Management
Timing
Early < 3 - 6 months
- most common


Early < 3 - 6 months
- most common
Prevent contractures
Prevent dislocations
Improve walking
Provide stable and painless sitting
Allow perineal care
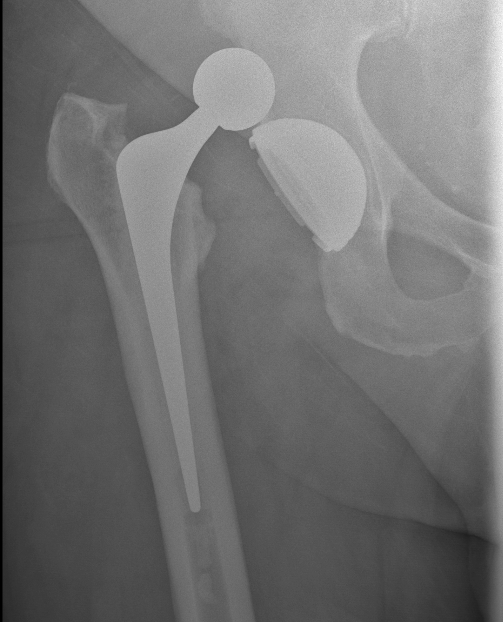
Hip Dislocation
Adductor contractures
Flexion contractures
In-toeing
Windswept hips
Accepted that a dislocated hip in CP is painful
Pigmented Villo-Nodular Synovitis
- benign inflammatory process that arises in synovial tissues
- contains significant amounts of hemosiderin
Age: 20 - 50
Sex: M > F
A. Diffuse
- throughout joint synovium
- more difficult to treat / excise fully
Chondroid Metaplasia of synovium affecting large joints
Nodules of hyaline cartilage
- formed in the subsynovial layer of joint capsules
Rare lesion
Most common in 20's and 30's
Sex: M > F (2:1)
Monoarticular
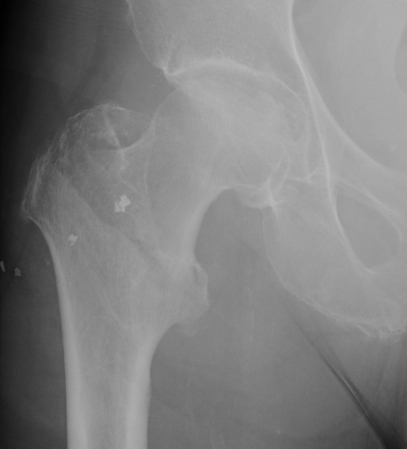
Fracture which extends between the trochanters of the proximal femur
- lower limit is inferior border of lesser tuberosity
Extra capsular / well vascularized
The key to stability is the posteromedial cortex
Stage 0
Natural history mixed
- depends on size of lesion and diagnosis
- treat if becomes asymptomatic
- may benefit from bisphosphonates
Stage 1 / Normal X-ray, abnormal MRI
Forage: 80% G/E
Bisphosphonates
Stage 2 / Abnormal X-ray with cysts and sclerosis
A: As for Stage I
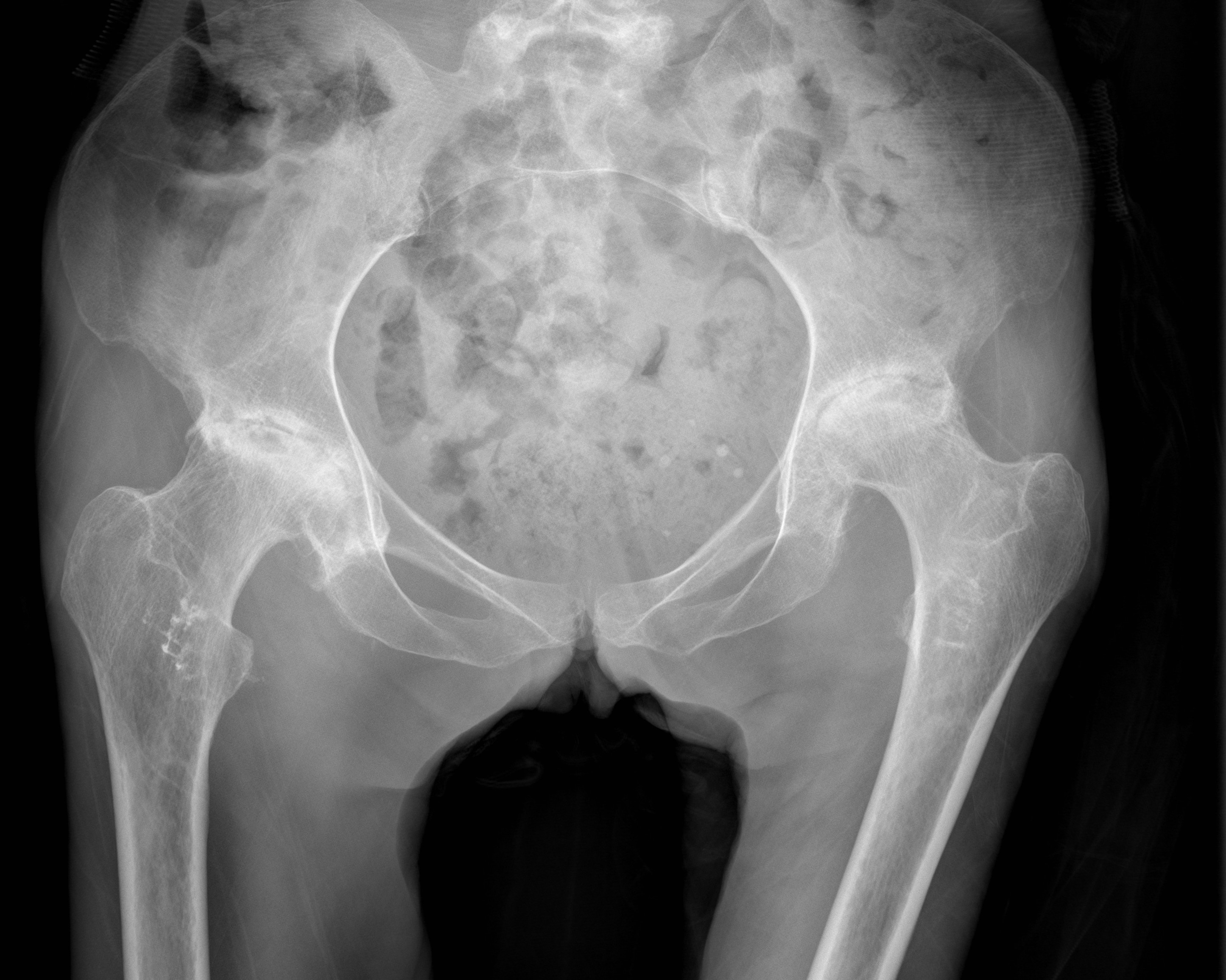
Non-traumatic or traumatic condition of femoral head with bone death
20 - 50 yo (average 38)
- M: F 4:1
70-80% with AVN will progress within 1 year
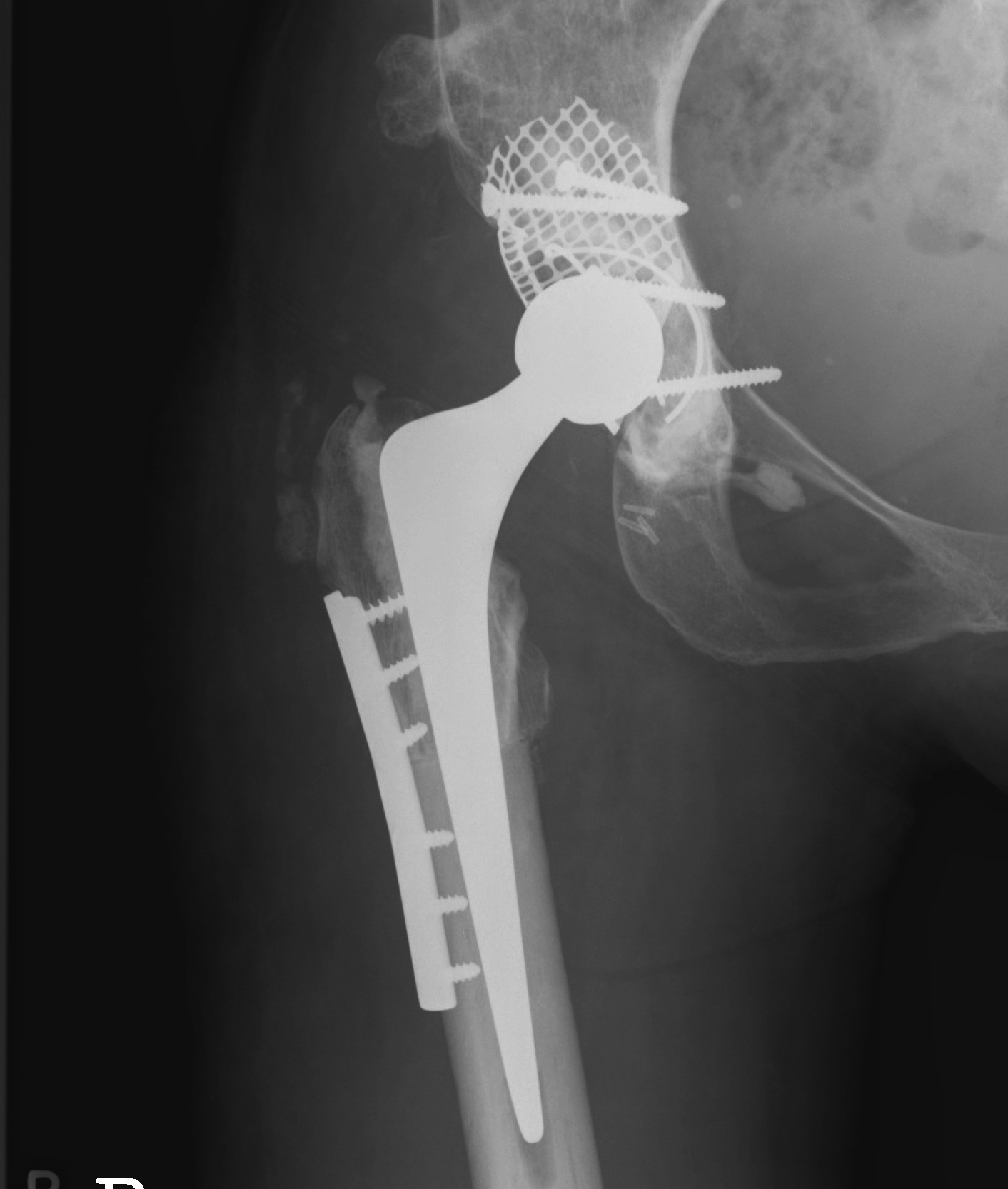
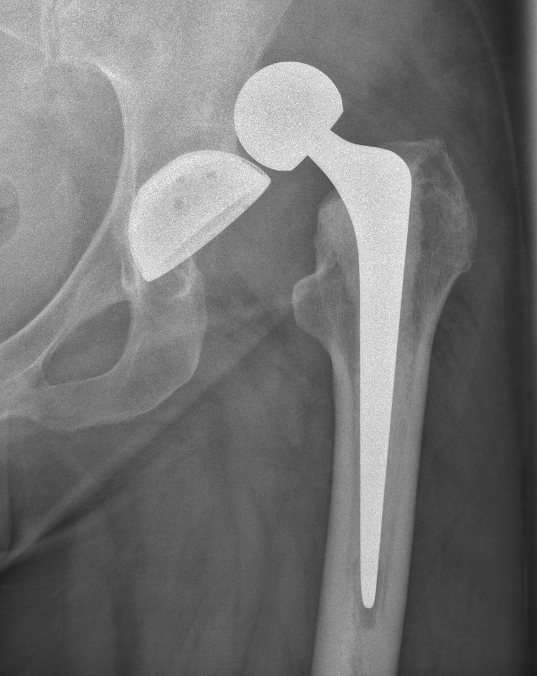
THR in dysplastic hips has a higher failure rate
- due to anatomic abnormalities
- due to generally younger age
Restore normal biomechanics and preserve bone stock
Soft tissues
Young adult
- 16 - 30 years old
- monoarticular disease
- heavy demand
Exhausted options of osteotomy
- risk of THA failure / multiple revision surgeries considered too high
Maximise bony contact
Minimise shortening