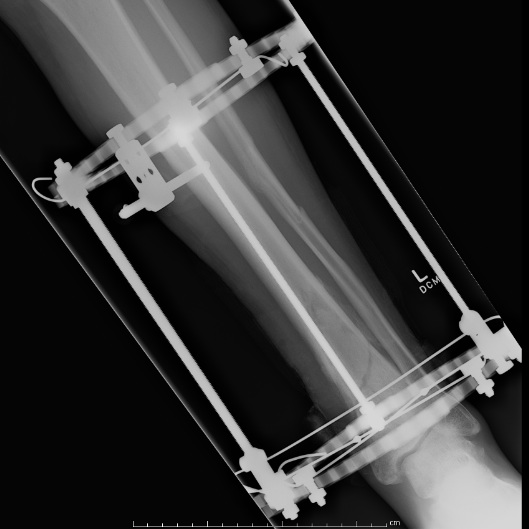
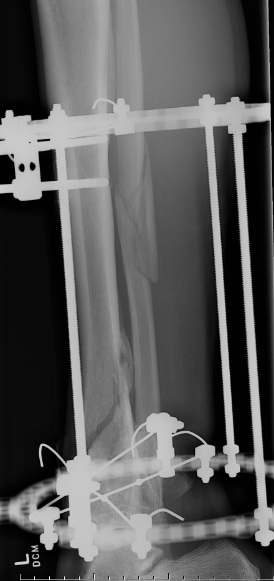
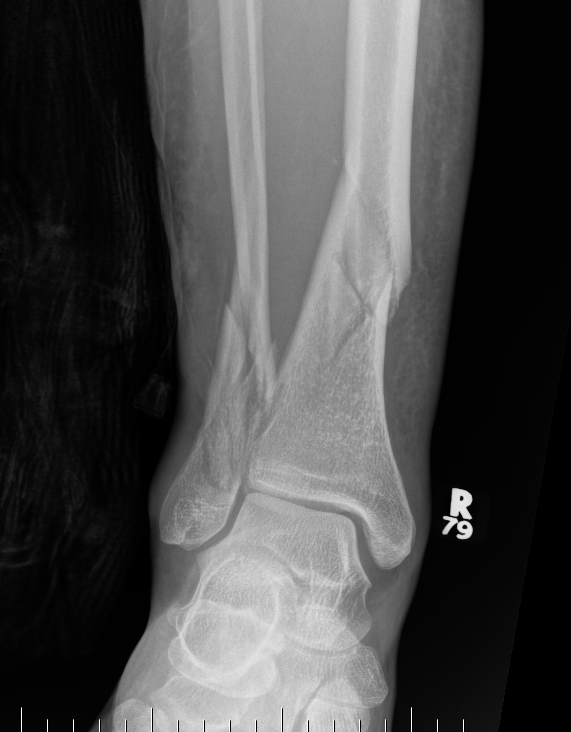
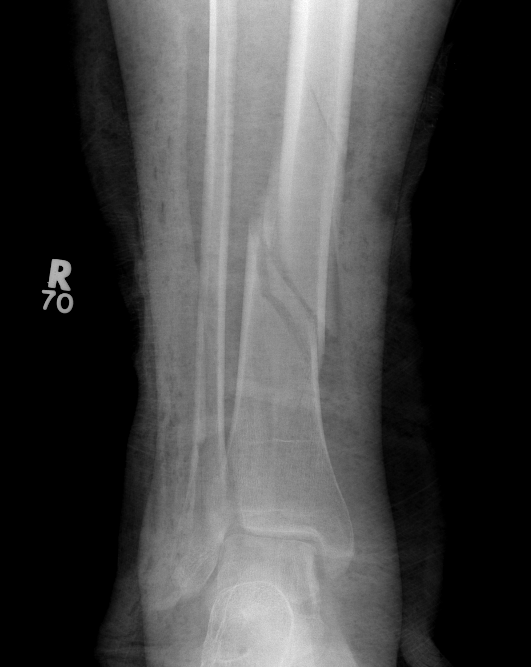
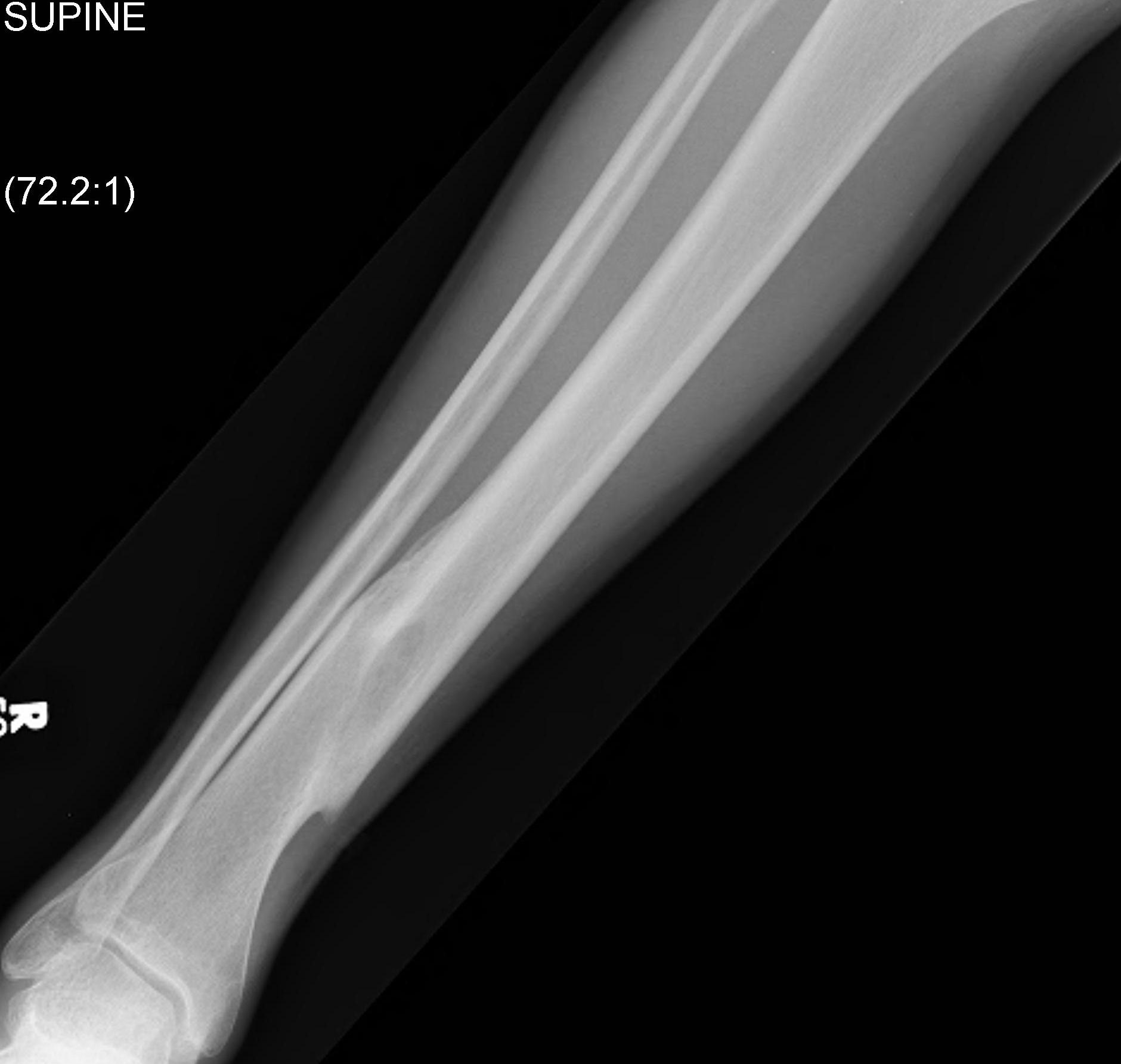
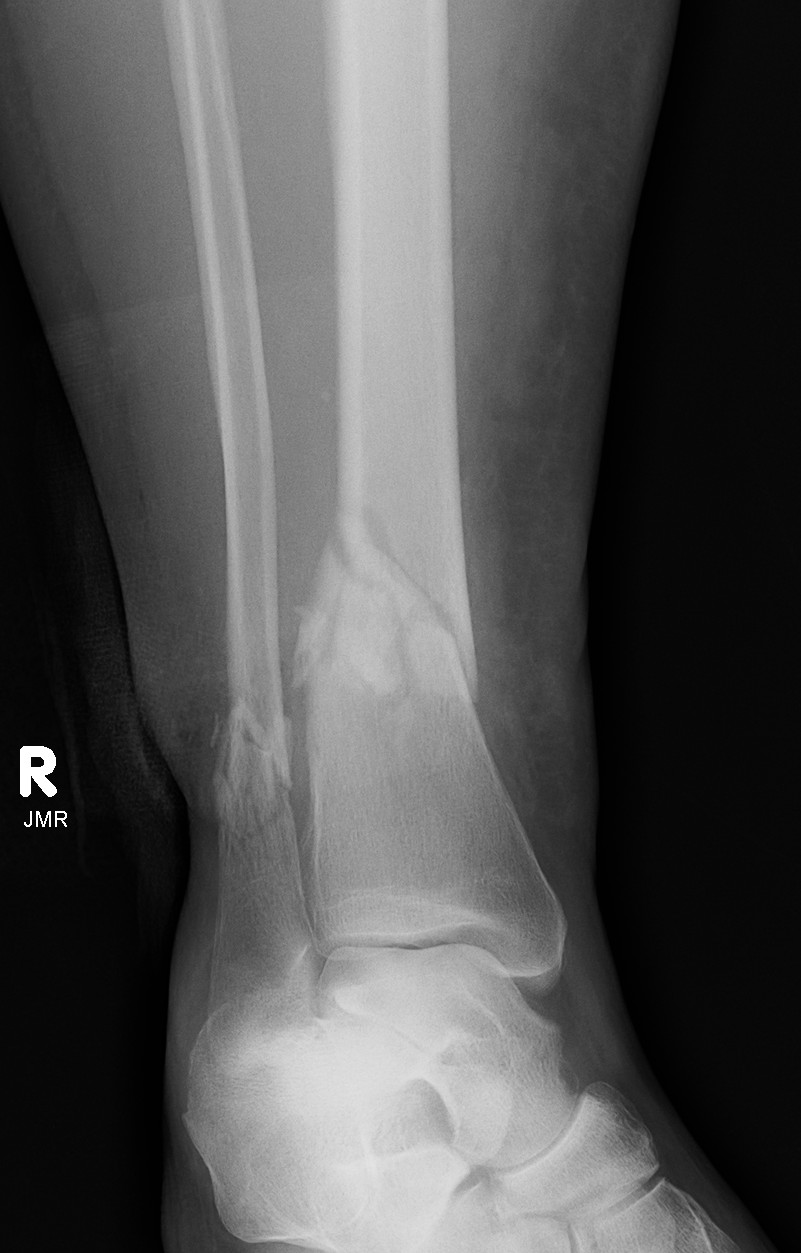
Distal Tibial Fractures
Definition
Metaphyseal
Extra-articular
Intra-articular Extension
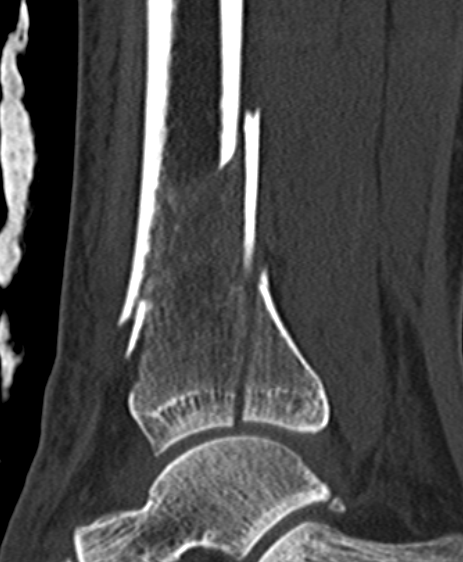
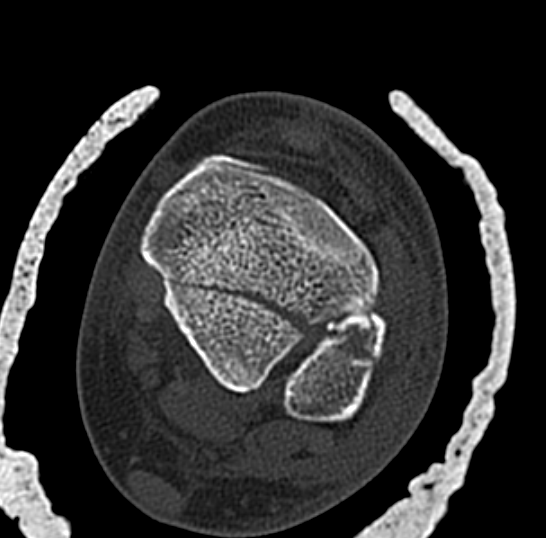
Posterior Malleolar Fractures
- occult in 70%
- especially with spiral distal tibial fractures
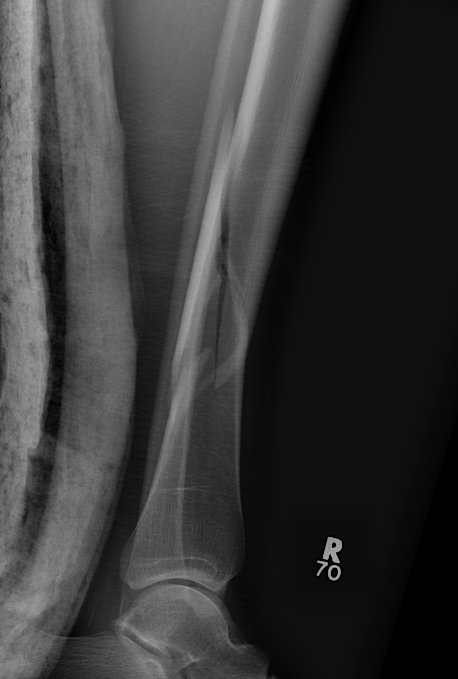
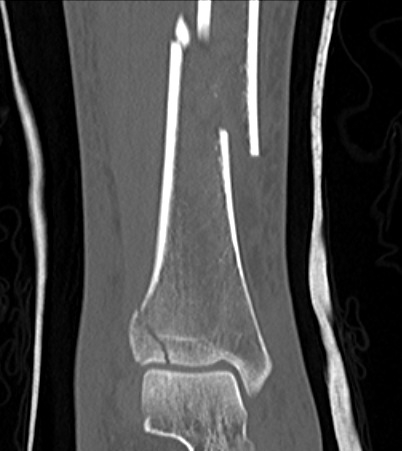
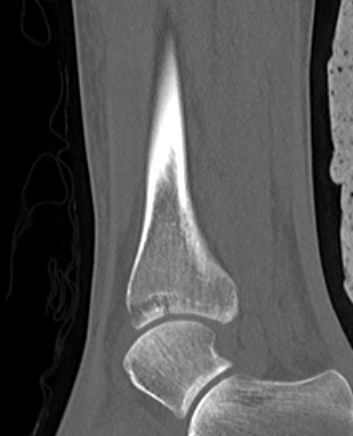
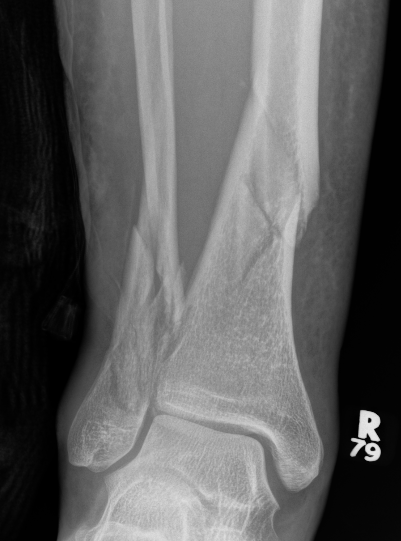
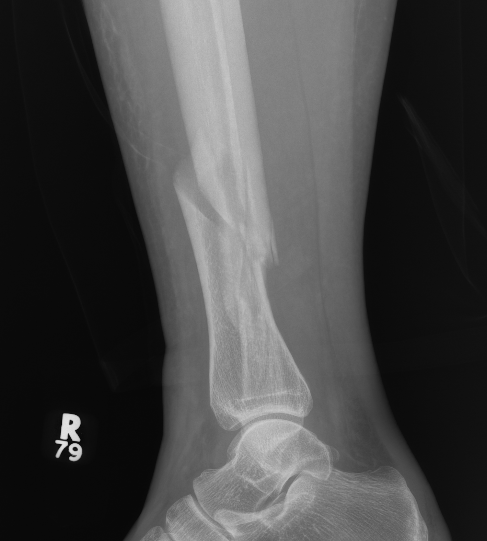
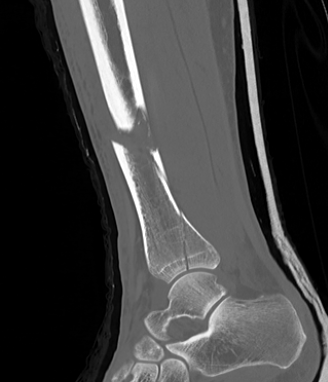
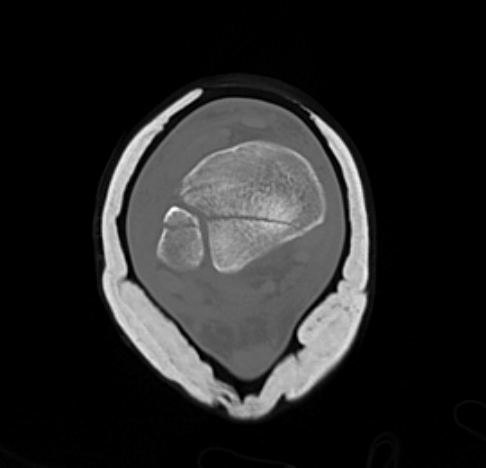
Wang et al. J Orthop Surg Res 2021
- systematic review
- incidence 70% occult fractures
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34074309/
Nonoperative Management
Operative Management
Options
1. Temporary external fixator
2. IM Nail
3. Plate
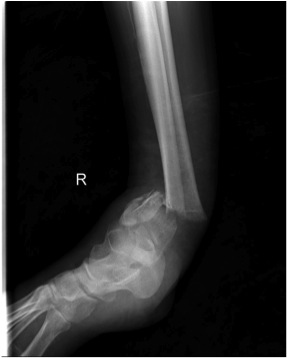
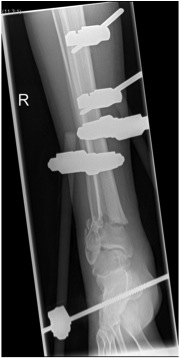
Temporary External fixation
Indications
- significant swelling
- significant displacement / non controlled in cast
- significant wounds, need for soft tissue coverage
Technique
- two pins proximal tibia
- trans-calcaneal pin
AO Trauma Ankle Bridging Delta Frame
Nail v Plate
Liu et al. Orthop Surg 2019
- meta-analysis of 10 RCTs, 911 patients
- no difference in nonunion, delayed union, or time to union
- reduced incidence of malunion with MIPO plate
- reduced wound problems with nail
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31823496/
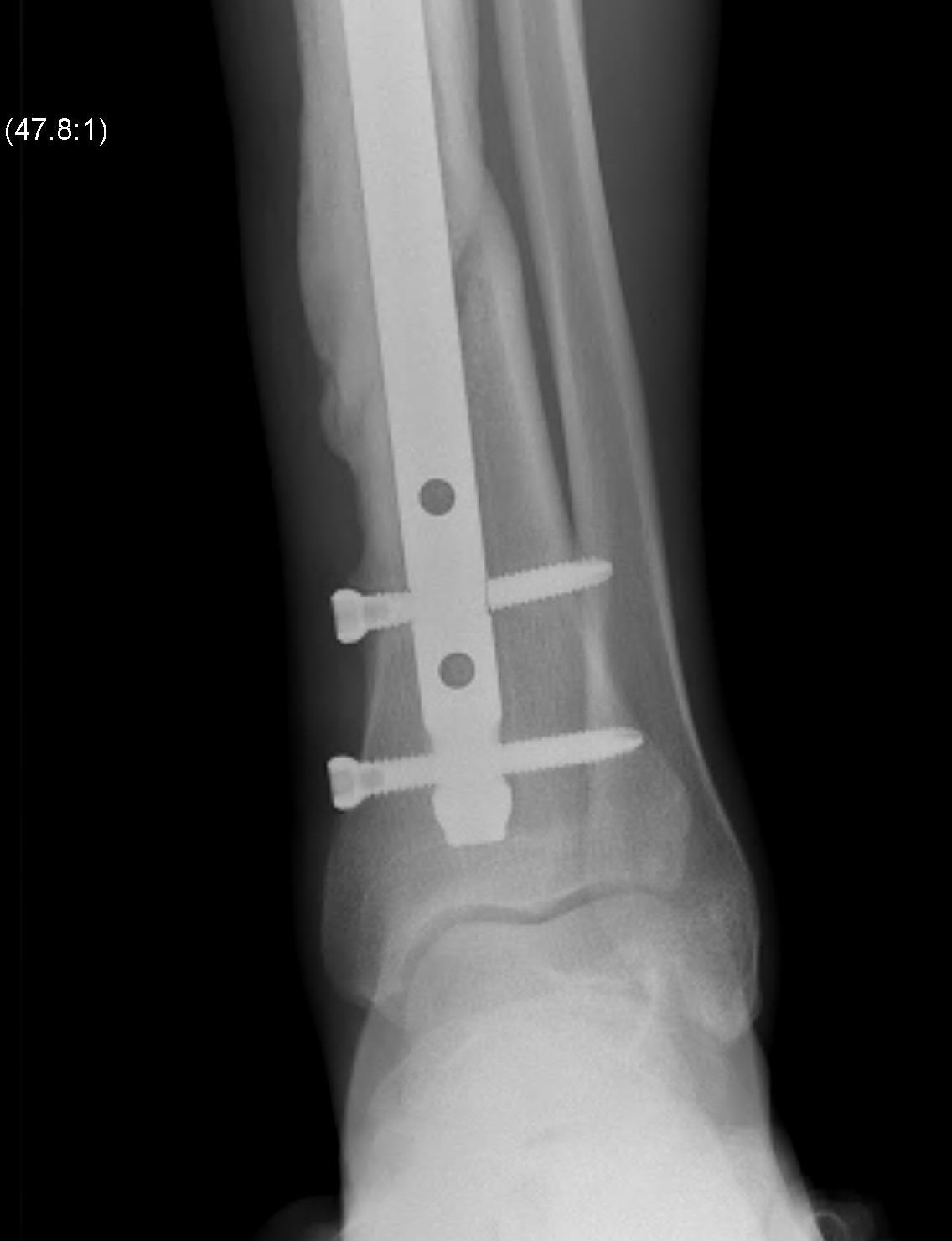
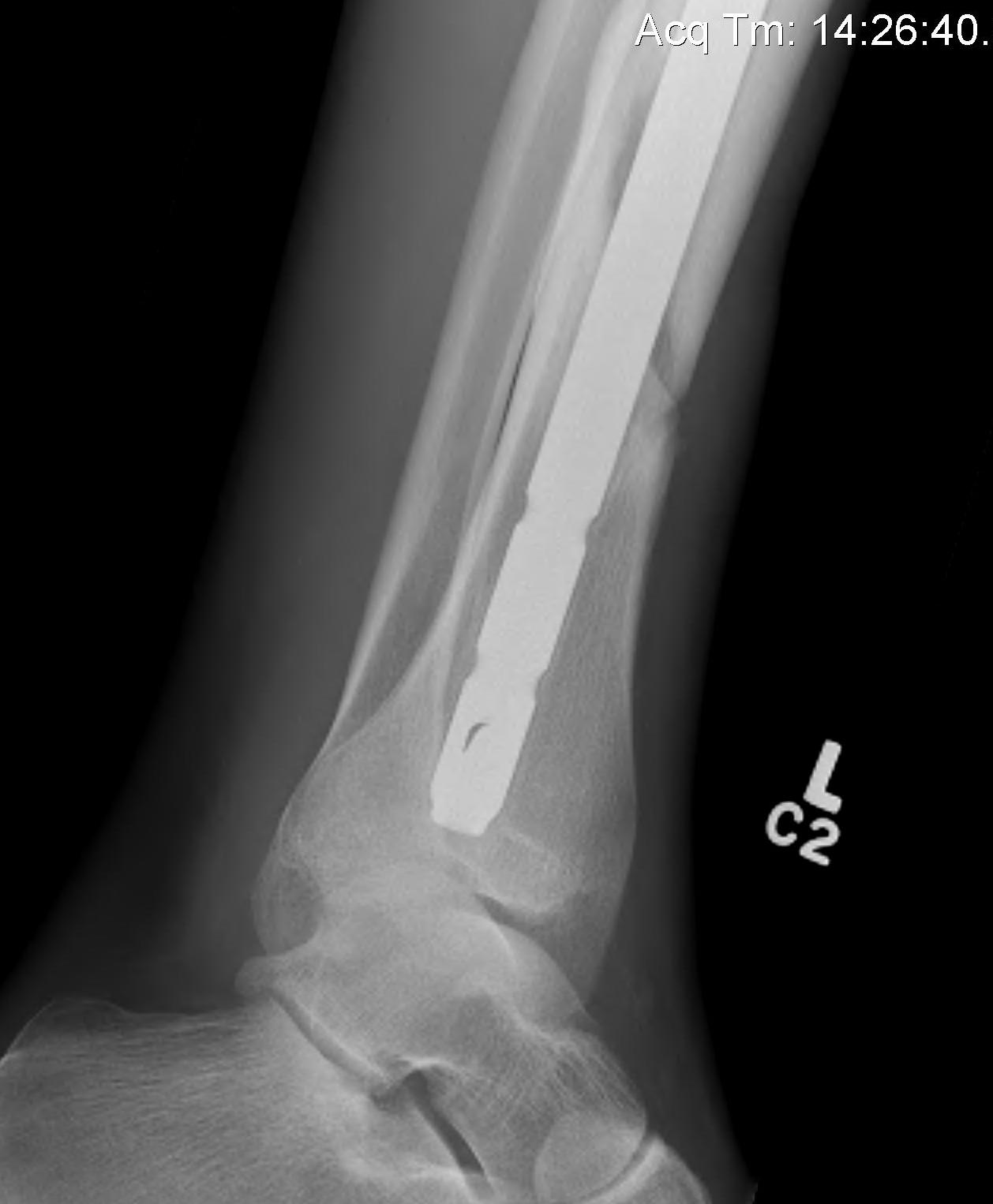
Intra-medullary Nail
Indications
- wounds / soft tissues not suitable to plate
- relatively stable
- sufficient distal bone
Design
Distal tibial nails
- multiple distal screws
- usually 2 medial-lateral and 1 AP
- most distal screw within 5 mm of end of nail
Smith & Nephew Tibal Meta Nail
Vumedi nail video
https://www.vumedi.com/video/distal-tibia-nailing-when-how/
Technique
Consider semi-extended suprapatella nail
- easier to reduce fracture
- easier to get AP and lateral fluoroscopy
Most important is to centre guide wire over talus
- in lateral and AP
- use finger reduction tools and pass across fracture site to exact centre in AP and lateral
- bone reduction forceps
- blocking screws
- universal external fixation
- plate fibula
Fibular fixation
Peng et al. J Foot Ankle Surg 2021
- tibial IMN +/- fibular fixation
- meta-analysis of 4 trials, 283 patients
- tibial malalignment of 67% (126 / 189) in non fibular fixation group
- tibial malalignment of 20% (19/94) in the fibular fixation group
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33218862/
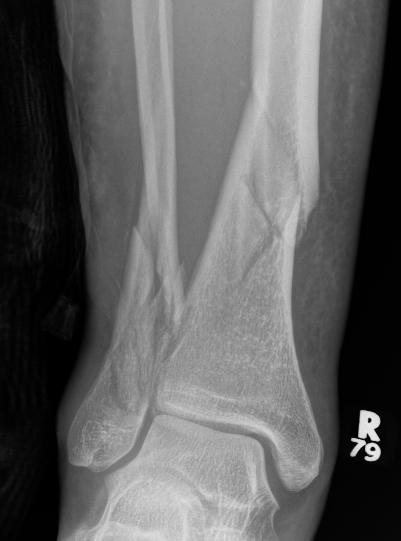
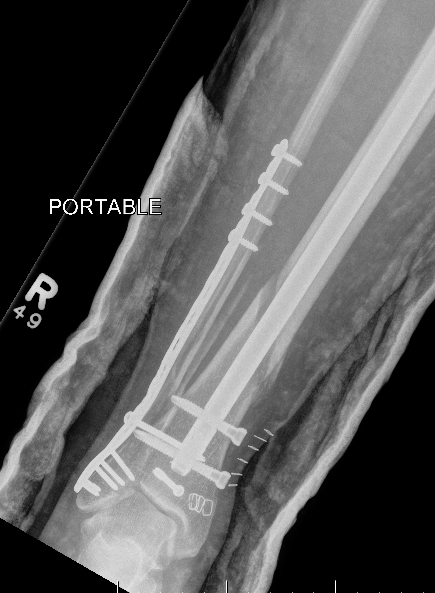
Posterior malleolar fixation
Typically stabilize intra-articular fracture first
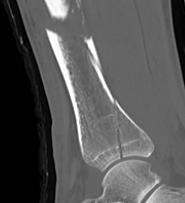
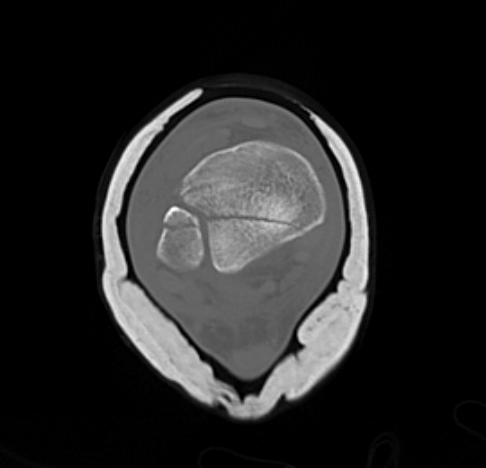
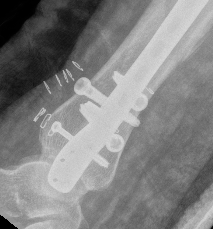
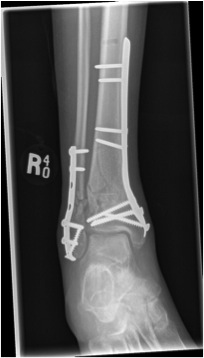
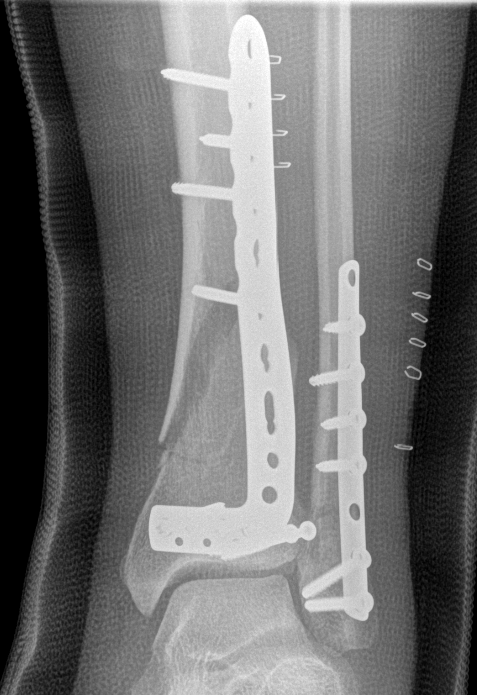
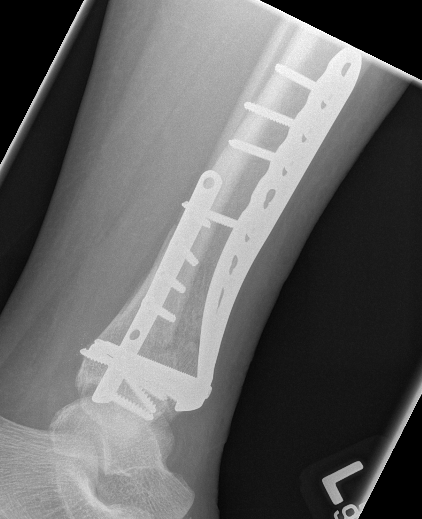
B. Distal Tibial ORIF with plate
Indications
- too distal to nail
- very comminuted / unstable
- intra-articular extension
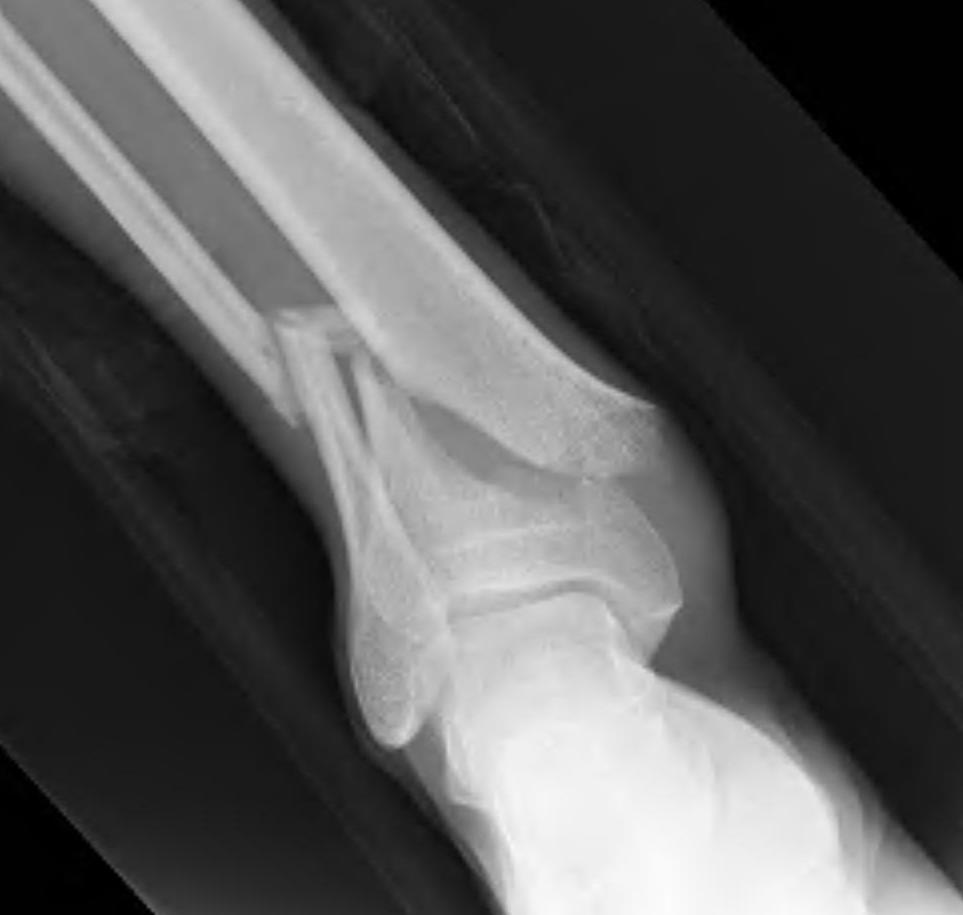
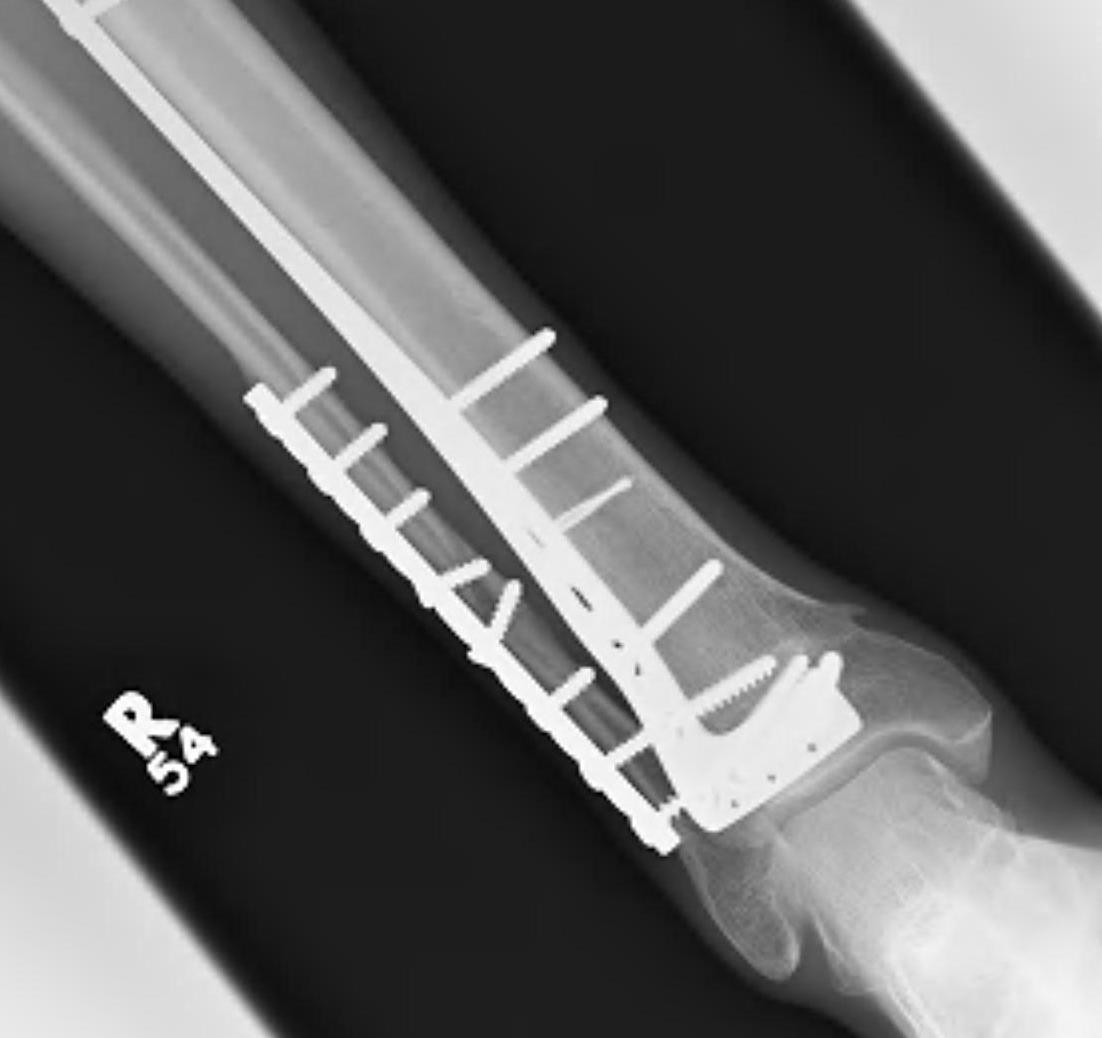
Technique
1. Consider fixing the fibula
- will aid reduction / avoid malunion
- help control very unstable fractures
2. Anatomically contoured plates
- options of medial plate v anterolateral plate
- medial plate for varus deformity
- anterolateral plate for valgus deformity
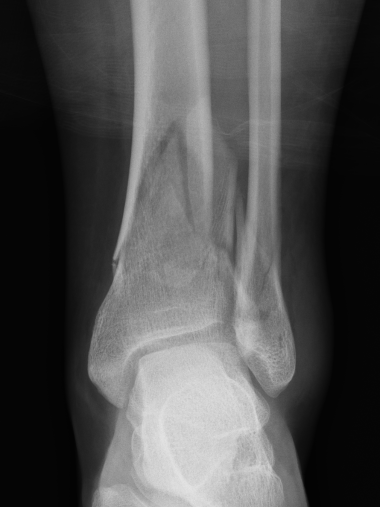
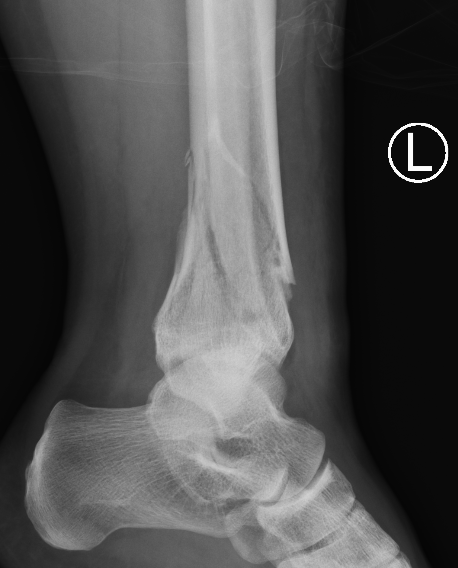
Complications
Barcak et al. J Orthop Trauma
- single surgeon, extra-articular fractures
- 43 IMN and 43 MIPO plate
- both groups similar
- nonunion rate 7 - 8%
- malalignment 3%
- wound complication 3%
- 26% of IMN required distal locking screws removed
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27101167/
Nonunion
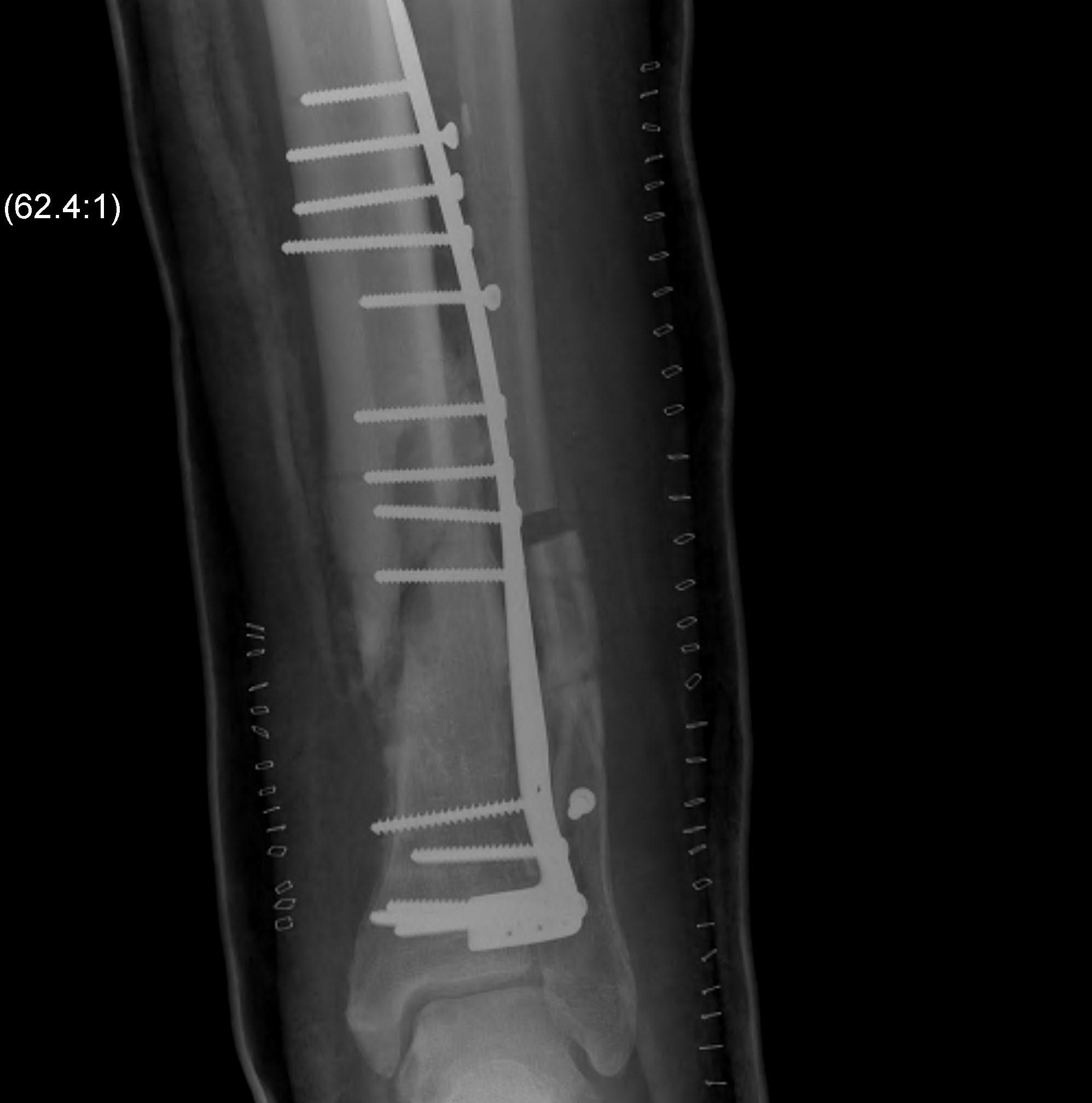
Plate and bone graft
Lin et al. Injury 2017
- 9 patients with distal tibia nonunion
- posteolateral approach to avoid poor anterior skin
- plate and iliac crest bone graft
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28342545/
External fixator
Schoenleber et al. Foot Ank Int 2015
- 8 patients treated with ilizarov / taylor spatial frame
- hypertrophic nonunions
- callous distraction - allowed correction of deformity and shortening
- all achieve union at 6 months
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25358806/
Malunion
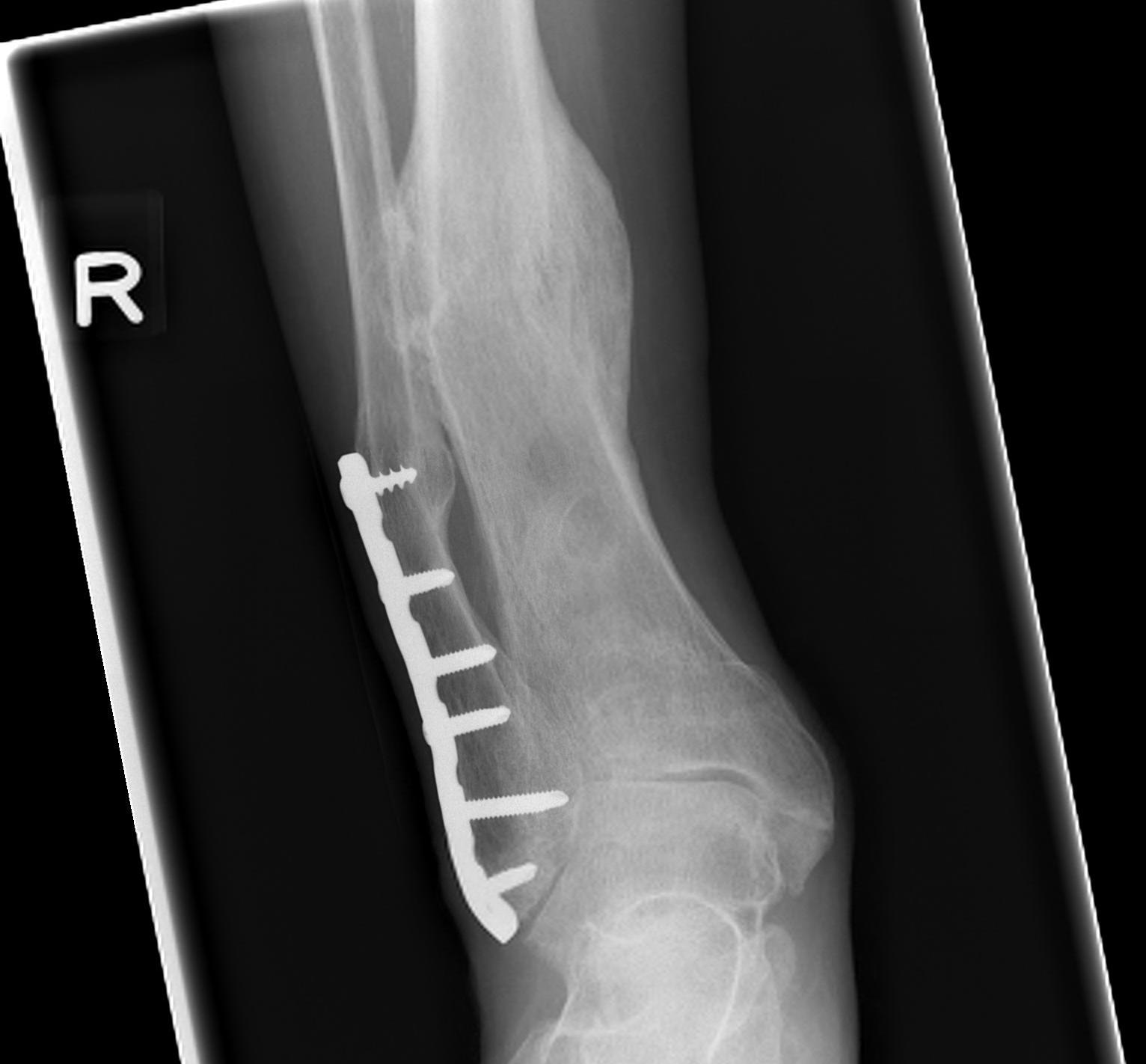
Infection
Persistent infected nonunion post distal tibial nail
- nail removed
- irrigation +++
- ilizarov frame with immediate weight bearing
- union obtained, infection eradicated