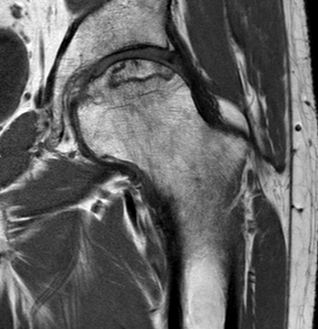
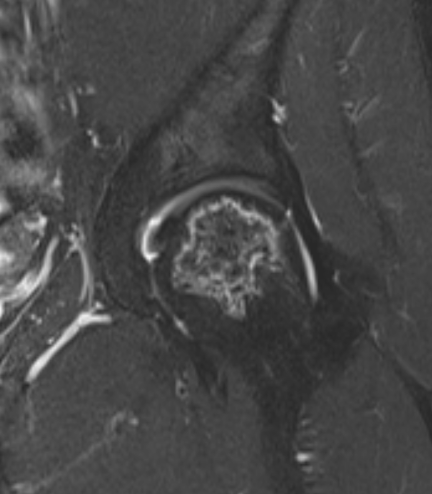
Non operative Management
Options
Bisphosphonates
Extra-corporeal shock wave
Hyperbaric oxygen
Bisphosphonates
Mechanism
- inhibit osteoclast absorption
- limit head collapse
Results
Hong et al Biomed Res Int 2014
- systematic review of 5 RCTS and 307 patients using alendronate for hip AVN
- alendronate decreased pain, improved function, and reduced collapse
ECSW
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy
Results
Hao et al J Orthop Surg Res 2018
- 4 RCTs and 200 patients
- ECSW improved pain and function
Hyperbaric Oxygen
Results
Camporesi et al J Arthroplasty 2010
- RCT of 20 patients treated with hyperbaric O2 or air
- improved pain and function with hyperbaric oxygen
Operative Management Stage I / II (Pre-collapse)
Options
Core decompression
+/- non vascularised bone graft
+/- vascularised bone graft
+/- tantalum rod
+/- cell therapy
Liu et al BMC Musculoskeletal disorders 2021
- meta-analysis of 17 RCTs and 918 hips
- core decompression +/- various interventions
- bone graft / vascularised bone graft / tantalum rod / cell therapy
- only core decompression + cell therapy demonstrated reduced collapse and progression to THA
Hua et al J Orthop Surg Res 2019
- 32 studies and 2400 hips
- overall success of core decompression 65%
Core Decompression
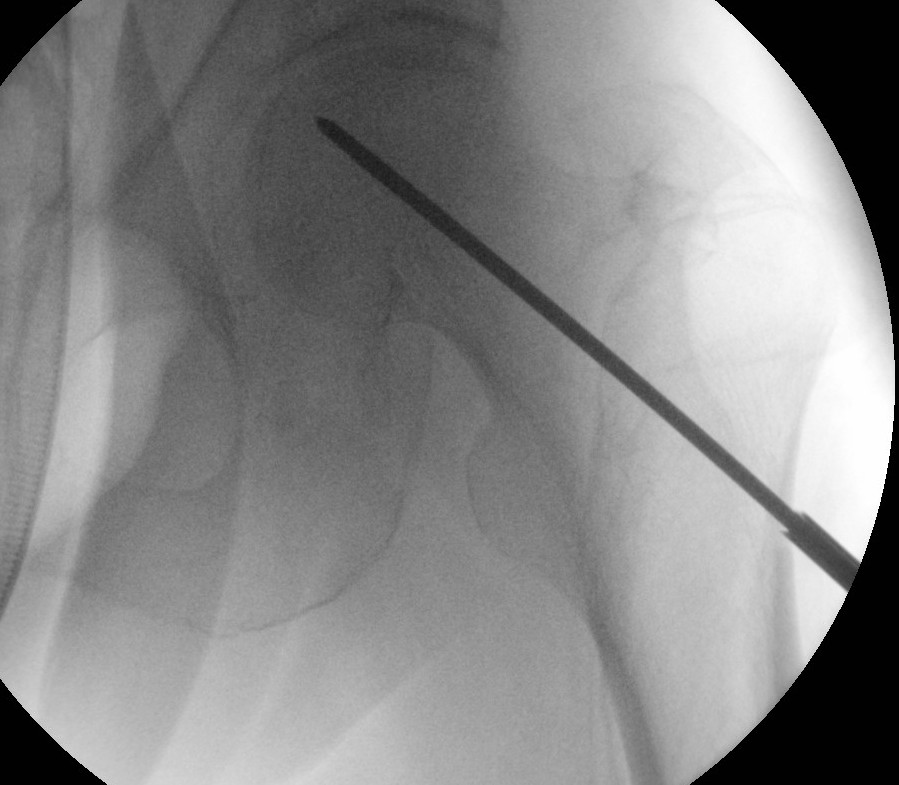
Concept
Theory
- decompress intraosseous hypertension
- promote revascularization
Options
1. Central core decompression through femoral neck
2. Hip arthroscopy and multiple small drill holes technique
Central Core Decompression Techniques
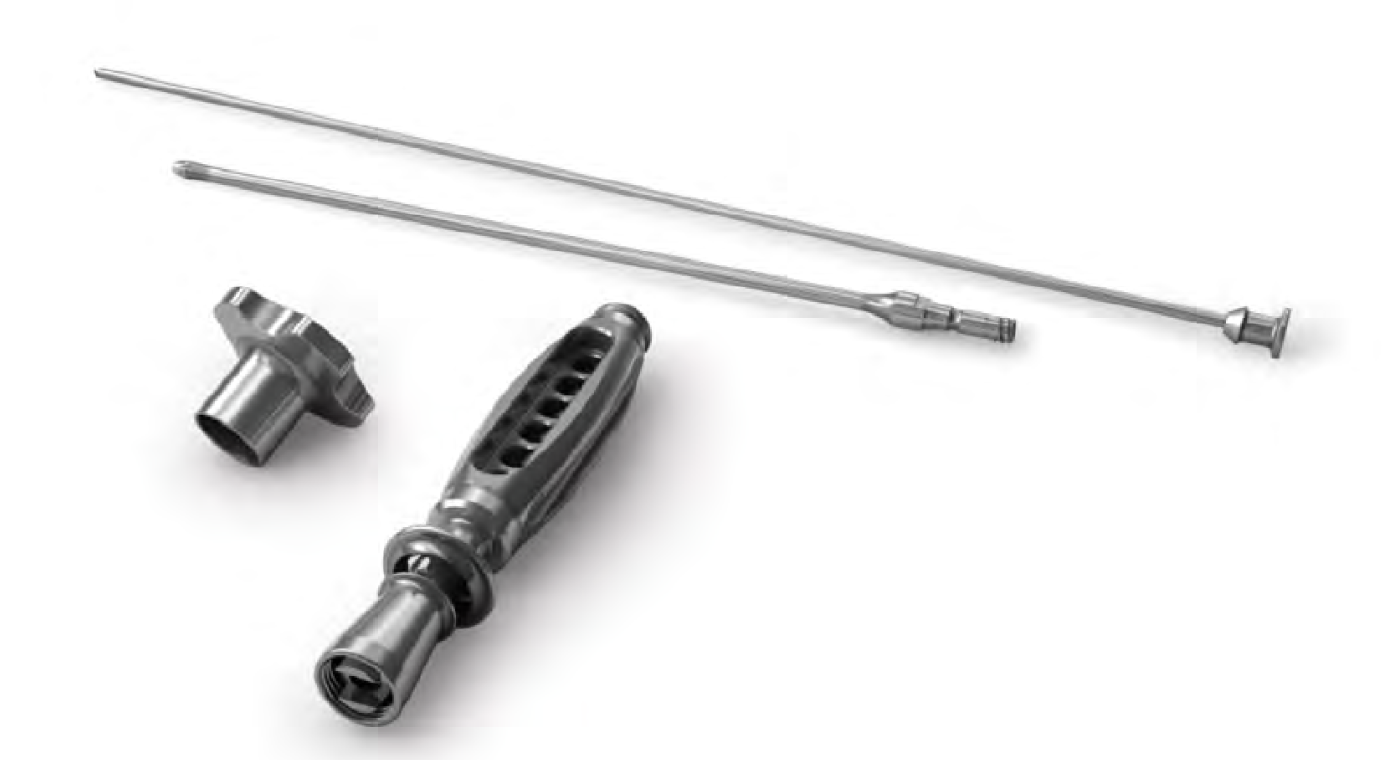

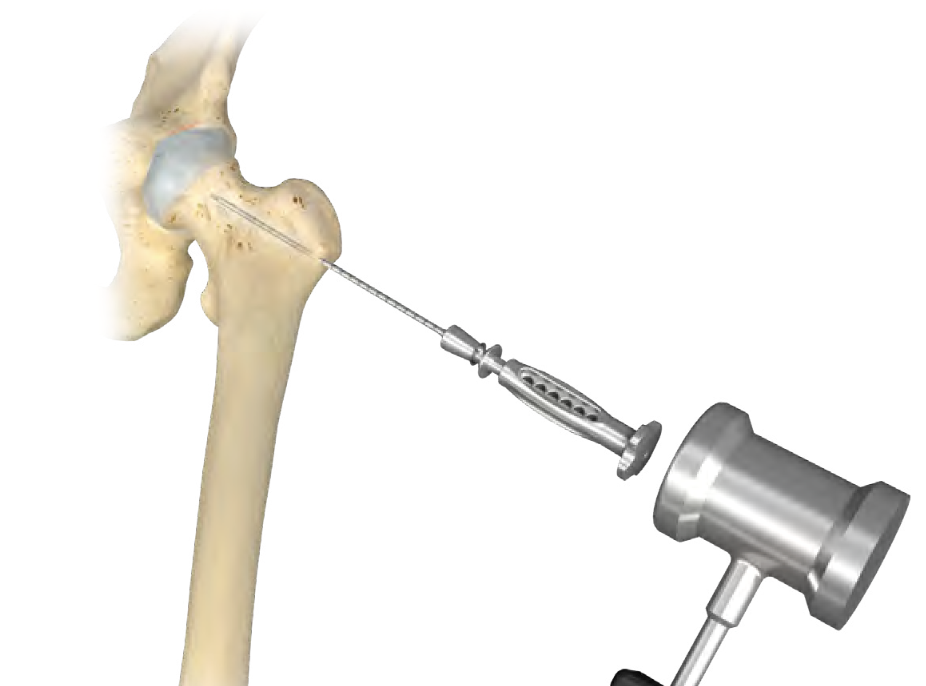
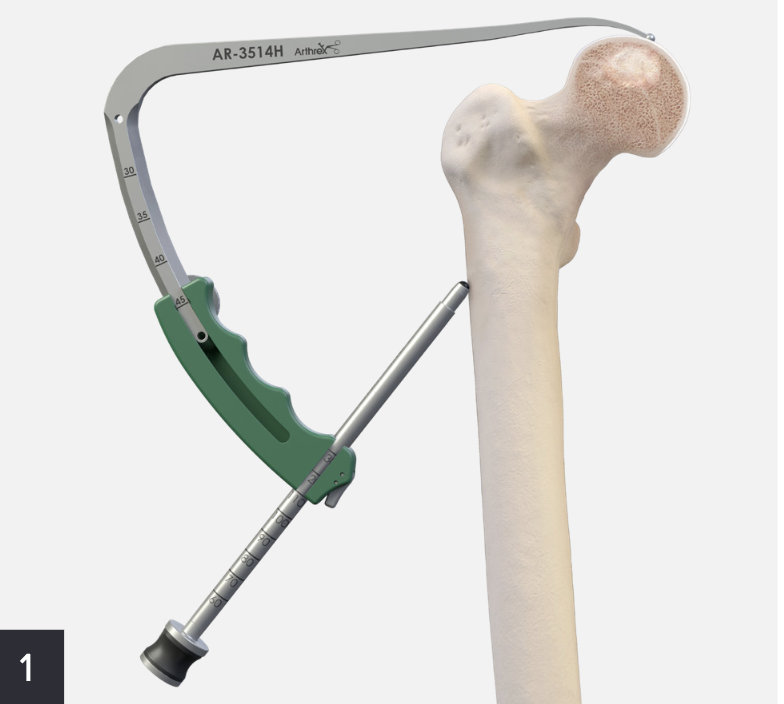
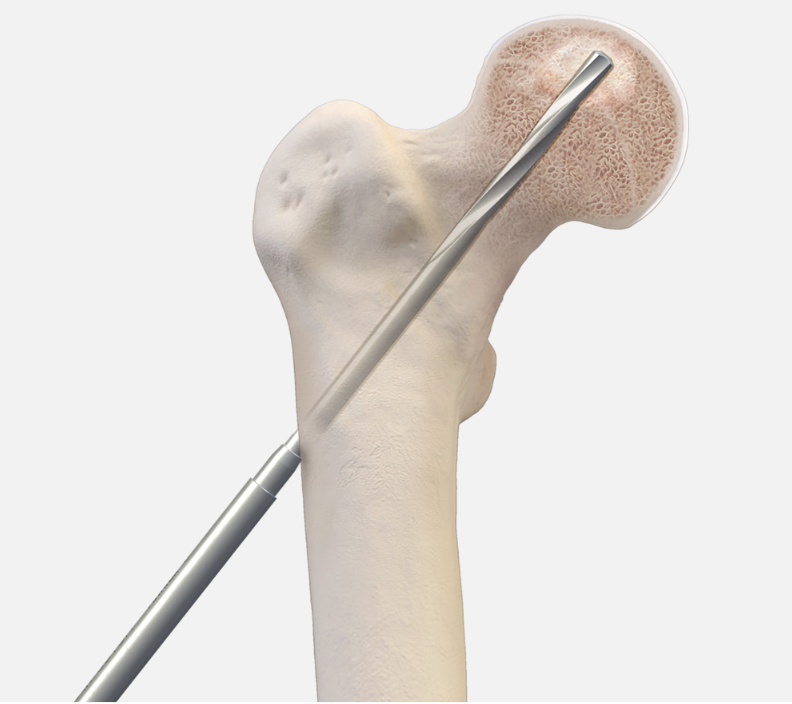
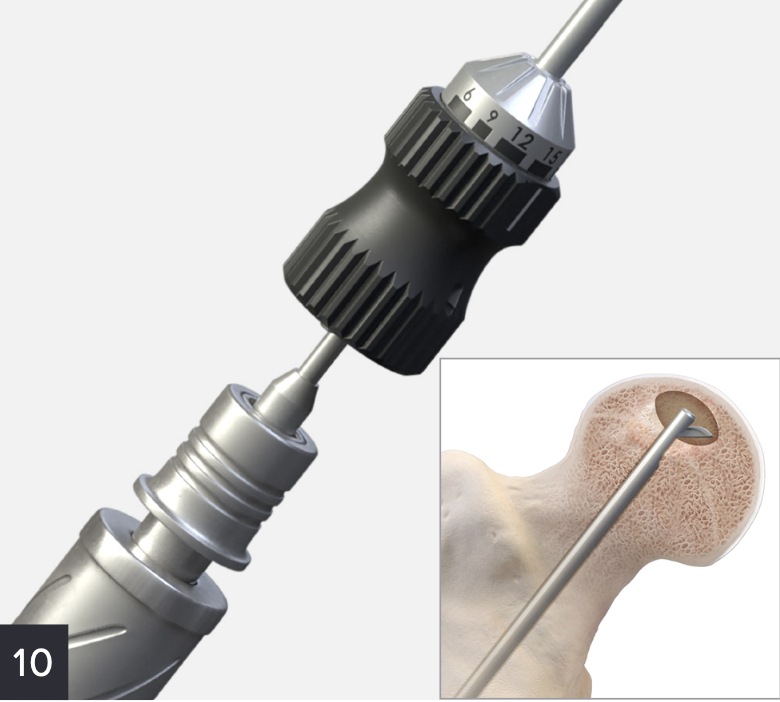
Zimmer PerFuse Percutaneous Decompression System
Vumedi Zimmer PerFuse Percutaneous Decompression
Arthrex Core Decompression Expandable Reamer
Vumedi arthroscopic core decompression and BMAC
Technique
- AP and lateral xray
- entry point through greater trochanter
- above lesser trochanter to reduce fracture risk
- enter site of AVN
- overdrill
- +/- bone graft / vascularized bone graft / tantalum rod / BMAC (bone marrow aspirate concentrate)
Arthroscopic multiple small drill holes techniques
Arthroscopy techniques hip arthroscopy and multiple small drill holes video
Technique
- hip arthroscopy
- central compartment
- identify head neck junction
- multiple 1.5 mm drill holes into lesion in femoral head
- +/- BMAC
- retrospective study of CD versus multiple small drill holes
- 98 hips
- at 6 months better hip scores with multiple small drill holes
Non vascularised bone graft
Techniques
1. Cortical strut graft
2. Trapdoor technique
- head neck junction or cartilage trapdoor
- evacuate necrotic bone
- pack with cancellous bone
Results
Hu et al J Musculoskeletal Neuronal Interact 2018
- RCT of core decompression (CD) versus CD + allogenic fibular strut graft
- 130 patients
- improved pain and MRI in fibular strut group
- no difference in collapse rates at 4 years
Vascularised Bone Graft
Technique
- fibula segment harvested with peroneal artery and vein
- stabilized with K wire
- anastomosed to lateral femoral cutaneous artery and vein
Results
- RCT of CD versus CD + vascularised fibular bone graft (VBG)
- 54 hips
- decreased progression of AVN stage with VBG
- improved hip scores with VBG
Core decompression + Tantalum rod
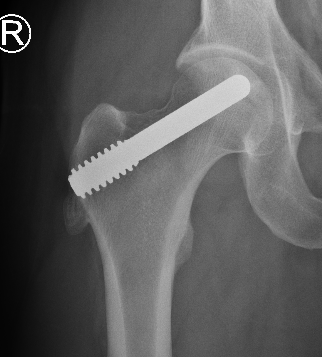
Results
- RCT of 60 patients with stage 1/2
- multiple 3.5 mm decompressions versus tantalum rod
- 1 year follow up
- no difference in outcome
Core decompression + Autologous stem cells / Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC)
- meta-analysis of core decompression +/- autologous stem cells
- 11 RCTs and 507 patients
- application of stem cells improved Harris Hip scores
- decreased necrosis / collapse / risk THA with stem cells
- RCT of 100 patients
- CD versus CD + expanded autologous bone marrow cells
- improved hip scores and reduced collapse / THA with bone marrow cells
Operative Management Stage III / IV (Collapse)
Options
Osteotomy
Limited resurfacing
THA
Osteotomy
Theory
Move the avascular segment away from weight-bearing area
- must have sufficient intact femoral head to bear weight upon
Indications
Young patient
Stage III / no osteoarthritis
Small lesion: CNA <200°
Not on steroids
Technique
CT / MRI decide osteotomy direction
- typically anterolateral AVN
- undergoes a varus flexion intertrochanteric osteotomy
Results
- 113 hips undergoing transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy
- 63% survival at 110 months
- age > 40, stage III, CNA > 2000 and BMI > 24 poor prognostic factors
Limited Resurfacing Arthroplasty
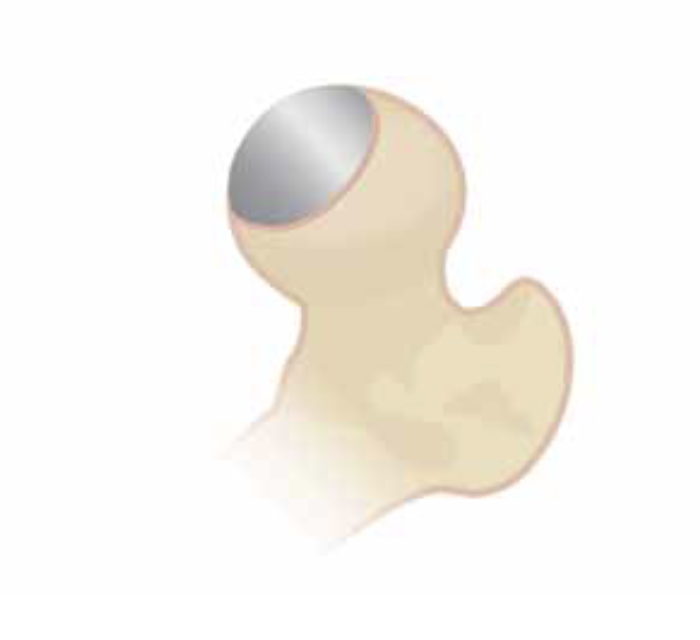

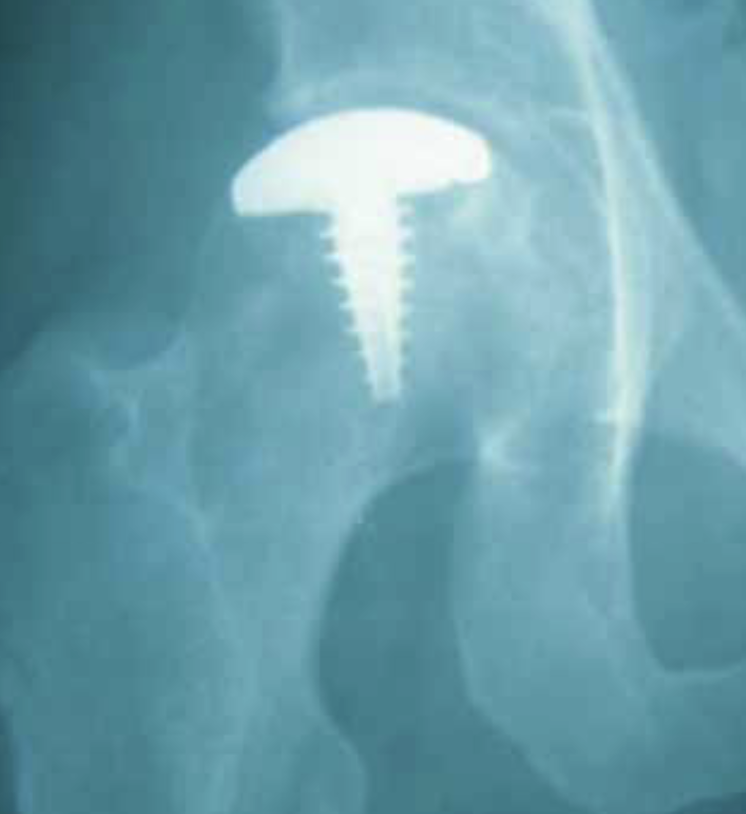
Hemicap Concept
Replace localized area on femoral head
- restores sphericity to femoral head
- limit progression to osteoarthritis
- need to have limited acetabular damage at time of surgery
Technique
Results
Floerkemeier et al Int Orthop 2017
- hemicap partial resurfacing in 16 patients with localized AVN or osteochondral defects
- 25% conversion to THA at 2 years due to loosening or acetabular arthritis
Total hip arthroplasty
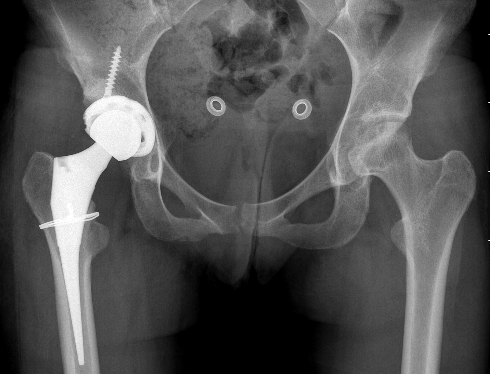
Issues
? Failure rate higher than in age matched OA patients
- also worse if caused by ethanol / steroids
Results
Australian Joint Registry 2022 Annual report
- 580,000 THA
- THA overall 20 year revision rate 11%
- THA for OA overall 20 year revision rate 8%
- 14,000 AVN (3% overall)
- THA for AVN 20 year revision rate 12%