Definition
Degeneration at the attachment of the plantar fascia to medial tuberosity of the calcaneum
Anatomy
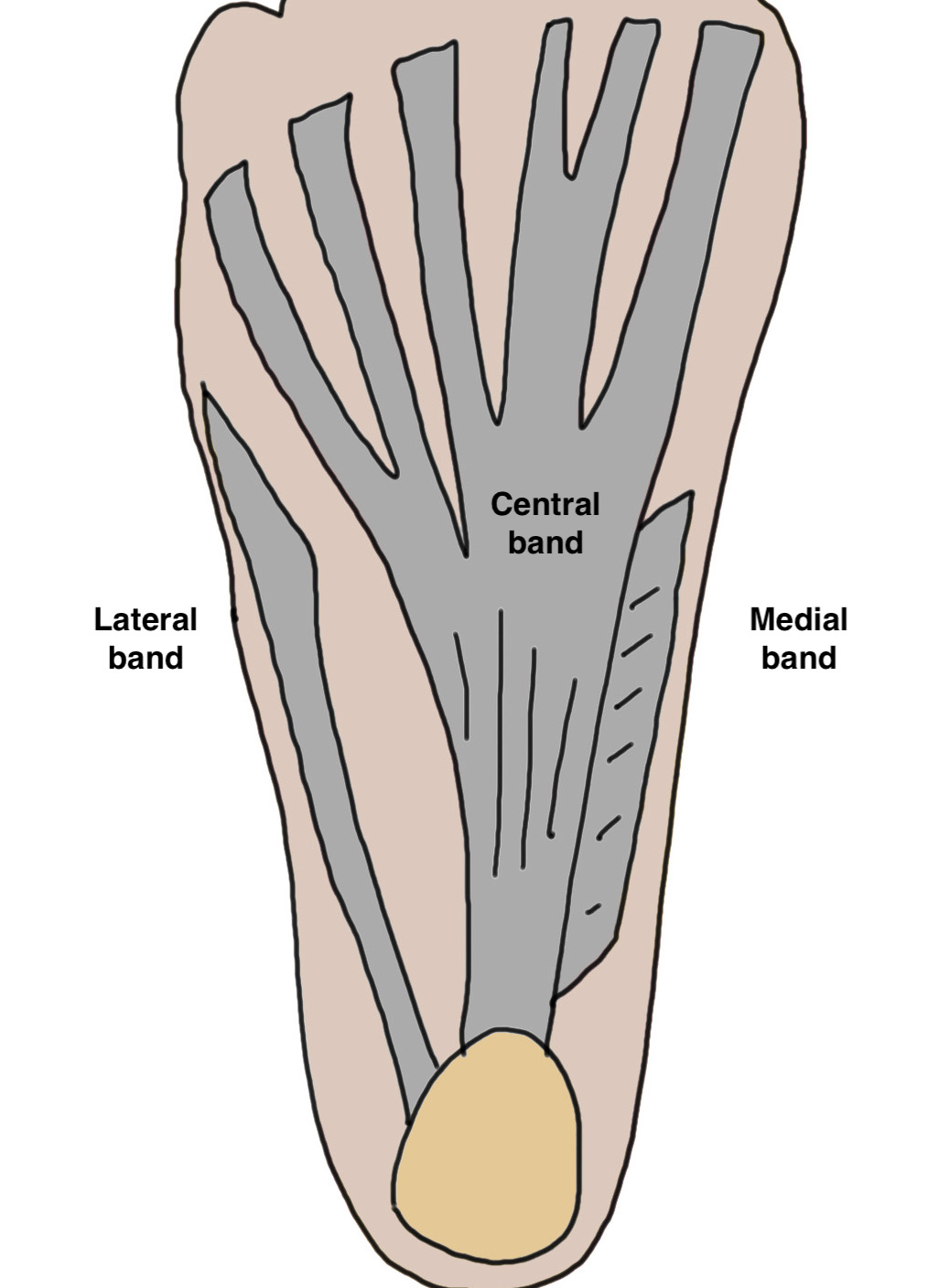
| Origin | Layers / insertions | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Medial calcaneal tuberosity |
3 bands - Medial - overlies hallux - Lateral - over base of 5th - Central - 5 bands inserts volar plate / base P1
|
Stabilizes arch of foot - windlass mechanism - toes dorsiflex in toe off - elevates arch of foot |
Epidemiology
Patients aged 40 - 60
Women > men
30% bilateral
Risk factors
Chronic overload - walking occupations / athletes / runners / military
Obesity
Inflammatory conditions - Reiter's Disease, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Gout
Pronated feet / cavus feet / planus feet
Poor footwear
Tight tendoachilles
Pathogenesis
Degenerative process
- repetitive stress at attachment
- microtears & cystic degeneration
Natural history
Davis et al Foot Ankle Int 1994
- 105 patients with plantar fasciitis
- treated with orthotics and stretching
- 90% resolved by 11 months
History
Pain at inferomedial aspect of heel
- worse when first rising from bed
- worse with prolonged standing or exercise
Examination
Local tenderness at inferomedial aspect of calcaneal tuberosity
Windlass / Jack test - pain aggravated by passive dorsiflexion of toes
Pec cavus / planus
Tight Tendoachilles / Silverskiold
- > 10 degree difference in ankle dorsiflexion with knee flexed and extended
X-ray
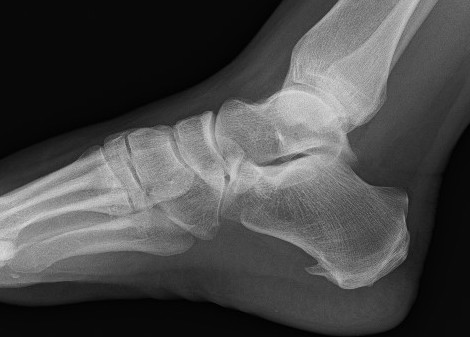
Calcaneal spurs
Moroney et al Foot Ankle Spec 2014
- 1100 foot xrays
- calcaneal spurs in 12%
- more common women / older / diabetes / OA
- associated with foot pain
Zhou et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2015
- 2 types calcaneal spur
- Type A: superior to plantar fascia
- Type B: located within plantar fascia
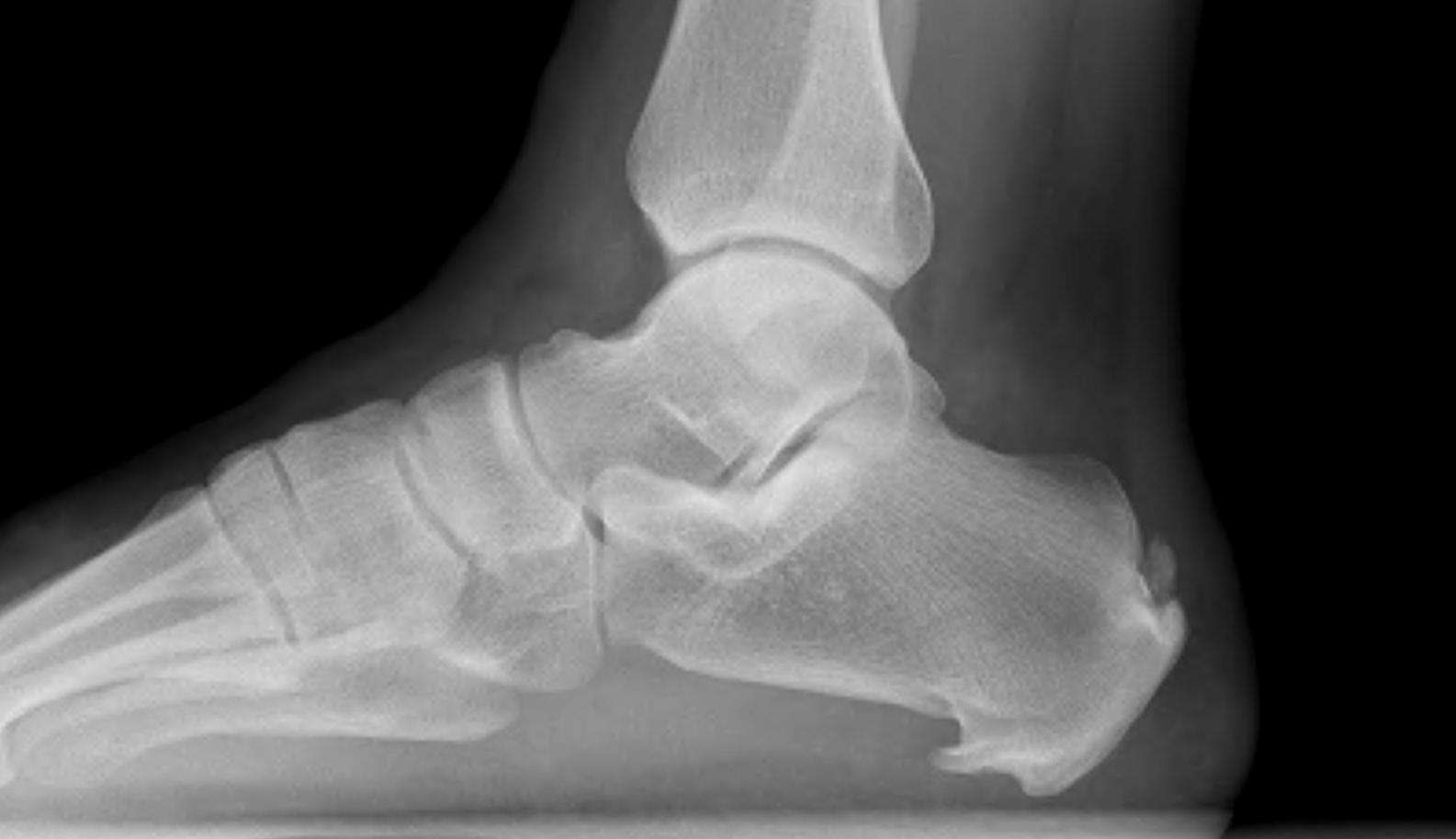
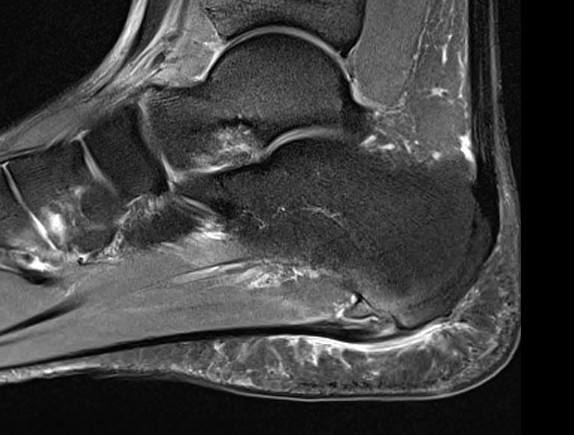
Calcaneal spur above plantar fascia which is thickened with tears
Ultrasound
Thickened plantar fascia > 4.5 mm
Hypoechoic areas consistent with tears
MRI
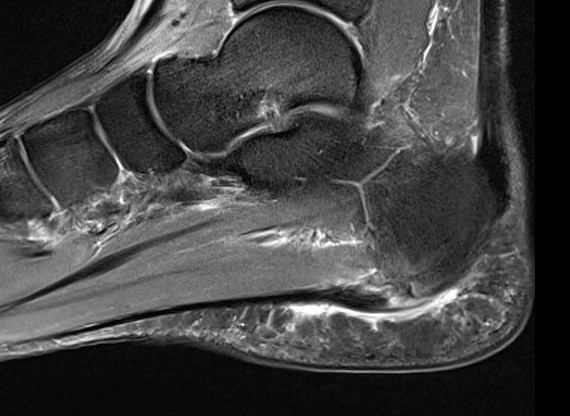
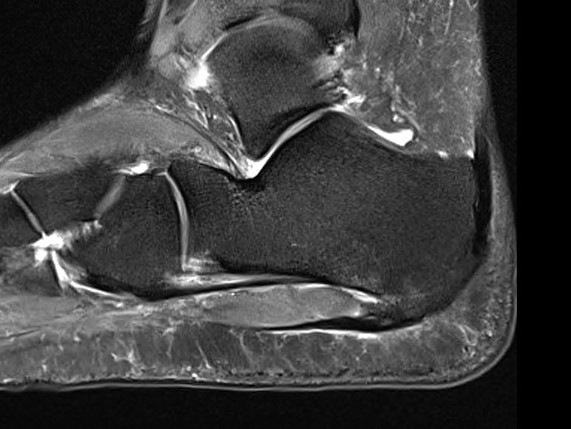
Thickened plantar fascia with tears
Exclude - retrocalcaneal bursitis / calcaneal stress fracture / Baxter's neuroma / tarsal tunnel syndrome
DDx
Calcaneal stress fracture
Fat pad syndrome
Tarsal tunnel syndrome - burning + numbness plantar aspect foot, EMG
Baxter's neuroma
- first branch lateral plantar nerve / Baxter's nerve
- mixed motor and sensory
- burning across heel pad
- motor to abductor digiti minimi
- EMG
- MRI shows atrophy of abductor digiti minimi
Posterior heel - Achilles tendonitis / retrocalcaneal bursitis / subtalar joint OA
Seronegative arthropathies - bilateral heel pain, young patients
Management
Non-operative
Options
Stretches
Orthotics / Night splints
ECSW
Injections - corticosteroid / PRP / Botox
Stretches
- RCT of 101 patients
- plantar fascia v tendoachilles stretching
- superior outcomes with plantar fascia stretching
Orthotics / Night splints
Schuitema et al J Sport Rehabil 2019
- systematic review of 43 articles and 2800 patients
- full length insoles superior to heel cups
- RCT of 116 patients
- no effect of night splint over 3 month period
ECSW
Cortes-Perez et al Clin Rehabil 2024
- systematic review of 16 RCTs and 1100 patients
- ECSW compared to cortisone injections
- ECSW superior at reducing pain and improving function at 3 and 6 months
Injections
Cortisone
- systematic review
- placebo RCT demonstrate significant effect cortisone
- short acting 4 - 12 weeks
Kim et al Foot Ankle Spec 2010
- retrospective review of 120 patients treated with cortisone injections
- 2.4% incidence of plantar fascia rupture
- average BMI 38 and average number injections 2.7 with rupture
PRP
Herber et al Foot Ankle Surg 2024
- meta-analysis of 21 RCTs and 1300 patients
- PRP superior to placebo / ECSW / cortisone
Botox
Roca et al Disabil Rehabil 2016
- 72 patient RCT of Botox v ECSW
- superior pain relief with ECSW
Ahmed et al Foot Ankle Int 2017
- RCT of saline v Botox in 50 patients
- significant improvement in botox group
Operative management
Options
Partial plantar fasciotomy - open / endoscopic
Medial gastrocnemius recession
Radiofrequency microtenotomy
Calcaneal spur removal
Decompression of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve (Baxter's nerve)
Results
Open v endoscopic partial plantar fasciotomy
Feng et al Foot Ankle Int 2021
- retrospective study of 62 patients
- open v endoscopic
- better results with endoscopic at 6 months
- no difference at 1 or 2 years
Medial gastrocnemius recession
Pickin et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2022
- systematic review of medial gastrocnemius recession for plantar fasciitis
- mean 76% reduction in pain at 1 year
Gamba et al Foot Ankle Int 2020
- RCT of gastrocneumius release v plantar fascia release
- 86% satisfaction in gastroc release
- 90% satisfaction in plantar fascia release
Open partial plantar fasciotomy
Technique
Medial longitudinal incision
- divide abductor hallucis fascia
- reflect this superiorly
- identify plantar fascia origin from tuberosity
- FDB is above plantar fascia
- insert homan retractors above and below
- lateral plantar nerve deep to abductor, above FDB laterally
Resect medial rectangle of plantar fascia
- divide 3/4 of fascia
- don't release in full unless very old and decrepit
- take 6 deep by 2 mm thick rectangle
+/- neurolysis
+/- Resect spur
- reflect FDB
- remove with osteotome / nibbler
B. Endoscopic release
Ogilvie-Harris Arthroscopy 2000
- 53 patients with 65 feet
- complete resolution of pain in 89%
- 71% returned to unrestricted sport
Results
