Definition
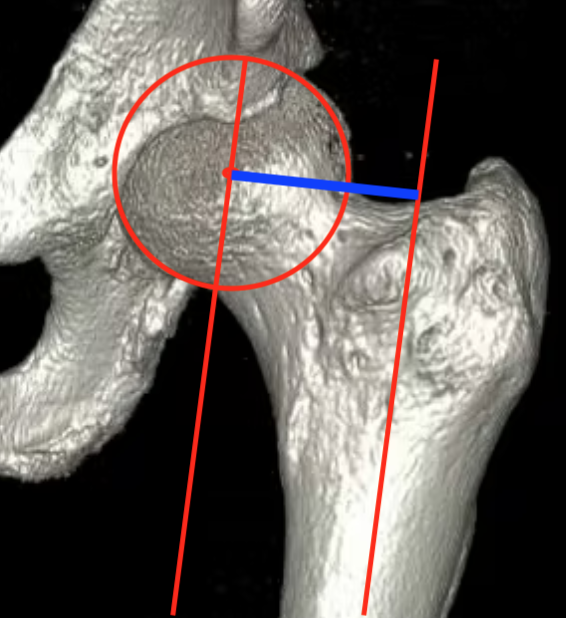
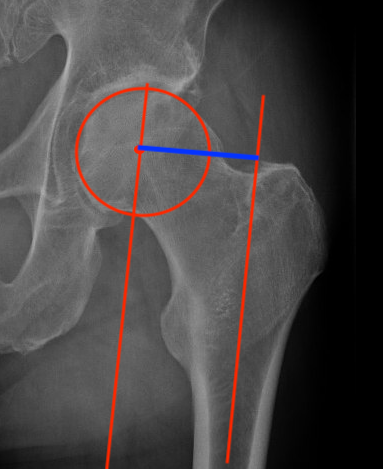
Femoral offset
- perpendicular distance
- from the centre of the femoral head
- to the long axis of the femur
Rubin et al J Arthroplasty 2019
- CT of 628 French patients (226 asian, 406 caucasian)
- males: 44.3mm; females: 40.6mm
- caucasian: 43.1mm; asian: 42.4mm
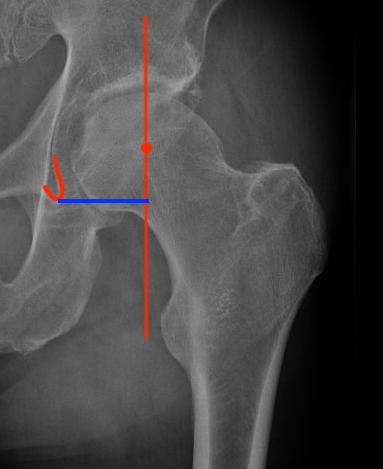
Acetabular offset
- perpendicular distance
- from the center of rotation of the femoral head
- to the vertical trans-teardrop line
Effect of short offset
Abductor weakness / Trendelenburg gait
Impingement
Lax soft tissues increase risk of instability / dislocation
Effect of increased offset
Theoretical increase in torque forces on stem and cement
? perception increased leg length
? abductor tendonitis
Factors affecting offset
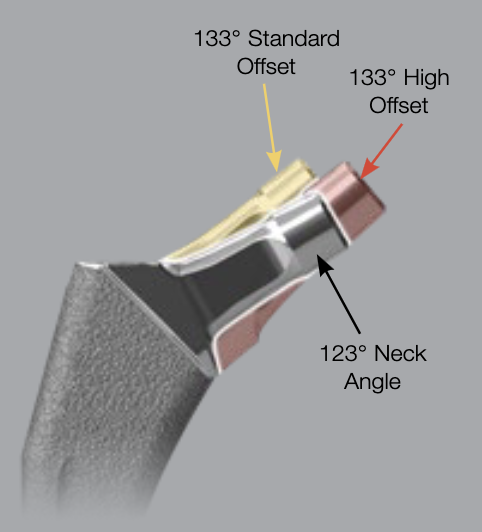
Zimmer Taperloc offset options
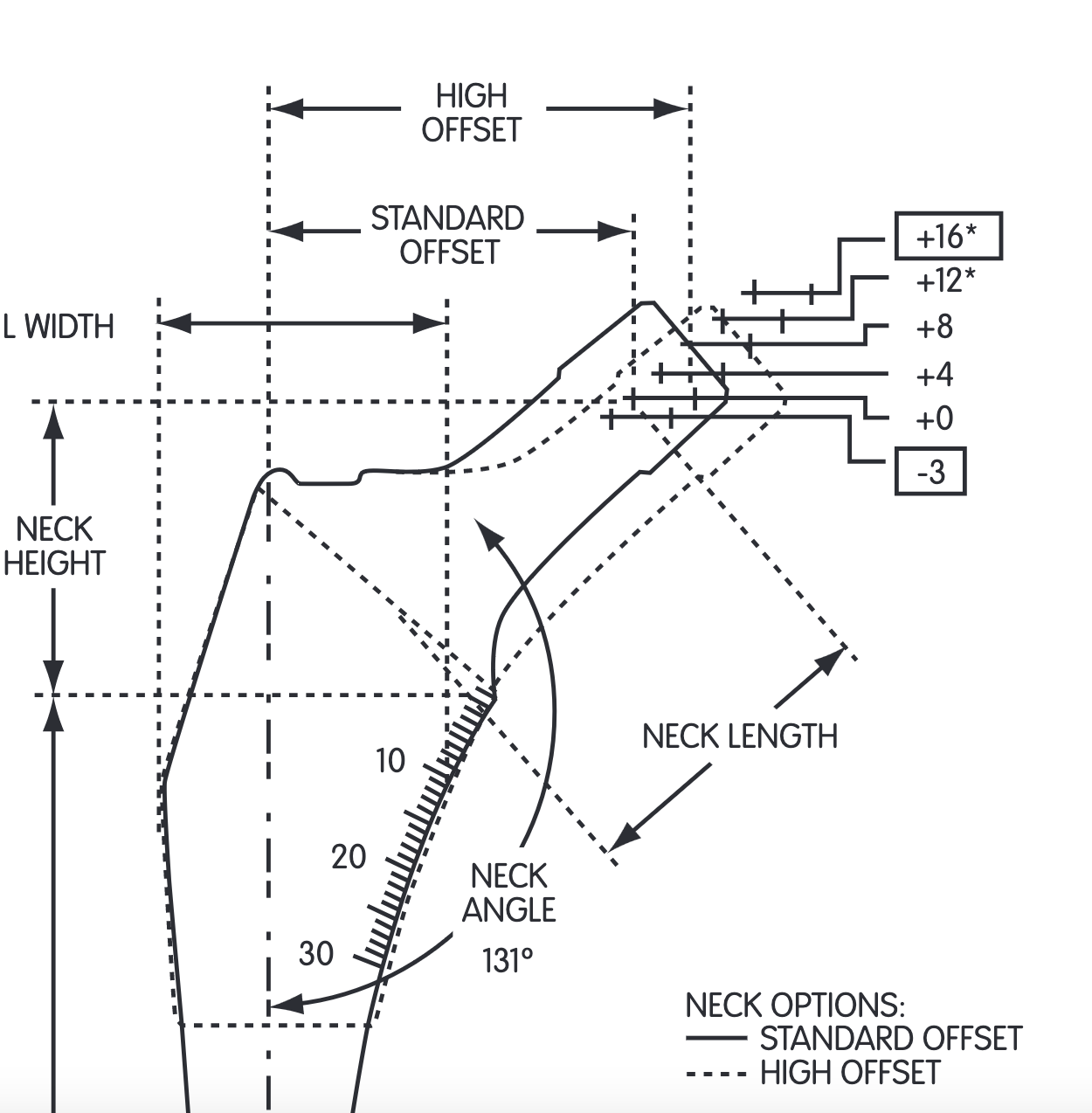
Neck shaft angle
Head neck length
Anteversion
Femoral osteotomy level
Position of acetabulum
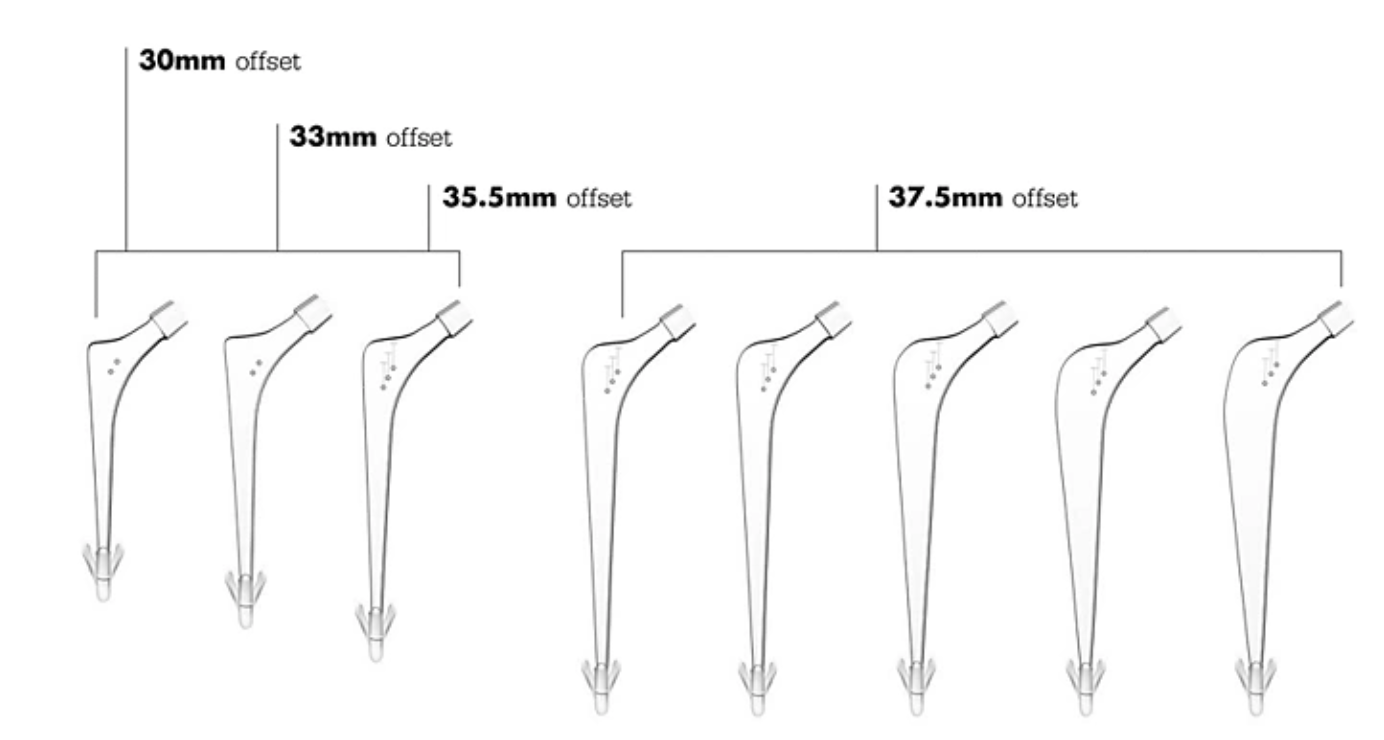
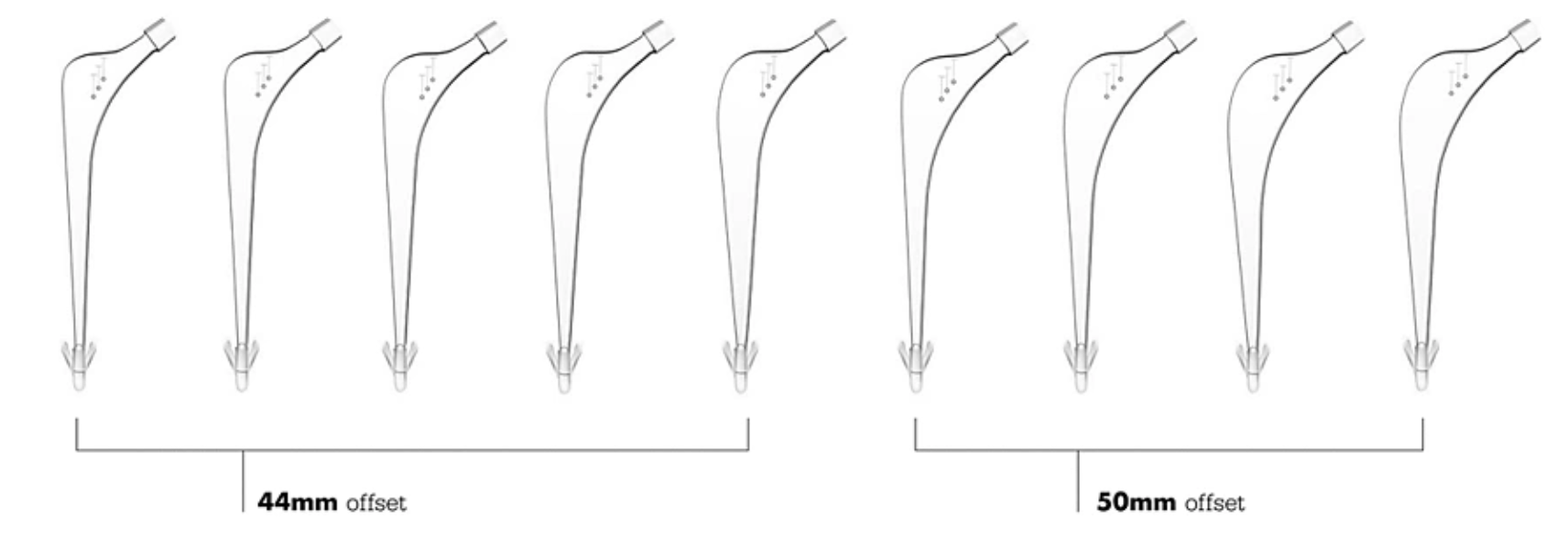
Stryker Exeter offset options
Mechanisms of altering offset in THA
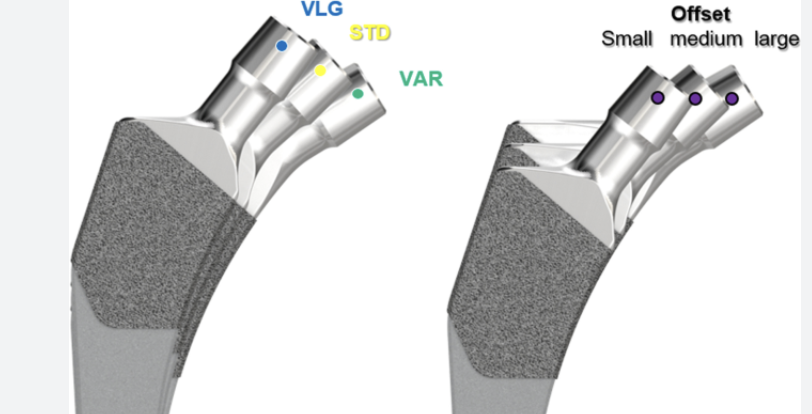
Smith & Nephew Anthology offset options
1. Decrease neck shaft angle
- more varus neck shaft angle increases offset
2. Increase head neck length
- improves abductor tension
- lengthens leg
3. Lateralized femoral stems
- stem is latealized, neck is medialized
- common design with high offset stems
4. Acetabular component
Lateralised liners
- increase offset whilst preserving leg length
Medialising acetabulum / centre of rotation
- decreases offset
Methods of restoring offset
1. Radiographic 2D preoperative templating
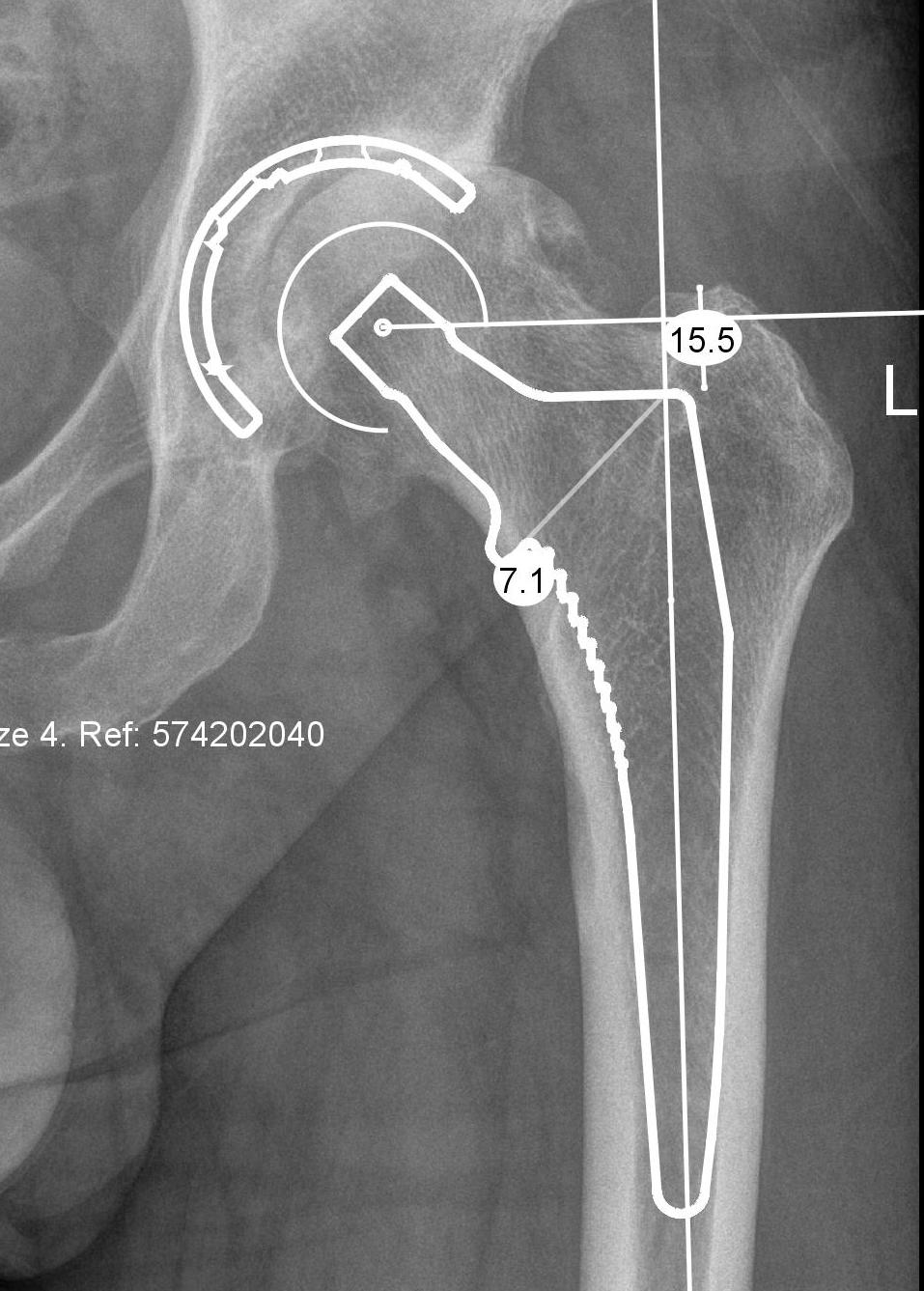
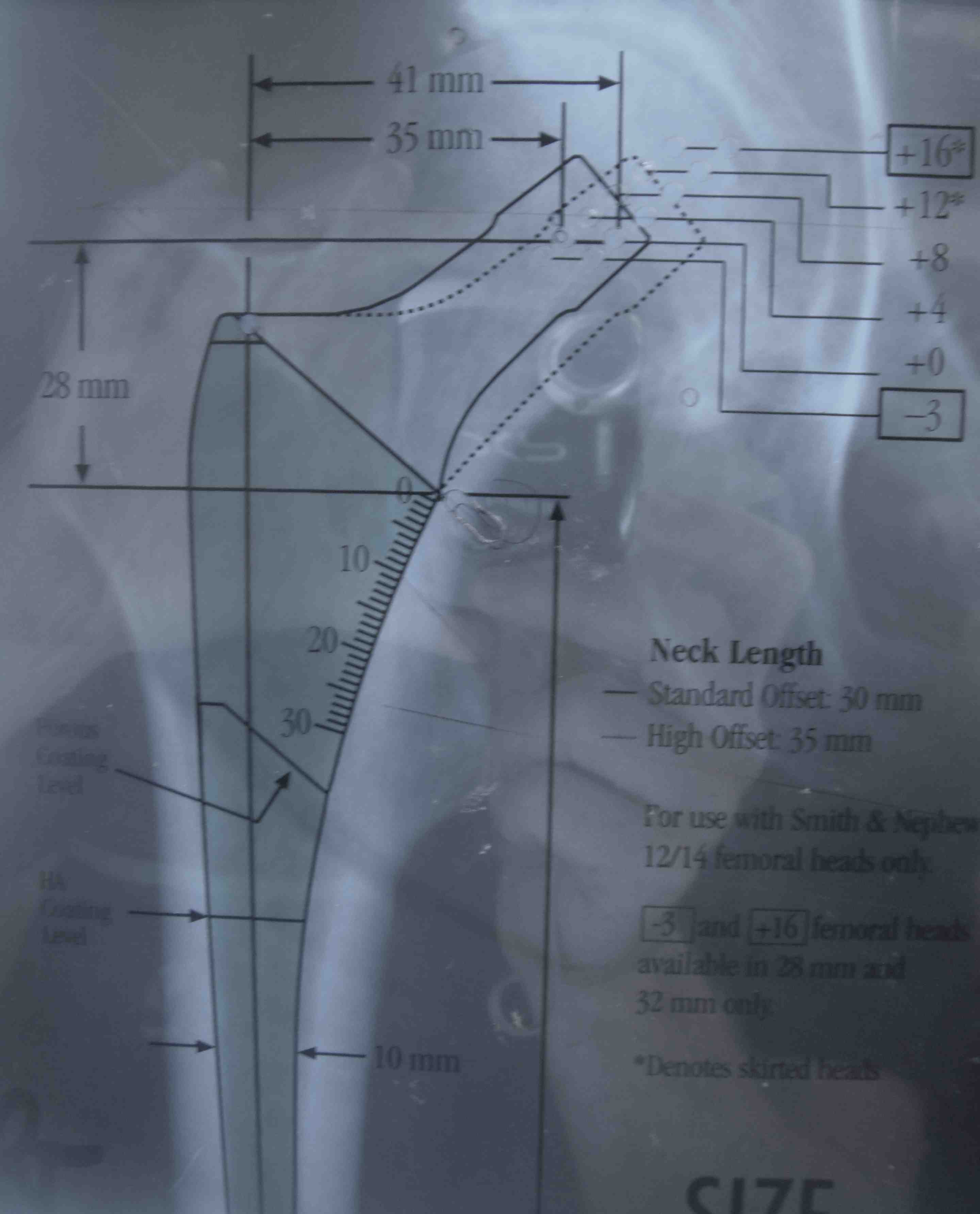
Issues
1. Affected by rotation
- take xrays with hip internally rotated by 20 degrees
- to account for femoral anteversion
- anteversion varies between patients
2. Accuracy
- 100 patients with OA with xrays and CT scans
- AP pelvis underestimated offset by 13%
- AP hip and CT scan hip correlation
2. 3D xray preoperative templating
EOS imaging system
- acquisition of simultaneous and orthogonal AP and lateral images of the patient
- create 3D reconstructions
Buller et al J Arthroplasty 2021
- EOS templated femoral and acetabular size to within 1 in 98% of cases
- femoral offset predicted in 83% of cases
2. 3D CT scan preoperative templaing
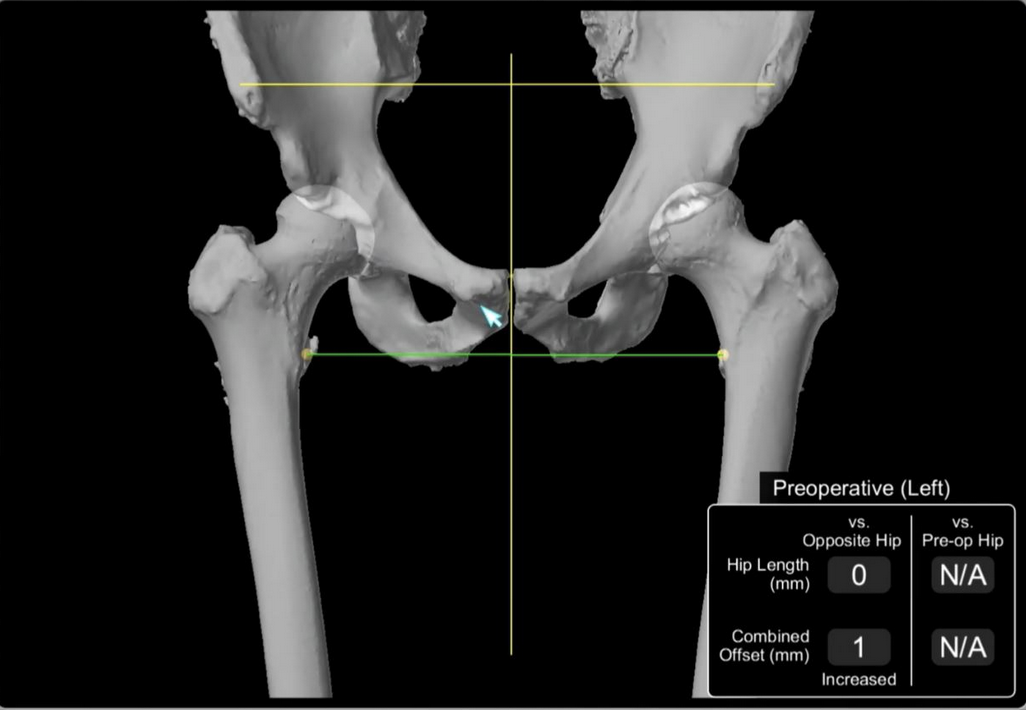
Stryker CT preoperative templating - compares offset from midline NOT femoral offset
Bishi et al EFORT Open Rev 2022
- meta-analysis
- 3D > 2D
- CT most accurate
2. Intra-operative measurement
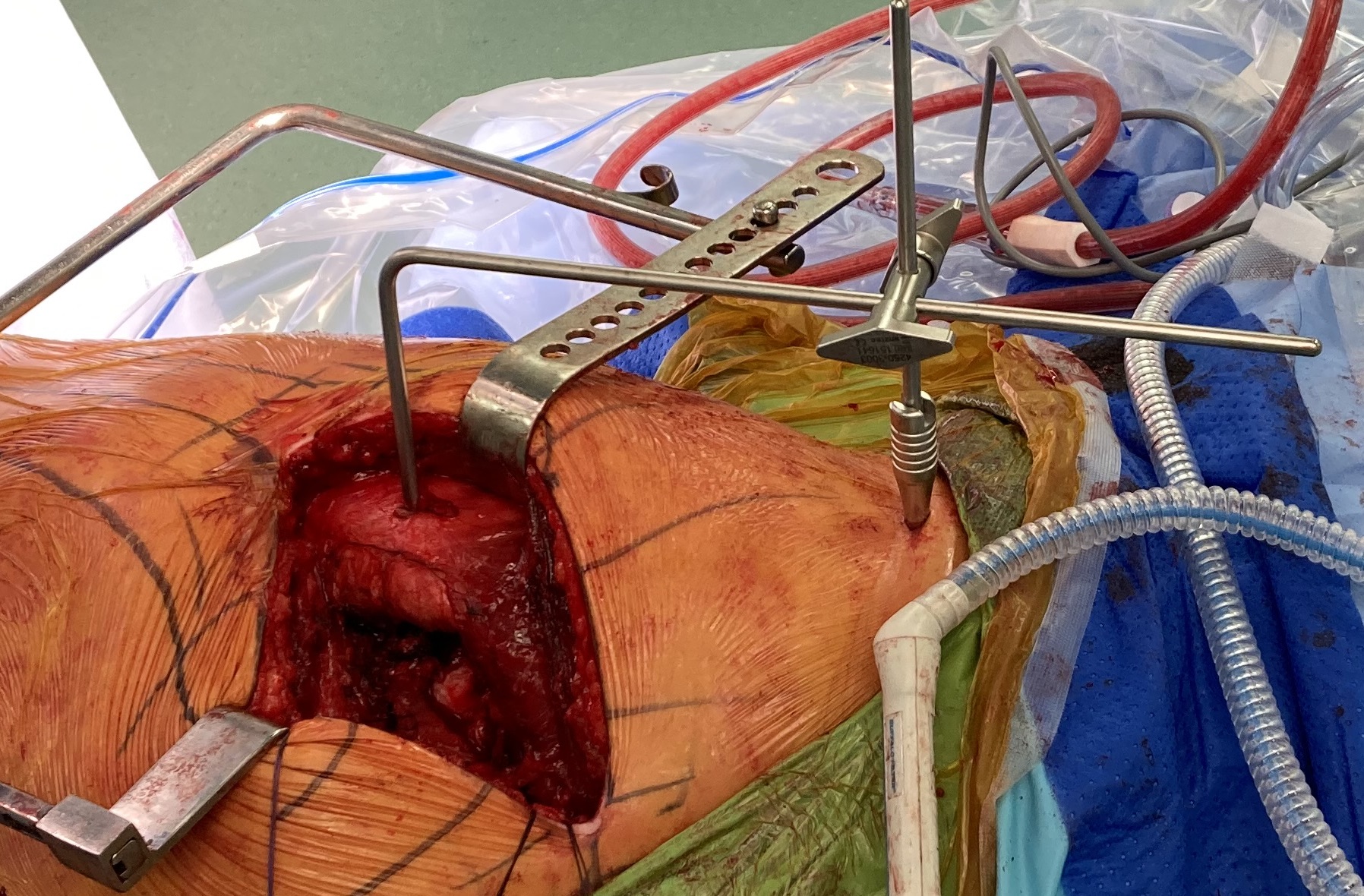
Measurement jigs
- 2 fixed reference points
- pelvic landmark and femoral landmark
- limb in consistent position
- measure length and offset
3. Intraoperative maneuvers
Shuck test
- distraction of hip joint with in line traction
Dropkick test
- hip extended, bend knee to 90o
- if too tight, rectus femoris is taut and passively extends the knee
4. Intra-operative xrays
Debbi et al J Arthroplasty 2020
- 100 patients with intra-operative xrays
- limb length within 5 mm in 100%
- offset within 5 mm in 97%
5. Computer navigation
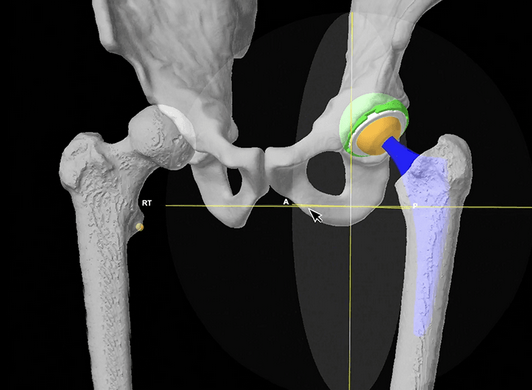
Stryker Mako Robot Navigation
Clave et al Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2015
- 325 cases THA with computer assistance
- 83% of leg length restored to within 5 mm of contralateral hip
- 88% of offset restored to within 5 mm of contralateral hip
