Region specific approaches
Theory
- want to traverse one muscle / one compartment
- as a rule perform open biopsy through compartment the tumour is in
- keep away from NV bundle
Rules
- need to be done under guidance or by tumour centre
Anatomical guidelines to core biopsy PDF
Lower Limb
Femur
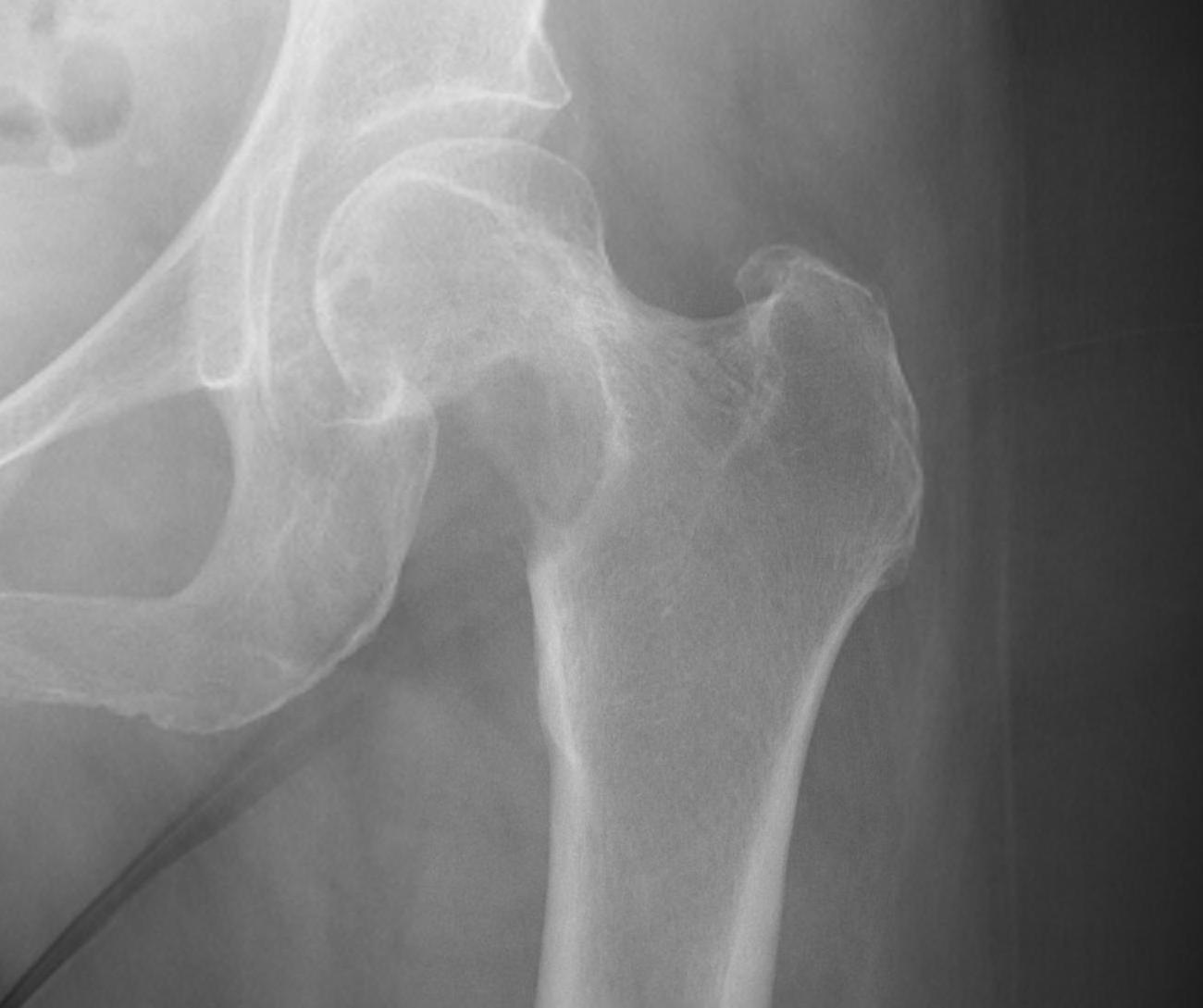
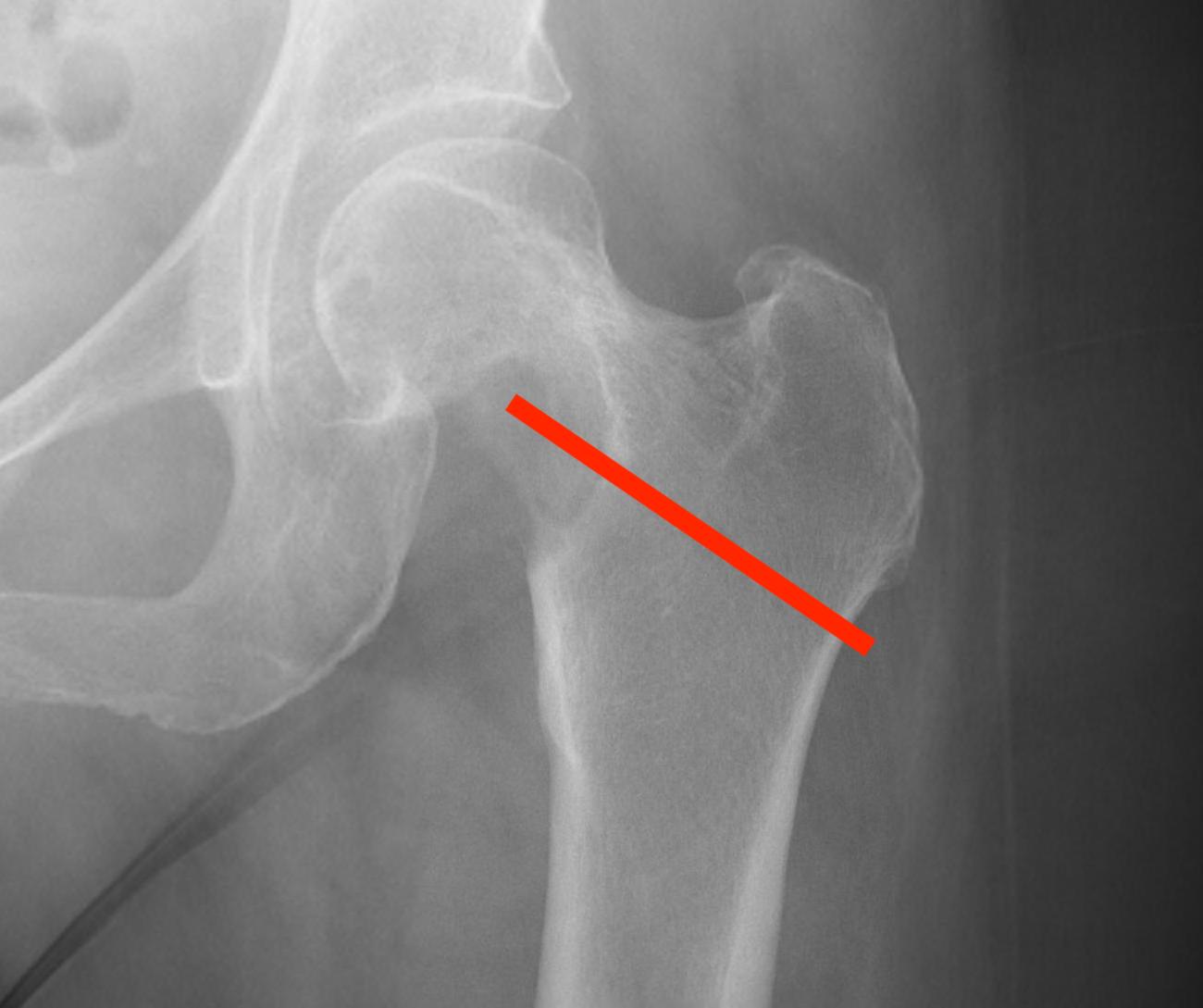
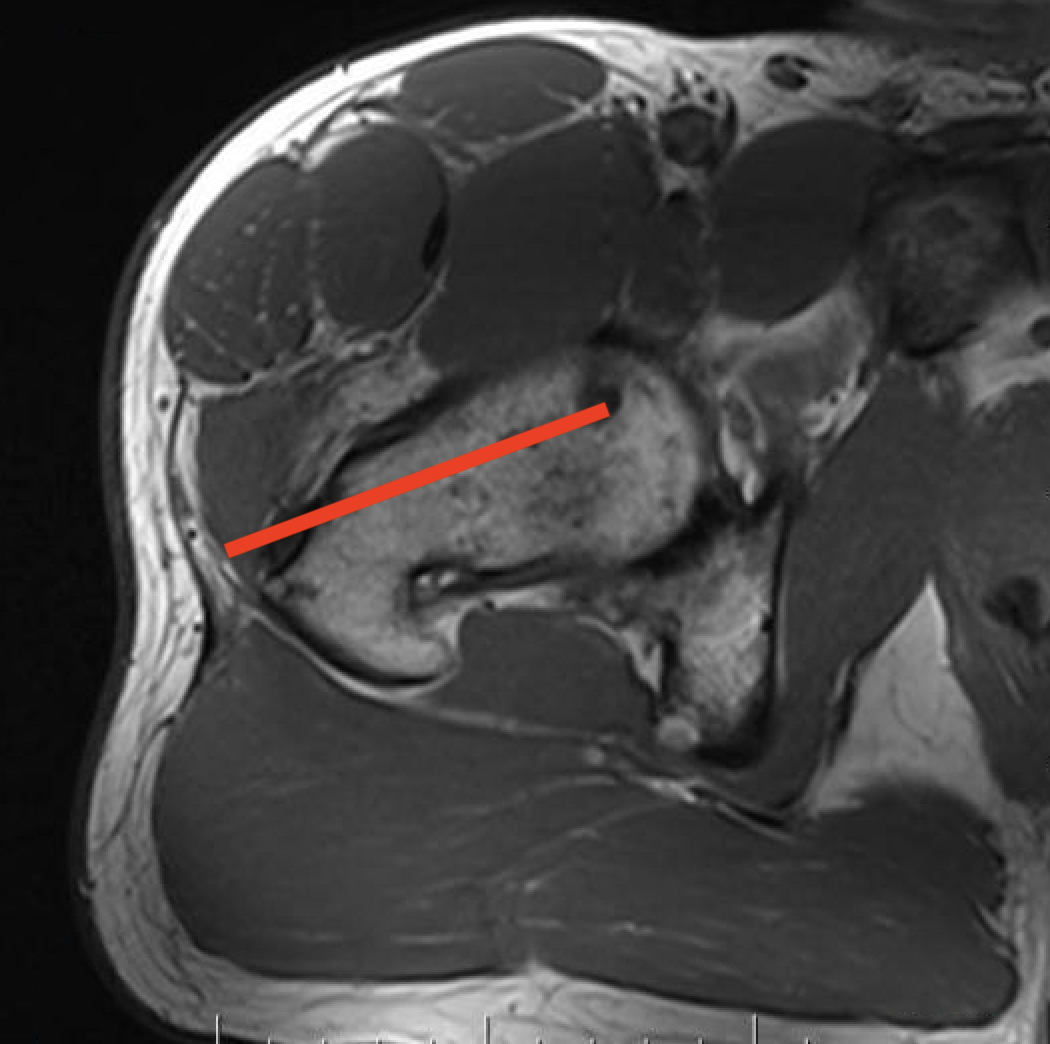
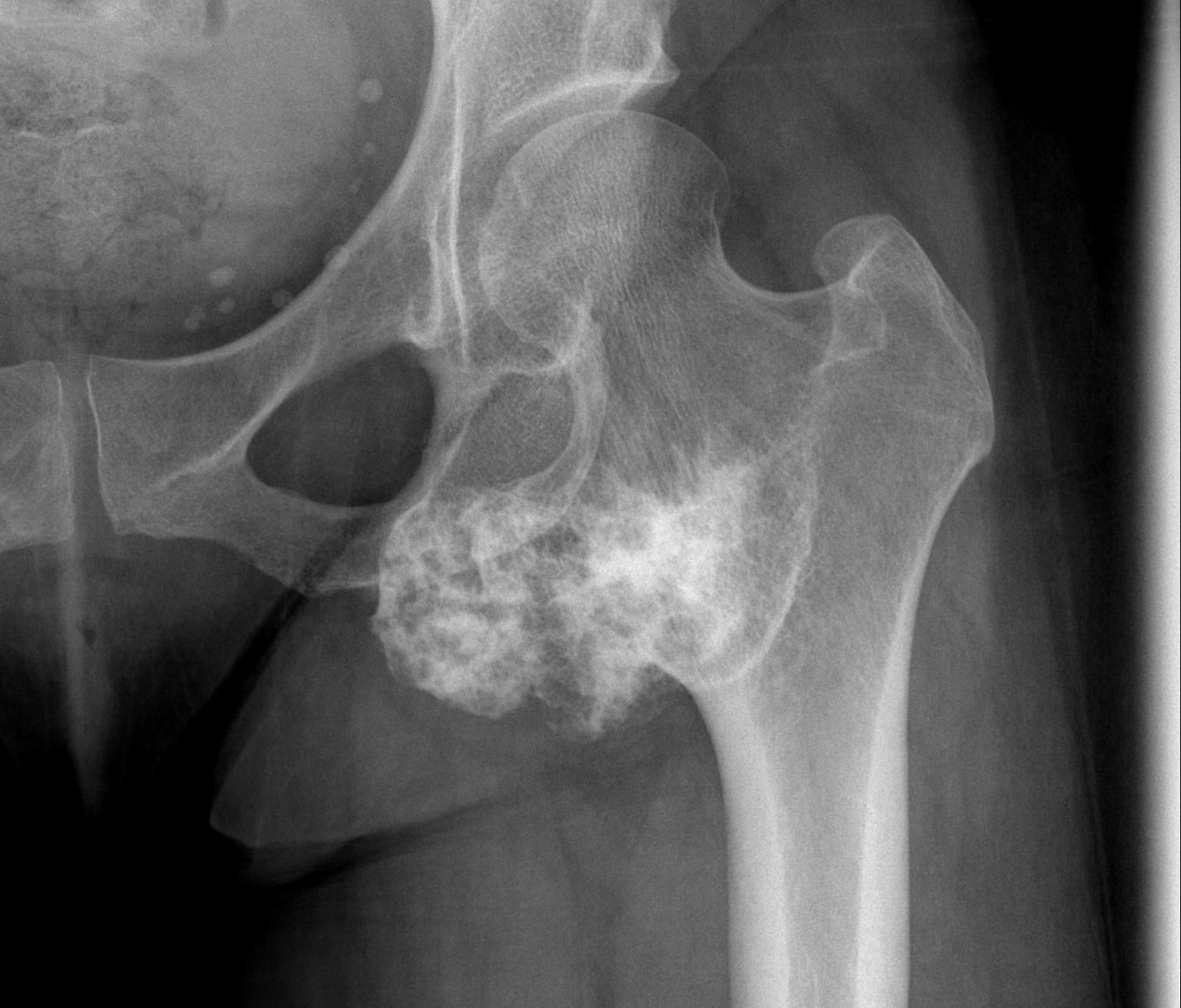
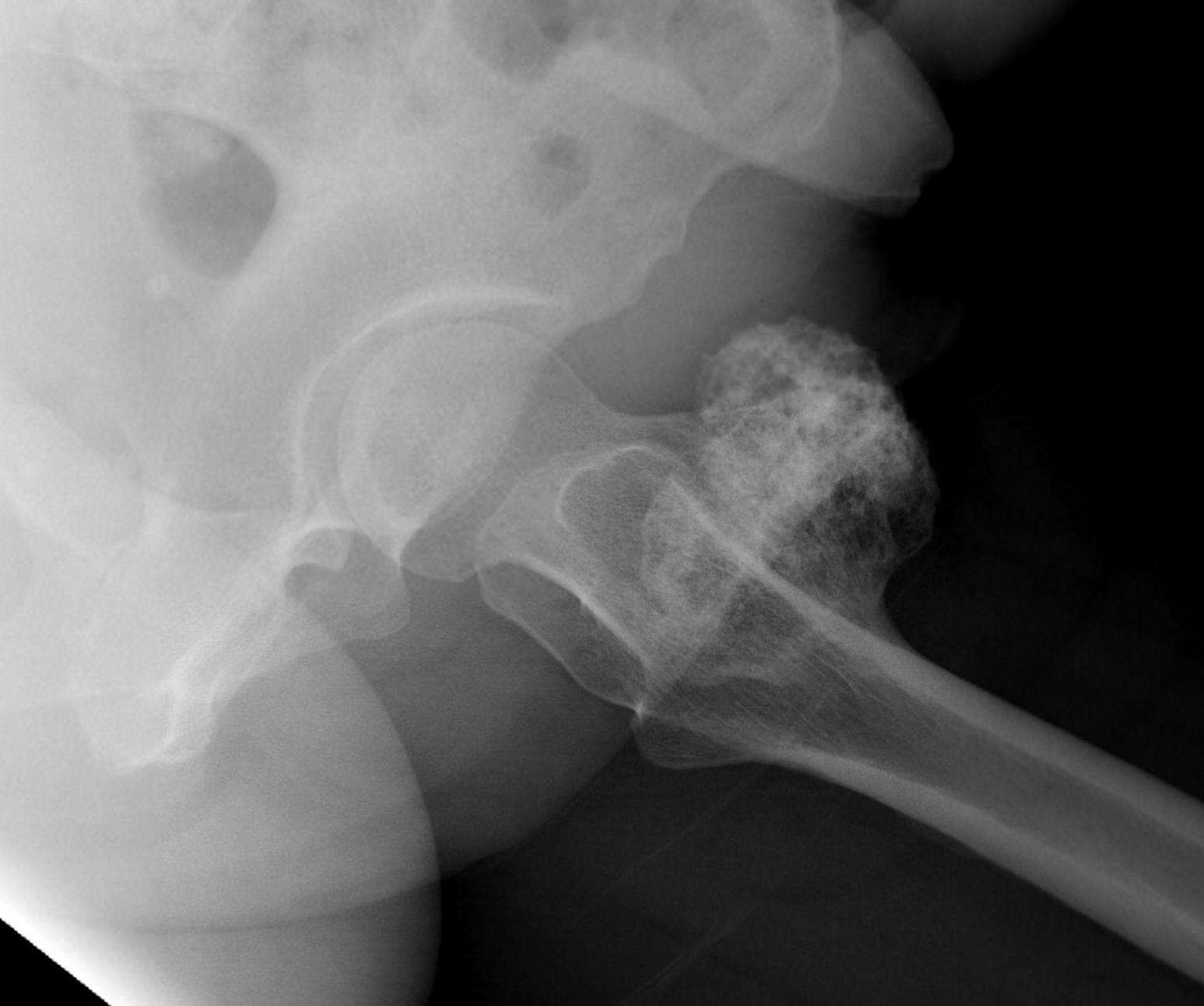
1. Femoral head / neck
- lateral approach
- trans trochanteric
- avoid NV bundle and quadriceps
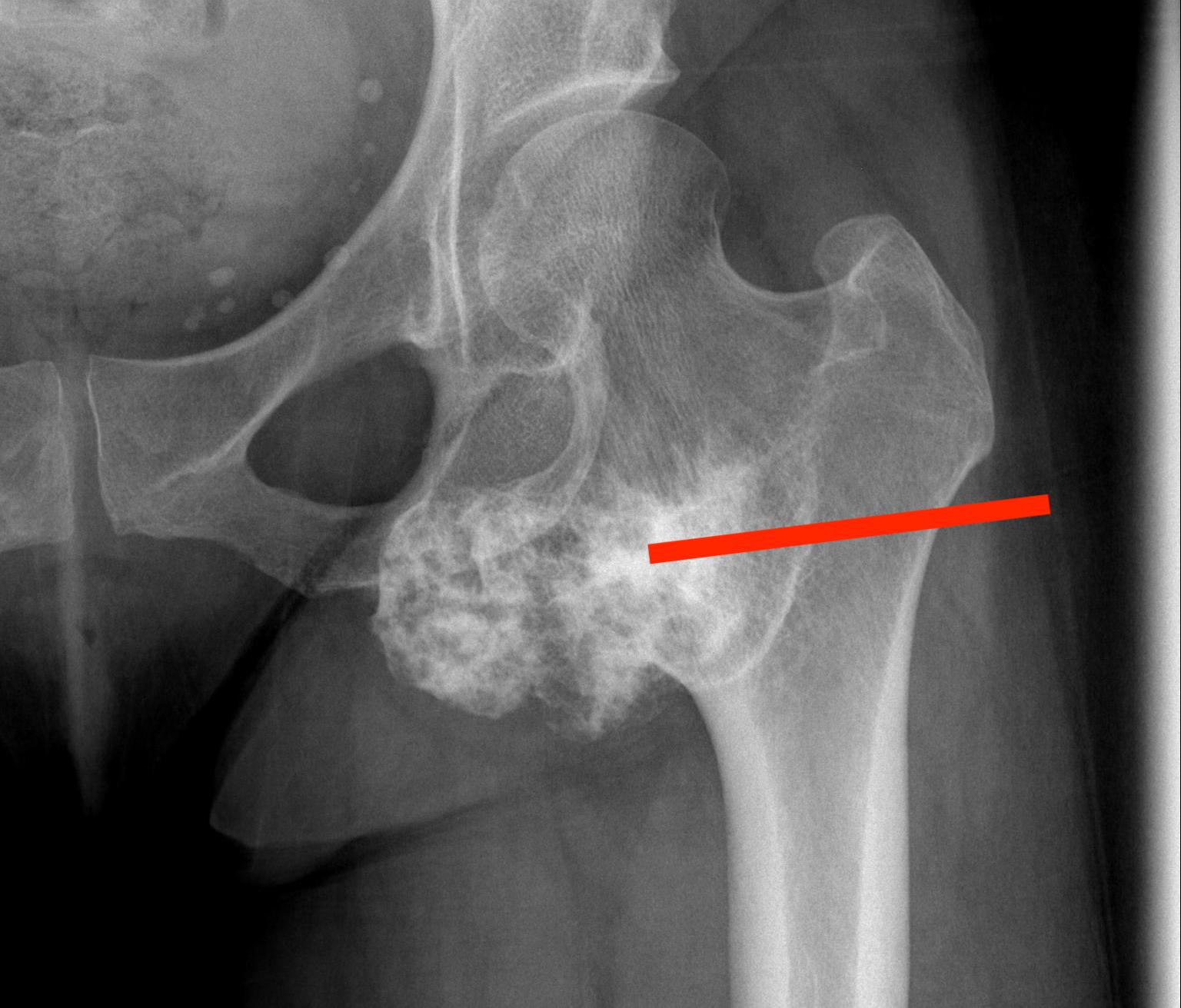
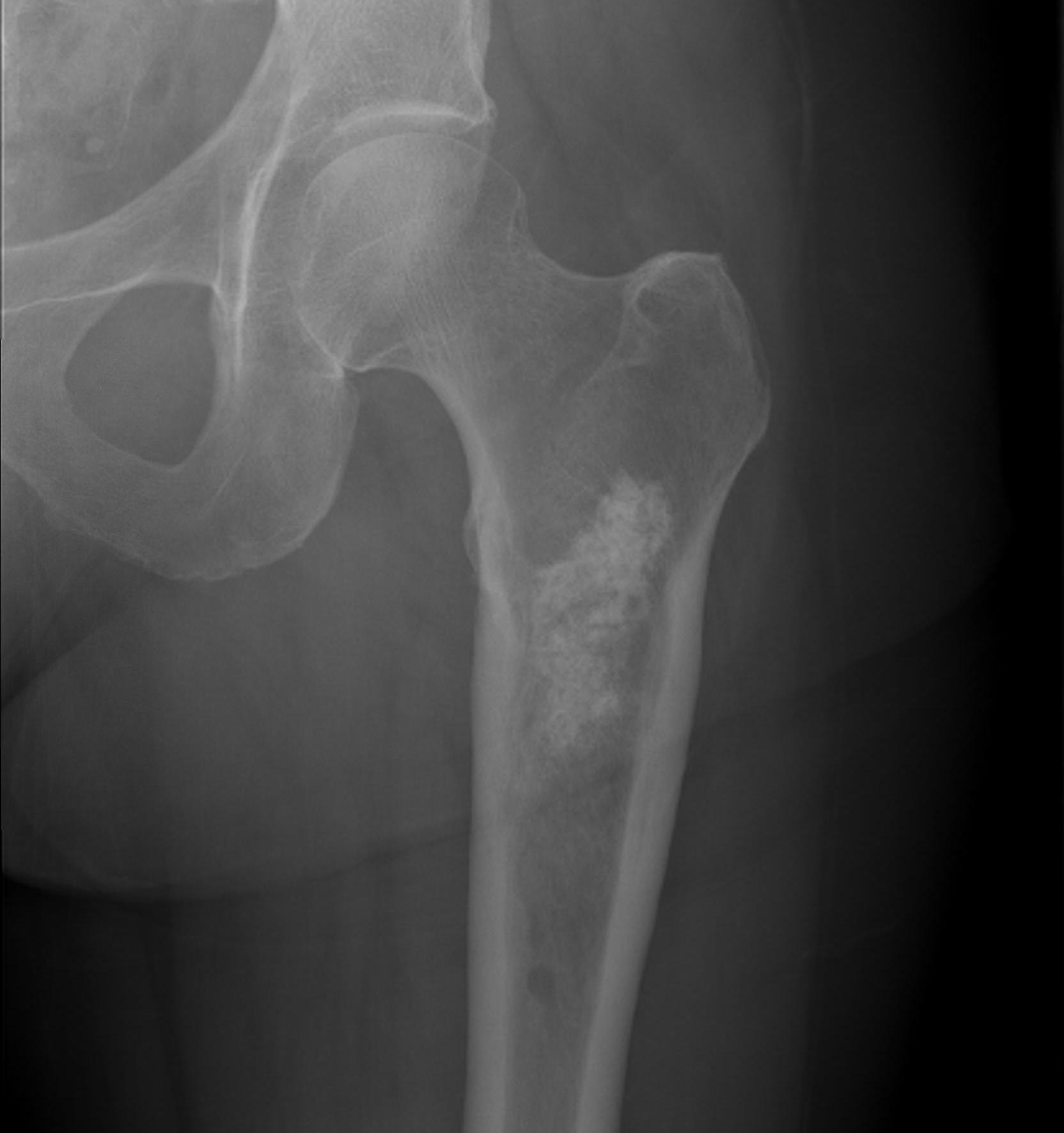
2. Subtrochanteric / femoral shaft
- lateral approach
- aim anterior or posterior to lateral intermuscular septum depending on compartment
- avoid rectus femoris / vastus intermedius
- ok to resect part of vastus lateralis or biceps femoris
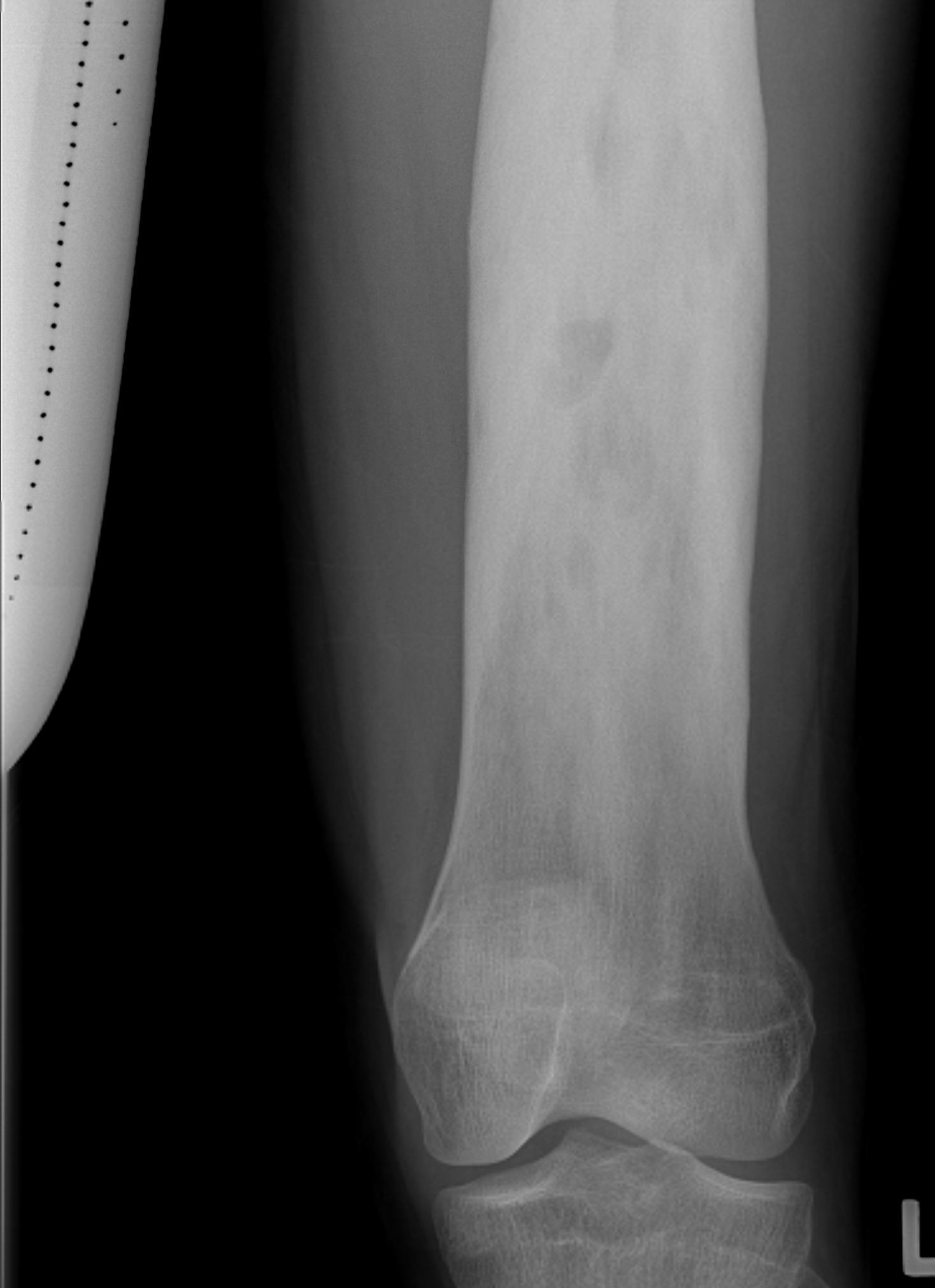
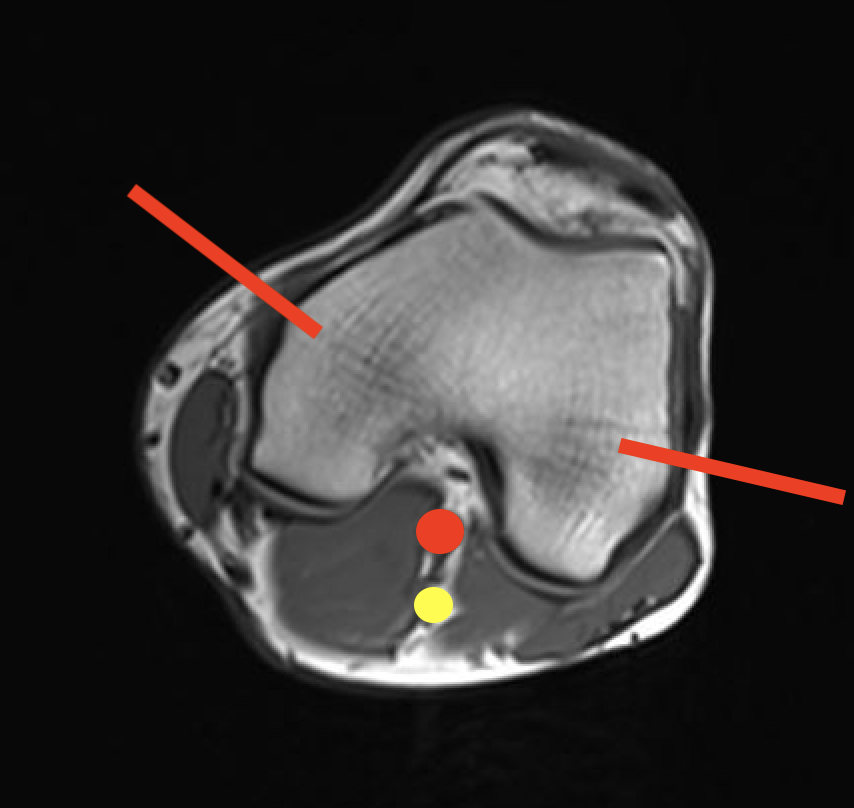
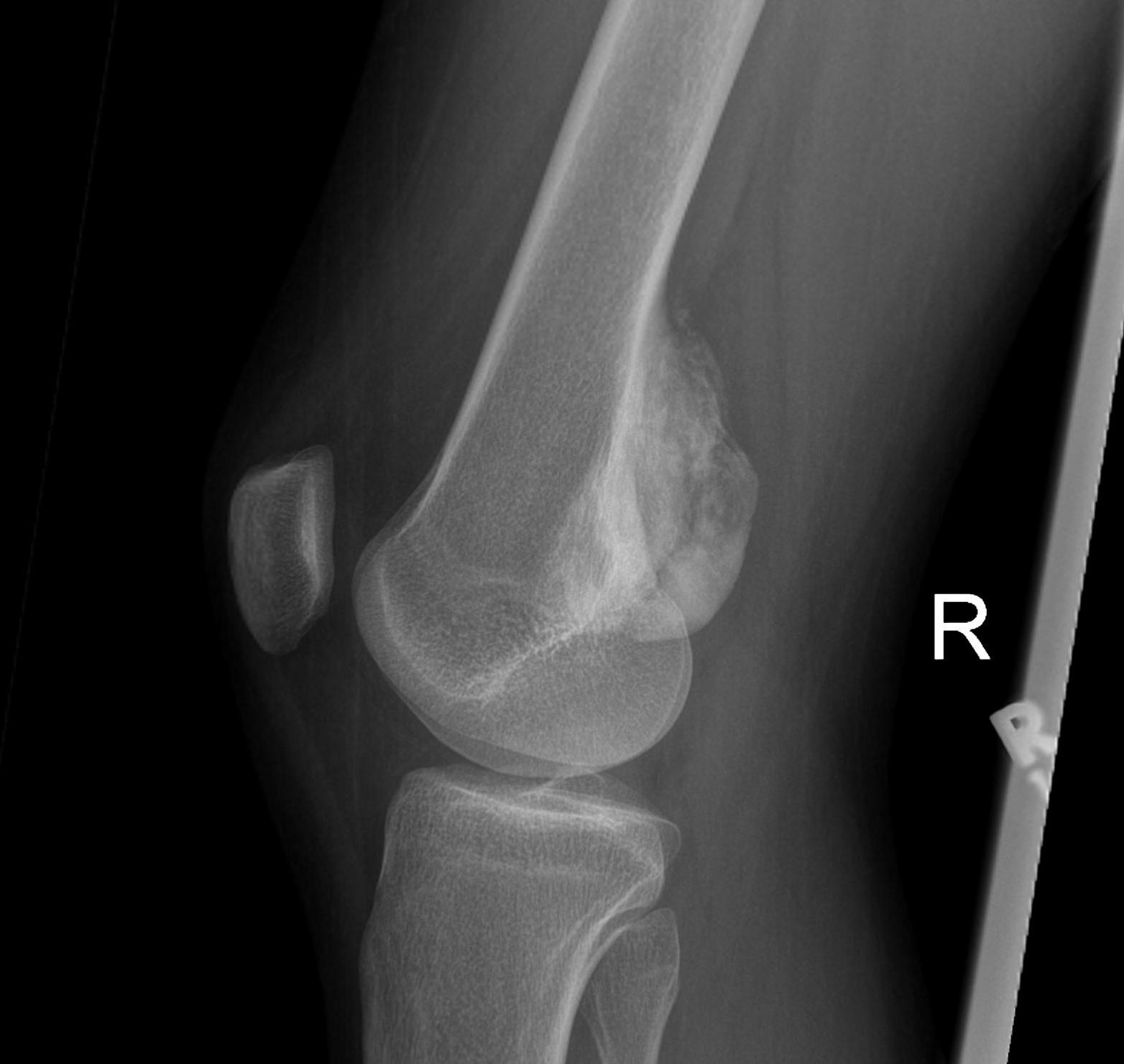
3. Condyles
- medial: incision through vastus medialis
- lateral: anterior to vastus lateralis
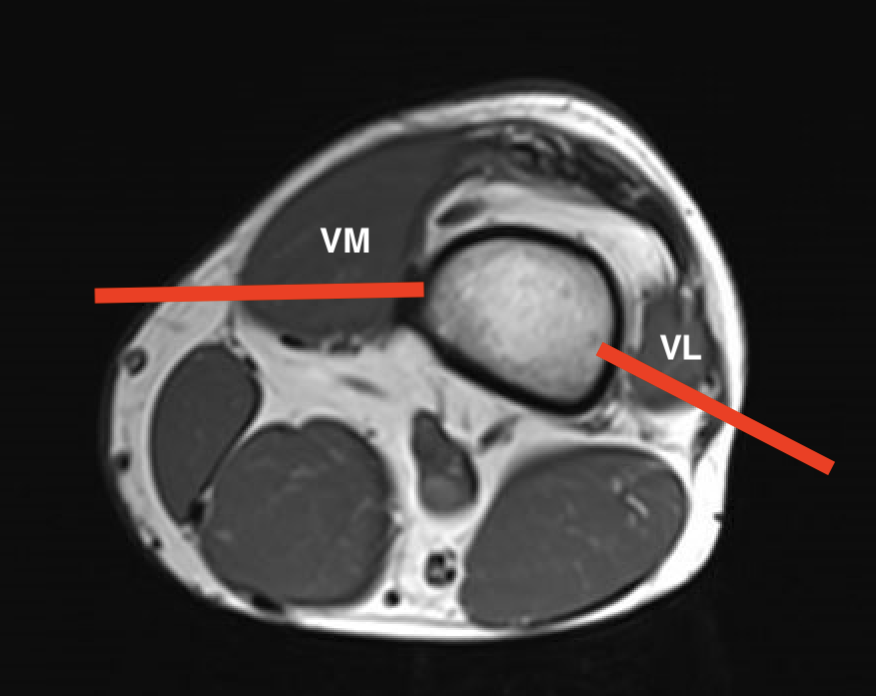
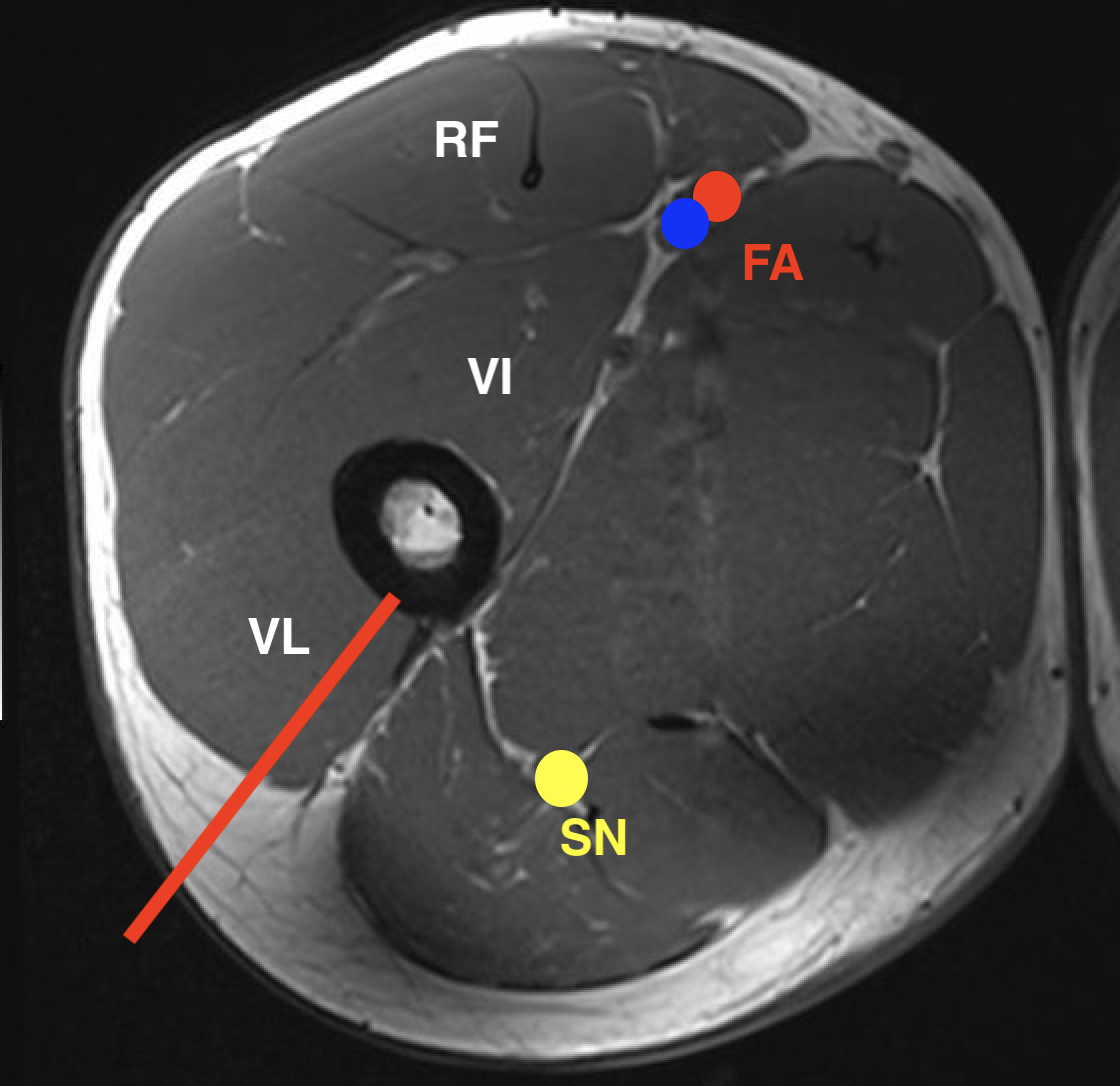
Thigh
1. Lateral compartment soft tissue tumour
- lateral approach through ITB
- through vastus lateralis / anterior to lateral intermuscular septum
2. Medial compartment soft tissue tumour
- medial approach through gracilis
- keep away from NV bundle
3. Posterior compartment soft tissue tumour
- posterior approach / transmuscular
Popliteal fossa
Popliteal fossa / parosteal OS
- posterior approach
- go through hamstrings or gastrocnemius
- depending on whether lesion medial or lateral
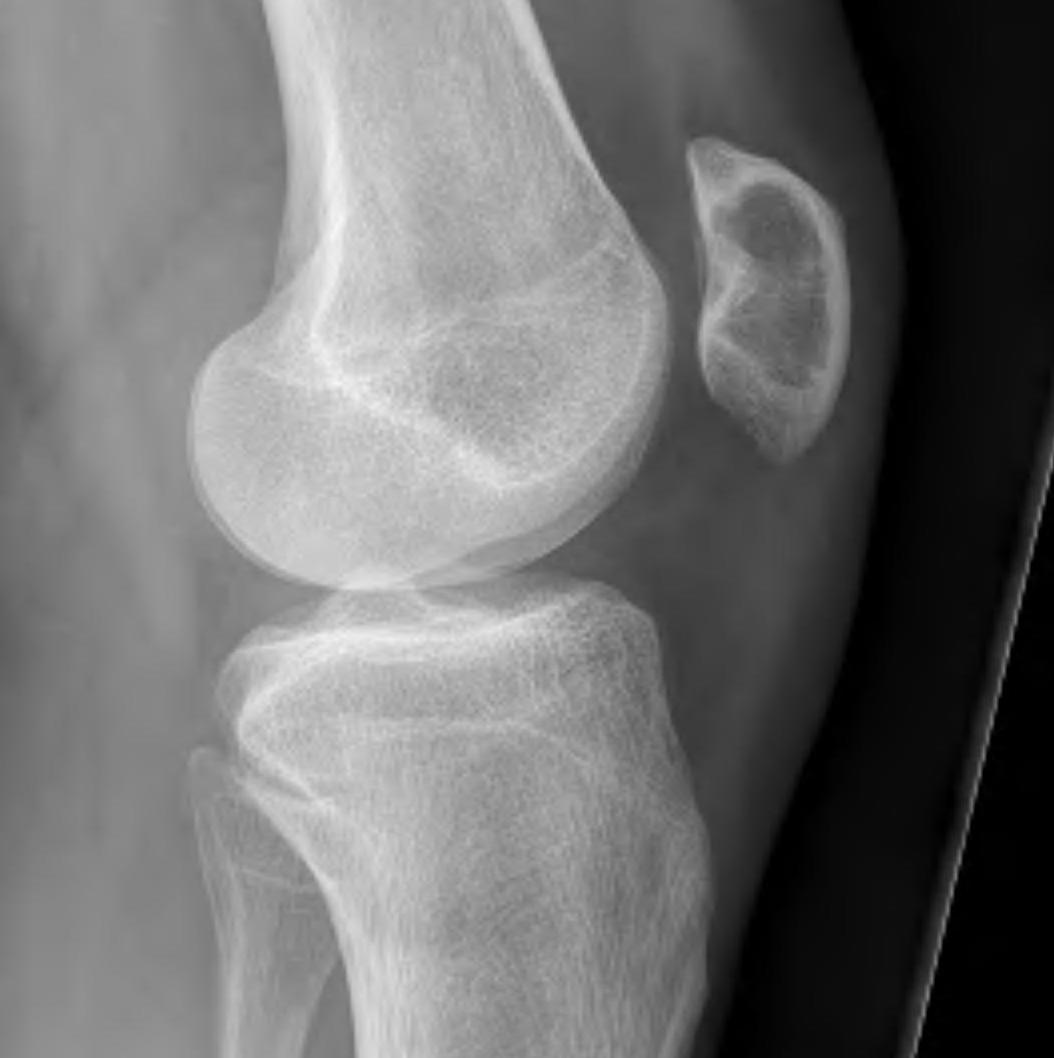
Patella
Direct anterior
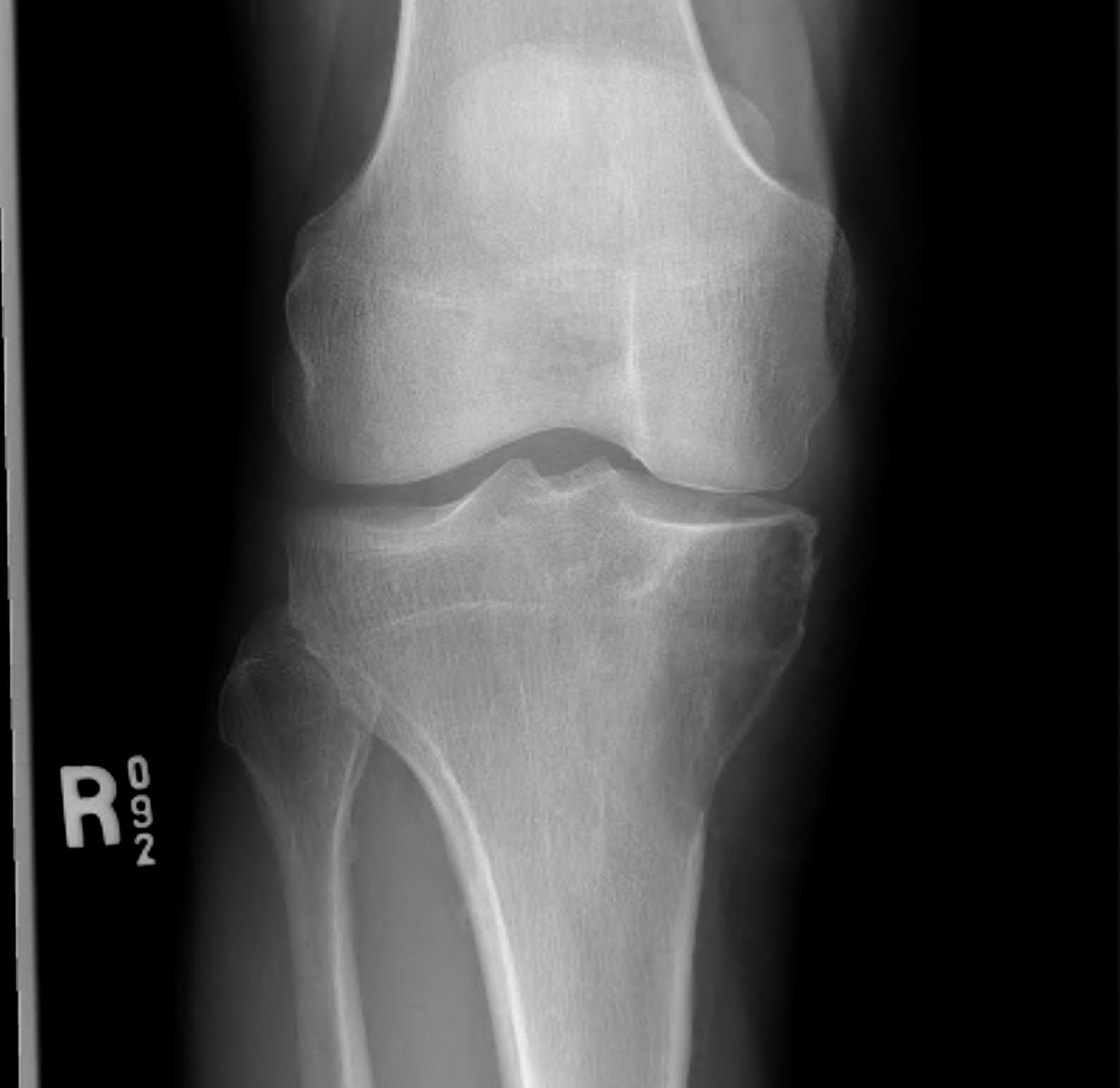
Tibia and fibular
Tibia: direct medial approach directly onto bone
Fibula: direct lateral or through peroneus, anterior to intermuscular septum
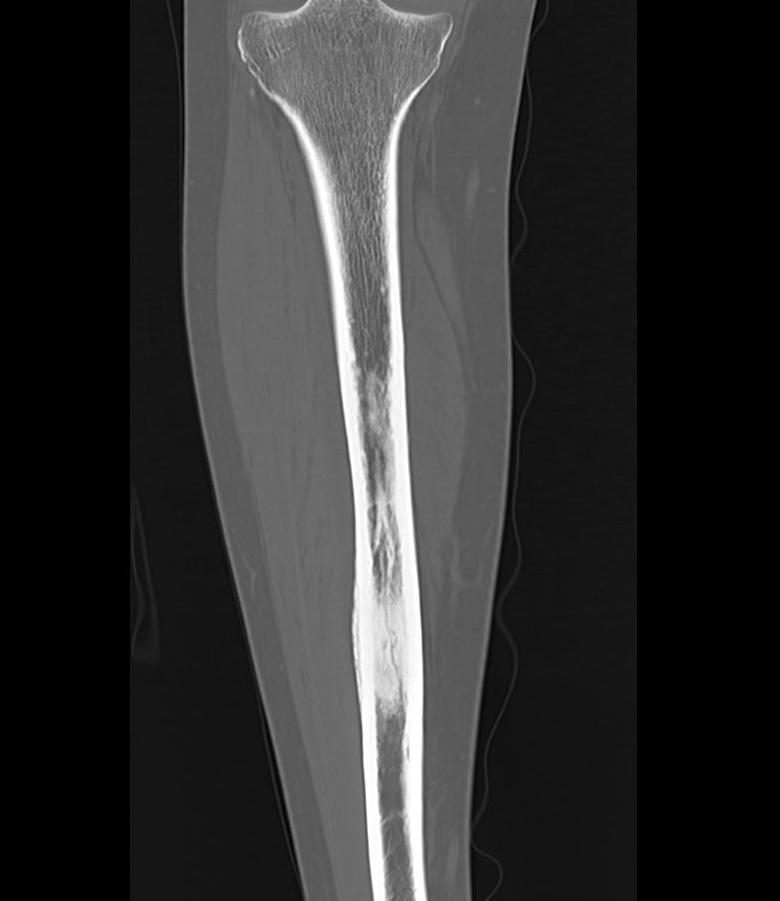
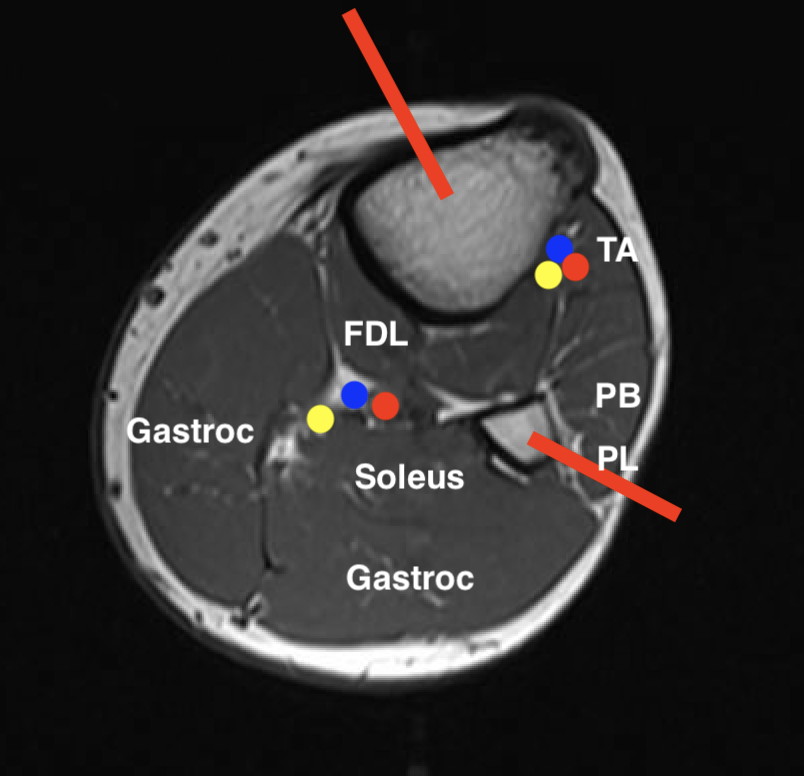
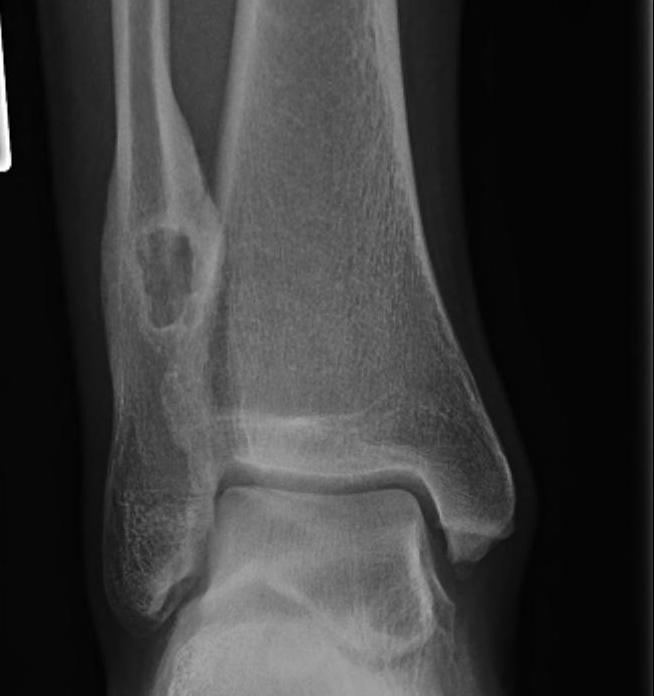
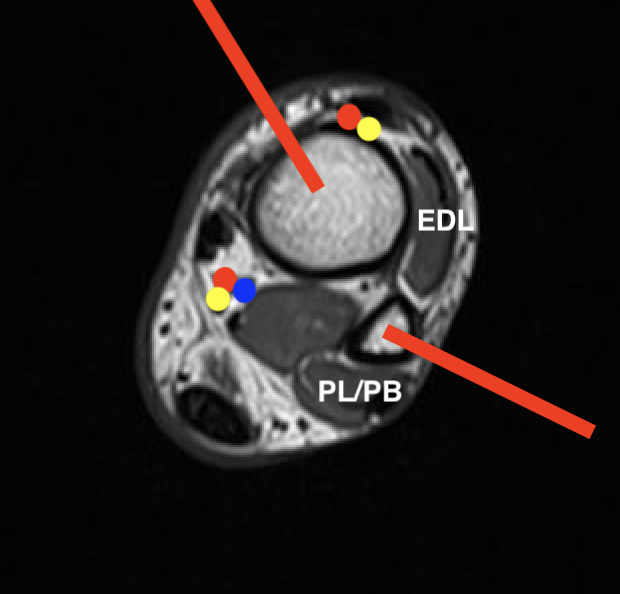
Leg
1. Proximal posterior compartment soft tissue tumour
- medial to tibia
- preserve anterolateral compartment
2. Proximal anterolateral compartment soft tissue tumour
- direct approach through tibialis anterior
- will likely not be able to preserve CPN
Talus
1. Head and neck
- medial approach between Tibialis anterior and Tibialis posterior
2. Body
- lateral Ollier's approach between Peroneus tertius and Peroneus brevis
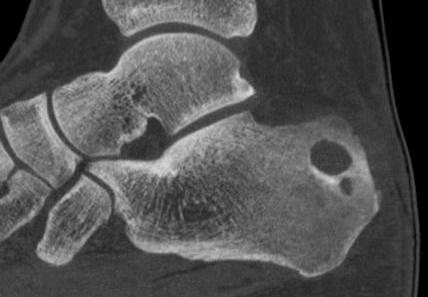
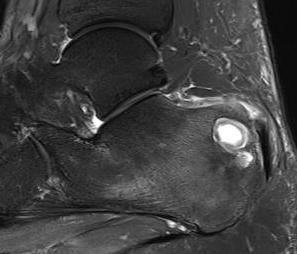
Calcaneum
Direct lateral approach
Foot
| Navicular / Medial cuneiform | Direct medial |
| Cuboid | Direct lateral |
| Intermediate cuneiform |
Between EHL and EDC Away from dorsalis pedis |
| Lateral cuneiform | Lateral to EDC |
| Metatarsals / phalangeals | Dorsal approach |
| Soft tissue tumour | Medial or lateral as required |
Pelvis
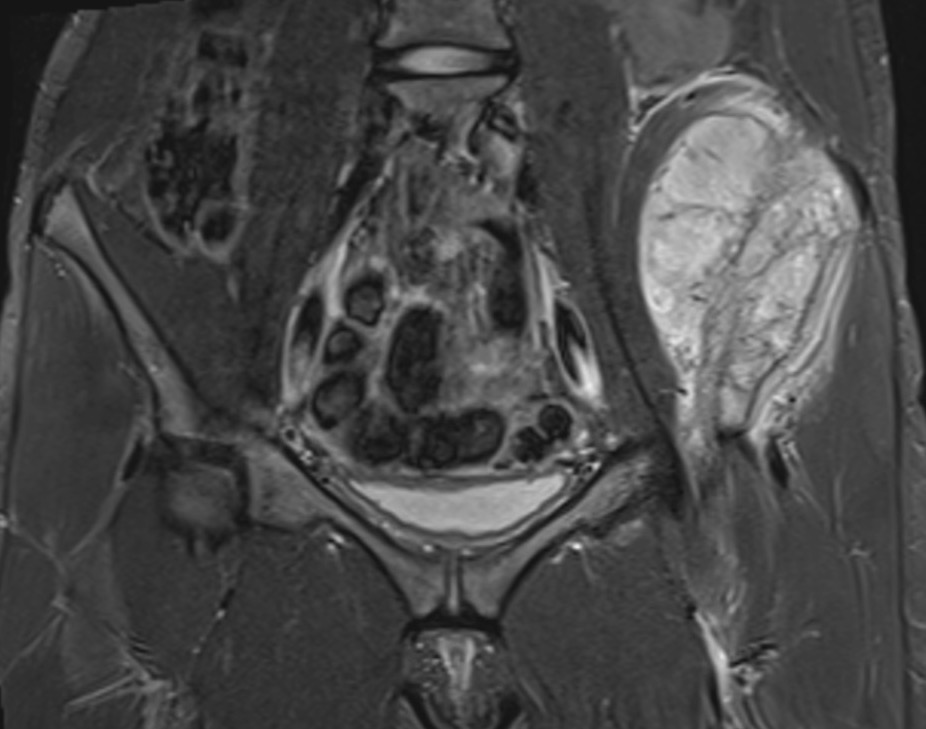
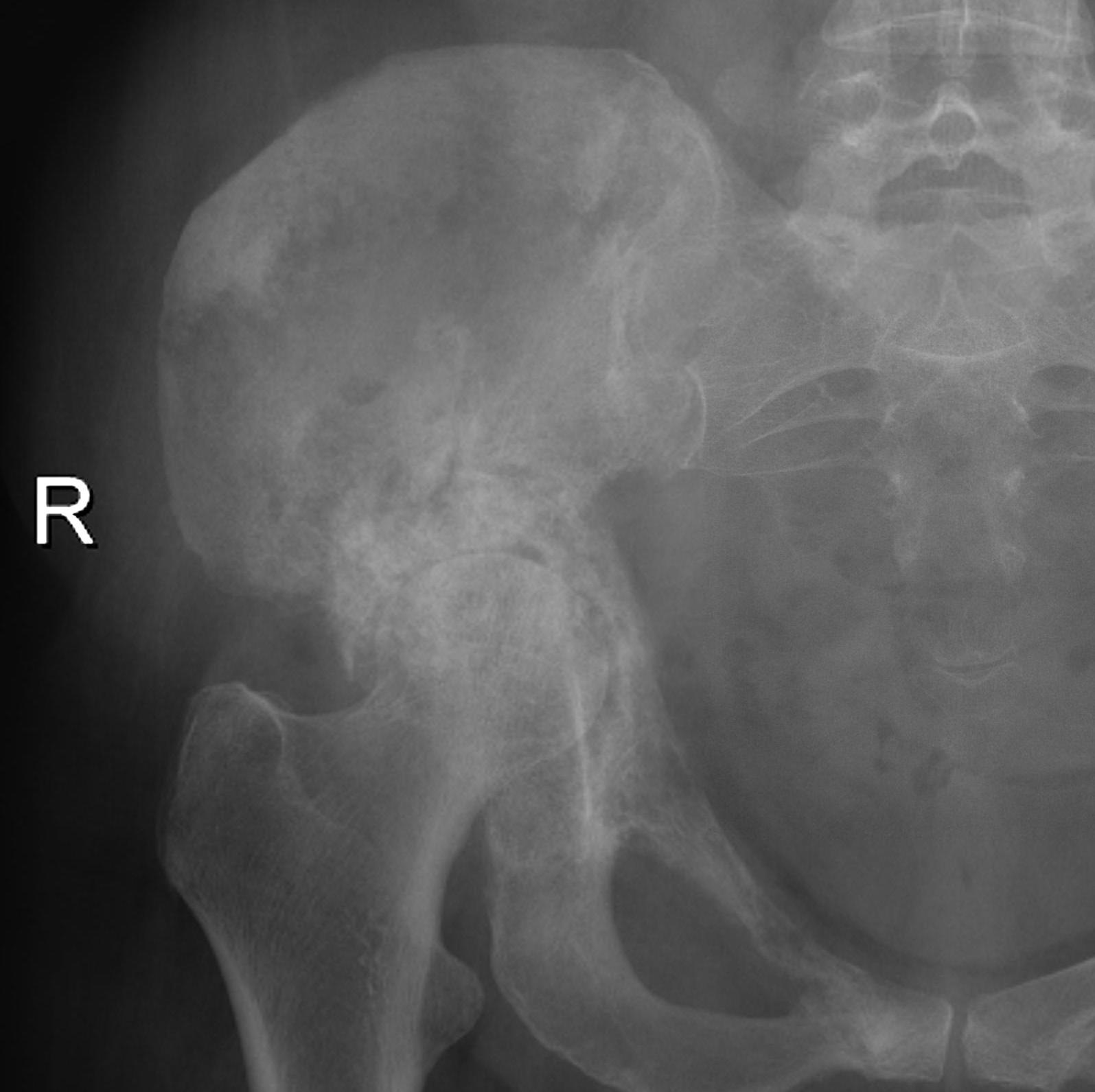
| Iliac crest | Ilioinguinal approach |
| Anterior column | Watson - Jones through G medius |
| Posterior column | Kocher - Lagenbeck through G maximus |
| Pubis | Pfannenstiel approach |
| Ischium | Posterior approach |
| Sacrum | Direct posterior approach |
Upper Limb
Humerus
1. Proximal humeral bony tumour
- direct lateral
- through deltoid muscle
- never deltopectoral (condemns patient to forequarter amputation)
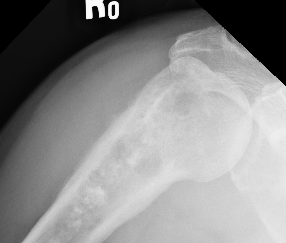
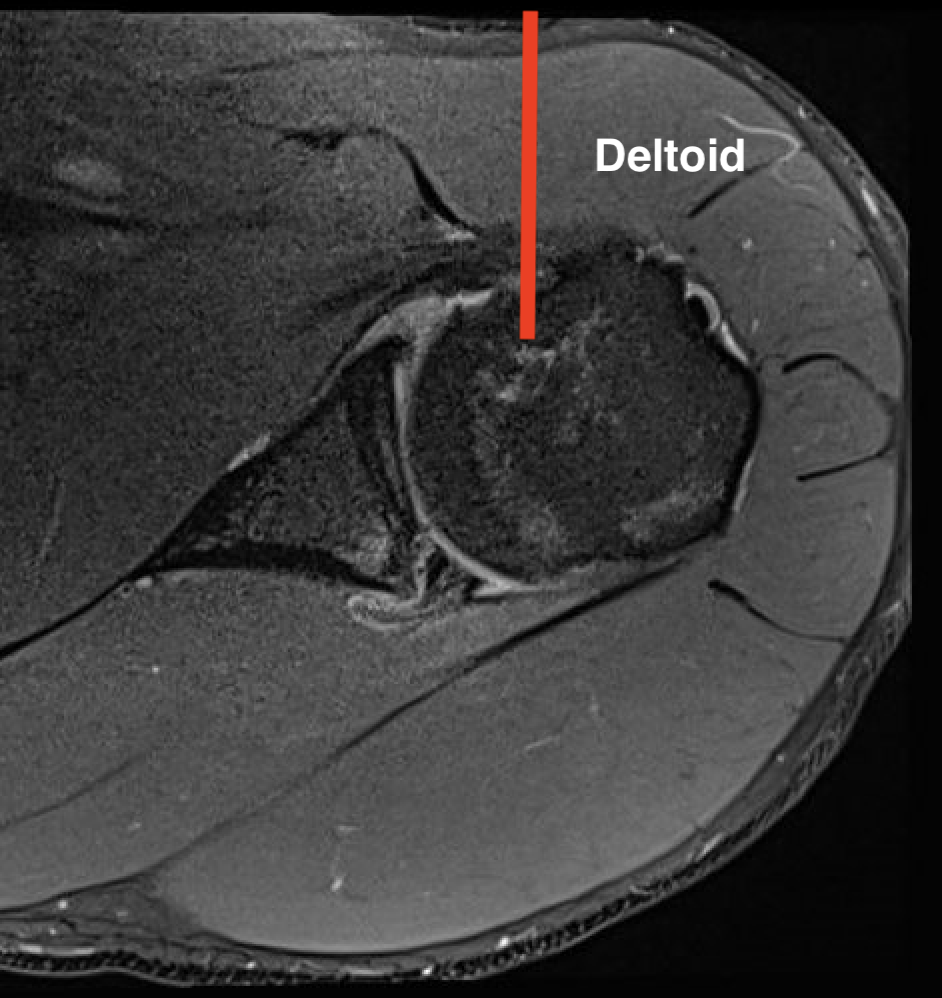
2. Shaft
- modified Henry
- lateral approach
- proximal: through deltoid
- distal: posterior to biceps, through brachialis
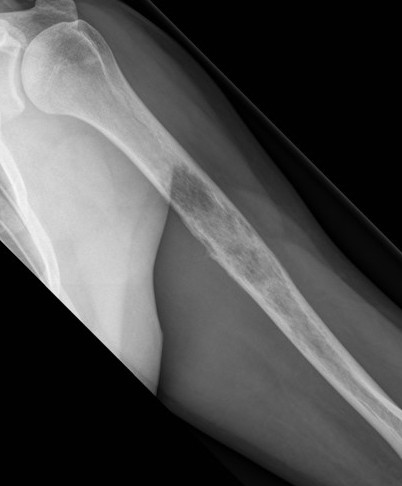
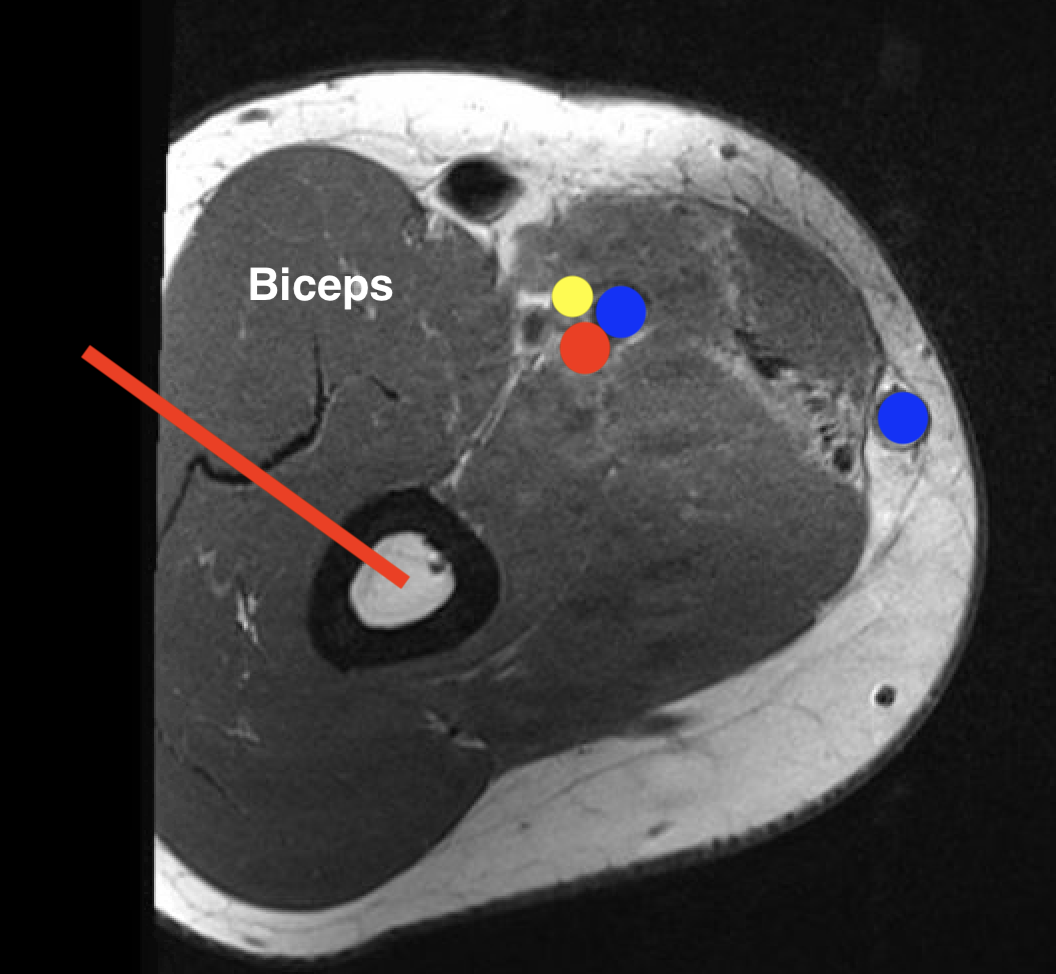
3. Distal humerus bony tumour
- lateral longitudinal to capitellum
- medial approach to trochlea
- both through brachialis
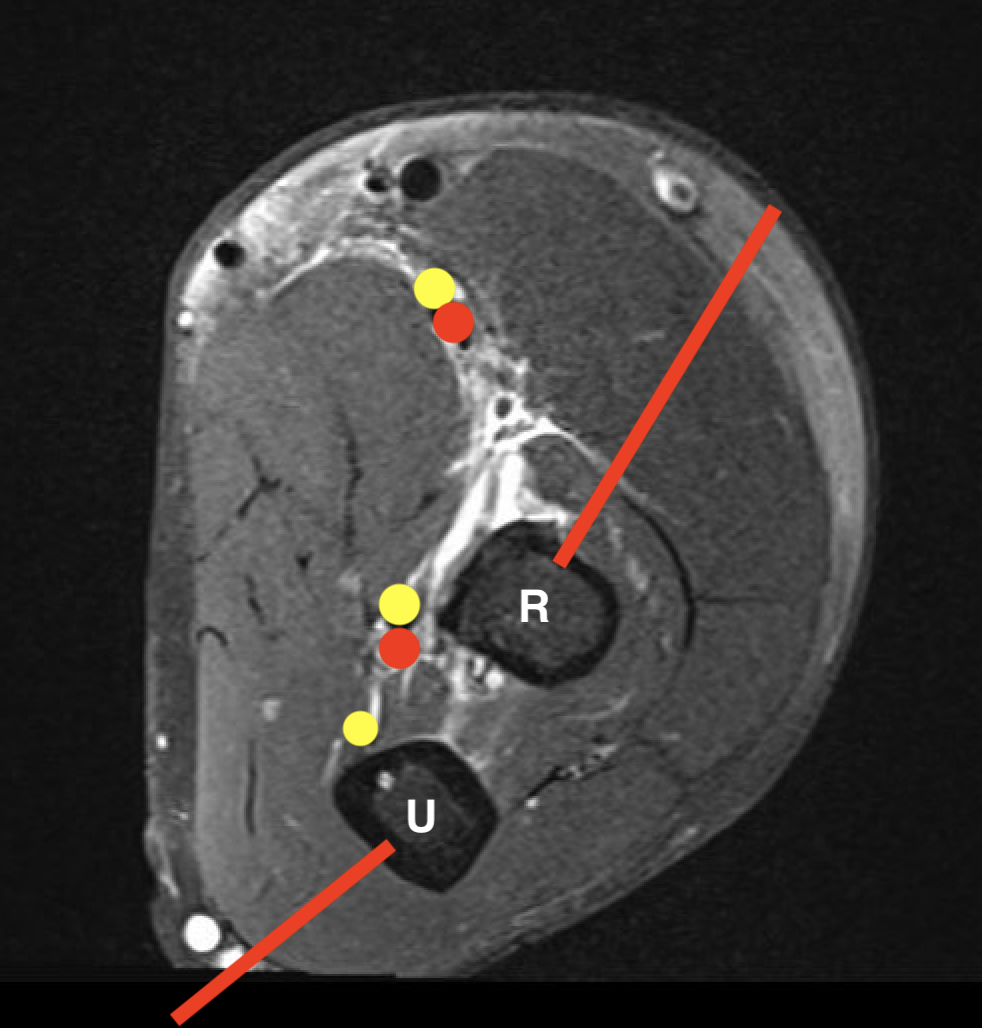
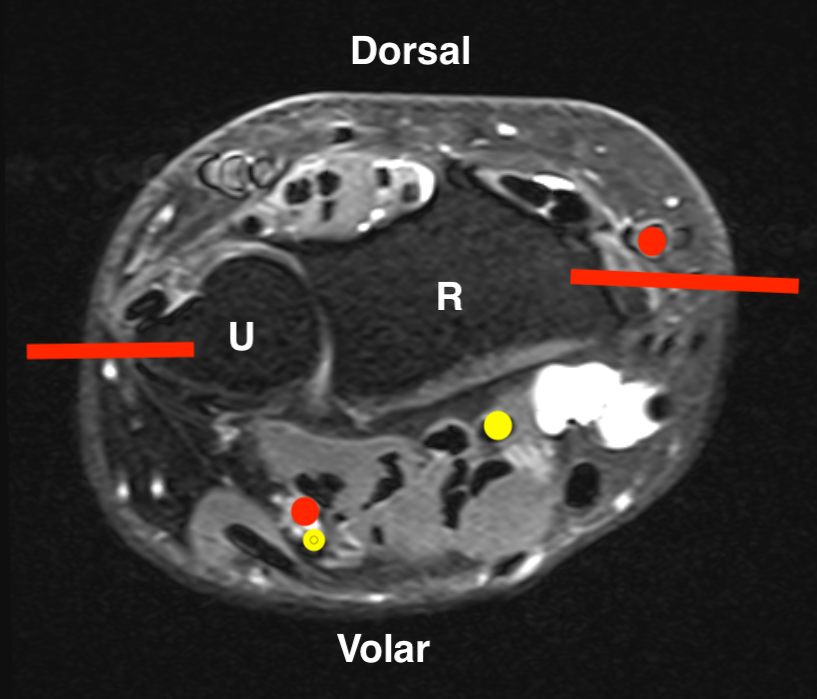
Radius and Ulna
| Radius | Ulna |
| Proximal - posterolateral | Olecranon - direct posterior |
| Shaft - direct lateral | Ulna shaft - direct medial |
| Distal radius - direct lateral |
Wrist / Hand
Carpus / metacarpal / phalanges - dorsal approach
Clavicle
Clavicle - direct subcutaneous
Scapula
Acromion - deltoid split
Spine - transverse approach
Body - Judet posterior approach
Glenoid - posterior approach, through Teres major
Coracoid - deltopectoral approach
