Steps
1. Establish a differential
2. Stage locally and systemically
3. Biopsy
4. Definitive Treatment
1. Establish a Differential
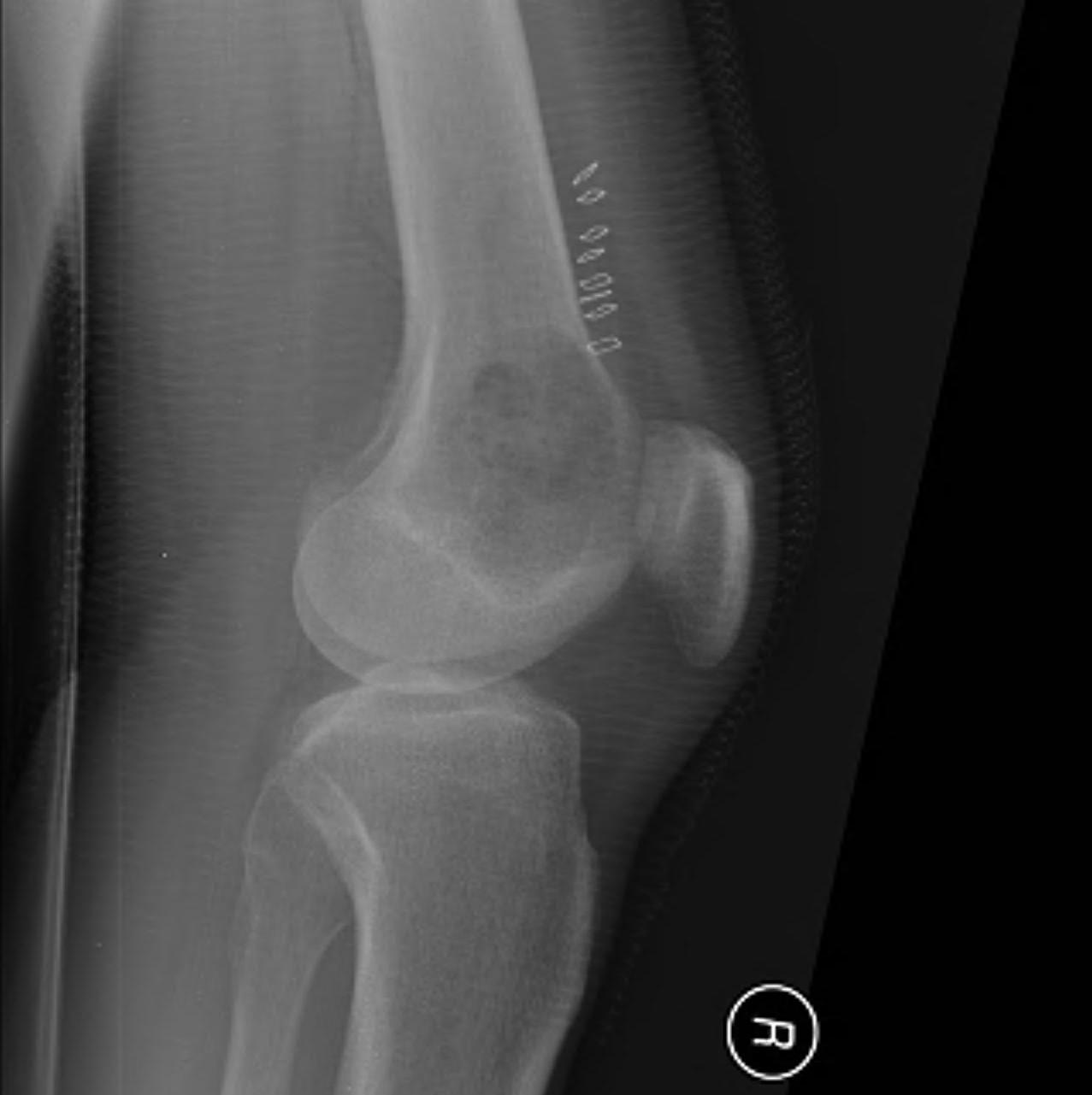
Lesion detected on X-ray
Questions
- what do you think it is?
- is it benign (latent, active, agressive)?
- is it malignant (primary or secondary)?
Enneking's four questions
1. Where is the tumour?
Flat bone / long bone
Epiphysis / metaphysis / diaphysis
Medullary canal / cortex
Eccentric in bone
2. What is it doing to the bone?
Cortical expansion
Cortical erosion / breakthrough
Fracture
Wide / narrow zone of transition / permeative margins
- narrow / can draw edge with a pen / good sign
- wide / infiltrative / bad sign
3. What is the bone doing to it?
Periosteal reaction
- Codman Triangle / Sunburst / Onion Skinning
Reactive rim
- Sclerotic = slow growing
- Ill defined = fast growing
4. Are there any clues to its histological diagnosis?
Bone formation / calcification
Soft tissue component
Radiolucent / ground glass
Matrix Osteoid / Chondroid / Myxoid / Collagen
DDx Lucent lesions
FOGMACHINES
Fibrous dysplasia
Osteoid Osteoma / Osteoblastoma / Osteosarcoma
Giant cell tumour
Metastasis / myeloma
ABC
Enchondroma / Chondroblastoma / Chondrosarcoma
Hemangioma / HPTH
Infection / Intraosseous ganglion or lipoma / Infarct
Non Ossifying Fibroma / Neurofibroma
EG
Simple bone cyst / Synovial Proliferation
History
Malignant pain - night time, severe, increasing
Trauma
Red flags - fever, night sweats, weight loss, anorexia
- 85% of osteosarcomas present with pain related to a "strain"
- only 21% of osteosarcoma present with night pain
Examination
Soft tissue mass = aggressive lesion
Pathology tests
Serum electrophoresis / urine Bence Jones (Multiple myeloma)
PSA - prostatic cancer (PSA < 10 suggests < 1% chance of metastatic prostate cancer)
ESR / CRP - non specific (increased in infection / Ewing's / multiple myeloma / lymphoma / metastasis)
ALP - increased in Osteosarcoma & Paget's
Calcium / PTH - think of hyperparathyroidism
Other Tests
Mammogram / Thyroid Ultrasound - metastasis
CT Chest / abdomen / pelvis - RCC, lung cancer, bowel cancer
Old X-rays
Consider observation if lesion unchanged from at least 2 years ago
2. Stage Locally and Systemically
Purpose
- accurately define the extent of the disease
- prior to proceeding with biopsy and definitive treatment
Local / Cross sectional imaging
CT
Best for assessing mineralisation & bony details
- benign bone tumours
- violation of cortex
- matrix mineralisation
- shows areas that plain xray visualises poorly i.e. spine / pelvis
MRI
Best for assessing soft tissue component
Assess
- cortical breakthrough
- soft tissue extension
- marrow involvement / intramedullary spread
- relationship to NV bundle
- joint & epiphyseal involvement
Distant
Bone scan
Determines if lesion polyostotic v monostotic
- this aids with differential diagnosis
- will identify metastasis
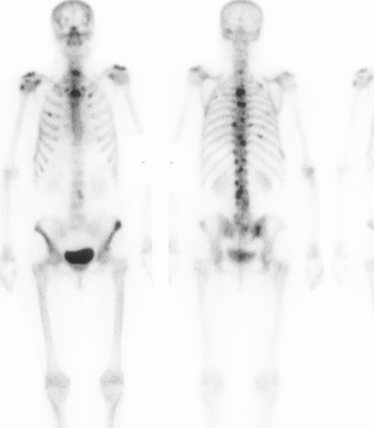
False negative / cold scan
- inactive benign tumours
- myeloma / EG / melanoma
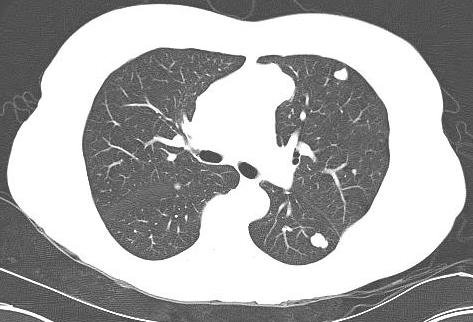
CT Chest / Abdo / Pelvis
Purpose
- identify primary lung cancer that may have metastasised to bone
- identify liver and lung metastasis
3. Biopsy
Aim
A. To determine whether benign or malignant
B. To determine specific cell type
C. To determine grade
4. Definitive Treatment
Sarcoma requires referral to specialist service
