Definition
Inflammation and degeneration of the achilles tendon in the midsubstance 2 - 6 cm from insertion
Classification of Tendon Inflammation
1. Peritendonitis - inflammation of paratenon
2. Tendinopathy - combination of inflammation + tendinous degeneration
3. Combination
Anatomy
Triceps tendon
- medial and lateral gastrocnemius + soleus
- surrounded by paratenon which allows gliding and supplies nutrition
Insertion
- middle 1/3 calcaneal tuberosity
- 2 x 2 cm area
- 90o rotation distally
Retrocalcaneal bursa (x2)
- proper is between tendon and calcaneum
- superficial is between tendon and skin
Etiology
Elite and recreational athletes in running sports
Also seen in diabetics / obesity
Symptoms
Pain 2-6 cm proximal to insertion
Usually worse in morning and improves with exercise
- compared to insertional that worsens with activity
Examination
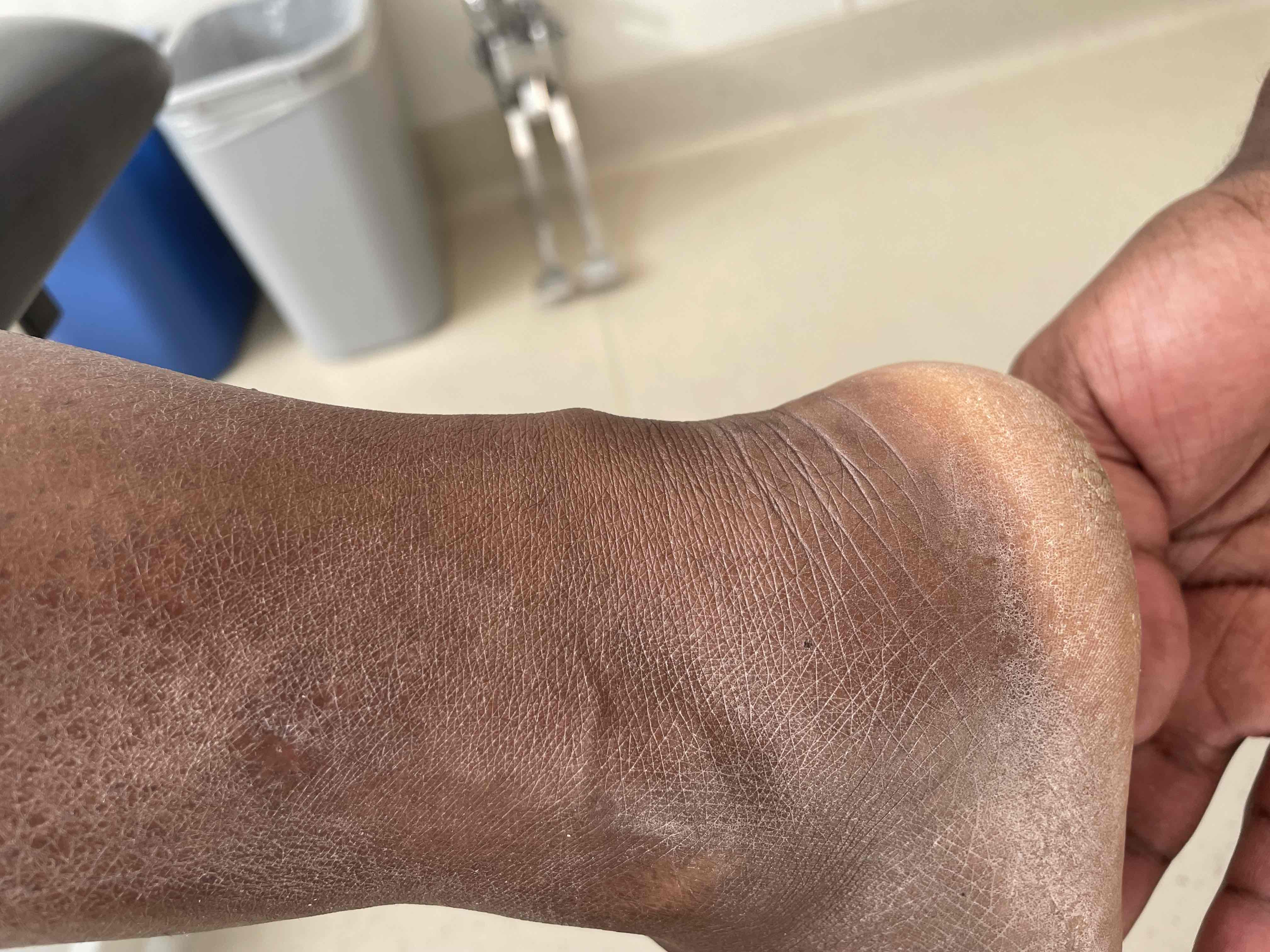
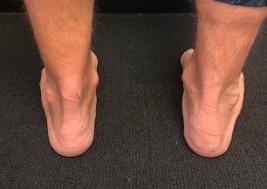
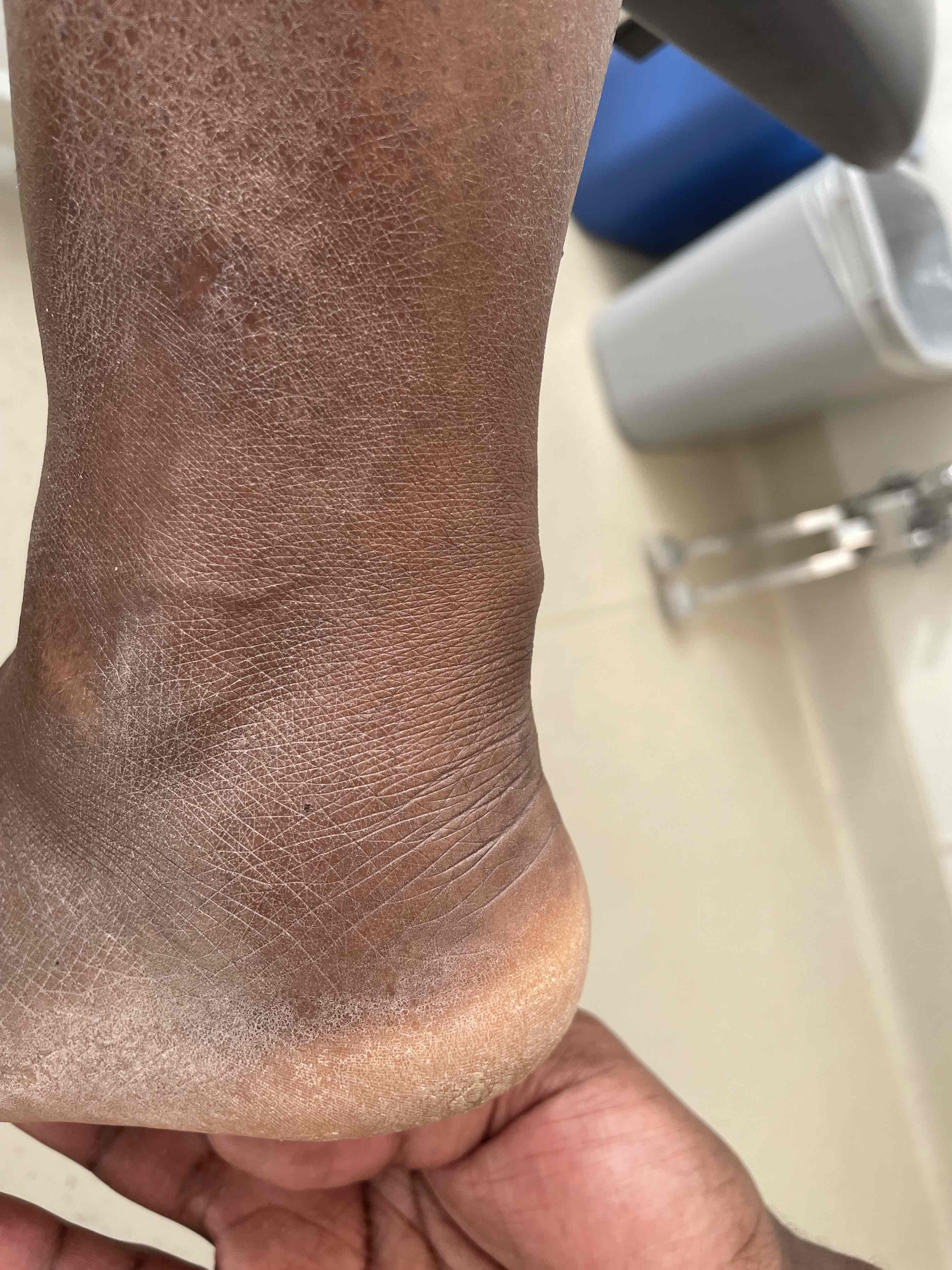
Localised tenderness mid tendon
Tendon may be palpably thickened
Pain with dorsiflexion and plantar flexion
Dorsiflexion may be limited
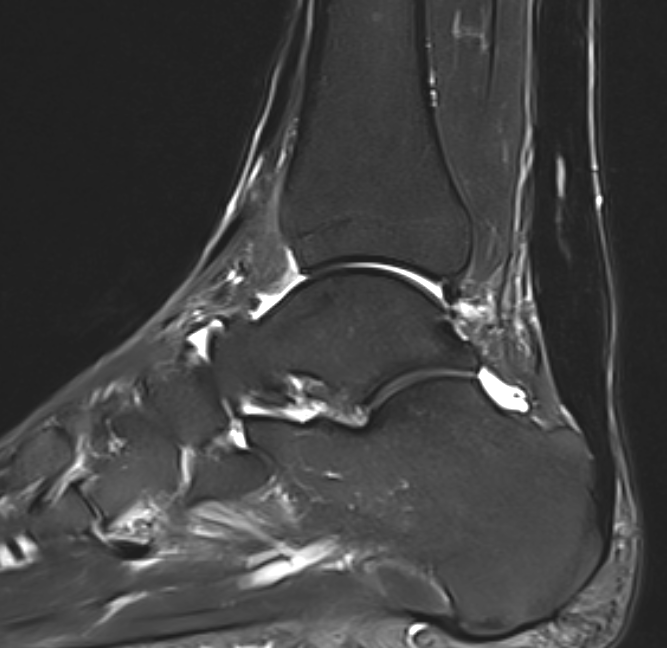
MRI
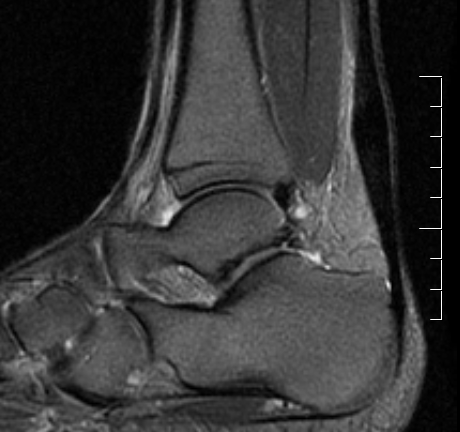
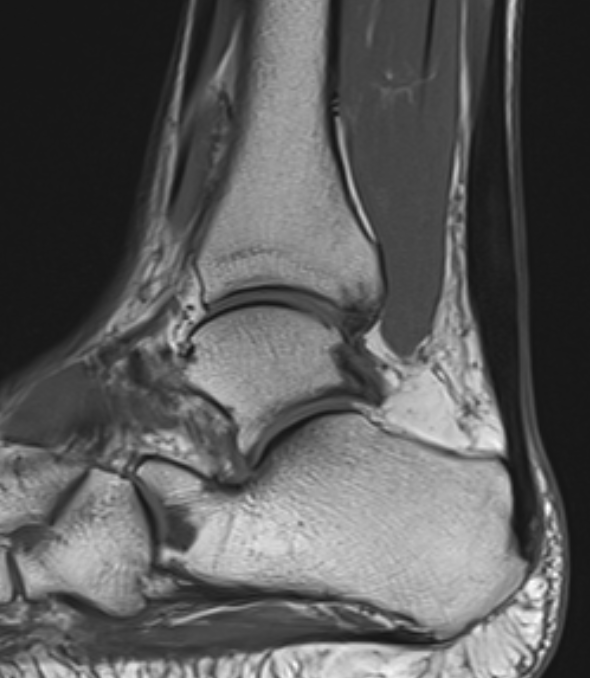
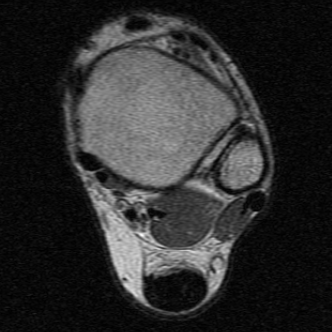
Tendon thickening

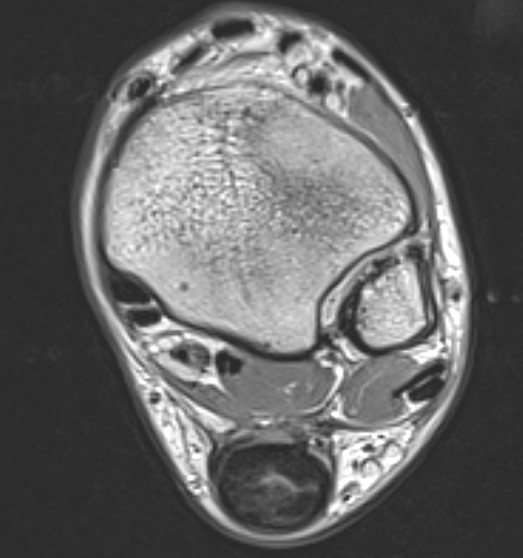
Thickening of the tendon with some intra-substance degeneration / partial tearing
Nonoperative Management
Eccentric exercises
Mainstay of treatment
Prudencio et al BMC Sports Sci 2023
- systematic review of eccentric exercises for midportion tendinopathy
- evidence for these exercises in reducing pain
Night splints
de Vos et al Br J Sports Med 2007
- RCT of eccentric exercises +/- night splints for non insertional tendinopathy
- no advantage with the addition of night splint
Extra-corporeal shockwave therapy
- systematic review of ECSW for non insertional achilles tendinopathy
- four RCTs
- consistent evidence that ECSW effective at reducing pain and improving function
Injections
Cortisone
Risk of tendon rupture
PRP
Nauwelaers et al Foot Ankle Surg 2021
- systematic review of PRP for non insertional achilles tendinopathy
- 4 RCTS
- no difference in clinical outcomes between PRP and placebo
Operative management
Options
Paratenon debridement
- open
- endoscopic
Vertical tenotomies
- open
- endoscopic
- ultrasound guided
Technique
Arthroscopy techniques endoscopic paratenon debridement
Results
Open versus minimally invasive
Lohrer et al BMC Musculoskeletal Disord 2016
- systematic review of surgical treatments
- 20 studies and 800 procedures
- open procedures: statisfaction rates 78%, complication rate 11%
- minimally invasive: satisfaction rates 79%, complication 5%
Ultrasound guided percutaneous tenotomy
- ultrasound guided percutaneous tenotomy
- 39 runners with average 17 year follow up
- 77% good or excellent results
Endoscopic debridement and tenotomy
Maquirriain et al Foot Ankle Surg 2013
- endoscopic debridement and longitudinal tenotomies
- 27 procedures with 5 year follow up
- 85% excellent outcome
