Definitions
Cervical spondylosis
- chronic disc degeneration & associated facet arthropathy
- cervical spine osteoarthritis
+/- radiculopathy / myelopathy
Epidemiology
- cervical spine MRI of 1211 healthy volunteers
- overall 87% of patients had evidence of significant disc bulge
- 70% of patients in their 20s had a disc bulge
- 5% of patients had evidence of spinal cord compression, mainly 50 years and over
- most common at C5/6 > C6/7 > C4/5
Lv et al BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2018
- cross sectional study 3800 patients
- symptoms of cervical spondylosis most common 40 - 60 years of age
- females > males
- associated with mental work / work posture / vibration / sleep < 7 hours
Pathology
Degenerative changes at disc / facet joints / uncovertebral joints
Disc dessication
- death of intervertebral disc cells
- reduced production of hydrophilic proteoglycans
- loss of disc height
Symptoms
Neck pain
Reduced ROM
"Atypical symptoms"
- dizziness / headache / nausea / tinnitus / palpitations / gastrointestinal disturbance / blurred vision
X-ray
Typical changes of spondylosis
- disc space narrowing
- osteophyte formation
- degenerative facet & uncovertebral joints
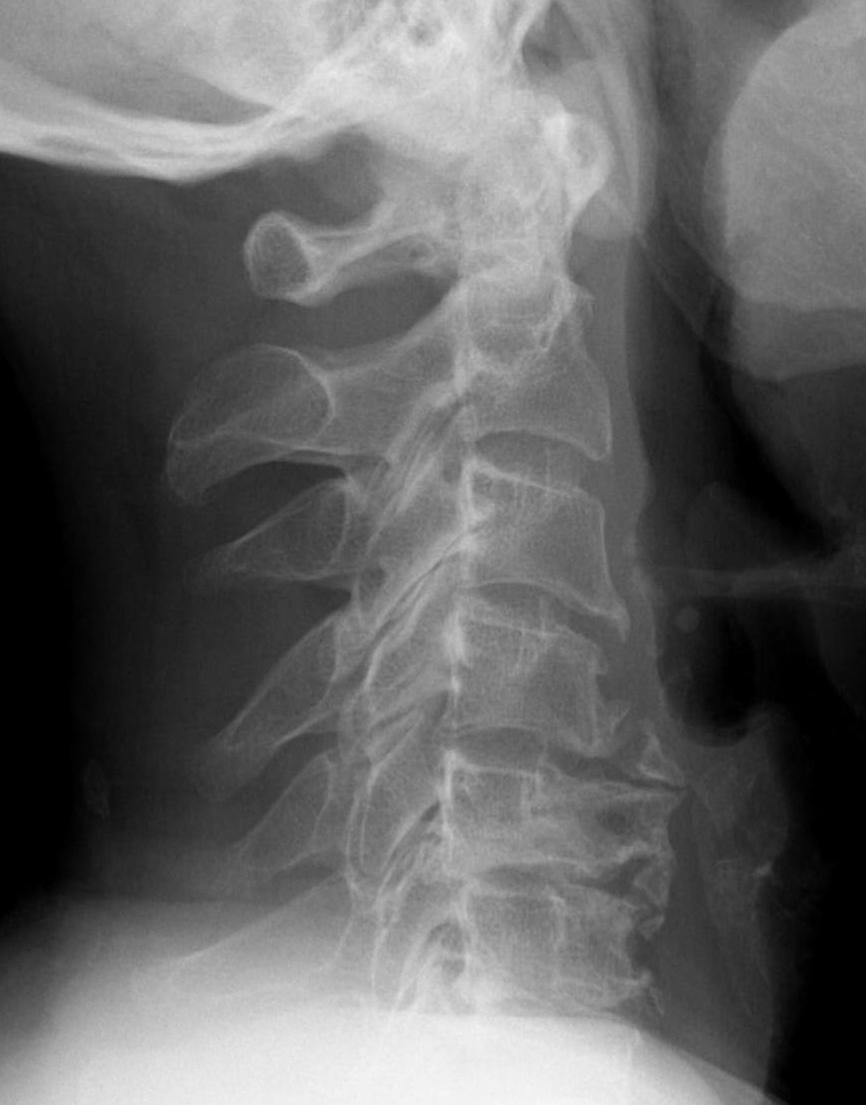
Severe C5/6 disc degeneration
CT scan
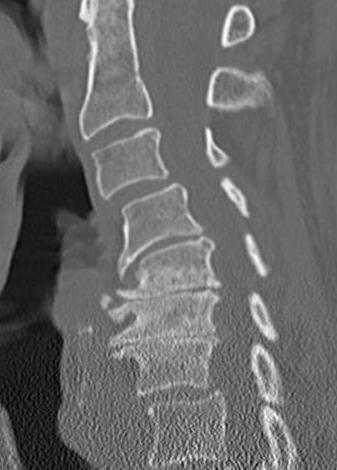
2 level disc degeneration on CT
MRI
Degenerative disc changes
- dessication (loss of fluid)
- narrowing
- end plate changes
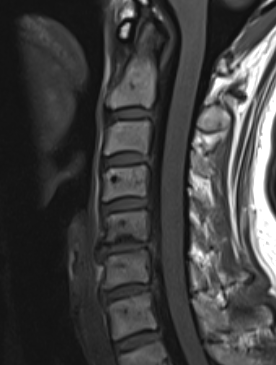
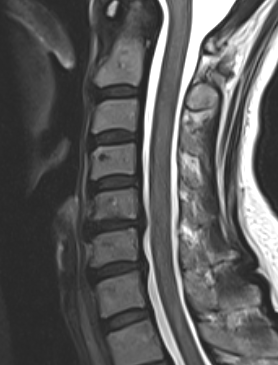
End plate changes Disc dessication with disc bulge
Management
Non-operative
Education & reassurance
Simple analgesics - paracetamol / NSAIDS
Exercise program
Acupuncture
Exercises
Kay et al Cochrance Database System Rev 2012
- exercises for neck pain
- 21 RCTs
- supports use of cervical stretching and strengthening in short and intermediate term
Acupuncture
- RCT of 835 patients undergoing acupuncture for neck pain
- improved neck pain at 4 weeks compared to sham or shallow needling
Operative
Indications
Persistent debilitating neck pain
Disease isolated to 1 or 2 levels
Options
ACDF
Disc replacement
Posterior Instrumented fusion
Results
Single level spondylosis
- meta-analysis of ACDF versus disc replacement for single level spondylosis
- 9 RCTS and 1700 patients
- better neck pain, arm pain, and lower neurological failure with disc replacement
Two level spondylosis
- meta-analysis of ACDF versus disc replacement for 2 level spondylosis
- 9 RCTs and 2700 patients
- improved outcomes for NDI and VAS scores for disc replacement
- meta-analysis
- comparison of ACDF versus hybrid surgery (ACDF and disc replacment) for multilevel spondylosis
- equivalent reduction in pain, improved neck scores, and better ROM with hybrid surgery
Atypical symptoms
Garg et al World Neurosurg 2022
- meta-analysis of success of decompression of relieving atypical symptoms
- surgery improved headache / nausea / tinnitus
- no effect blurred vision / GI upset / palpitations
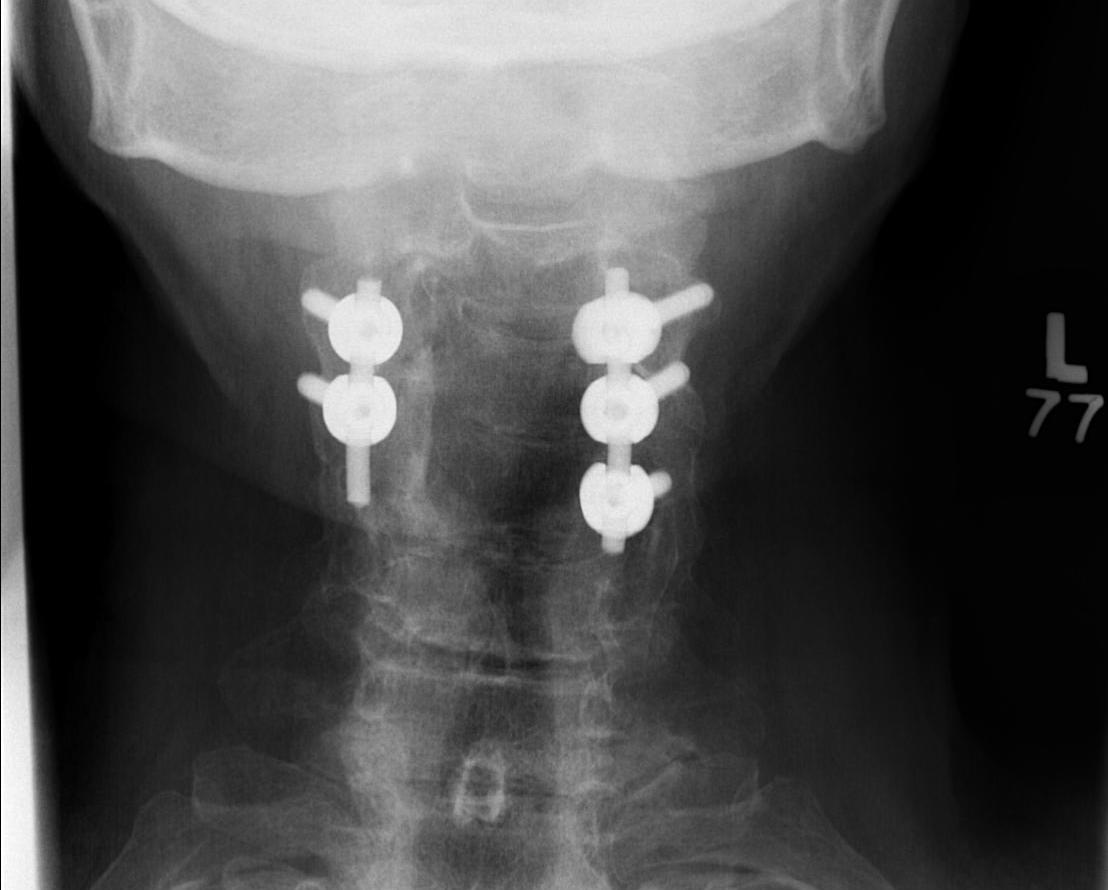
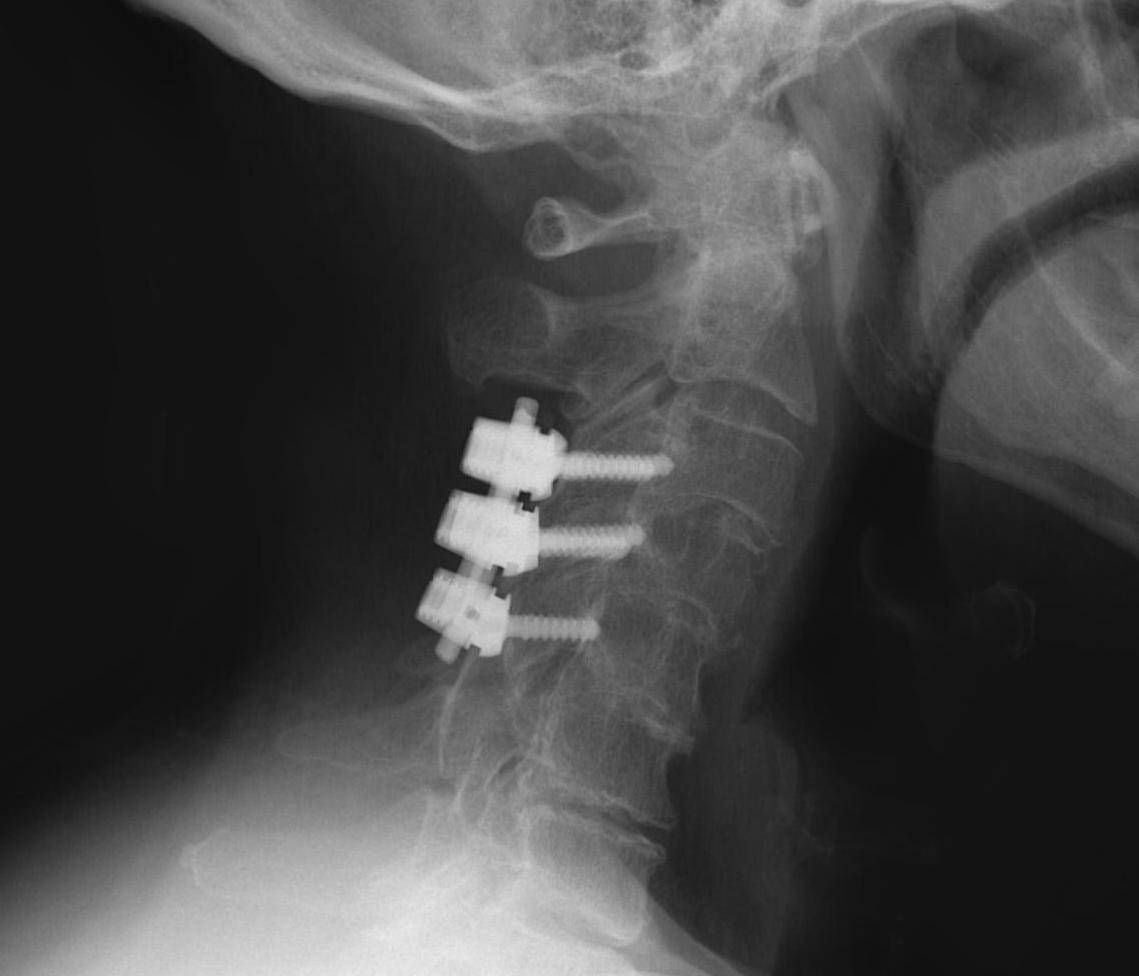
ACDF
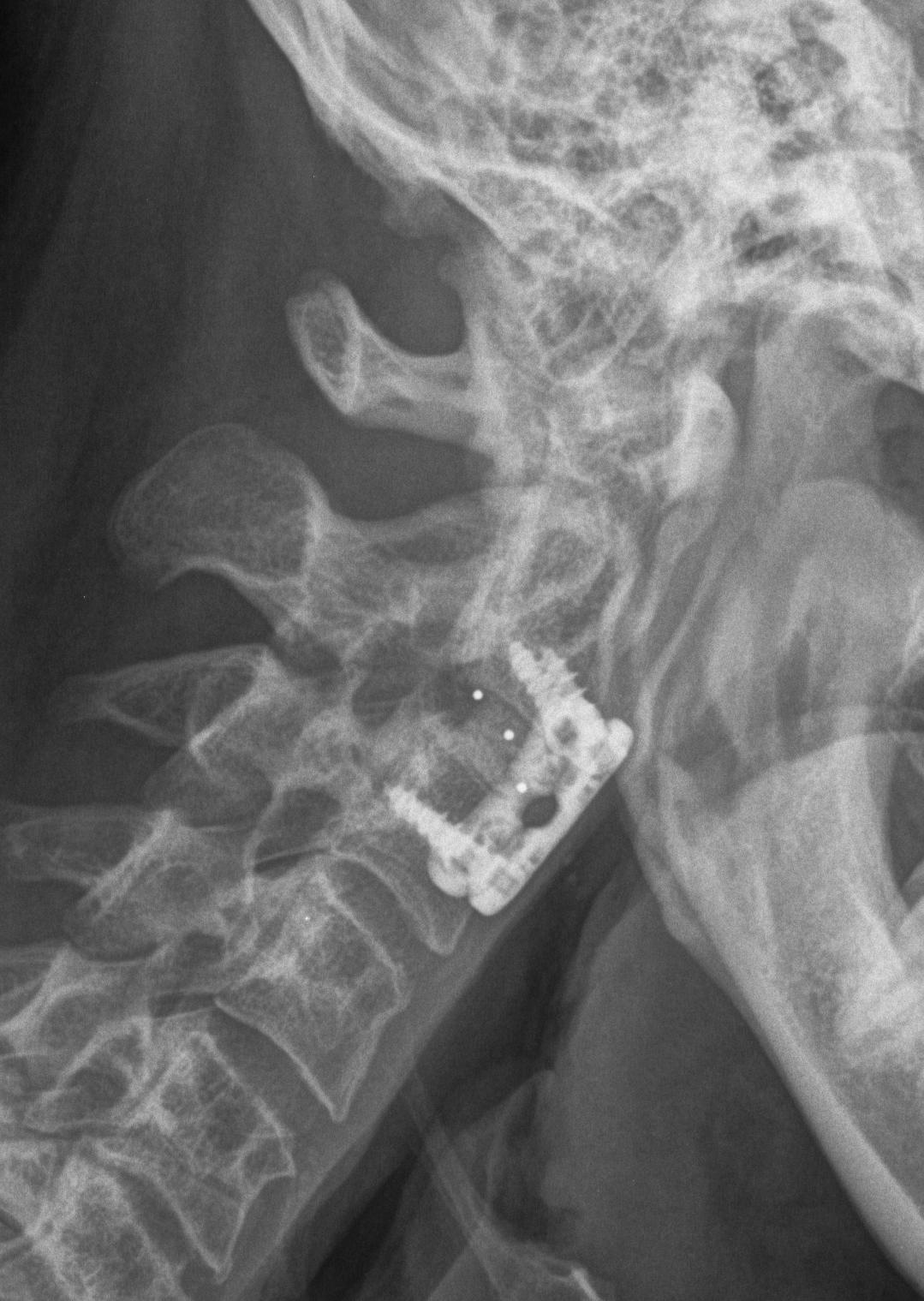
Technique
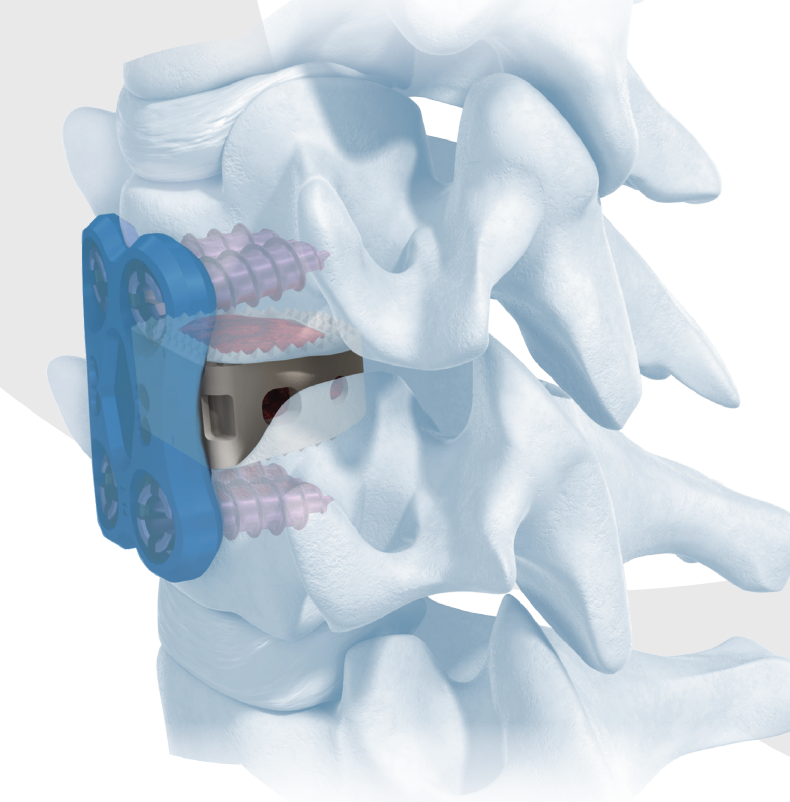
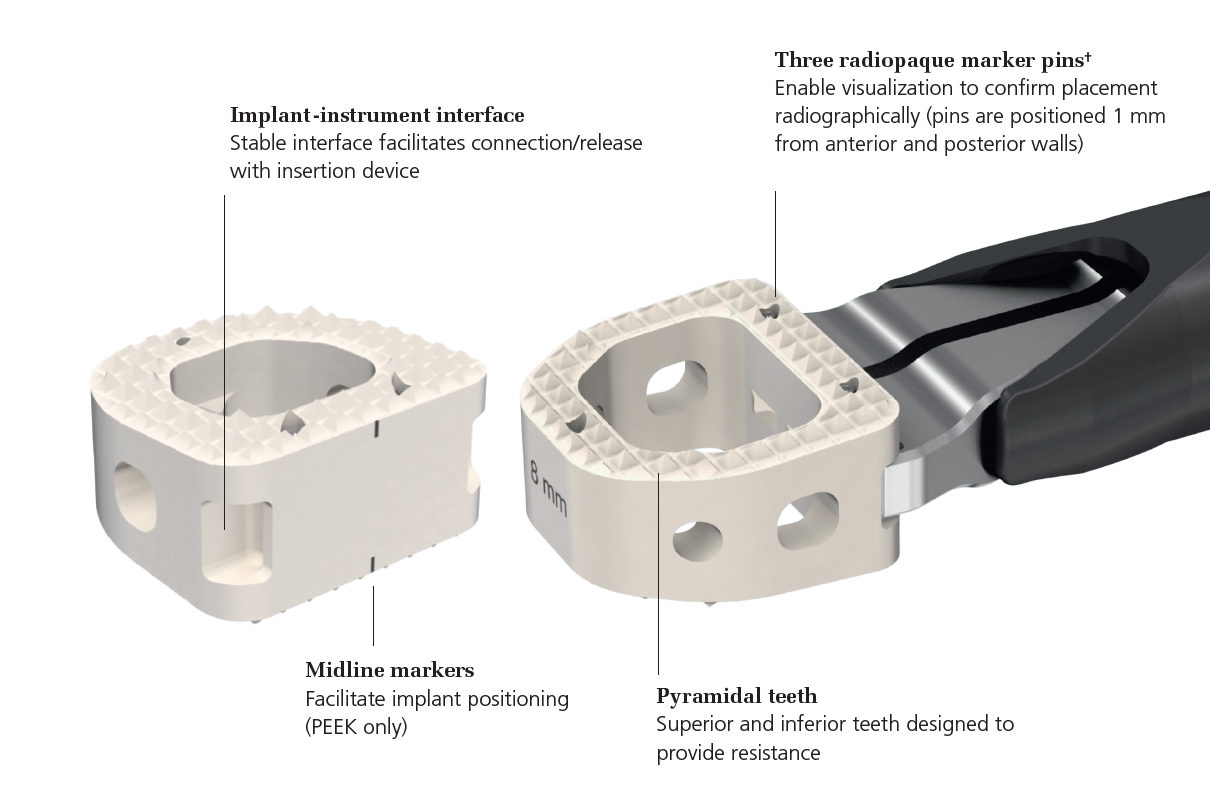
Depuy Synthes surgical technique article
Vumedi anterior discectomy technique
Anterior approach / Smith Robinson
- discectomy
- decorticate end plates
- interbody fusion with bone graft +/- interbody spacer
- anterior low profile plate
Complications
Risks of Smith Robinson / Anterior Cervical Approach
Specific
- pseudarthrosis 0 - 4.3%
- hardware failure
- insufficient decompression
- degeneration at second level
Disc replacement
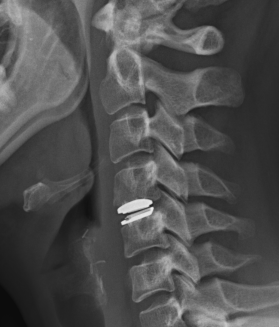
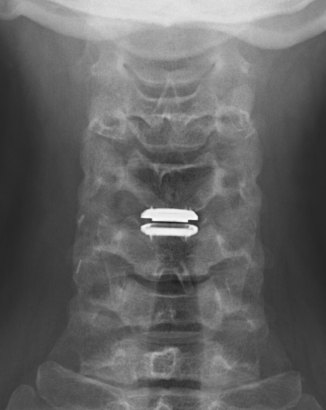
Advantage
Theoretically maintain some motion and preserve other disc segments
Contra-indications
Instability / Severe deformity / kyphosis - risk prosthesis displacement
Osteoporosis - risk of subsidence
Facet joint arthropathy - continued pain with disc motion
Technique
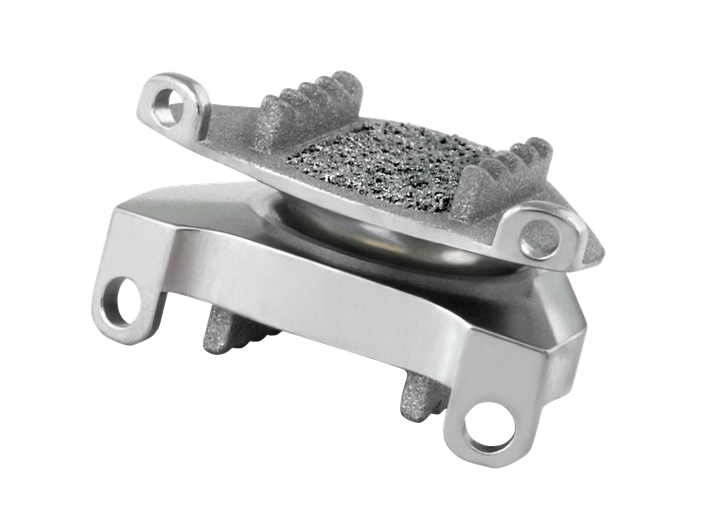


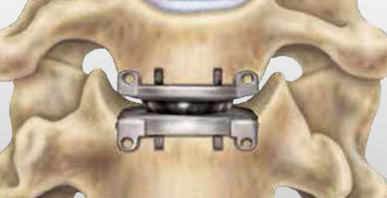
Depuy Discover Medtronic Prestige
Vumedi disc replacement technique
You tube prodisc C surgical technique animation
Complications
Risks of Smith Robinson / Anterior Cervical Approach
Specific
- anterior displacement
- posterior displacement and spinal cord injury
- subsidence 3% - higher risk if remove or disrupt end plates
- osteolysis
- implant failure
- heterotopic ossification
Posterior Instrumented Fusion
High complication rate
Leckie et al, Global Spine J 2016
- Database study of 1269 patients
- Adverse events 3 times more likely in posterior compared to anterior