Braces
1. Motion Control
2. Spinal Realignment
3. Trunk Support
4. Weight Transfer
Soft Collar
Cheap & Comfortable
- ineffective
- allows 70% Flexion Extension / 80% Rotation / 90% Lateral bend
Philadelphia Collar
Better than soft collar but less comfortable
- allows 35% Flexion Extension / 40% Rotation / 60% Lateral bend
- excellent immobility in acute situation when combined with sandbags & forehead tape
SOMI Brace
Sterno-Occipital Mandibular Immobilizer
- effective control C1/2 & C2/3
- allows 30% Flexion Extension / 30% Rotation / 60% Lateral bend
Yale Brace
Cervico-Thoracic Brace
- Philadelphia Collar but with chest extension & strap
- best of conventional braces
- allows 10% Flexion Extension / 50% Rotation / 25% Lateral bend
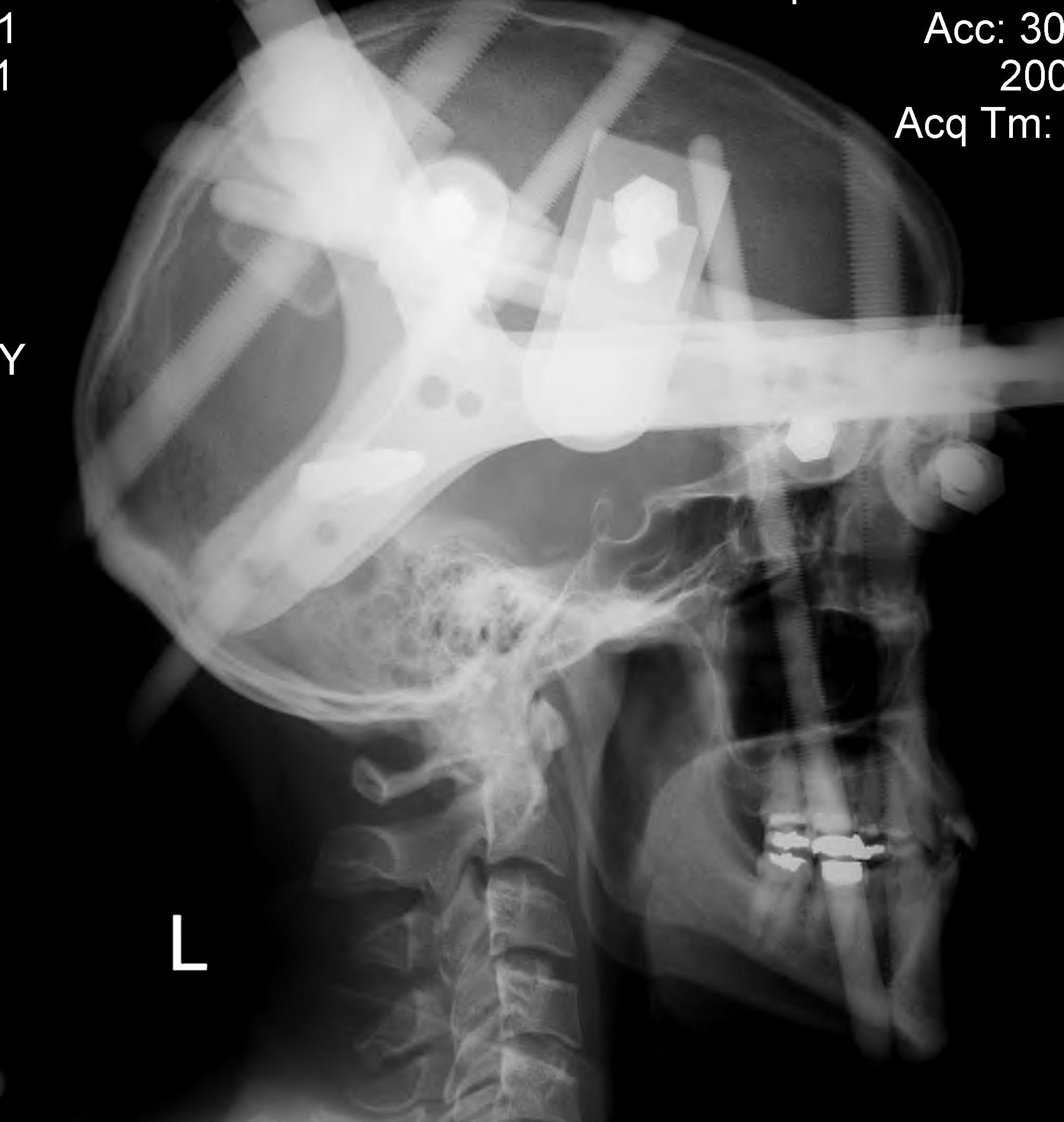
Halo-Thoracic Brace (HTB) / Halo Vest
Indication
External immobilization for upper cervical spine injuries
- occipital condyle fractures
- stable C1 / atlas fractures
- C2 fractures include odontoid fractures
- C1 C2 instability
Less effective for subaxial spine
Contra-indications
Elderly
Horn et al J Neurosurg Spine 2006
- 53 patients > 70 treated with HTB
- 6 patients (14%) died of respiratory distress related to HTB
- compared HTB in 129 old patients (average age 80)
- 289 young patients (average age 40)
- mortality rate 40% in old versus 2% in young
Effectiveness
Restricts atlanto-axial flexion / extension by 75%
Banat et al Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2022
- systematic review of HTB in pediatric population
- high success rates with only minor complications
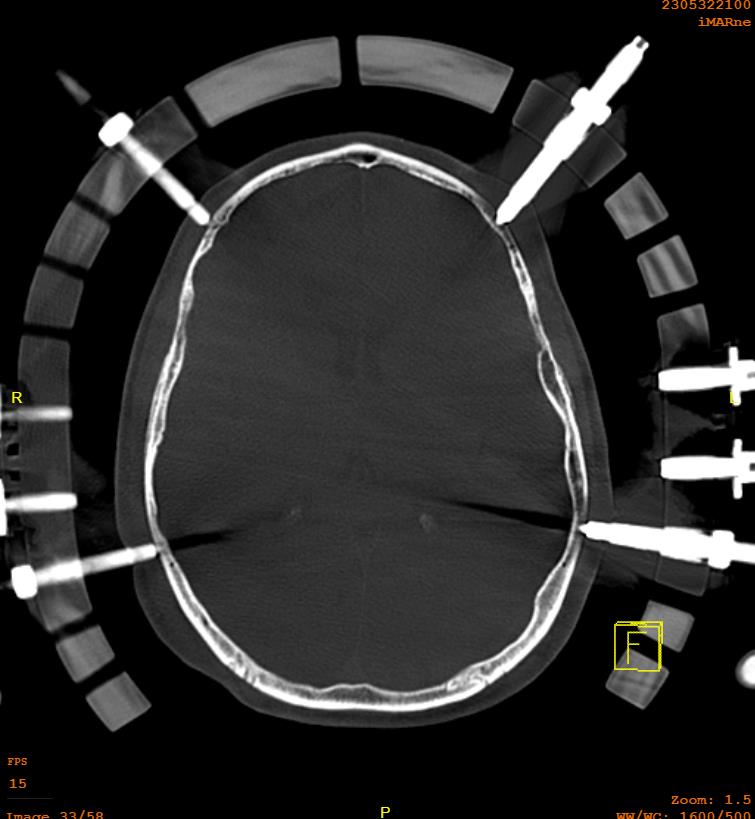
Pin safe zones
Frontal cranium
- above lateral 2/3 of the orbital rim / eyebrow
- 1 cm above top of ears
- medial to this zone is supraorbital nerve and frontal sinus
Technique
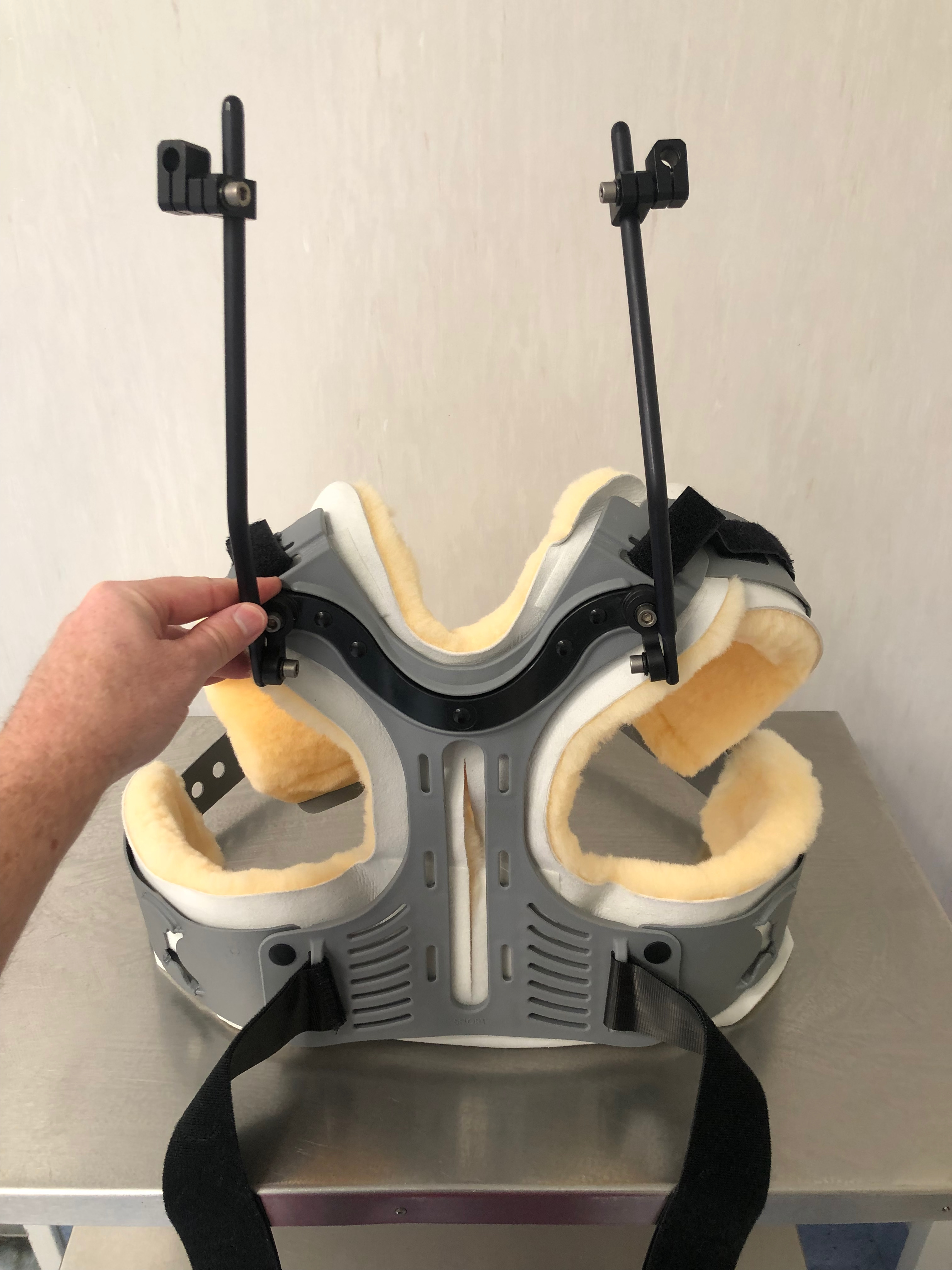

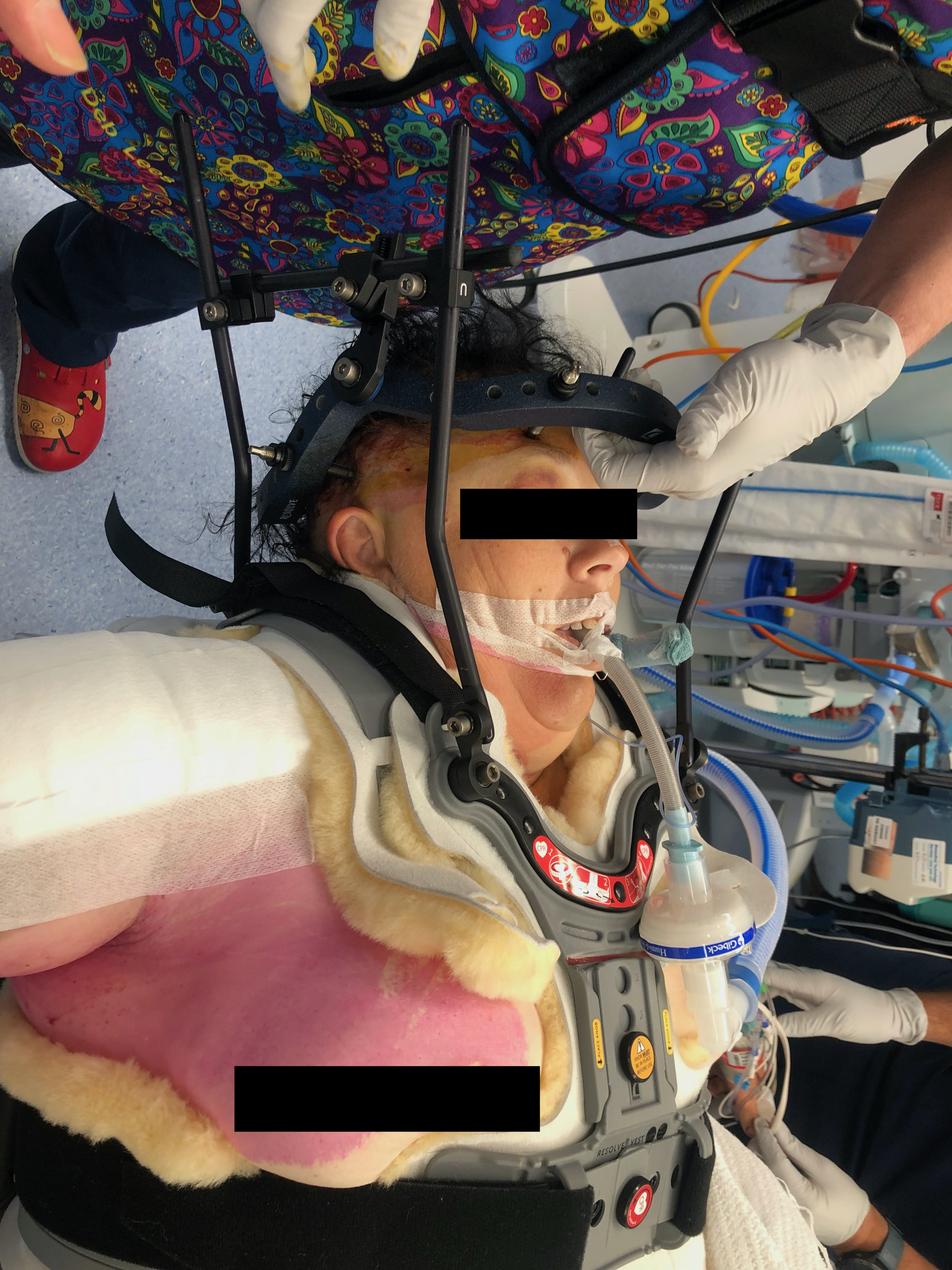
Vest
- roll patient on side in controlled manner
- fit posterior chest brace
- roll back, apply anterior chest brace, tighten
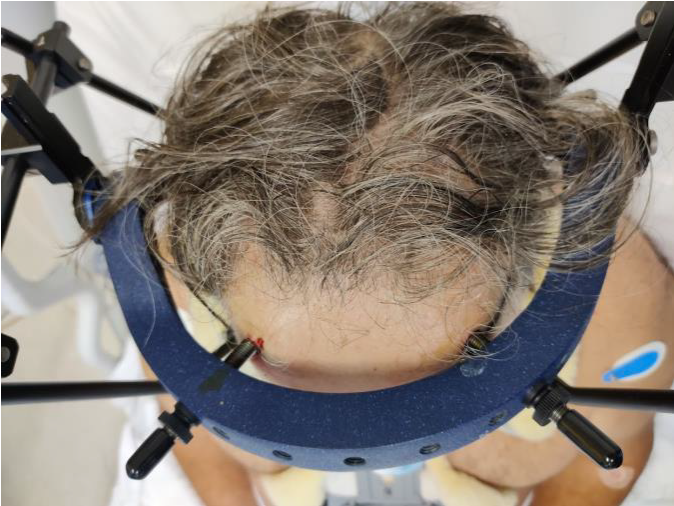
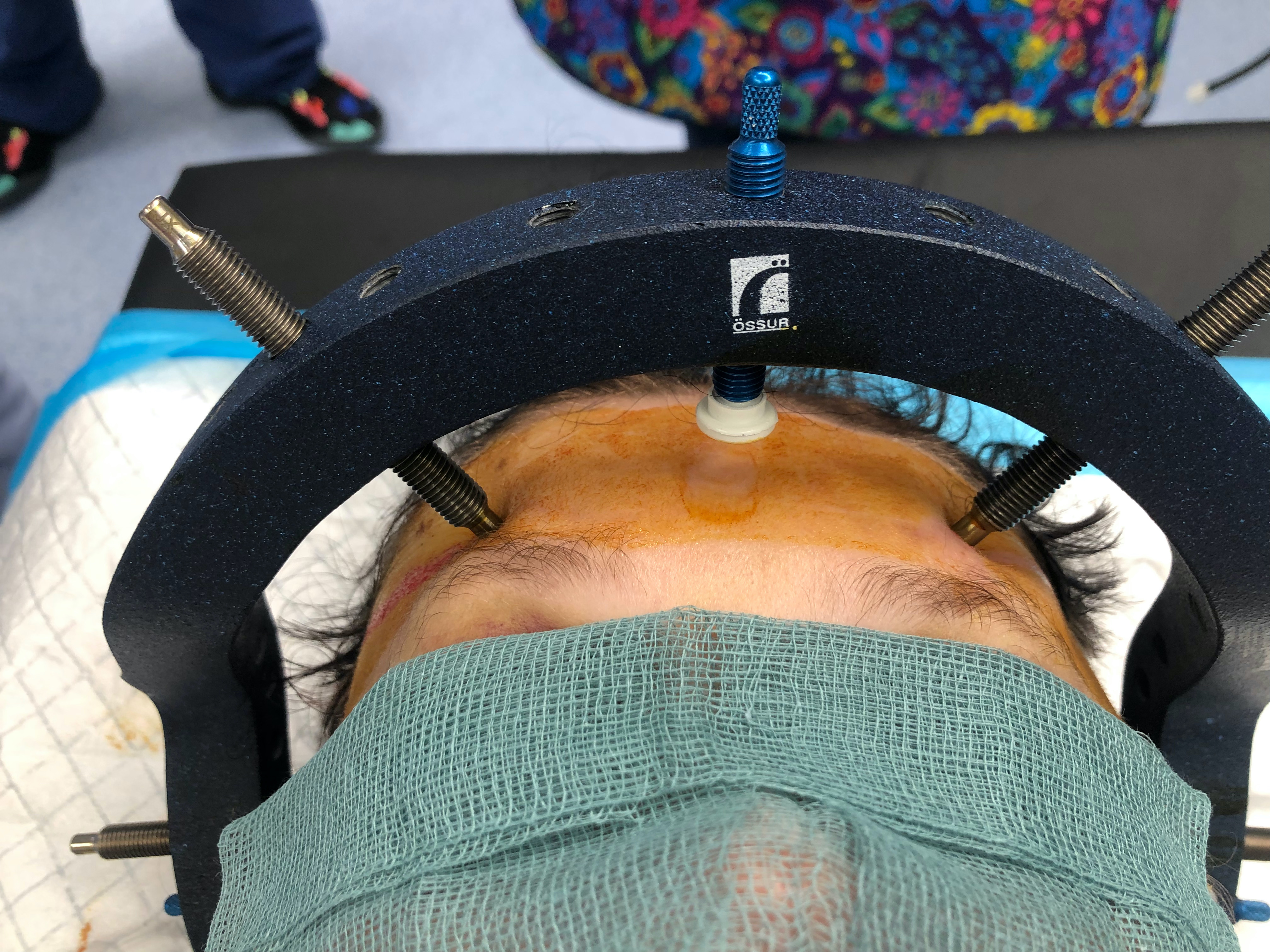
Halo
- size halo around maximum diameter of skull
- should have 1 - 2 cm gap from skull
- sits 1 cm above pinna and eyebrows
- 4 pins
- 2 above pinna, 2 above upper and outer eyebrow
- can shine torch through holes to mark sites of pins
- local anesthetic to sites
- must close eyes before supraorbital pins to avoid problems closing eyes
- tighten to 8 pounds / square inch
- often come with snap lock pins
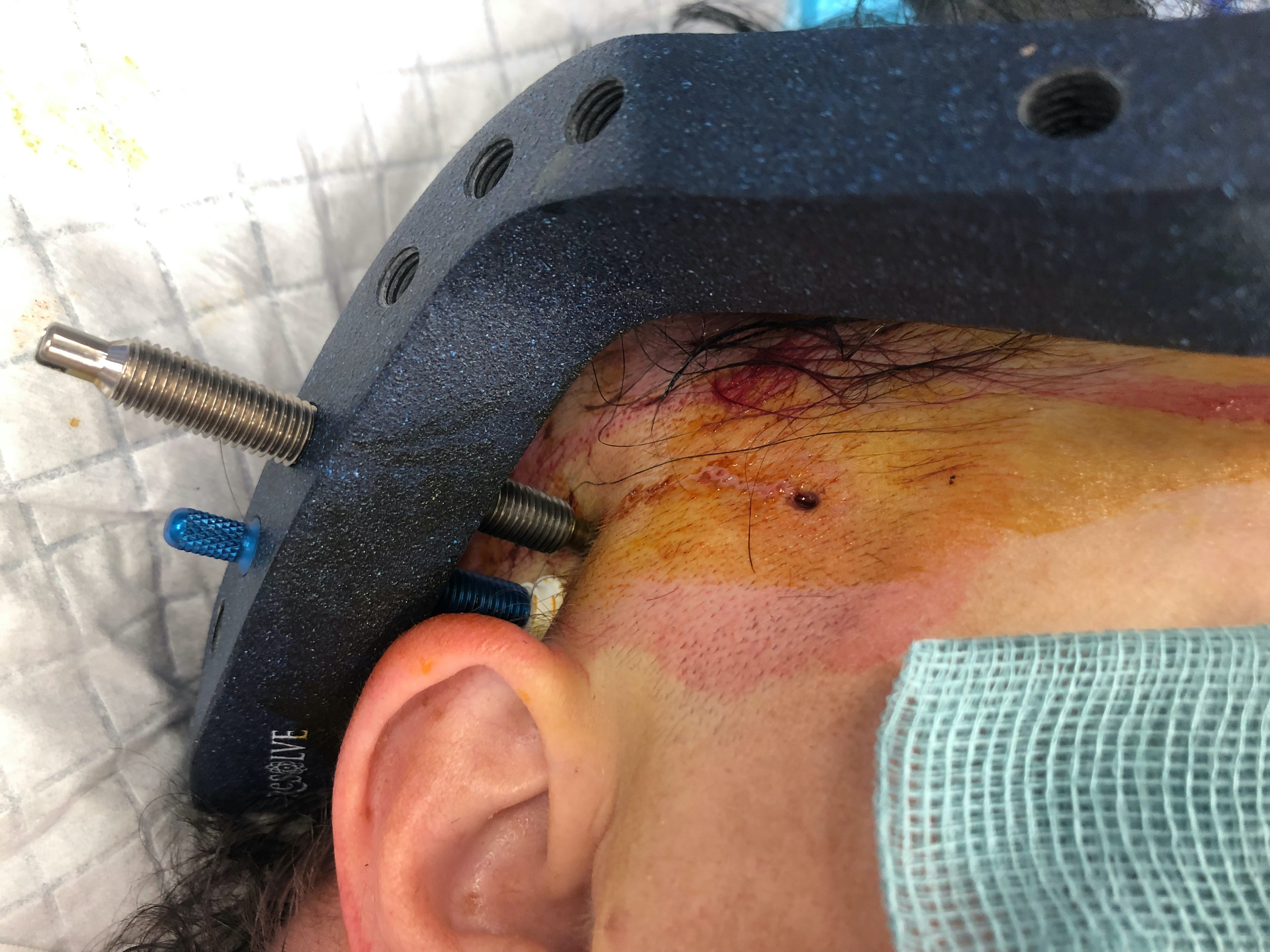
Complications
Malnik et al Br J Neurosurg 2021
- 67 patients mean age of 52 treated with HTB
- 25% pneumonia initial hospital stay
- 22% loose pins
- 18% pin site infections
Gardner Wells Tongs
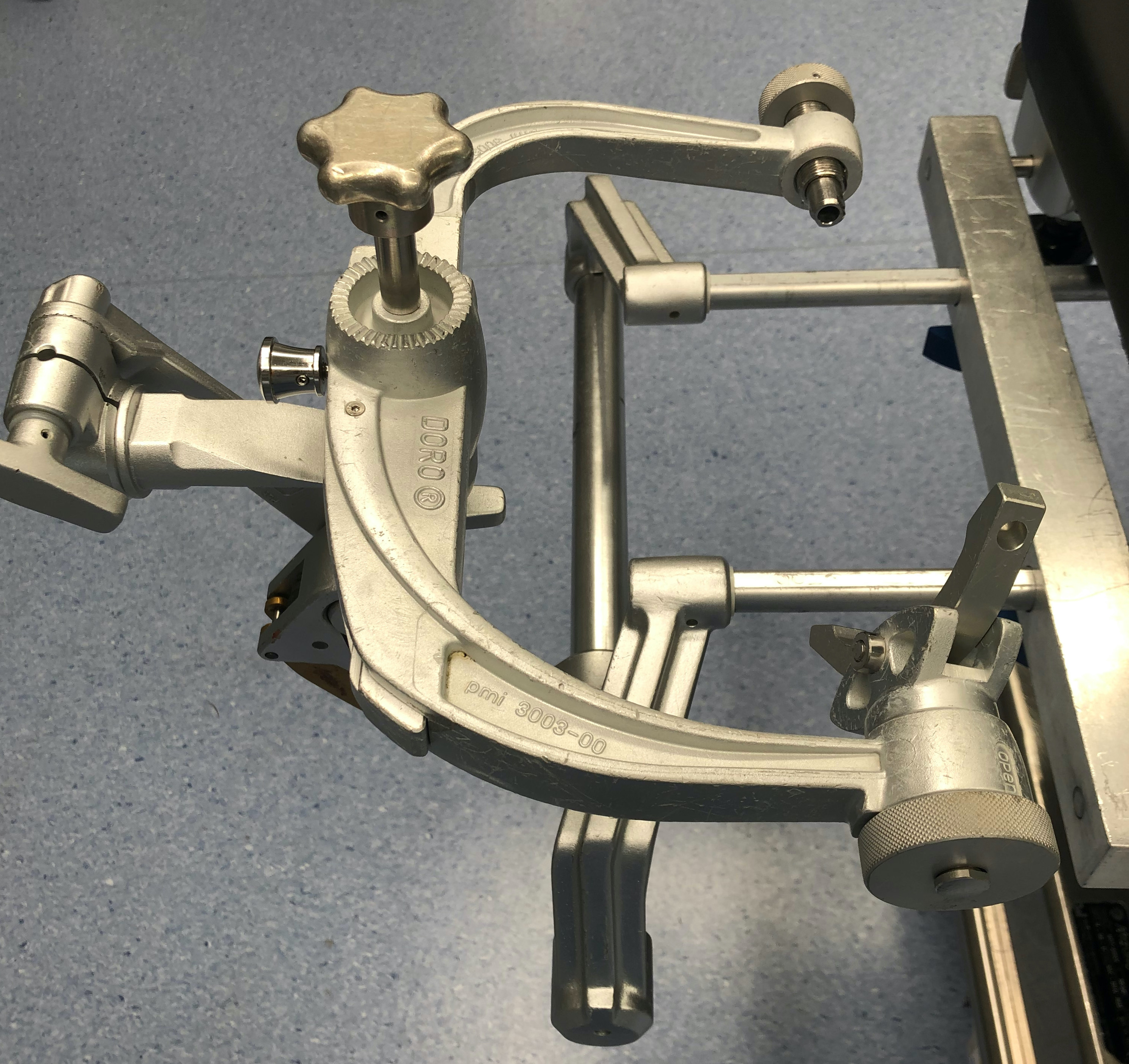

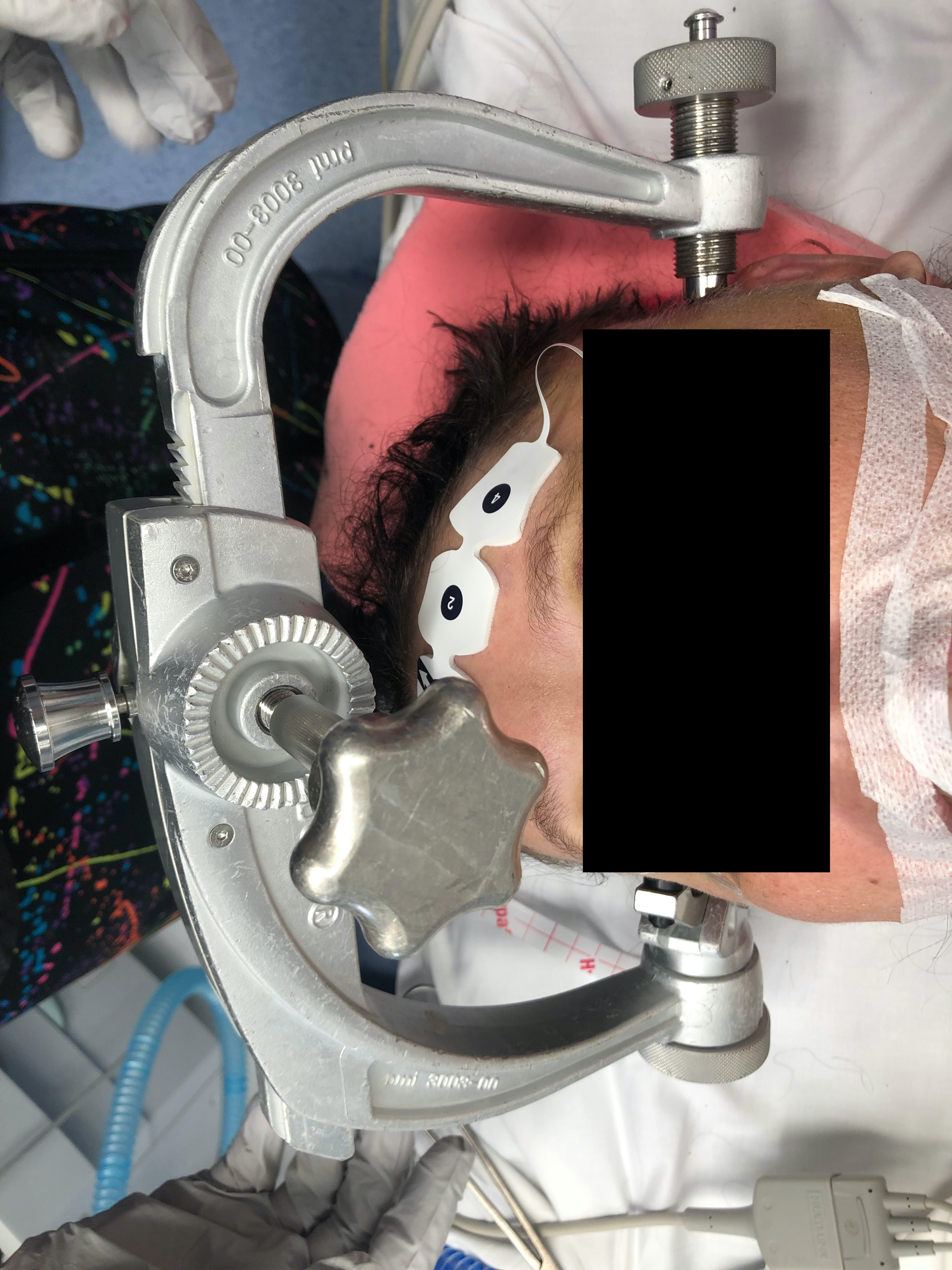
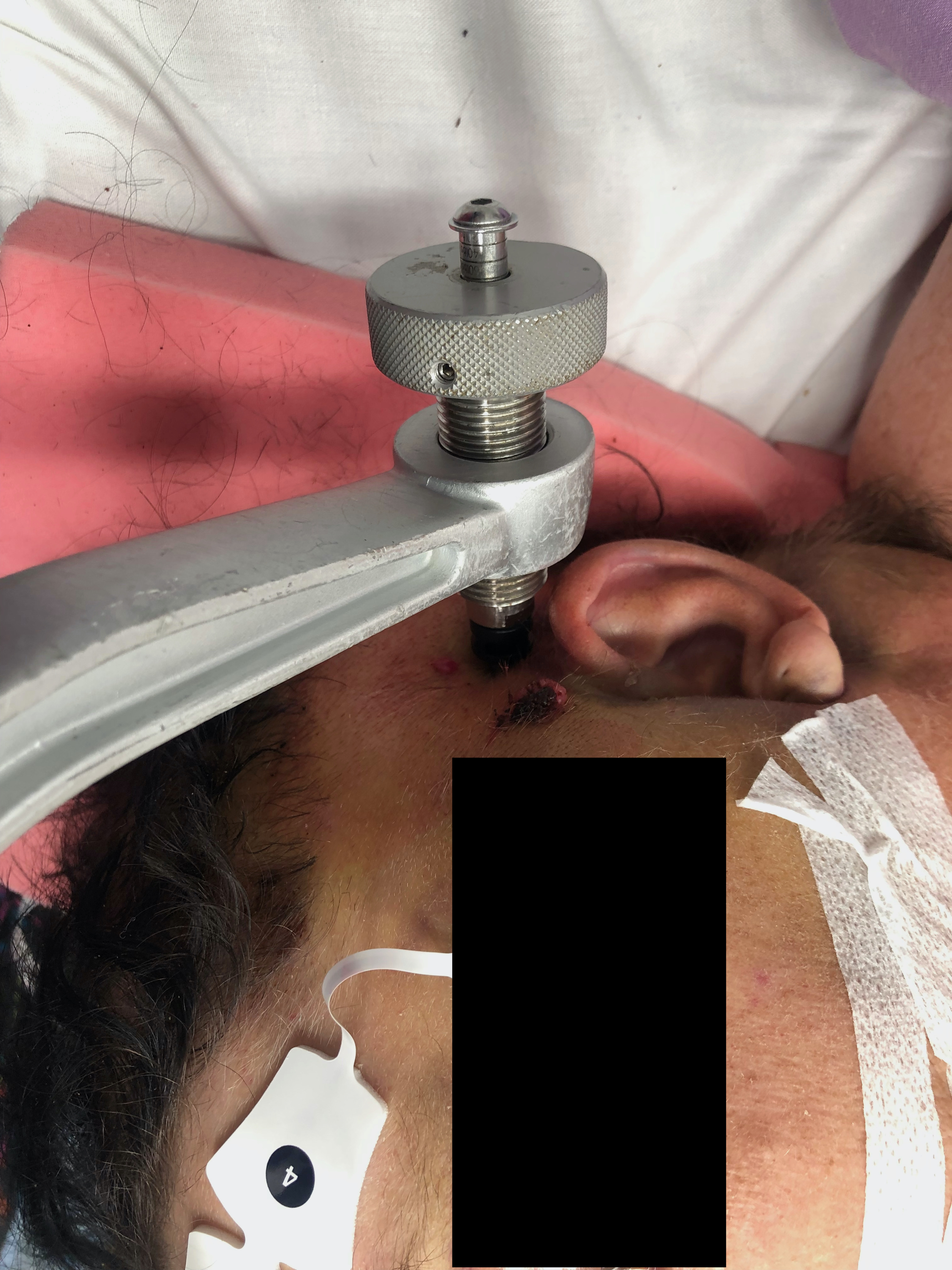
Indications
Cervical traction - i.e. rotatory atlanto-axial subluxation
Reduction of acute facet joint subluxations / dislocations
Patient positioning during spine surgery
Skeletal traction during deformity correction such as scoliosis surgery
Technique
Pin insertion sites as per HTB
Results
- complication rate generally low
- superficial infection, pin loosening, asymmetrical pin positioning
- major complication such as skull perforation, brain abscess rare
Thoraco - Lumbar Orthosis / TLSO
Types of TL Orthosis
1. TLSO
2. Three point brace
3. Moulded Body Jacket
CTLSO / Milwaukee
TLSO with neck brace
For lesion with apex above T8
