Assume all malignant until proven otherwise
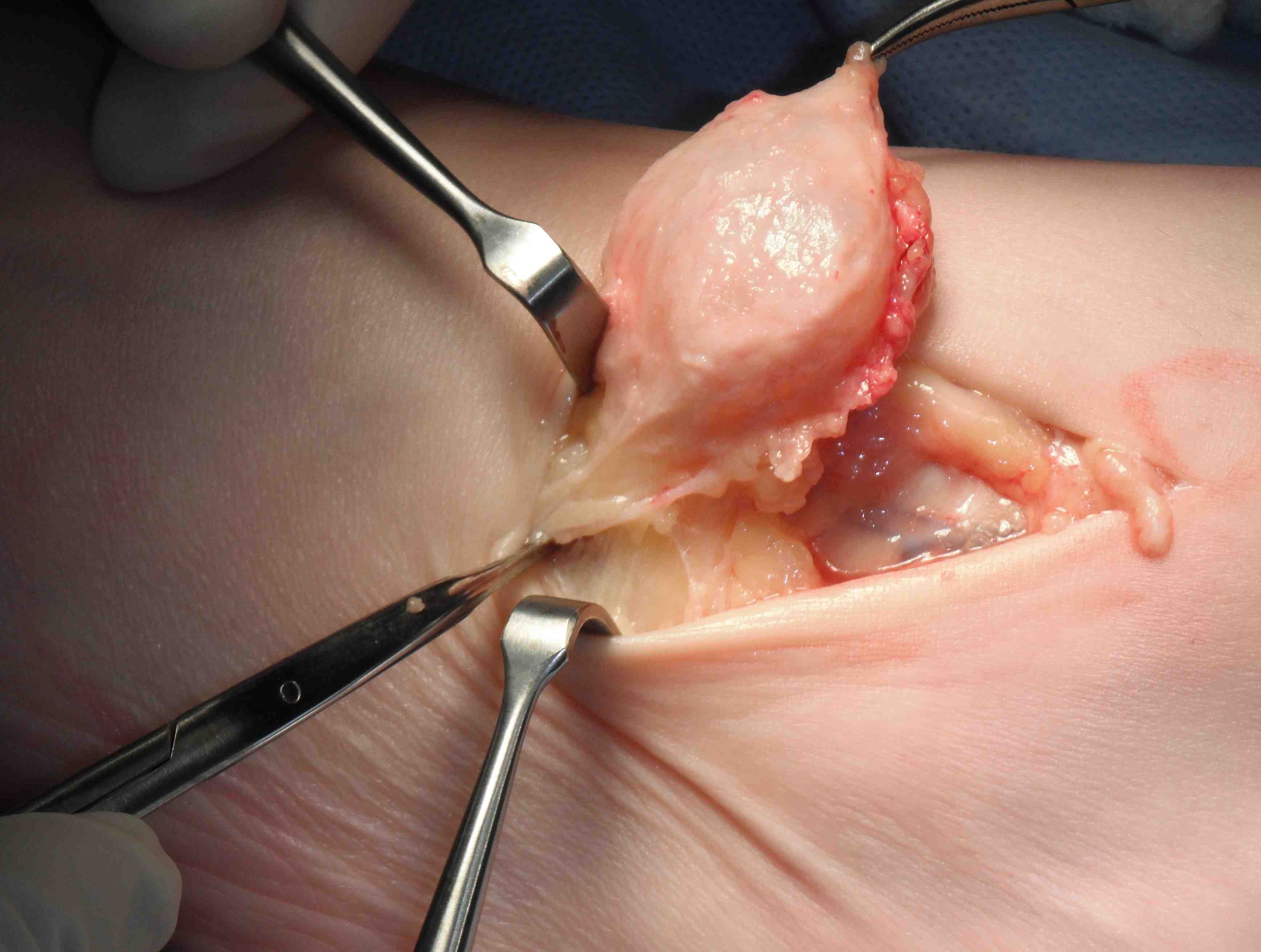
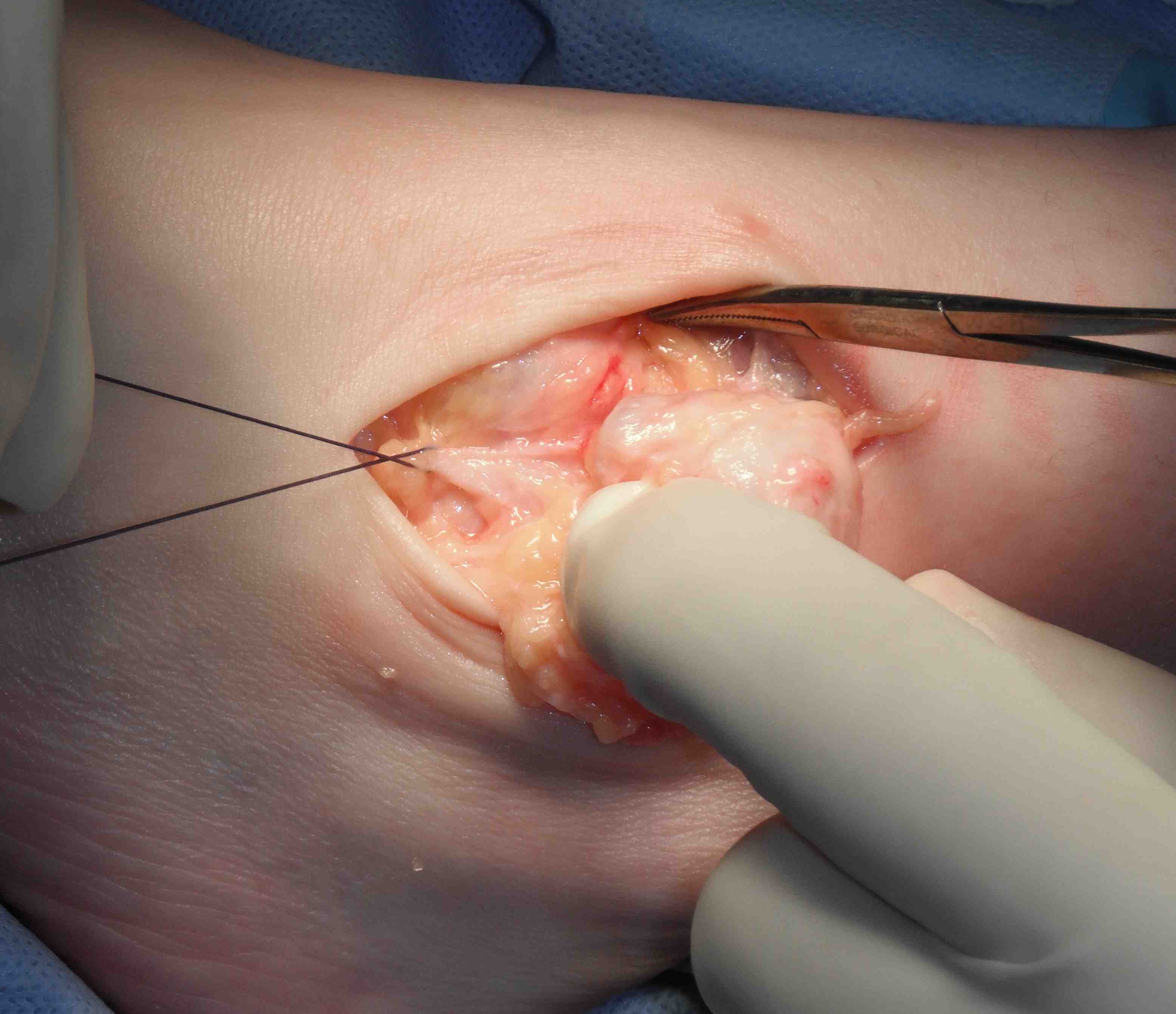
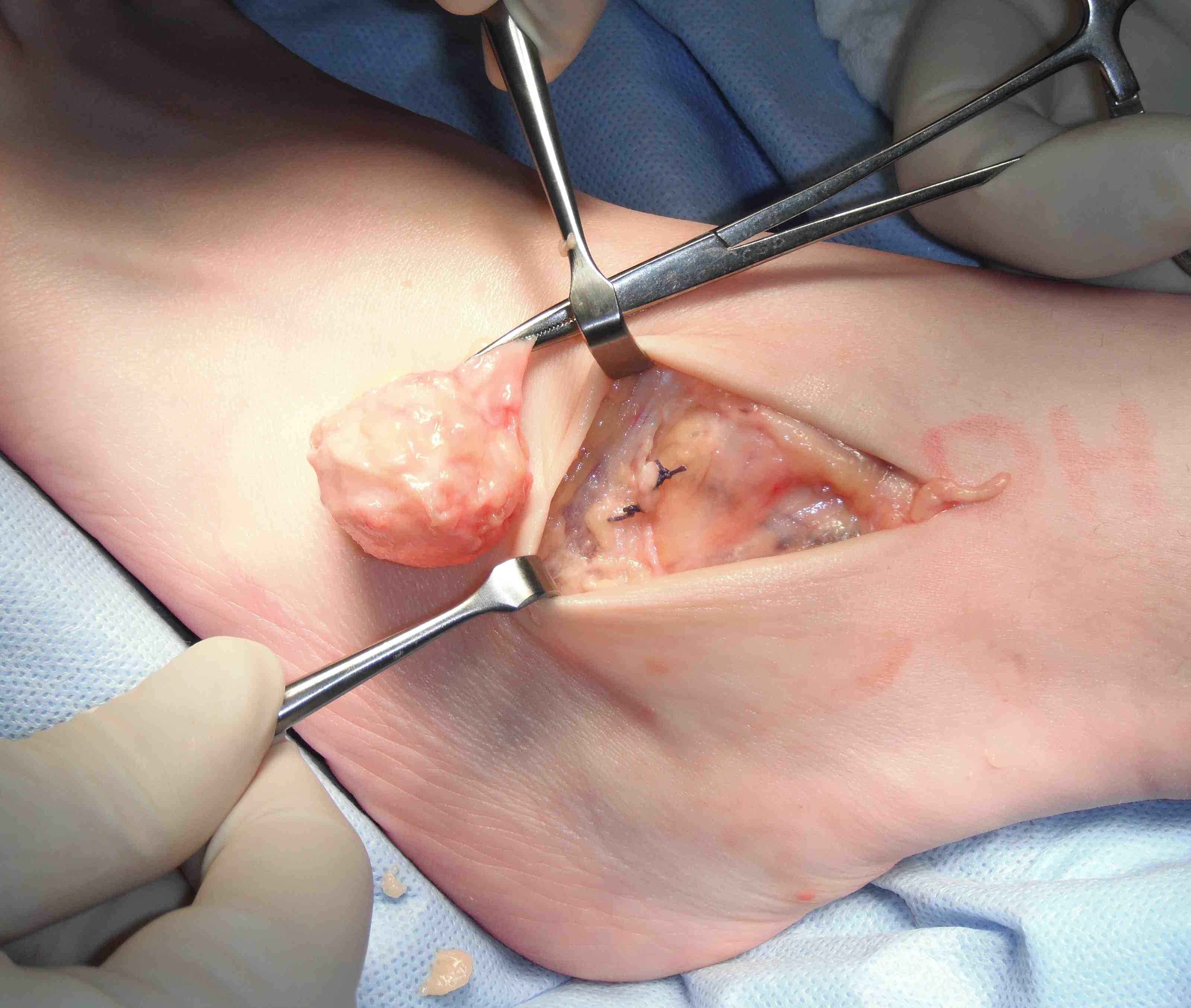
1. Ganglion
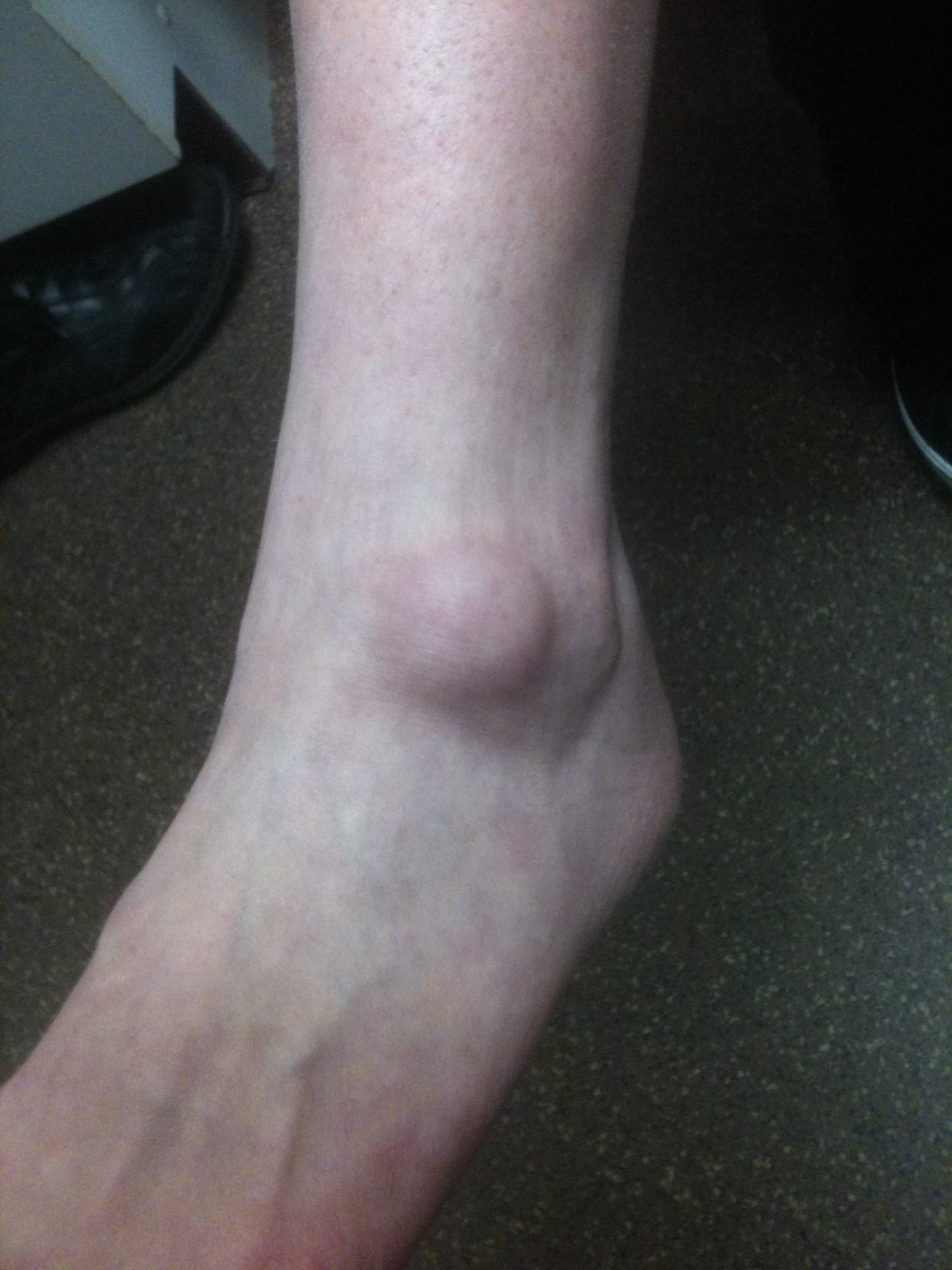
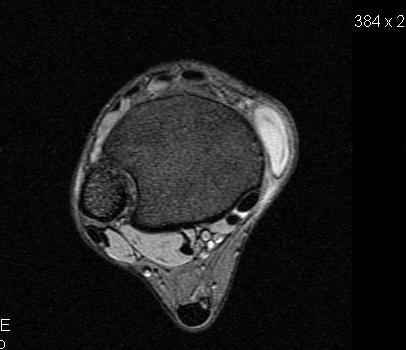
Mucoid degeneration of a joint capsule or tendon sheath
- may fluctuate in size or disappear
- firm subcutaneous nodule
- may be painful, especially if compressed
- often transilluminate
Treatment
- observe
- multiple aspirations / cortisone injections
- surgical excision
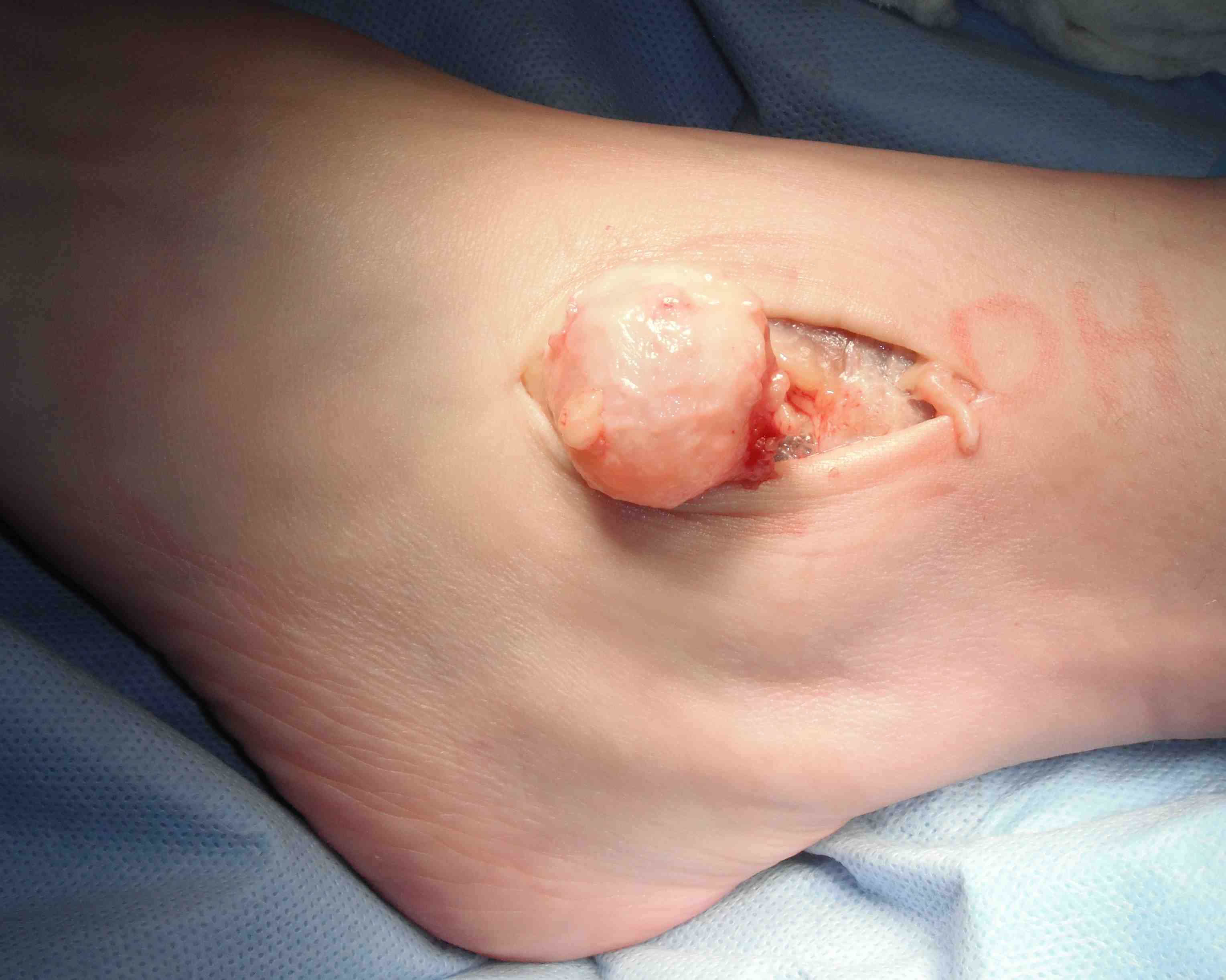
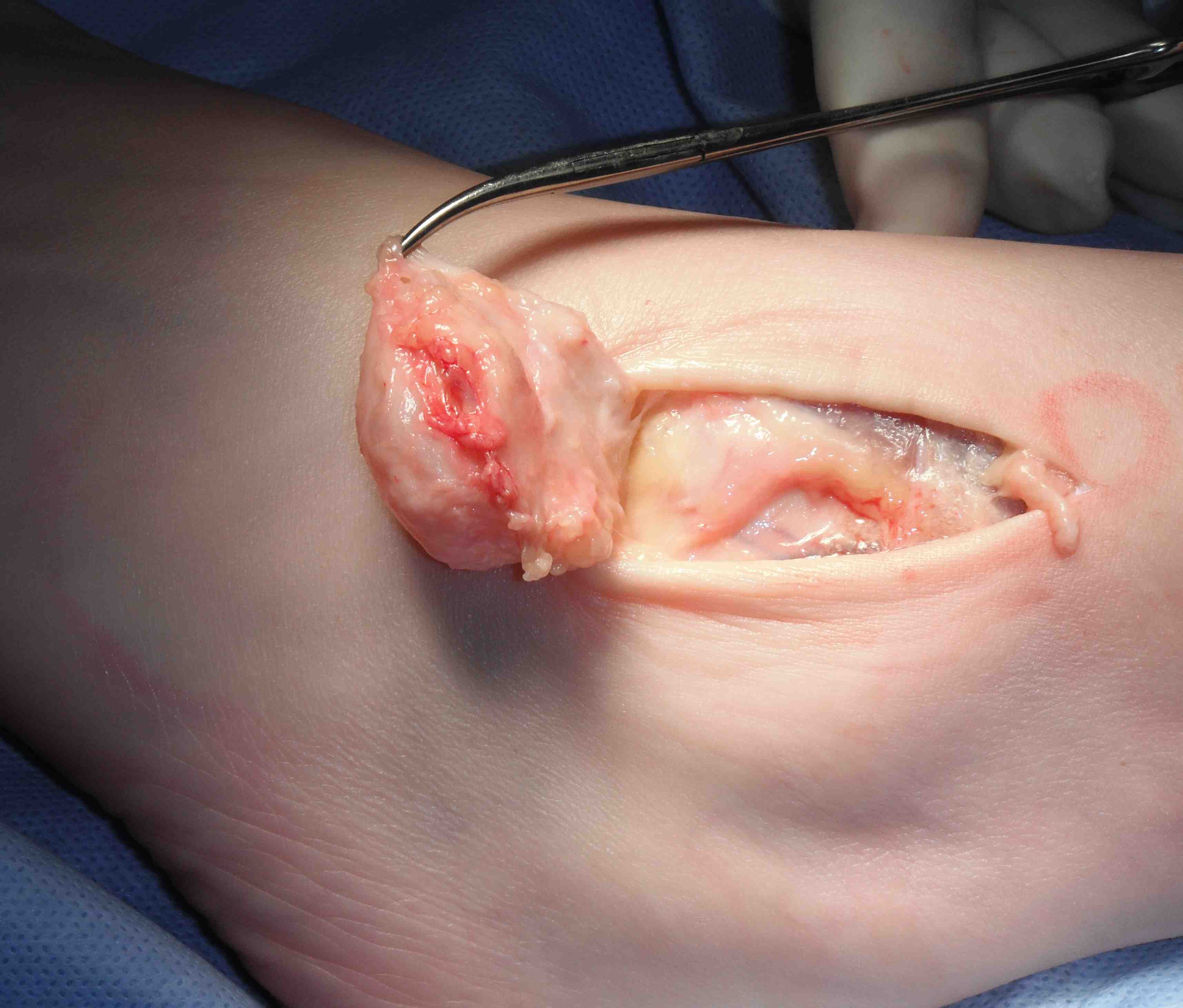
Surgical excision
- need to find neck
- may arise from AKJ / STJ / T post tendon
- tie off neck or excise segment of capsule
2. Plantar fibromatosis
Most common soft tissue tumour in the foot
- see other notes
3. Fibroma
Discrete nodule of well differentiated fibroblasts
- on sole or dorsum
- slow growing
- pain uncommon
- usually subcutaneous, firm, not attached to skin
Treat
- local excision if required
(recurrence rare)
DDx
- Fibrosarcoma
- Plantar fibromatosis
4. Giant cell tumour of the tendon sheath
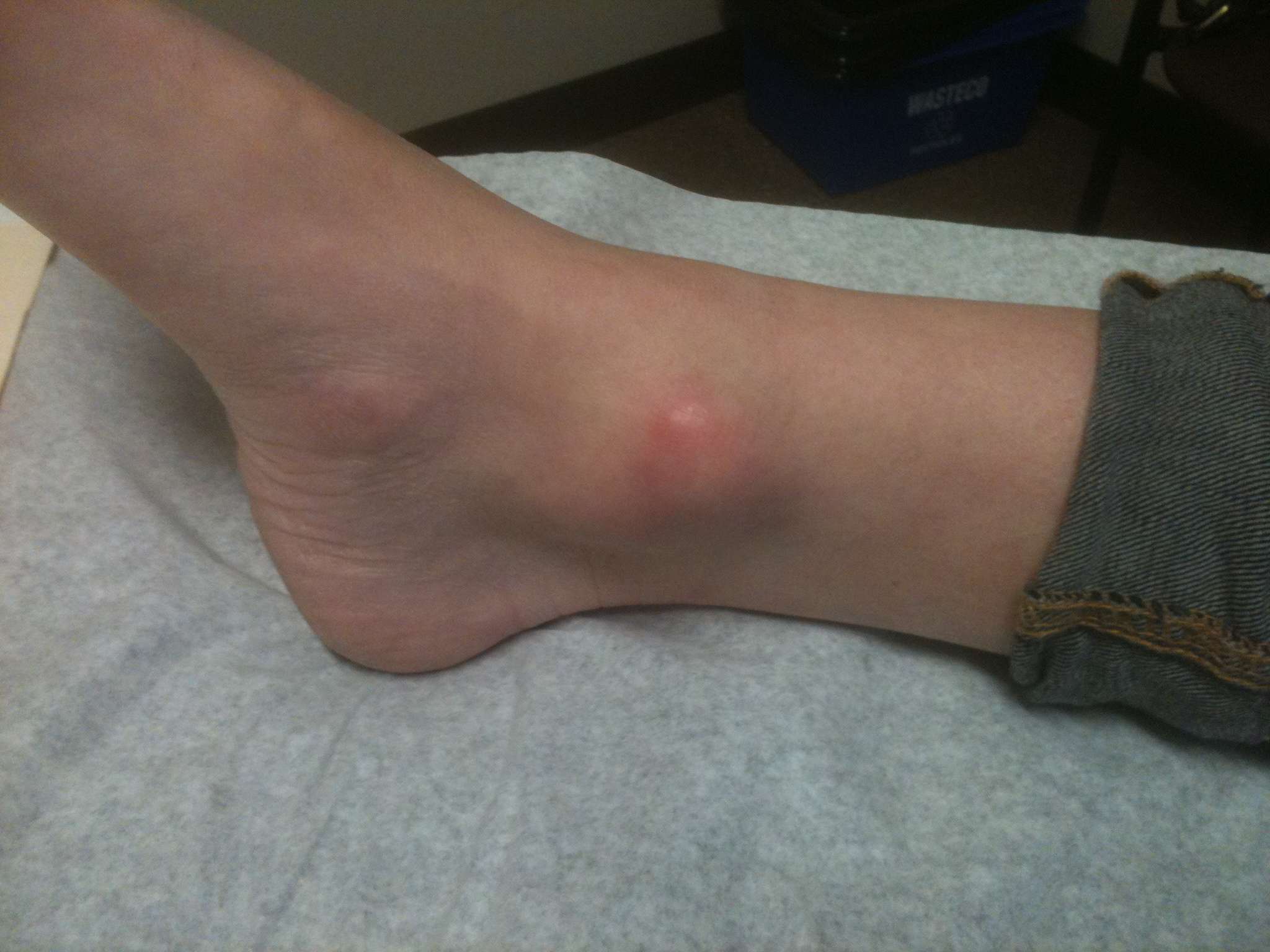
Usually in tendon adjacent to ankle (can be anywhere)
- well defined firm nodule with an obvious capsule
- not always painful
- pain with direct pressure
Treatment
- observe (may involute)
- surgical excision (recurrence rare)
5. PVNS
Common around the ankle or midfoot
- may involve multiple bones
- usually in young adults
X-ray
- may show bony erosions
- brown villonodular synovium
Treatment
- excision include complete synovectomy
- recurrences common but not all symptomatic
- DXRT if severe
6. Lipoma
Most common on dorsum
- subcutaneous
- soft feeling / mobile / grape like
- painless unless compressed
Treatment
- marginal excision
(local recurrence rare)
7. Neurilemmoma
Benign schwannoma
- well encapsulated solitary tumour
- originates from nerve sheath
- slow growing
- nerve fibres spread over its surface
- painful if compressed or causes compression
MRI
- hyperintense rim on T2
Management
- separate nerve fascicles
- excise neurilemmoma
- marginal excision
- attempt to preserve normal nerve fibres
8. Neurofibroma
Singular or multiple
- extend along course of the nerve
- 1/2 not associated with NF
Often local pain especially with compression
- may affect distal nerve function
- malignant change rare in solitary lesion (occurs with NF)
MRI
- target sign
- can be seen with neurilemmoma
Treatment
- tumour arises from within the nerve
- excision usually cause further loss of function
9. Solitary Hemangioma
Present with episodes of dependent swelling
- often after local trauma
- diffuse edges / can be difficult to palpate
Diagnose on MRI
- hyper-intense on T2 FS
Treatment
- only needs excision if limits function
- often incomplete - recur
10. Glomus tumour
Presents as painful toe, sensitive to cold
- pain with local pressure
- usually subungual
X-ray
- may scallop adjacent bone on x-ray
Treatment
- marginal excision for pain
11. Synovial osteochondromatosis
