Issues
Limb alignment
Risk that late posterolateral corner reconstruction will fail in the setting of the varus knee
- varus knee alignment and varus thrust in stance phase
- consider osteotomy first in this setting
Options
1. Posterolateral Corner Reconstruction
Moulton et al. Am J Sports Med 2016
- systematic review of posterolateral corner reconstruction for chronic injuries
- 450 patients
- 90% rate of objective stability, 10% failure
2. High tibial osteotomy
Arthur et al Am J Sports Med 2007
- opening wedge high tibial osteotomy for patients with varus knee and chronic posterolateral corner
- 21 patients
- 8/21 (38%) did not require subsequent reconstruction
- 4/6 with isolated posterolateral corner did not require subsequent reconstruction
- 10/14 with multiligament injuries did require subsequent reconstruction
Examination
LCL
- grade 3 laxity in extension
Dial test
- confirm PLC instability
- > 10 - 15o compared with other side
PCL / ACL
Xray
Stress radiographs useful
- Telos
- confirm PCL / LCL
Long leg views
- assess for varus malalignment
MRI
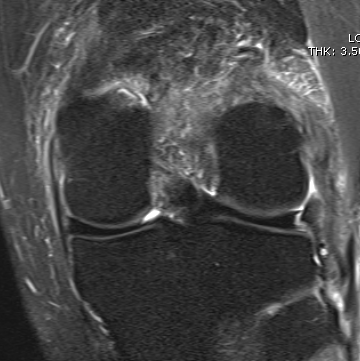
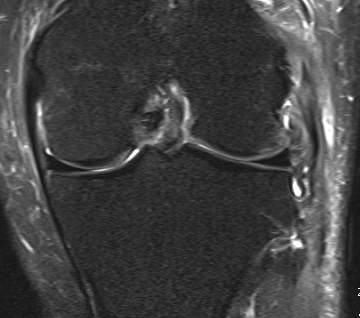
Chronic proximal avulsion LCL / Popliteus
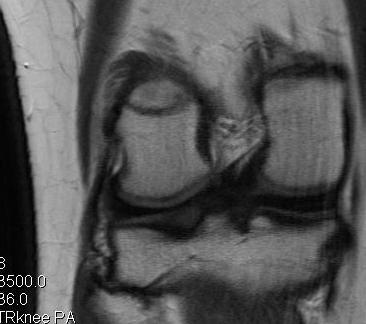
Chronic distal avulsion LCL
Limb alignment
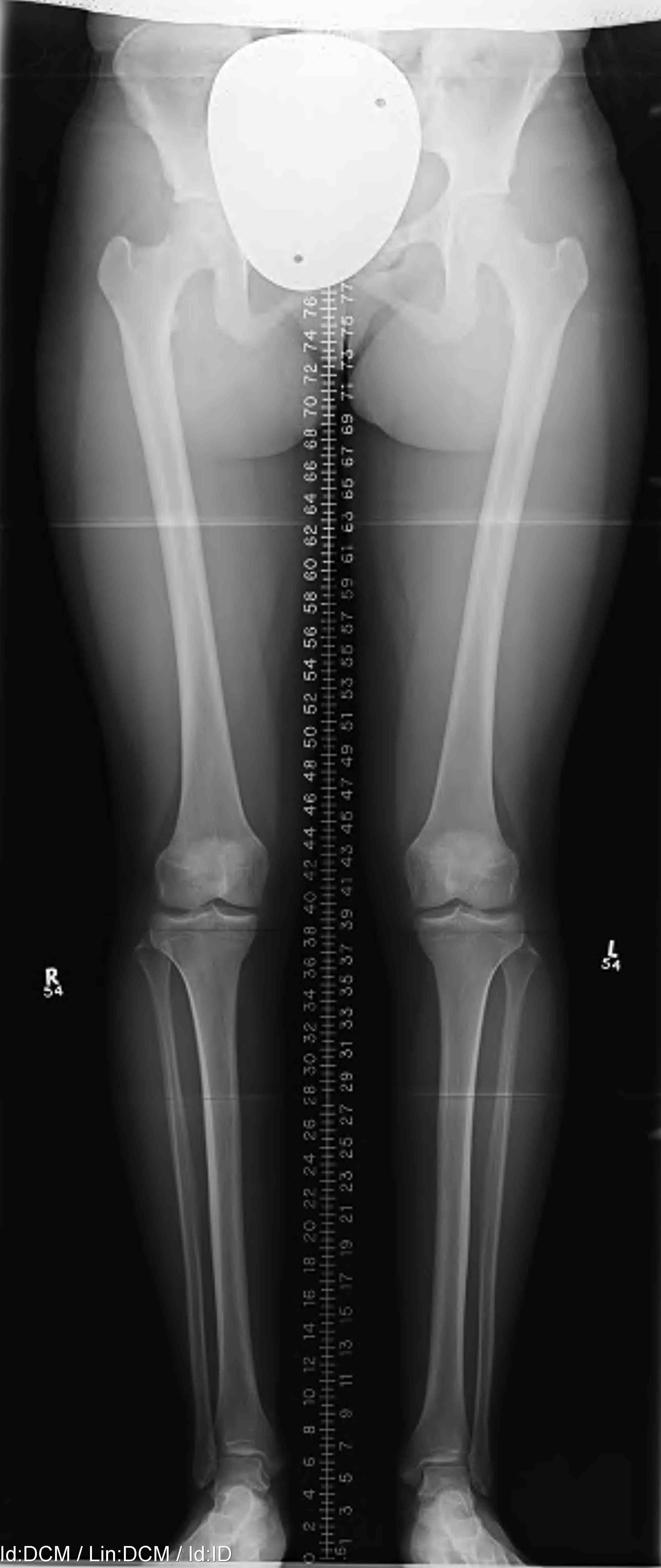
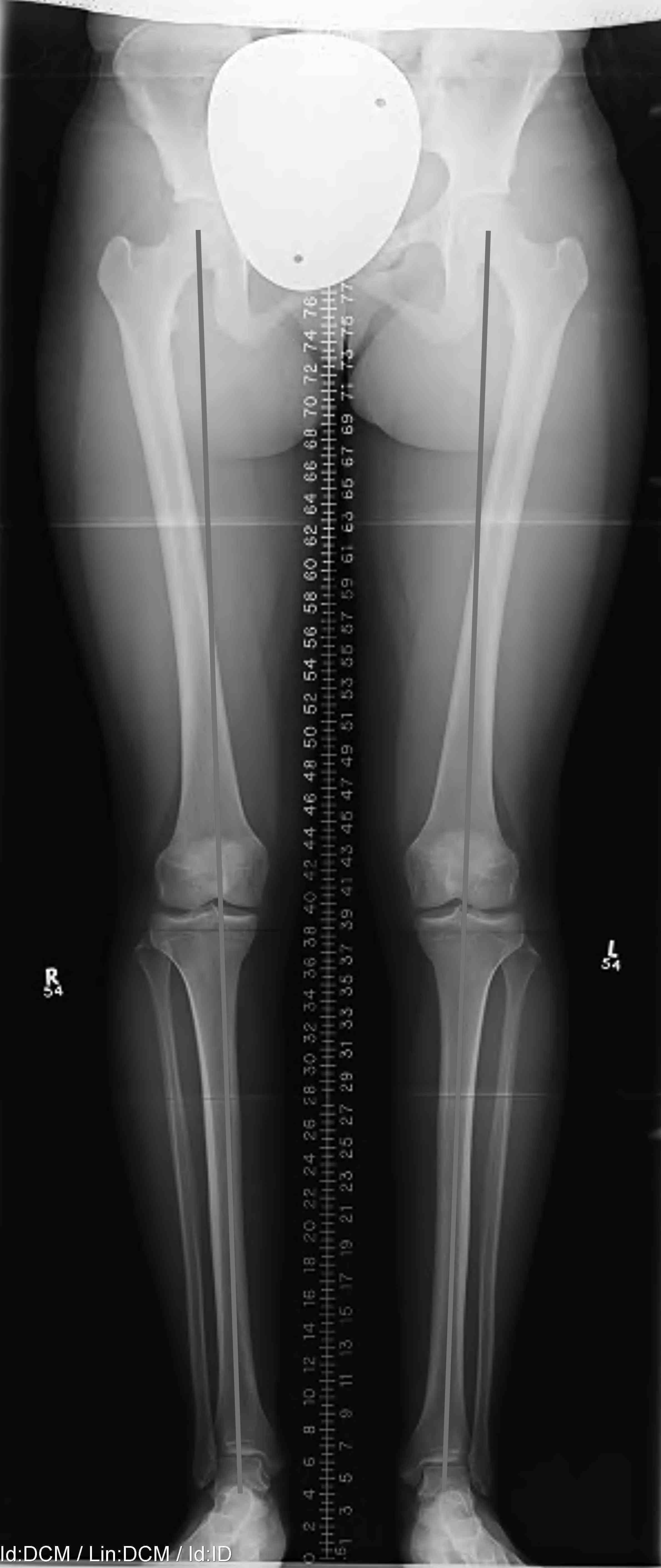
Mild varus of right knee
Definition Varus Malalignment
Mechanical axis passes medial to tip of medial tibial spine on long leg view
Surgical Technique - Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy
Advantages Opening wedge HTO
- avoids disruption of proximal tibio-fibular joint (for lateral PLC reconstruction)
- tighten the posterior capsule
- allows variation of the posterior slope (in setting of ACL / PCL)
Must be very careful not to overcorrect
- chronic posterolateral corner instability
- in a standing long leg view, the measured femoro-tibial angle is abnormally large
- the joint line is opened up laterally due to ligament insufficiency
- with correction, the joint line will close with standing
- the amount of valgus obtained will be more than that calculated at surgery
- one solution is to subtract the opening angle in the knee joint
- the other solution is to calculate the alignment of the other limb and calculate correction to normal valgus alignment
Technique
- medial opening wedge with plate and allograft bone
- correct so that mechanical axis passes through down slope of lateral tibial spine
- decrease posterior tibial slope with ACL deficiency
- increase posterior tibial slope with PCL deficiency
ACL + High tibial osteotomy for ACL + chronic posterolateral corner
ACL / Posterolateral corner / patient in varus
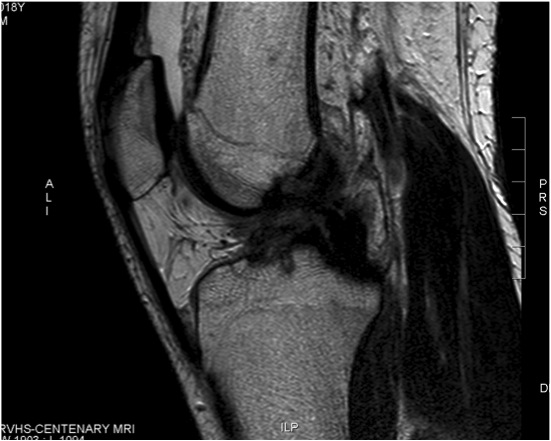
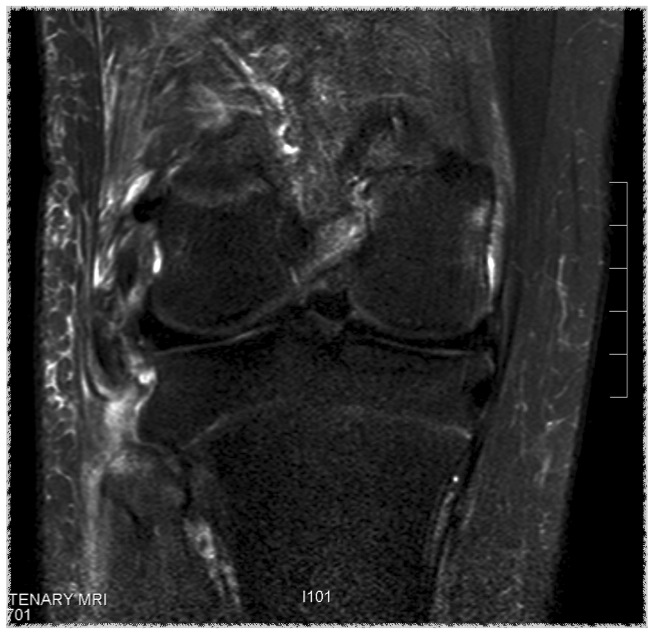
Sagittal MRI showing torn ACL Coronal MRI demonstrating chronic avulsion LCL fibula head
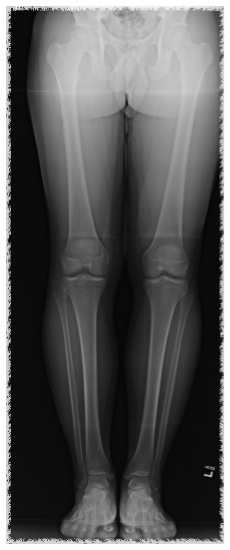
Varus malalignment left knee
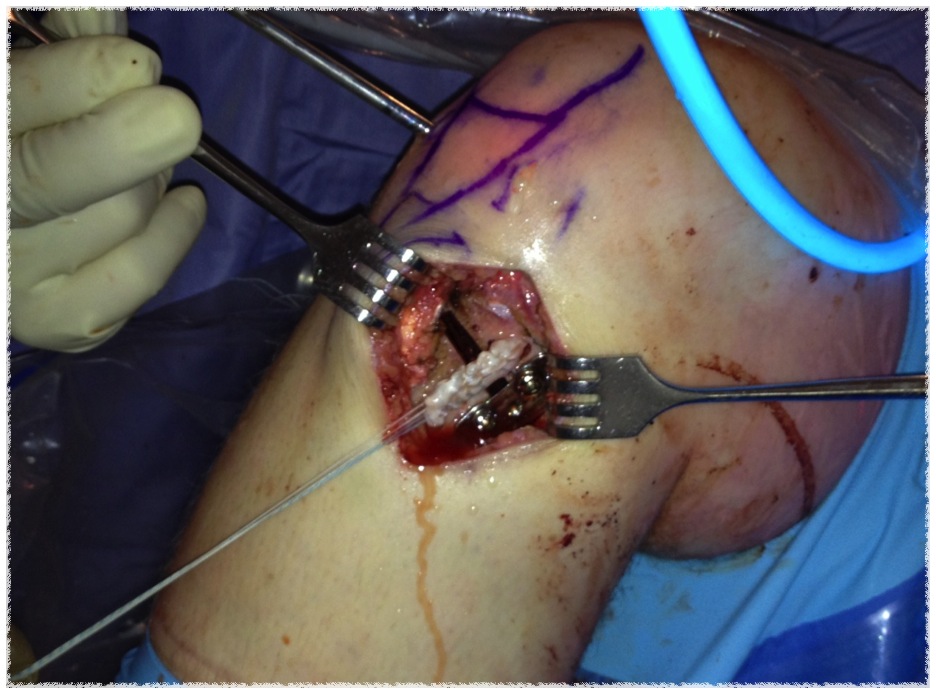
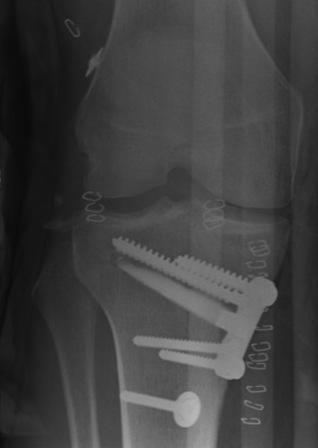
ACL + high tibial osteotomy
