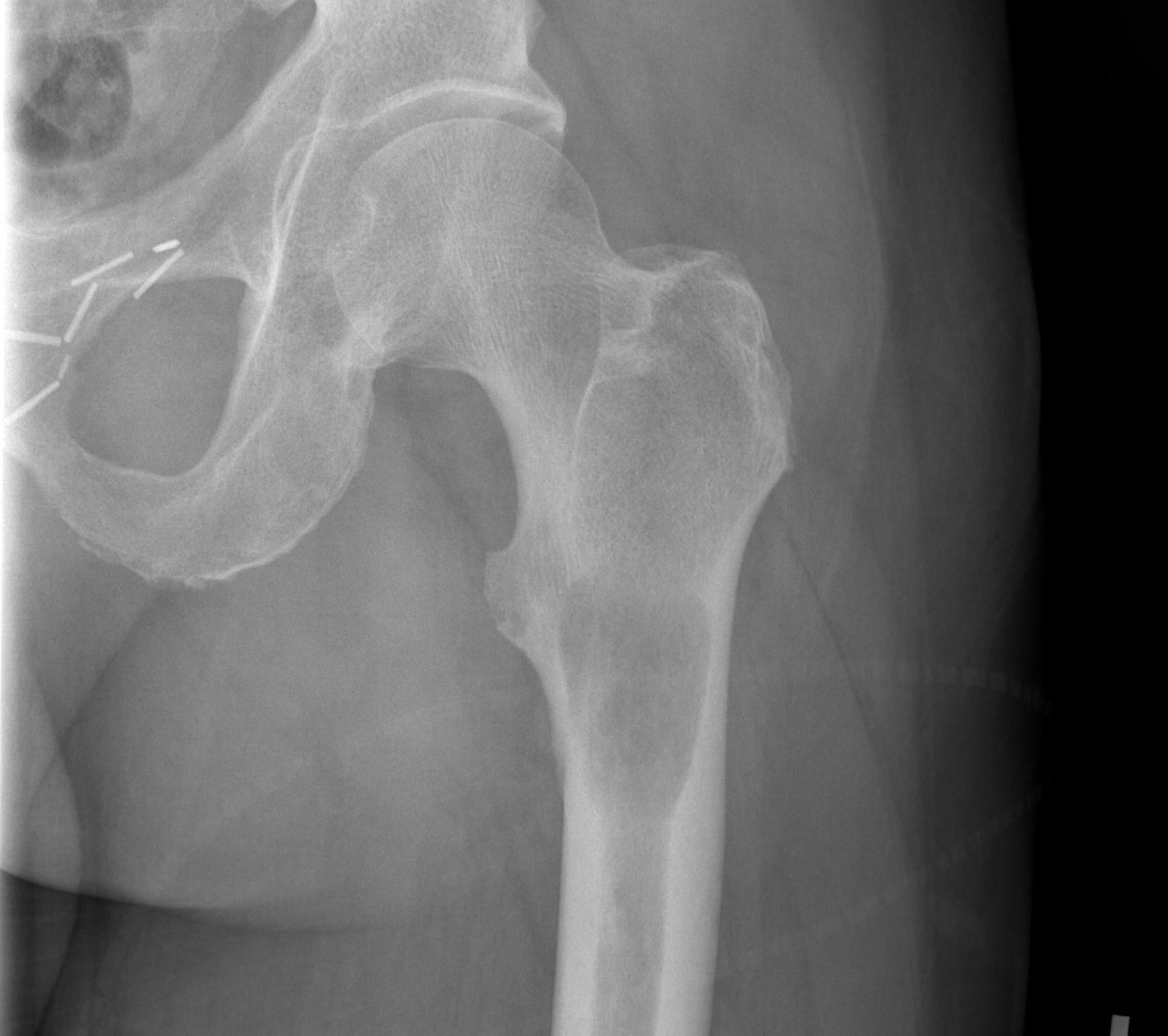
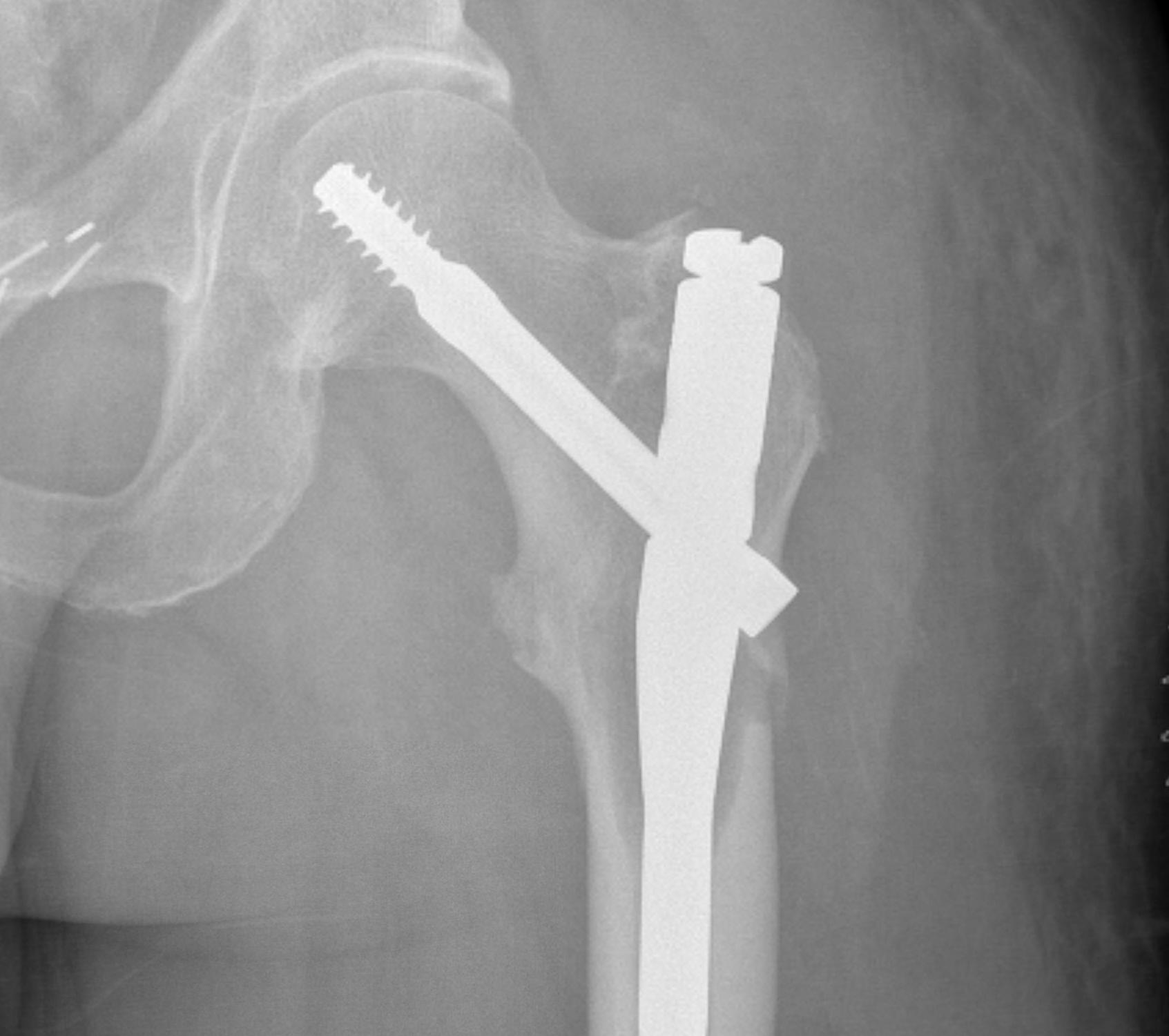
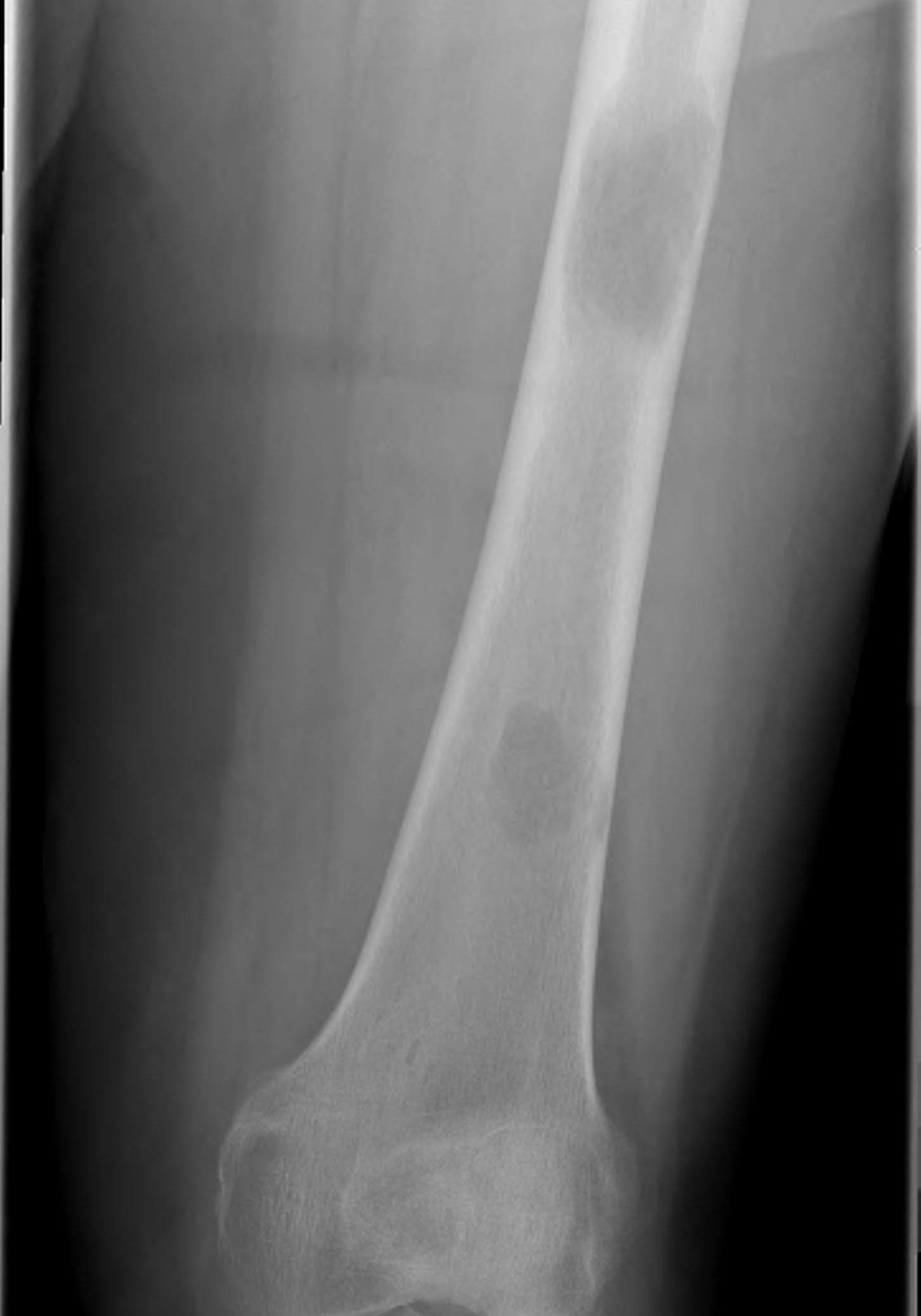
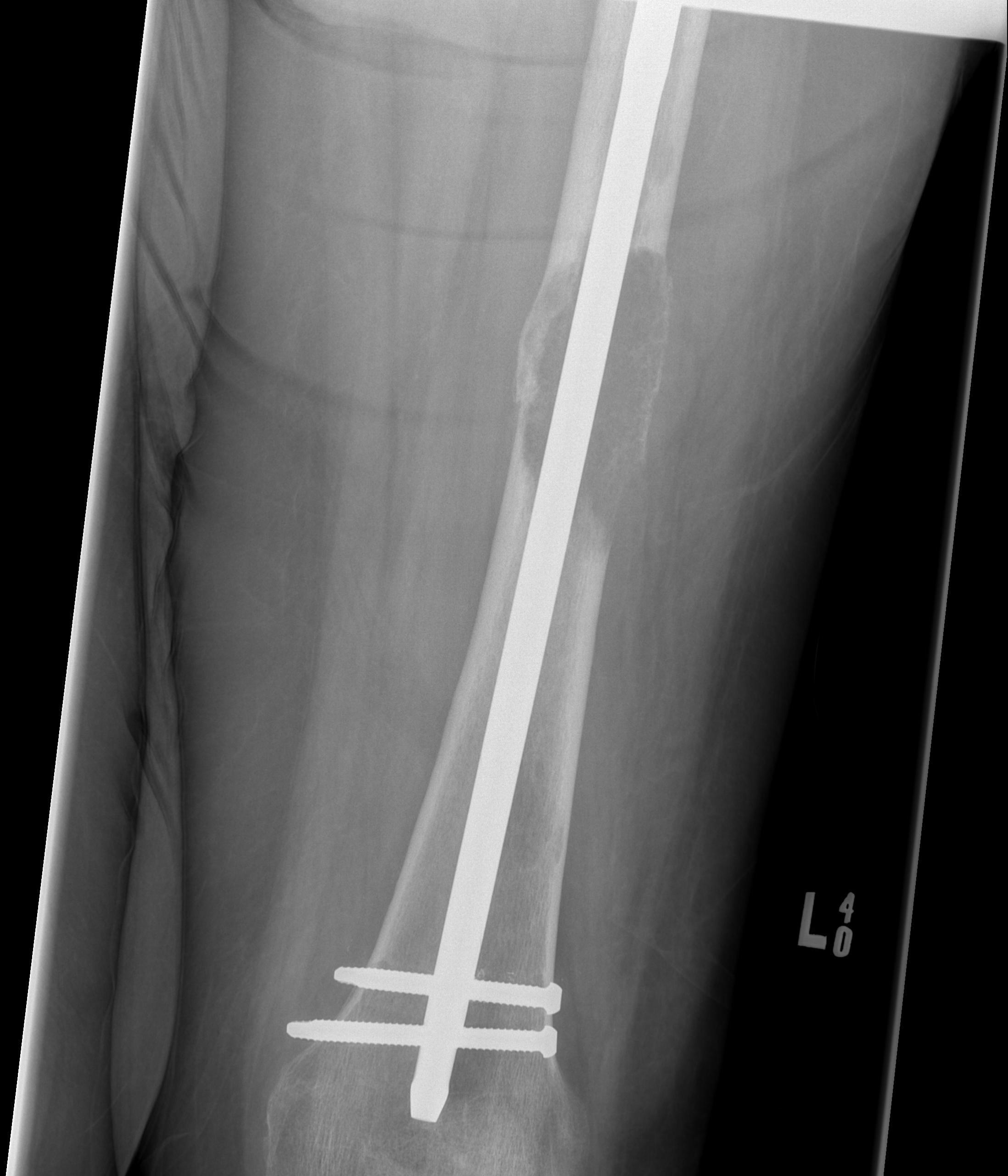
Management
Reconstruction nail
- consider cement
- consider venting
Durability
- 217 patients treated with cephalomedullary nails for proximal femoral metastasis
- revision surgery required in 10%
- more common with survival > 7 months
Cement
- 43 patients with IMN + cement of femur and humerus versus 27 IMN
- lower pain scores with cement
- some reduction of metastasis progression with cement
Venting / Negative pressure reaming / Reamer Irrigator Aspirator
Risk of cardiopulmonary complications from fat / air / cancer emboli
- 73 femoral nails for metastatic impending fracture
- 2 deaths from fat embolism
Bilateral nails
- systematic review of staged versus simultaneous IMN for femoral metastasis
- 156 IMN in 78 patients
- lower total complications with staged
- no difference in mortality
Acetabular Metastasis
Harrington classification
| Type | Defect |
| Type I |
Minor cavitary defect Medial and superior walls intact |
| Type II |
Major deficit in medial wall Rim intact |
| Type III | Massive deficit in lateral wall & superior cortex |
Options
Tantalum augmented cups
Cemented Harrington technique / steinmann pins
Cup-cage
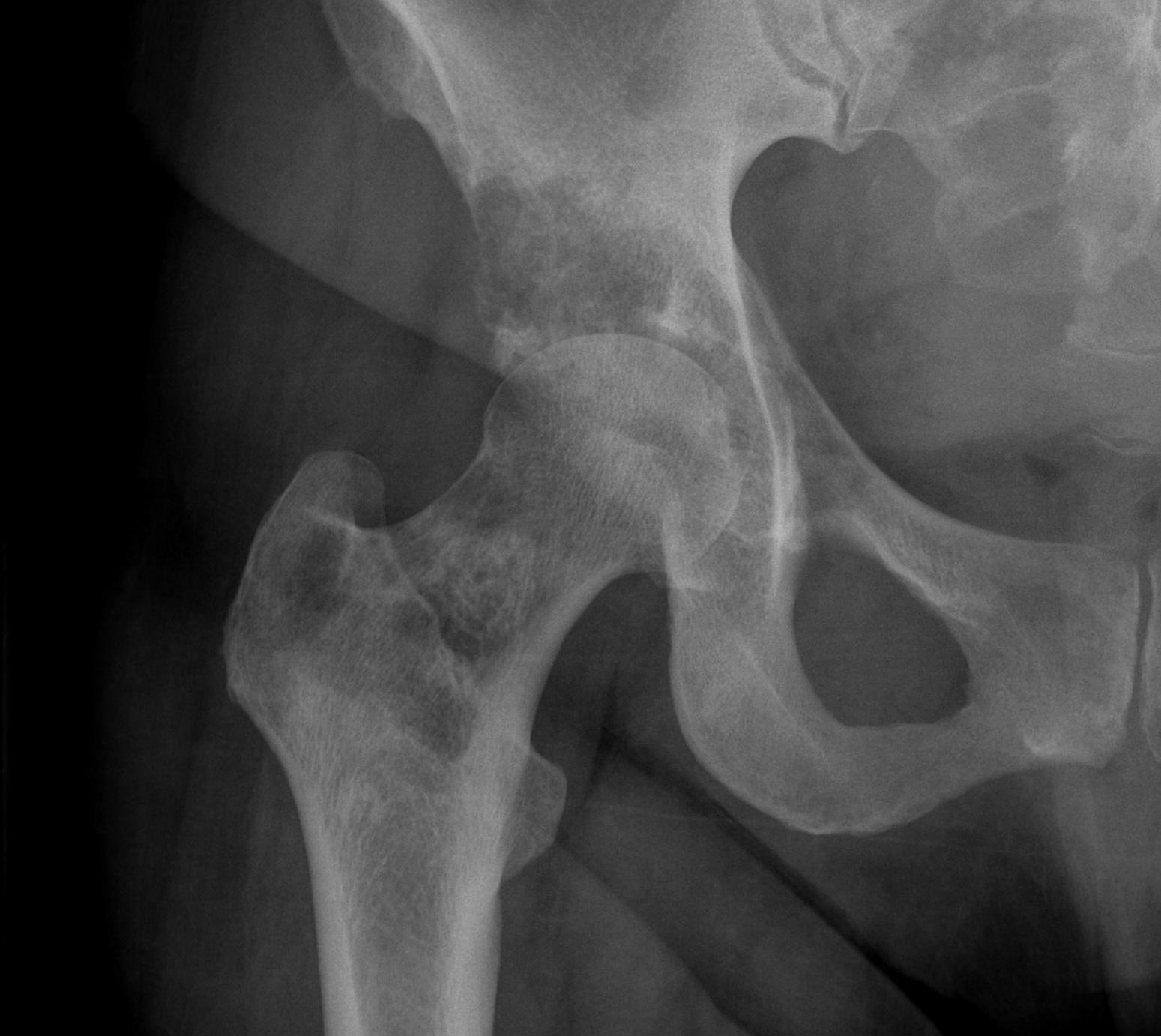
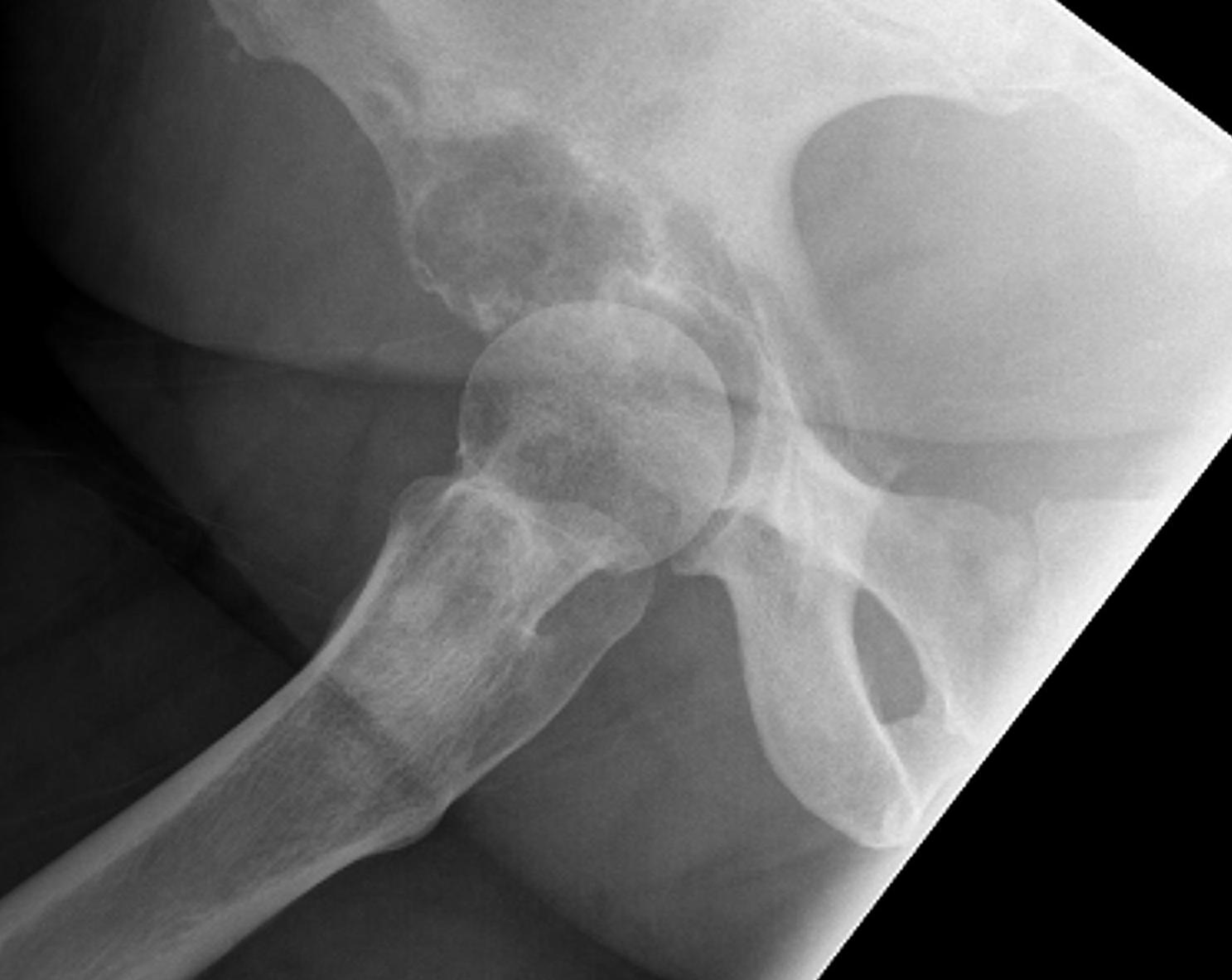
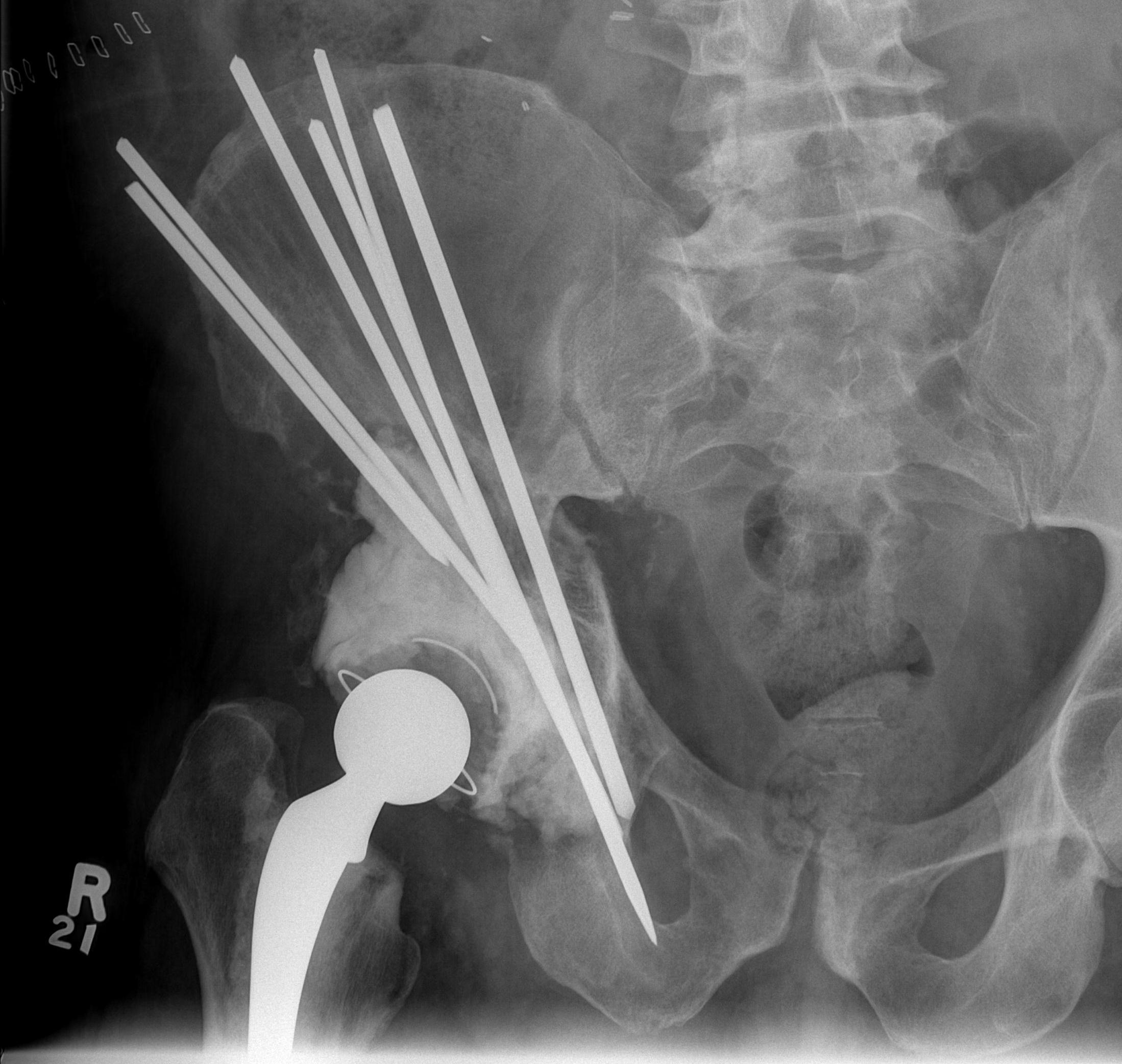
Harrington technique
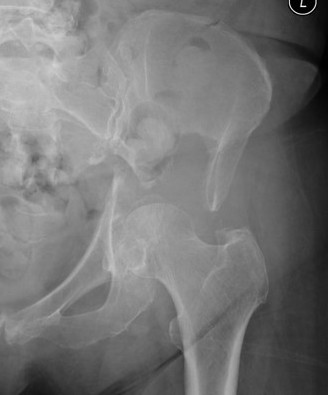
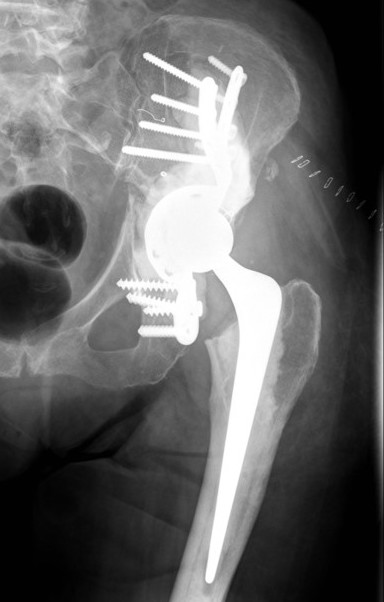
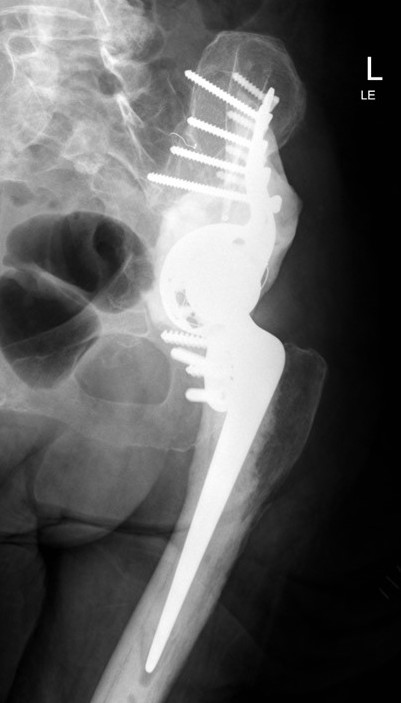
Cup-cage technique
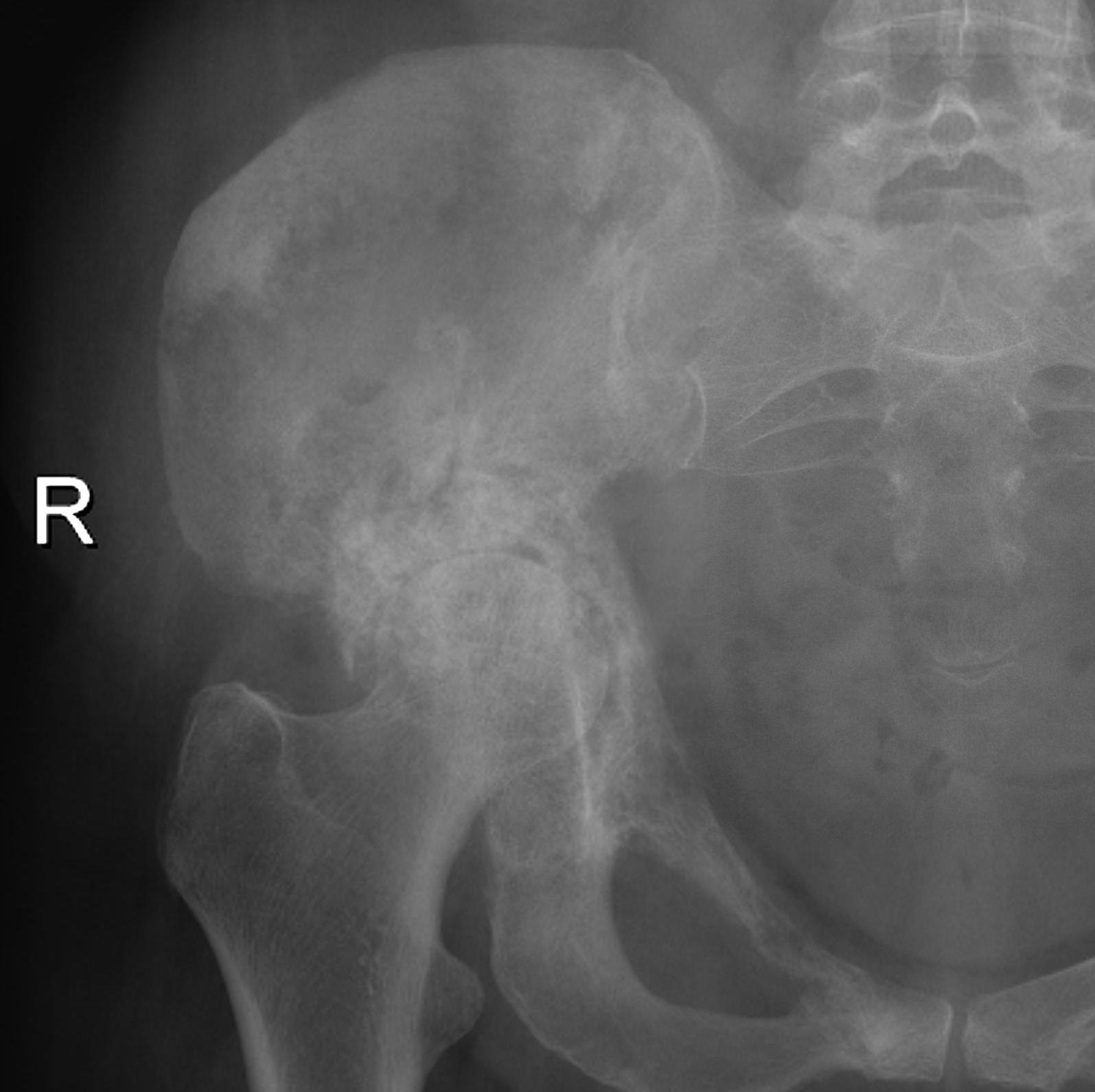
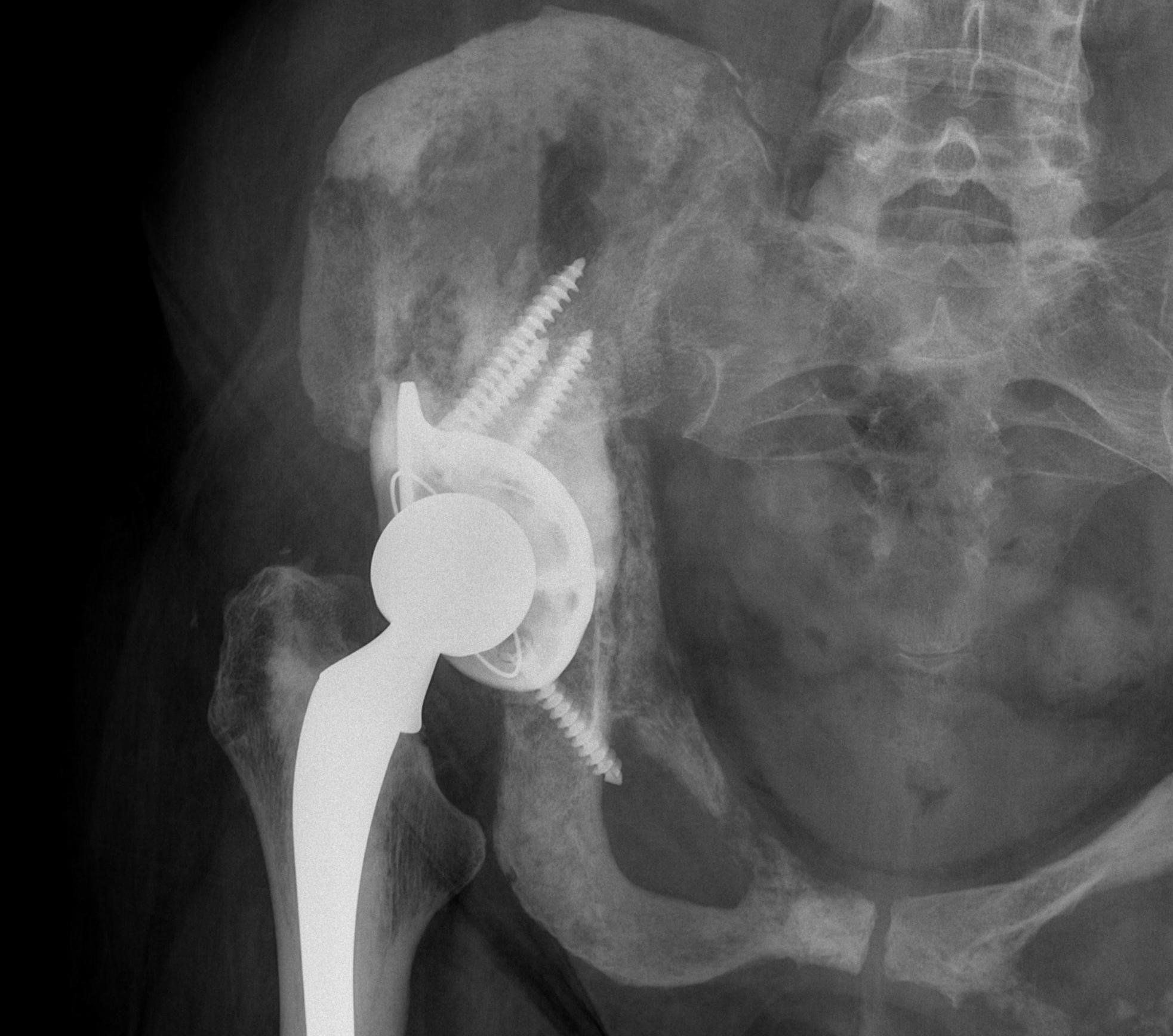
Results
- 78 patients with Harrington technique versus 37 tantalum acetabular reconstruction
- overall, 21% required additional surgical procedures
- tantalum cups more durable with fewer complications
- cup cage in 47 hips with acetabular metastases
- one patient had loosening due to recurrence 8 years post surgery
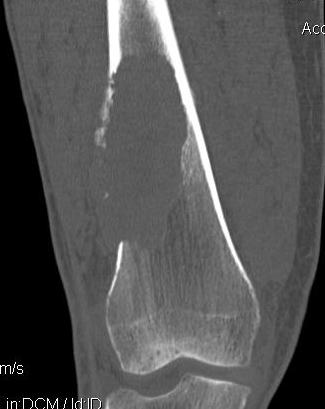
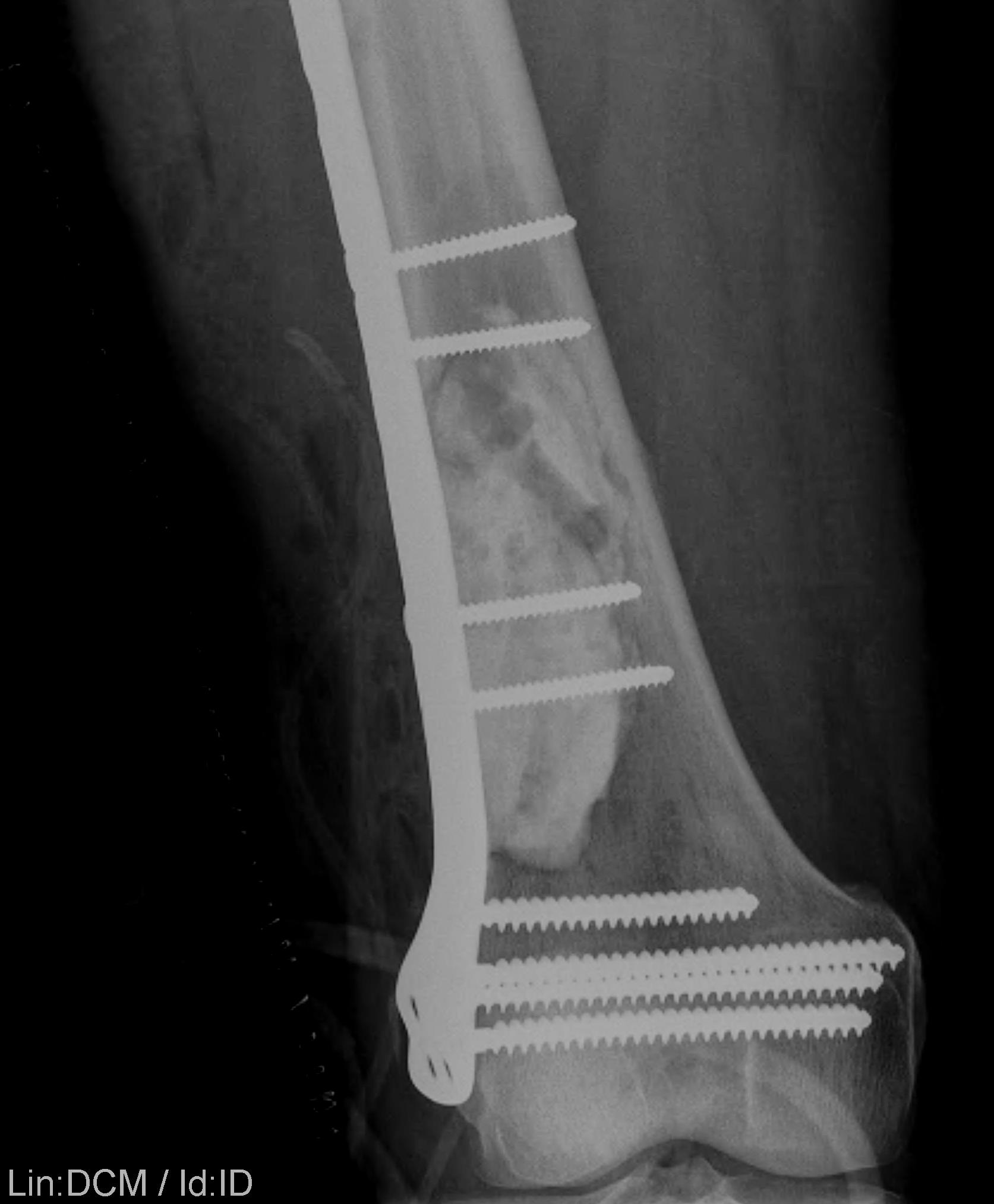
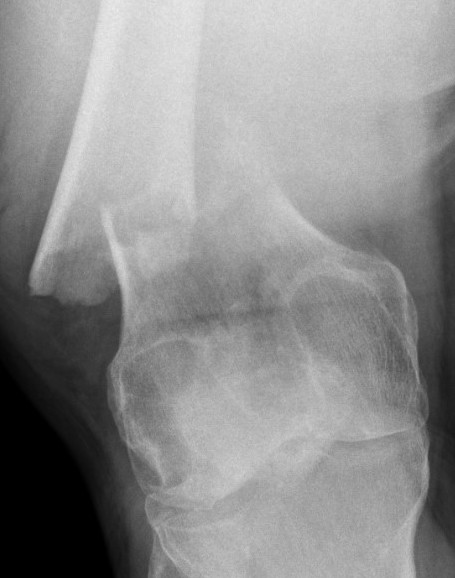
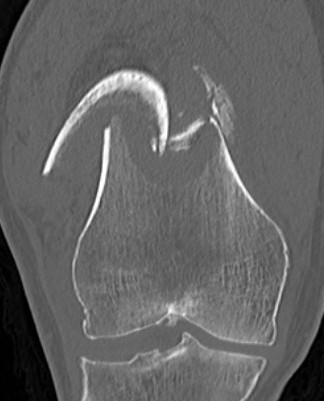
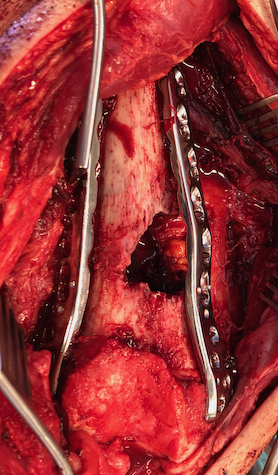
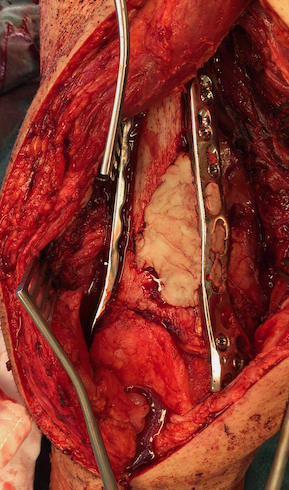
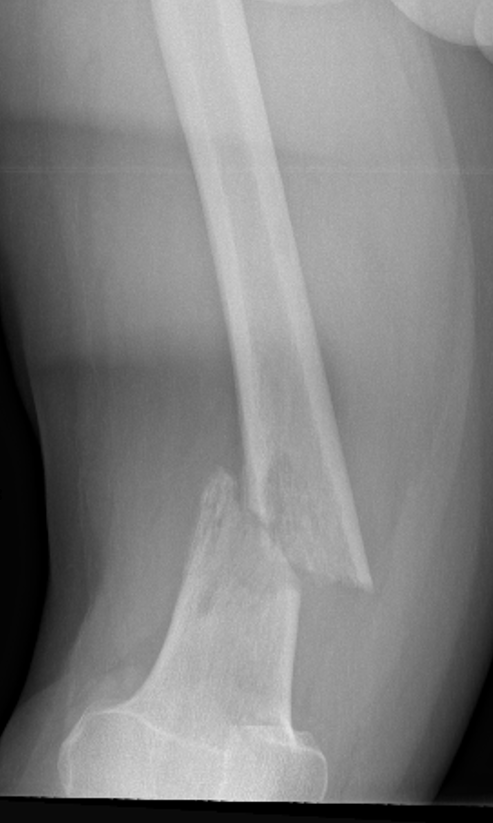
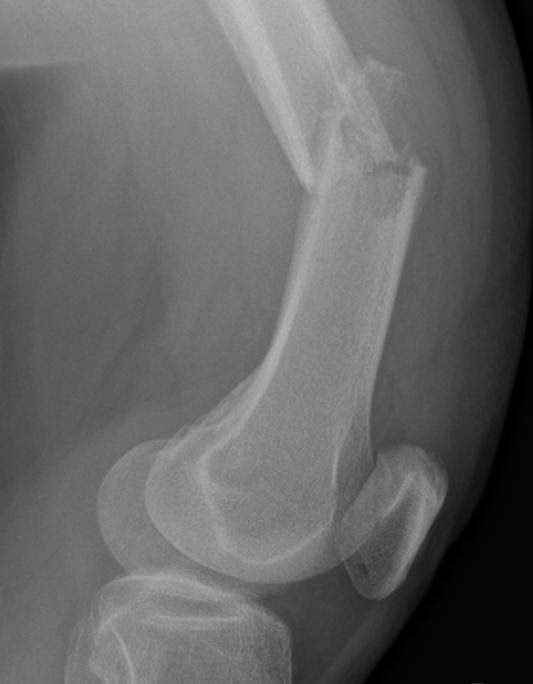
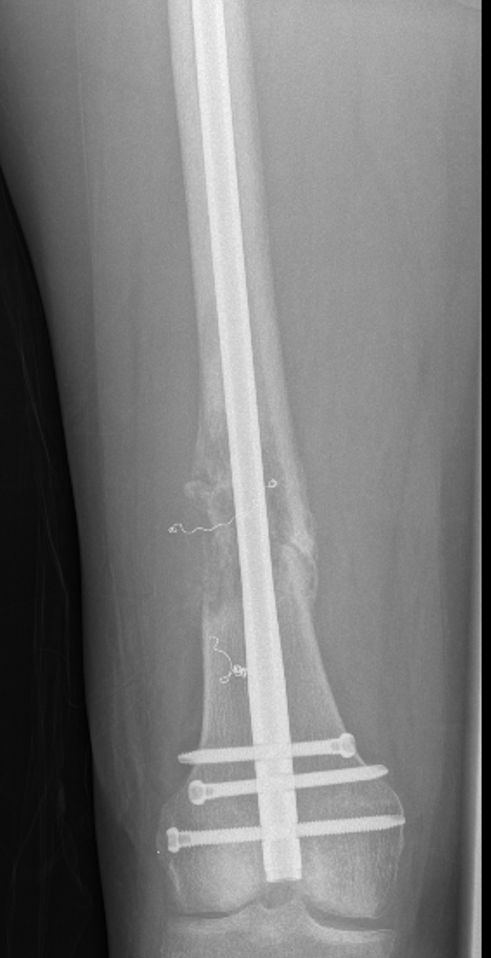
Supracondylar Femur
Options
Plate / dual plate
Retrograde nail
Modular knee prosthesis
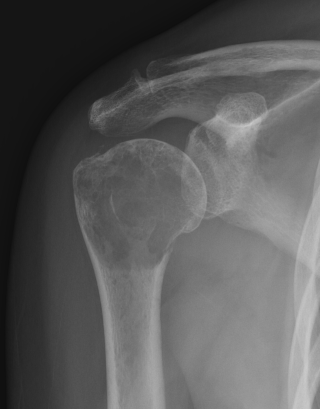
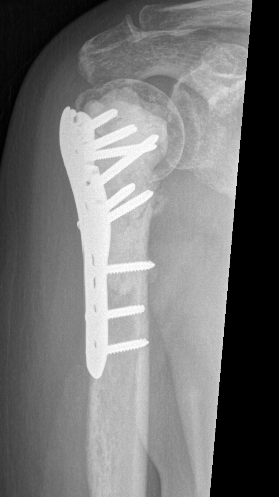
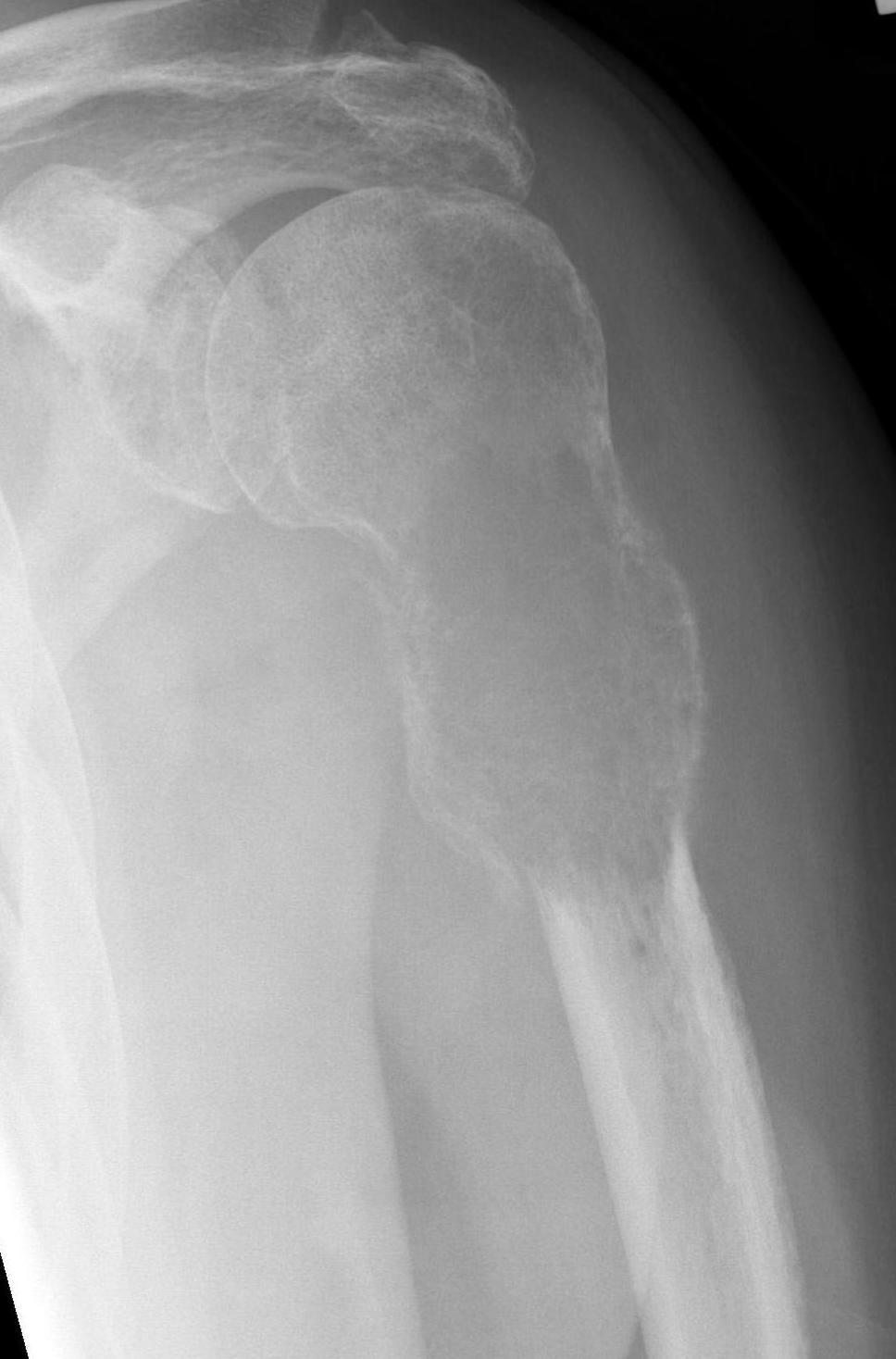
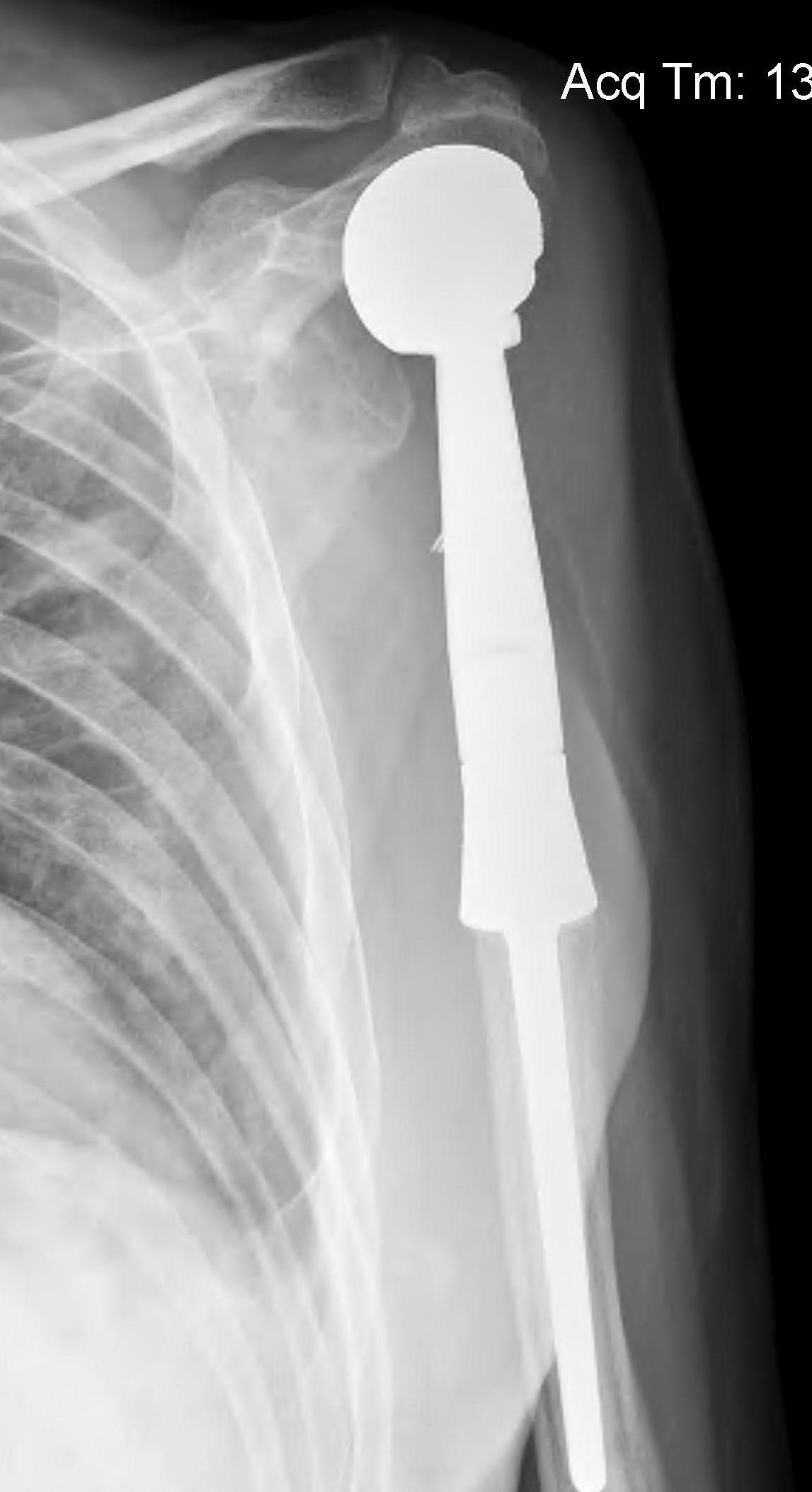
Proximal Humerus
Options
ORIF with plate +/- cement
IMN +/- cement
Tumour prosthesis
Results
Wu et al J Orthop Traumatol 2023
- 45 patients with proximal humerus metastasis
- IM nailing + cement versus plate
- lower blood loss and shorted hospital stay with IMN
- better pain relief with IMN
Humeral shaft
Options
Plate +/- cement
IMN +/- cement
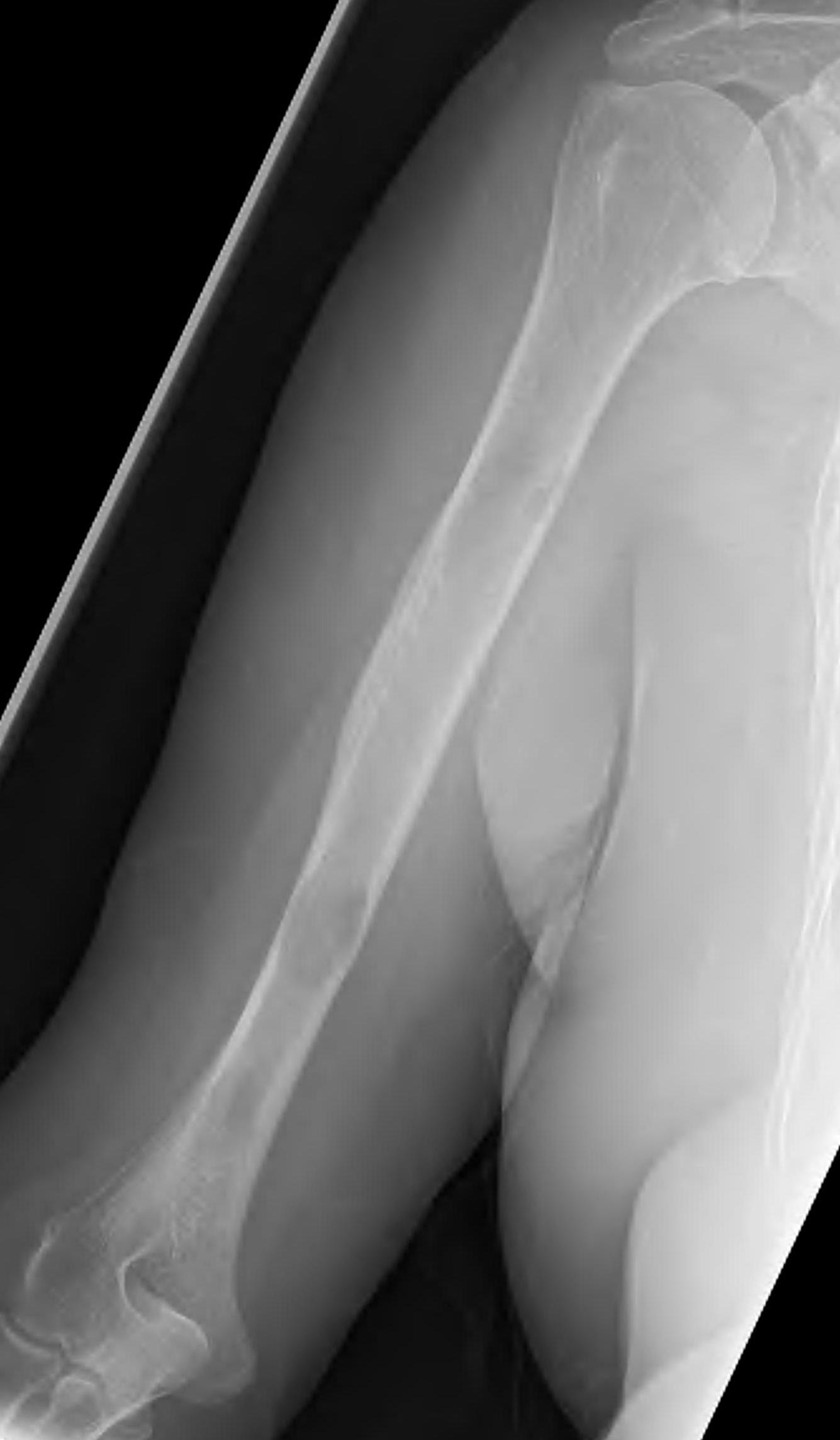
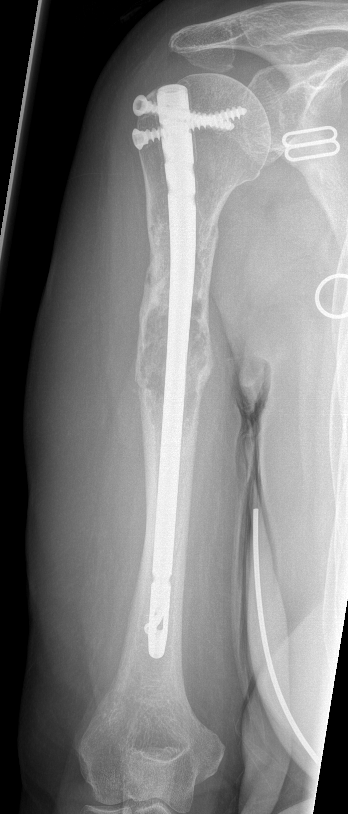
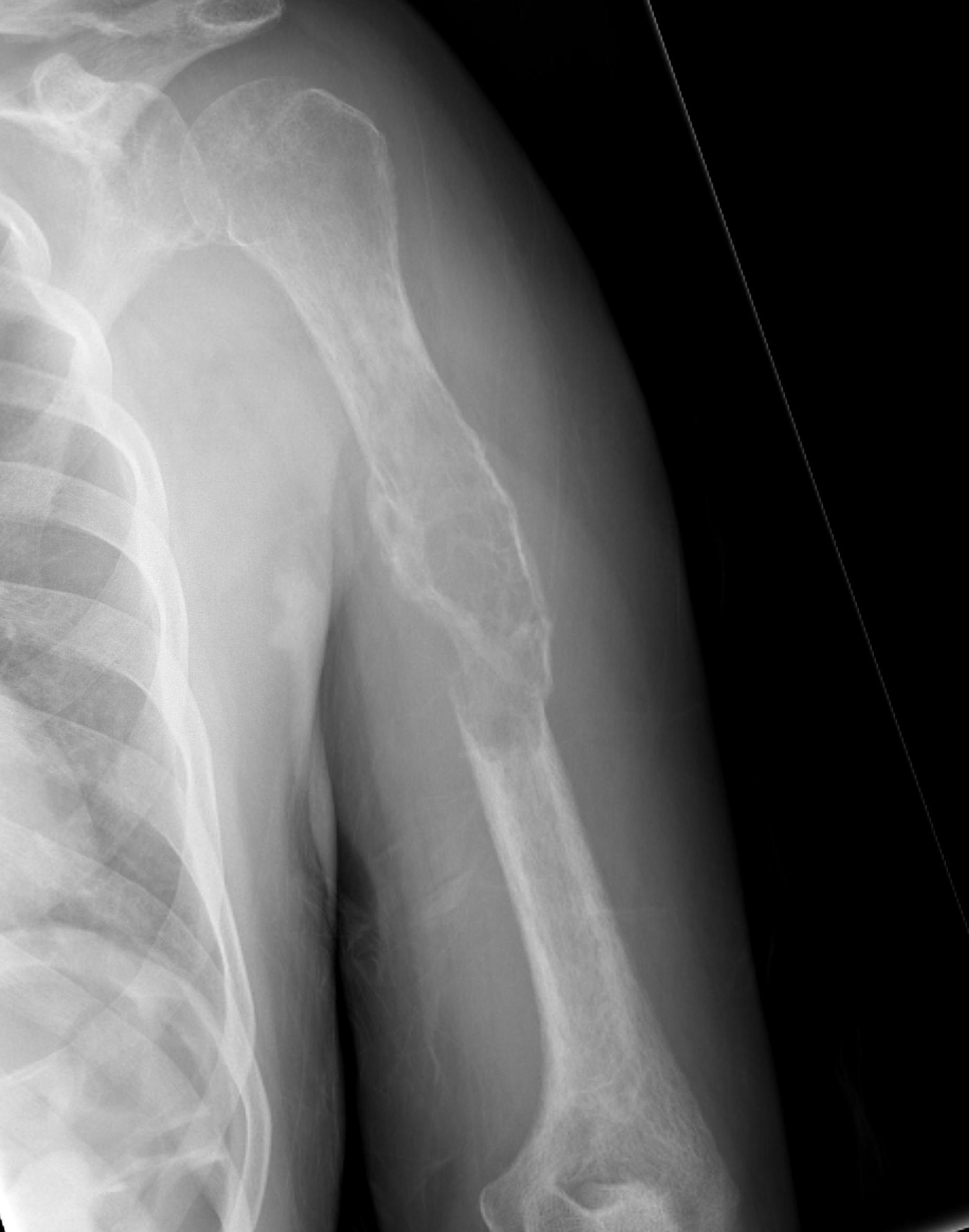
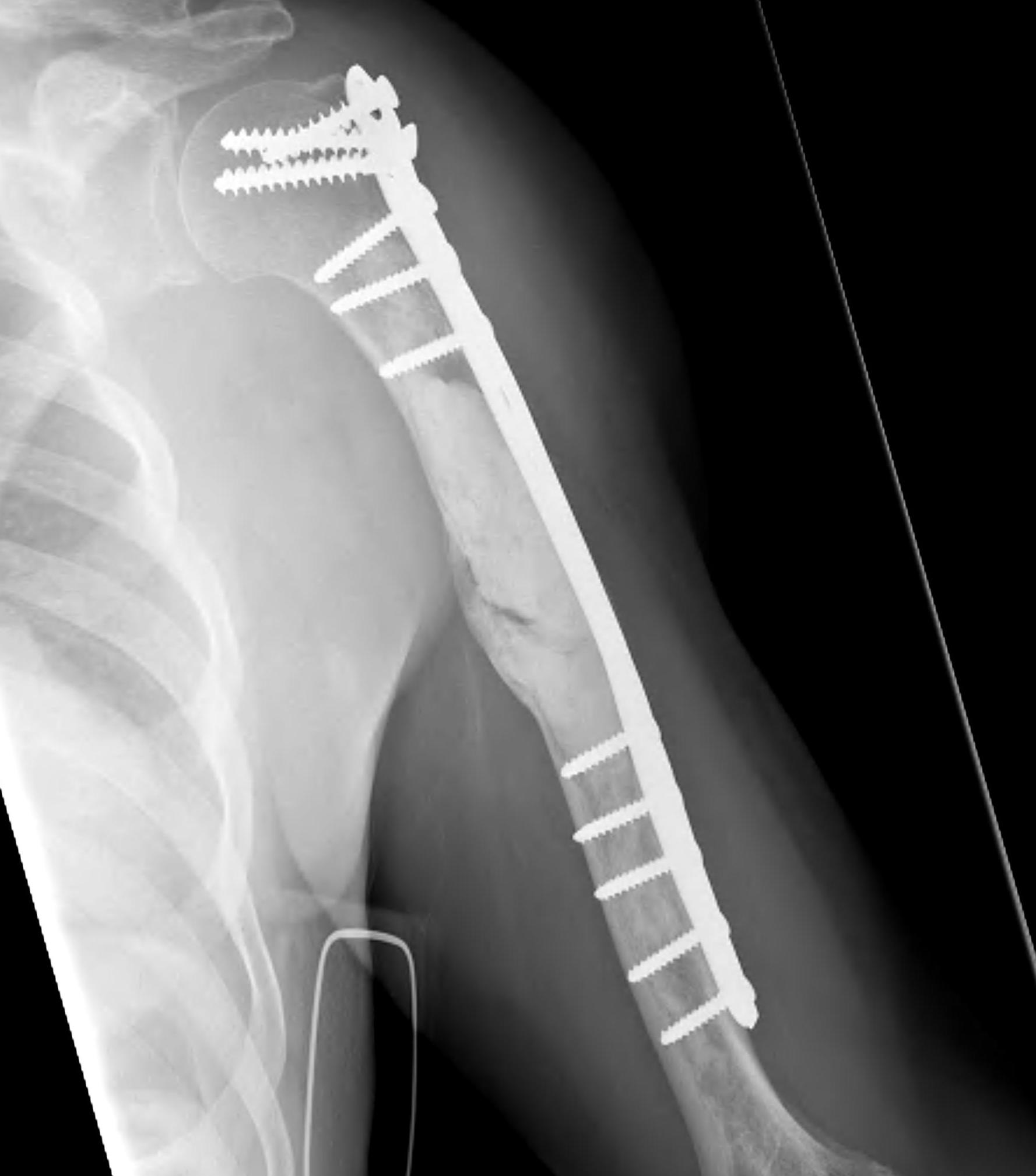
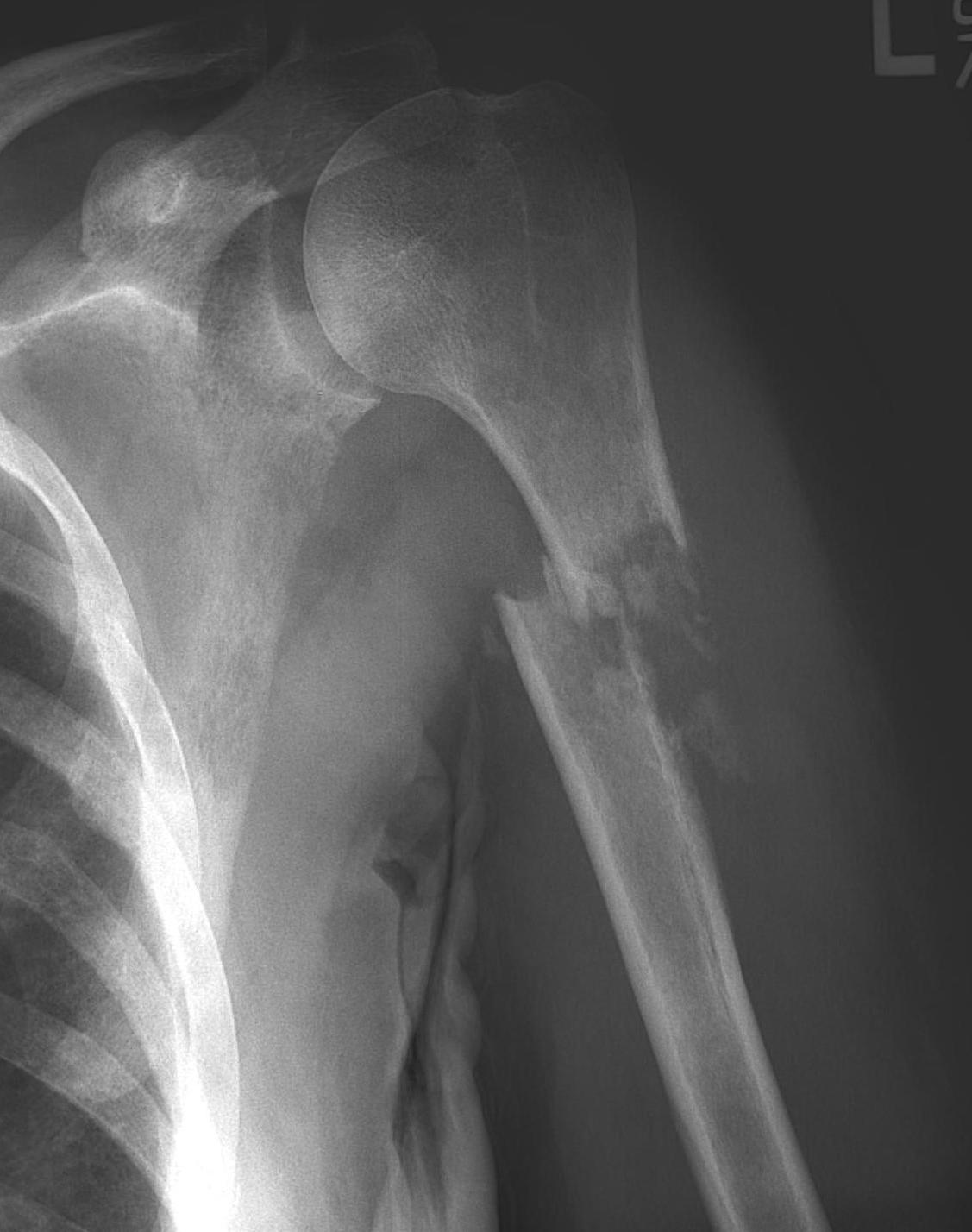
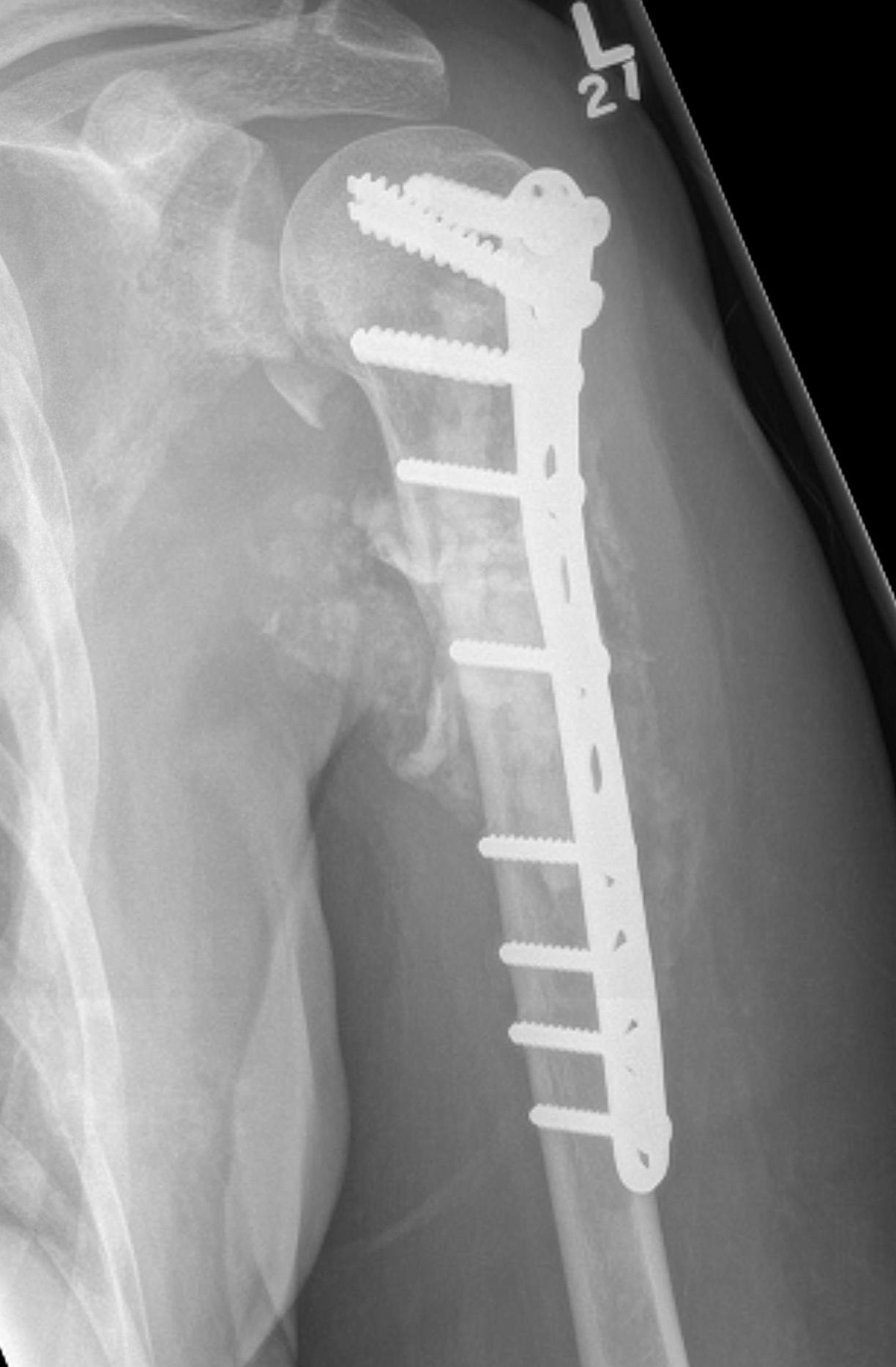
Results IMN
Moura et al Rev Bras Ortop 2019
- 86 pathological humeral fractures treated with IMN
- 5% surgical complication rate
- 100 IMN for pathological humerus fracture
- surgical complication rate 11% with cement, 4% without
Results plate
- 63 pathological humerus fractures
- all treated with cement + plate
- 11% reoperation rate
IMN versus plate
- stabilization of humerus pathological fracture
- broken implant 0% IMN at final follow up
- broken implant 14% plate + cement at final follow up
Tibia
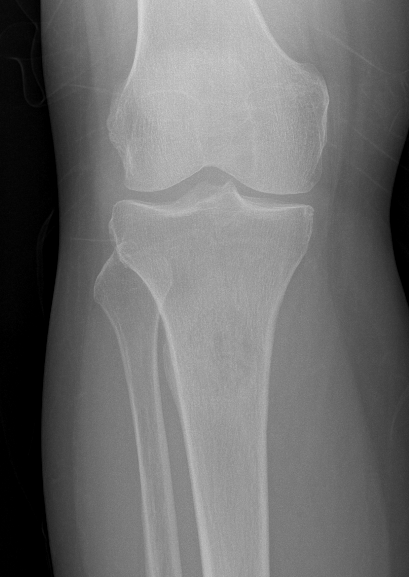
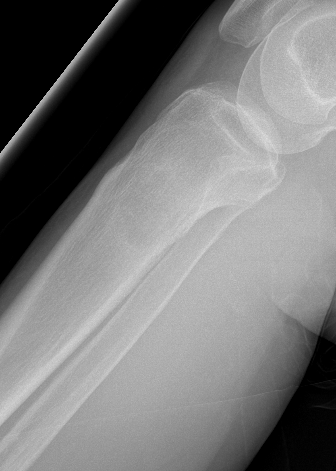
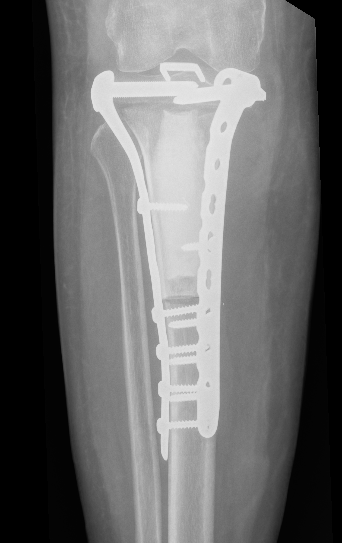
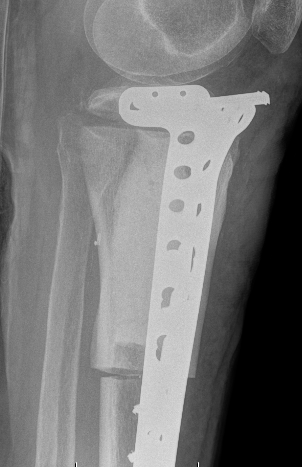
Greenbaum et al Am J Orthop 2017
- 43 tibial metastasis
- proximal tibia most common
- variety of treatements
- plate / nail / arthroplasty
