Definition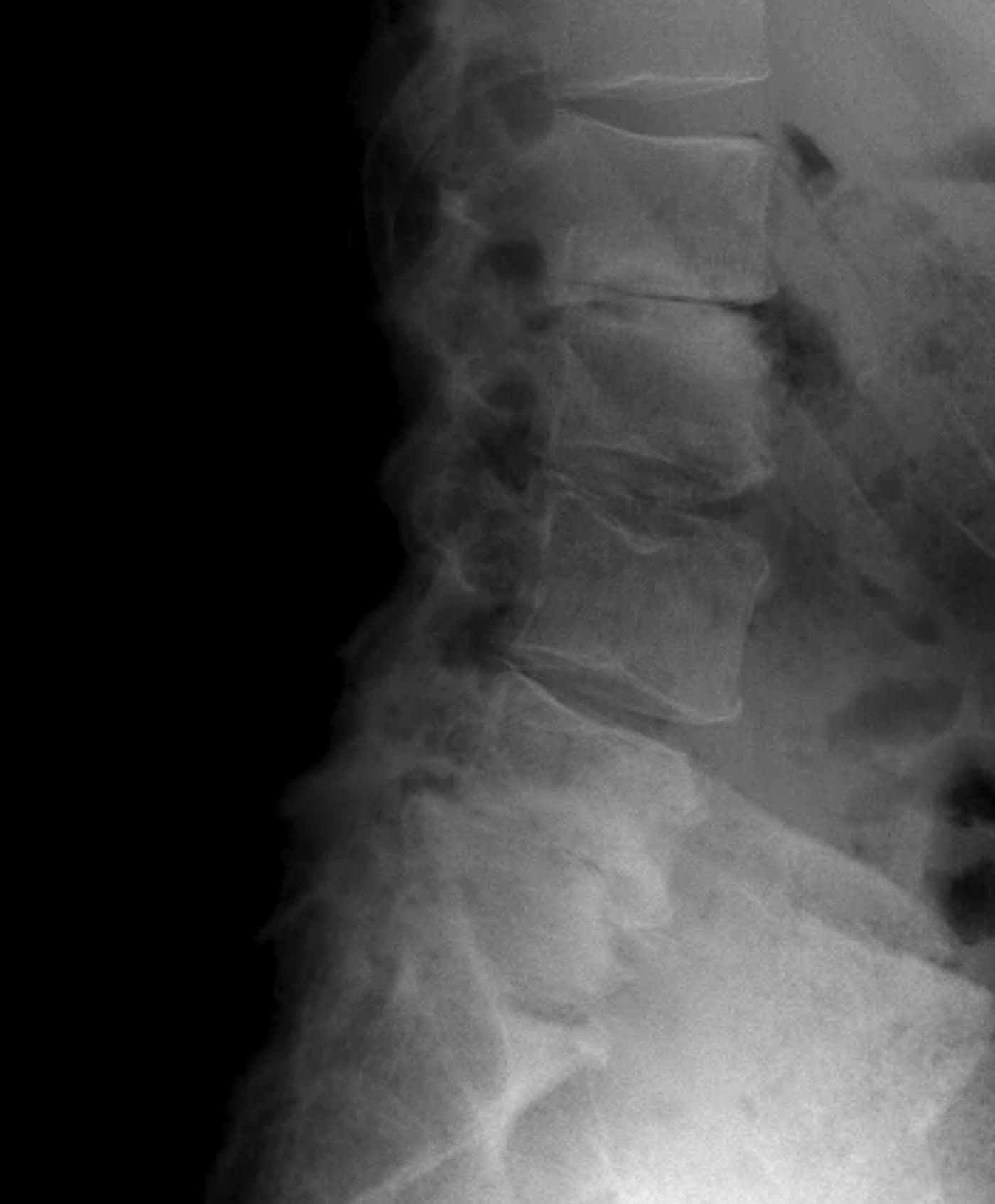
Lumbar spondylosis
- disc degeneration causing arthritis / lower back pain
Discogenic lower back pain
Anatomy
Annulus fibrosis
- outer aspect of disc
- type I collagen
- fibres continuous with endplate & ALL/PLL
- provides tensile strength to contain NP
Nucleus Pulposus
- water + type II collagen + PG
- semifluid gel
- turns solid as ages and becomes brown
- Keratan : Chondroitin ratio increases as age
Epidemiology
100% at autopsy > 90 years
- males > females and earlier
Brinjikji et al AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2015
- systematic review of incidence degenerative change on CT / MRI by age
- disc degeneration:
- disc bulge:
- disc protrusion:
Aetiology
Unknown in 90%
Associations
- heavy labour
- obese & tall
- driving / vibration
- smoking
- previous back injury
Pathogenesis
1. Dysfunction (15 - 45 years)
Disc degenerates with age / dessication
- concentration of PG declines
- decrease number of chondrocytes
- decrease water content
- collagen fibres thicker in cross section
Lose ability to resist torsional loads
- circumferential & radial tears in disc
- localised synovitis of facets
2. Instability (35 - 70 years)
- disc herniation
- resorption of disc
- degeneration of facet joint with capsular laxity / subluxation & erosion / osteophytes
3. Stabilisation (>60 years)
- ankylosis of discs & facets
Symptoms
Lower back pain
- usually worse with activity
- especially bending & lifting
Maybe referred to
- buttocks / posterior thigh / groin
Signs
General
- loss of lordosis
- decreased ROM, especially flexion
X-ray
Unexpected finding in 1:2500
- infection, fracture, tumour
Disc degeneration
- disc space narrowing
- vertebral sclerosis
- osteophytes
MRI
Disc
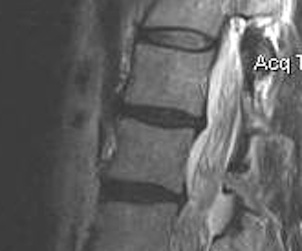
Normal disc / bright T2 signal
Degenerative disc / dark T2
Very sensitive
- 30% of asymptomatic patients < 60 years have abnormality
- 60% > 60 years have abnormality
Modic End Plate Changes
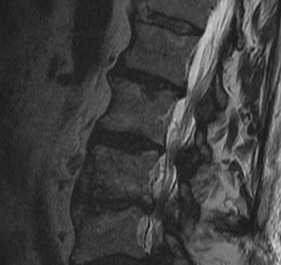
Classification of bone marrow changes in bone marrow adjacent to vertebral end plates
Type 1: High on T2 / Low on T1
Type 2: High on T2 / High on T1 (lipid changes)
Type 3: Low on T2 and T1 (sclerotic)
Discography
Aim
- confirm isolated disc degeneration responsible for pain
- must check disc below and disc above
Technique
- inject contrast under pressure / LA and II guidance
- look for dye leak
- look for reproduction of symptoms
Alternative / Discoblock
- inject LA
- positive test if relieves pain
Results
Ohtori et al Spine 2009
- only operative on patients with positive discogram or discoblock
- 15 patients in each group
- treated with anterior discectomy and interbody fusion
- significantly improved results in discoblock group
Natural History
90% lower back pain resolves < 2/12
- 10% chronic
- prognosis poor if pain > 6/12
DDx
Traumatic
- crush fracture / isthmic spondylolisthesis
Infective
- vertebral osteomyelitis / discitis / epidural abscess
Tumour
- Benign (Haemangioma / OO / OB / EG / Giant Cell / ABC)
- Malignant (Chordoma / Myeloma / Metastasis)
Inflammatory
- AS / Reiter's / Psoriatic arthritis / Enteropathic disease
Neurogenic
- primary pathology of nerve roots (Neurilemmoma, neurofibromata, ependymoma)
Viscera / Vascular
- Pelvic viscera / retroperitoneal cancer
- AAA / Superior gluteal artery claudication / Claudication 2° PVD
Management
Non-operative Management
Acute LBP
Initial
- rest 2 days
- local measures - massage / local NSAIDs
- pain relief - acetominophen / NSAIDS
Once pain settles
- exercise
- general fitness important
- core strengthening
- brace no benefit
Chronic LBP
Back School / Structured rehab programme / Lifestyle modification
Relaxation \ Exercise
Avoid narcotics
Epidural Steroids
Indication
- lumbar pain without HNP / radiculopathy
Manchikanti et al Pain Physician 2010
- HCLA epidural injections
- 86% significant pain relief at 12 months
Operative Management
Indications
Unremitting pain & disability > 1 year
MRI single level disc degeneration
Options
1. PLF / Posterolateral Fusion +/- instrumentation
2. Instrumented PLIF / Posterolateral Interbody Fusion
3. ALIF / Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
4. Disc Replacement
PFL
Concept
- decortication of pedicles / lamina / transverse process
- bone graft applied
- instrumentation added to improve fusion rate
Advantage
- high fusion rate
- no risk of interbody graft / cage migration
- low risk neural injury
Results
Fritzell et al Spine 2001
- RCT of surgical treatment v non surgical with 2 year follow up
- back pain reduced 33% to 7%
- return to work 36% v 13%
Fritzell et al Spine 2002
- RCT of PLF v instrumented PLF v PLIF
- no significant difference in reduction in pain and disability
- complications 6% v 16% v 30%
- fusion rate 72% v 87% v 91%
Instrumented PLIF
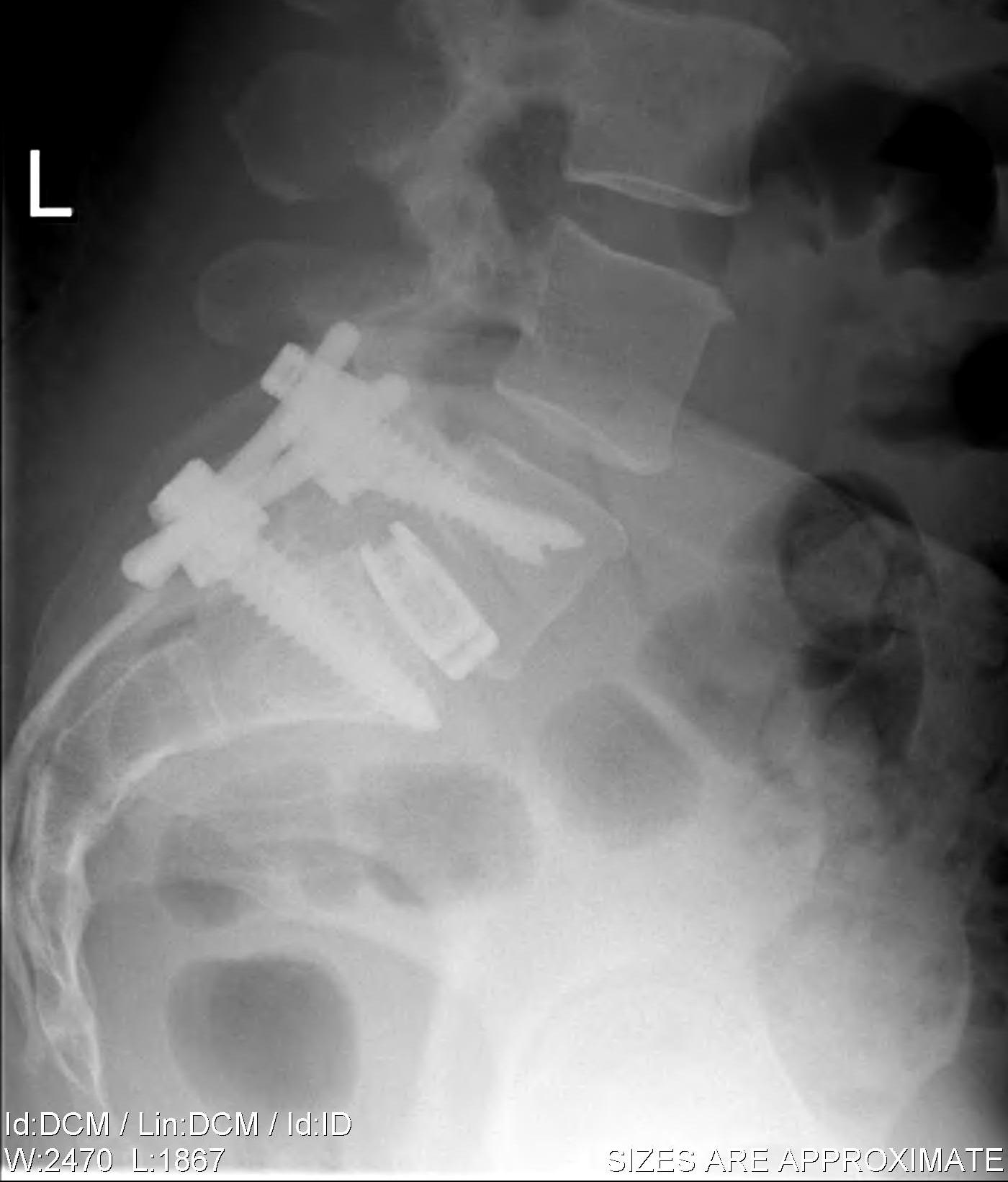
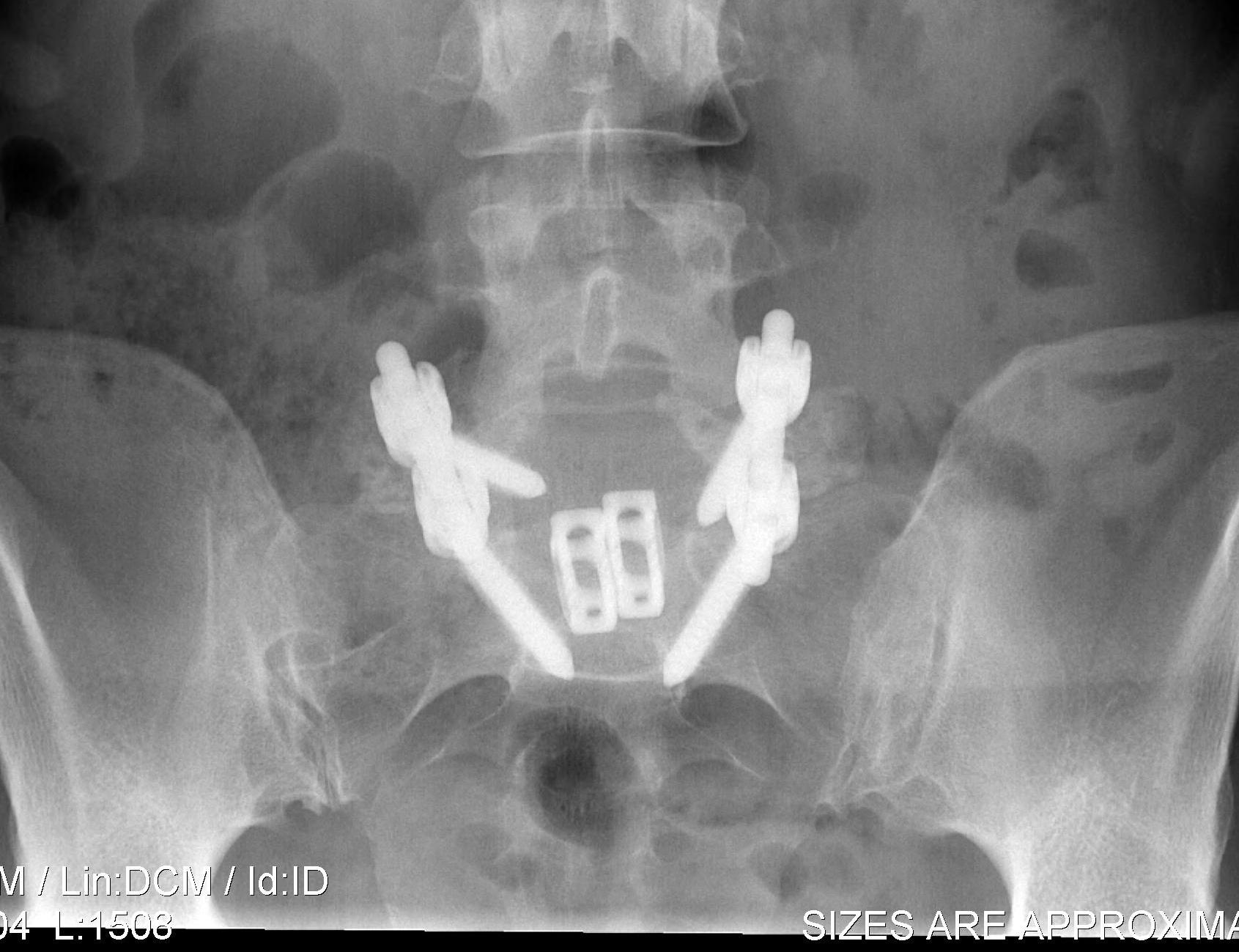
Principles
- wide post decompression and removal of entire disc
- graft / fusion cage placed between vertebral bodies
- 360o fusion (PLF + interbody)
Advantages over PLF
- excise disc & decompress nerve roots
- disc height restored with graft decompressing foramina vertically
- fusion of anterior column / increased fusion surface / site of arthrodesis compressed
Disadvantages
- wide post decompression needed / newer minimally invasive techniques
- risk of canal compromise by graft
Results
Leufven et al Spine
- 29 patients treated with PLIF
- fusion in 27/29
- excellent results in 31% and good in 21%
- fair in 21% and poor in 27%
ALIF
Concept
- anterior approach + complete discectomy and graft
Results
Penta et al Spine
- 108 patients with ALIF at 10 years
- only 34% good or excellent
- not related to fusion rates
- psychological rating intially and at review correlated with outcome
Disc Replacement
Concept
- maintain small degree of motion
- prevents adjacent level degeneration
Results
Herkowitz et al JBJS Am 2006
- RCT of disc replacement v ALIF
- 304 patients with single level disease L5S1 or L45
- 2 year follow up
- clinical success 64% in disc replacement v 56% ALIF
- better ROM and restoration disc height in disc replacement
Harrop et al Spine 2008
- systemic review looking at adjacent level degeneration in lumbar fusion v disc
- radiographic degeneration 34% in fusion v 9% in disc replacement
- symptomatic degeneration 14% in fusion v 1% in disc replacement
Complications
Mortality 0.2%
Infection 1.5%
DVT 4%
PE 2%
Neural injury 3%
Instrument failure 7%
Failed back surgery syndrome
