Definition
Entrapment neuropathy of posterior tibial nerve within the tibial tunnel
Anatomy
Flexor Retinaculum
- medial malleolus to posterior calcaneum
Tarsal tunnel
- roof is flexor retinaculum
- tibia anteriorly
- talus and calcaneum laterally
Contents
- T. Post
- FDL
- Posterior tibial artery, tibial nerve
- FHL
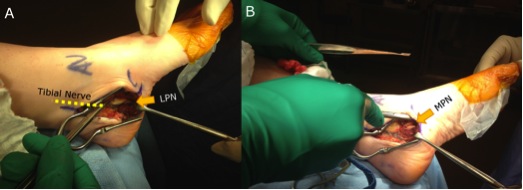
Tibial nerve
- 3 terminal branches
- medial and lateral plantar
- medial calcaneal
- usually divide within tunnel
Aetiology
Specific cause identified in 60% cases
Idiopathic
- 40% cases
- most common
Post-traumatic
- scarring after sprain
- bony prominence 2° calcaneal fracture
Inflammatory
- RA
- tenosynovitis
SOL
- tumours
- ganglion of tendon sheath
- lipoma
- neurilemmoma (Schwannoma)
- varicose veins
- medial talo-calcaneal bar
Accessory muscles
- FDL
History
Diffuse pain plantar aspect
- burning, tingling or numbness
- 1/3 have proximal radiation to leg
Aggravated by activity
Examination
Tenderness over Tarsal Tunnel
Positive Tinel's sign
Palpate for thickening or swelling (cyst, ganglion etc)
Usually no sensory loss or weakness
May see wasting of abductor hallucis
NCS
At best 90% accurate
- Prolonged sensory conduction time in 75%
- Prolonged motor latency in 50%
- conduction velocity of CPN done to exclude peripheral neuropathy
MRI
MRI positive in 85%
- FHL synovitis, dilated veins, mass, fracture, scar, etc
- 25% have contralateral MR findings with no symptoms
Diagnosis
At least 2 of
- Hx of tingling & burning
- positive tinels
- positive NCS
DDx
Local
- plantar fasciitis
- fracture
- tenosynovitis
Neurological
- peripheral neuritis
- diabetic neuropathy
- leprosy
- neurilemmoma
- neuroma
- spinal compression
Management
Non-operative
Of little benefit
- try NSAIDs
Operative
Surgical release by division of Flexor Retinaculum
Incision
- 10 cm proximal to medial malleolus
- curved distally to TNJ
Release
- flexor retinaculum
- proximal investing fascia
- individual tendon sheaths / tibialis posteror in separate sheath
- abductor hallucis fascia
Follow and release both plantar nerves
- protect medial calcaneal branch
- runs off lateral plantar
Post op
- NWB for 3/52
Results
75% success if no underlying causes
