Aim
Tumour removal to gain local control and minimize recurrence while maintaining functional limb
Margins
1. Intralesional
Within lesion
- macroscopic tumour remains
2. Marginal
Within reactive zone
- microscopic tumour remains
3. Wide
Intra-compartmental and outside of reactive zone
- remove tumour and cuff of normal tissue
4. Radical
Extra-compartmental
- removal of all compartments that contain tumour
- at least two compartments
- limb salvage possible with radical resection
- however, amputation may be only practical method
Limb Salvage
Principles
Must have same survival rates
Must not delay adjuvant treatment
Reconstruction should be enduring with minimal complications
Function should approach that achieved by amputation
Absolute and Relative Contraindications
PIN LEG
- Pathological fracture
- Infection
- NV bundle involvement
- LLD > 8 cm
- Extensive muscle loss
- Good v poor biopsy
Absolute
1. Can't obtain wide margins
2. Major NV bundle involvement
3. Infection
Relative
1. Pathological fracture
- hematoma spreads tumour beyond accurately defined limits
- may necessitate amputation
2. Inappropriate previous biopsy
- contamination of other compartment
3. Significant skeletal immaturity
- predicted LLD > 8cm
- adjustable / growing joint replacements available
4. Extensive muscle involvement
- resection leaves leg non functional
5. Medically unfit
Technique principles
Radical or wide resection
- extra-articular resection is preferred if a tumour is adjacent to or involves a joint
- prophylactic antibiotics
- no tourniquet if possible
- biopsy site excised
- tumour and/or pseudocapsule not visualised during procedure.
- distant flaps should not be developed until the tumour has been removed
- all dead space should be eliminated and hematoma formation should be prevented
- surgical wound marked with clips for later radiotherapy
- regional muscle transfer
- adequate soft tissue coverage
Reconstruction Options
Modular Endoprosthesis
Allograft reconstruction
Autograft reconstruction
Modular Endoprosthesis
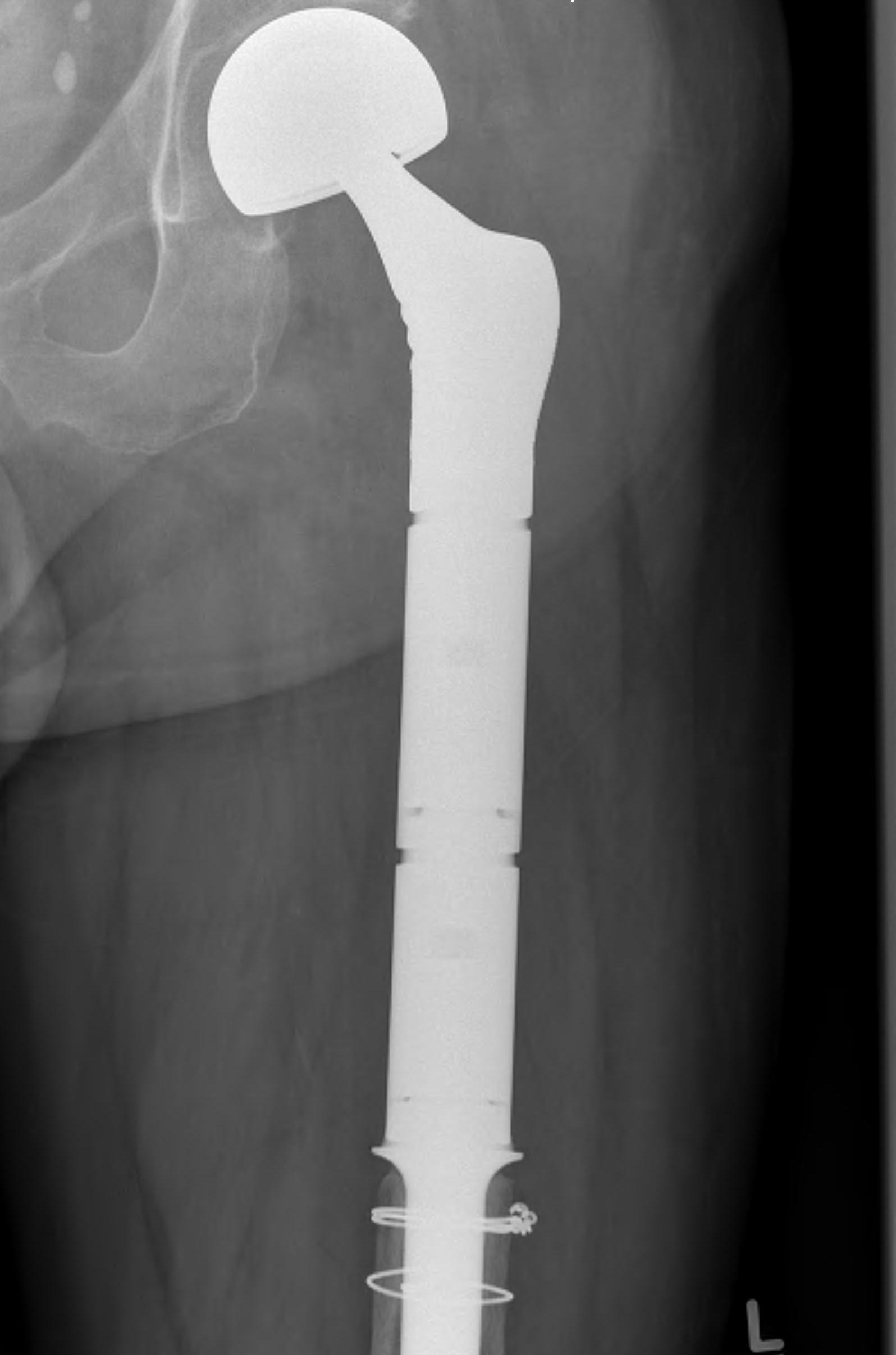
Advantage
Early weight bear and rehabilitation
No risk of non union like allograft
Massive Allograft
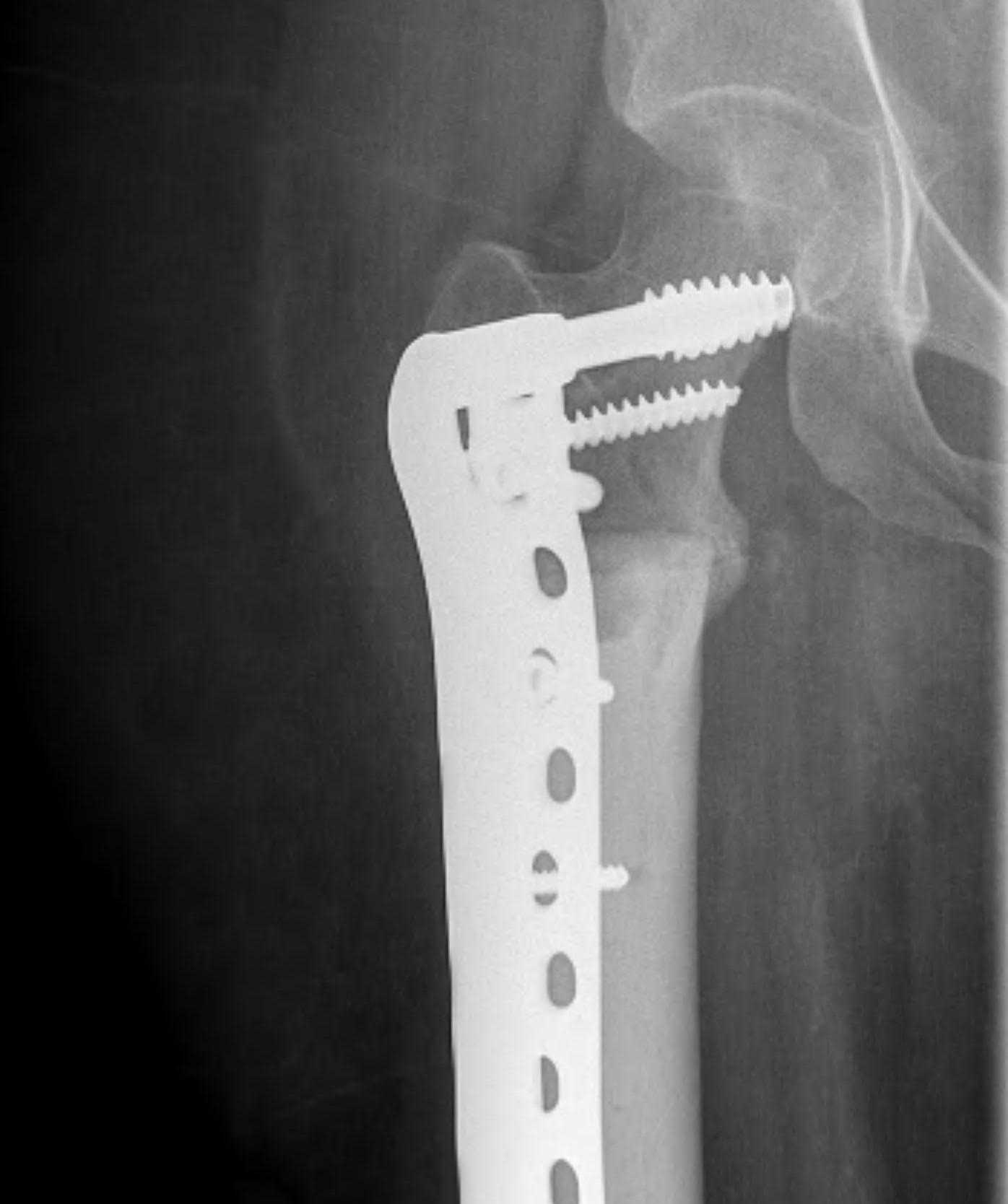
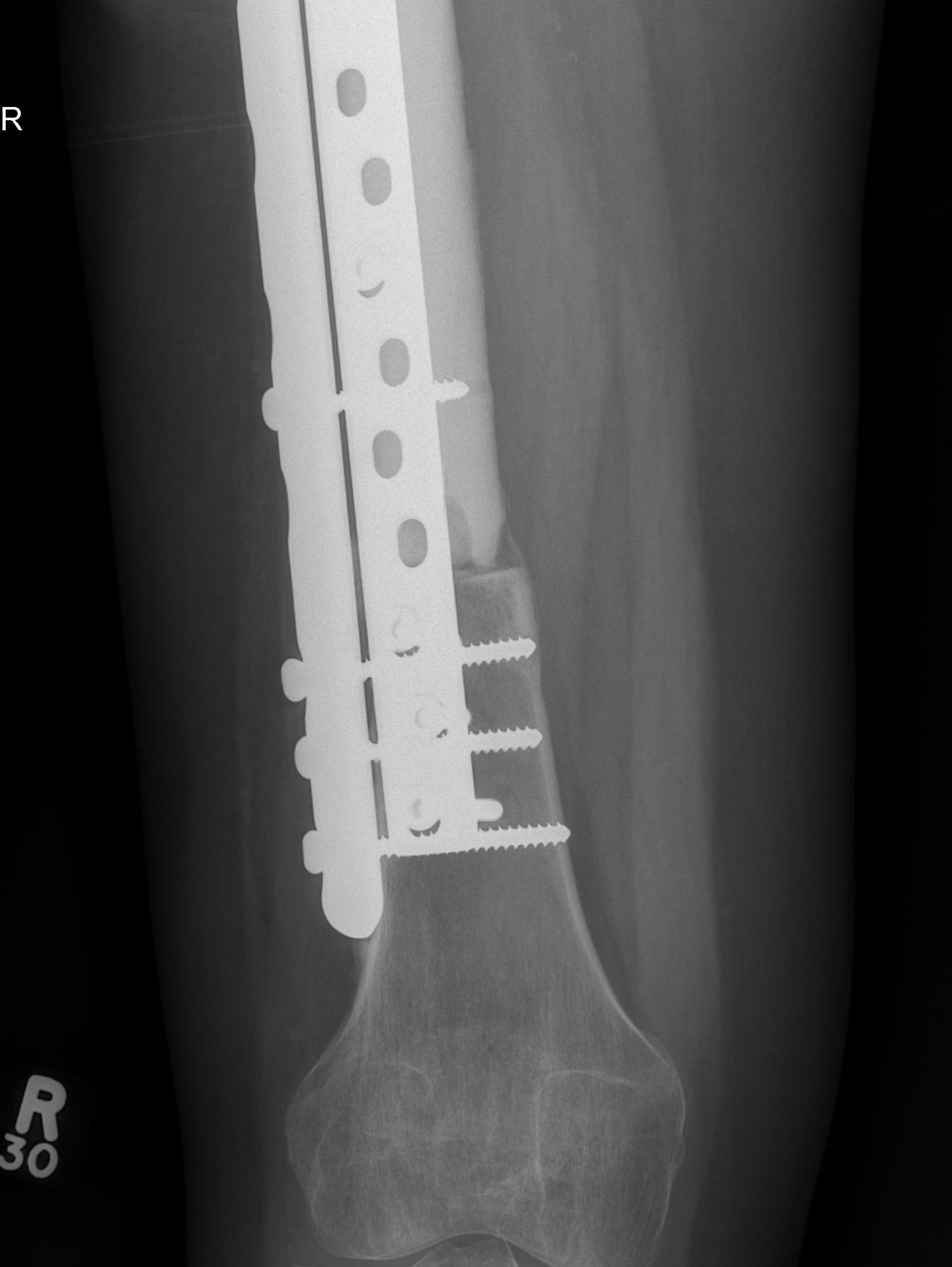
Advantage
- biological reconstruction
- intercalary
- osteochondral
Disadvantage
- incorporation is a slow and incomplete process
- risk of nonunion / fracture
Autograft / Vascularised fibula graft
Advantage over allografts
- more rapid incorporation
- stronger initial construct secondary to graft hypertrophy
Disadvantage
- increased surgical time
- surgical site morbidity
- size limitations
- stress fractures
Outcomes
Rosenberg et al, Ann Surg 1982
- Landmark article
- 43 sarcomas randomised to amputation vs salvage
- Salvage had more recurrence, but 5y disease-free and overall survival the same
