Indications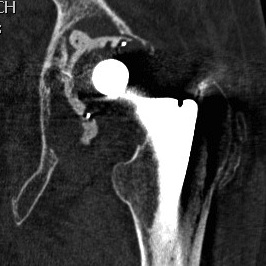
1. Loosening
2. Infection
3. Instability
4. Periprosthetic fracture
Objective
1. Exclude infection
2. Re-establish the structural integrity & bone stock
3. Establish normal Joint mechanics
- restore the centre of rotation of the hip
4. Initial rigid fixation of bone graft
5. Adequate containment of the new prosthesis
Aetiology Bone Loss
1. Osteolysis
2. Surgical / iatrogenic (with implant removal)
3. Acetabular dysplasia
4. Fracture
5. Infection
Preoperative Assessment
1. Exclude infection
2. Quantify bone loss
Classifications
Femoral
- Paprosky
- AAOS
Acetabular
- AAOS
- Paprosky
Femoral Bone Loss
Paprosky Classification
I Minimal metaphyseal cancellous bone loss / intact diaphysis
- i.e. seen after removal of uncemented component without biological ingrowth on surface
II Extensive metaphyseal cancellous bone loss / intact diaphysis
- often seen after removal of cemented prosthesis
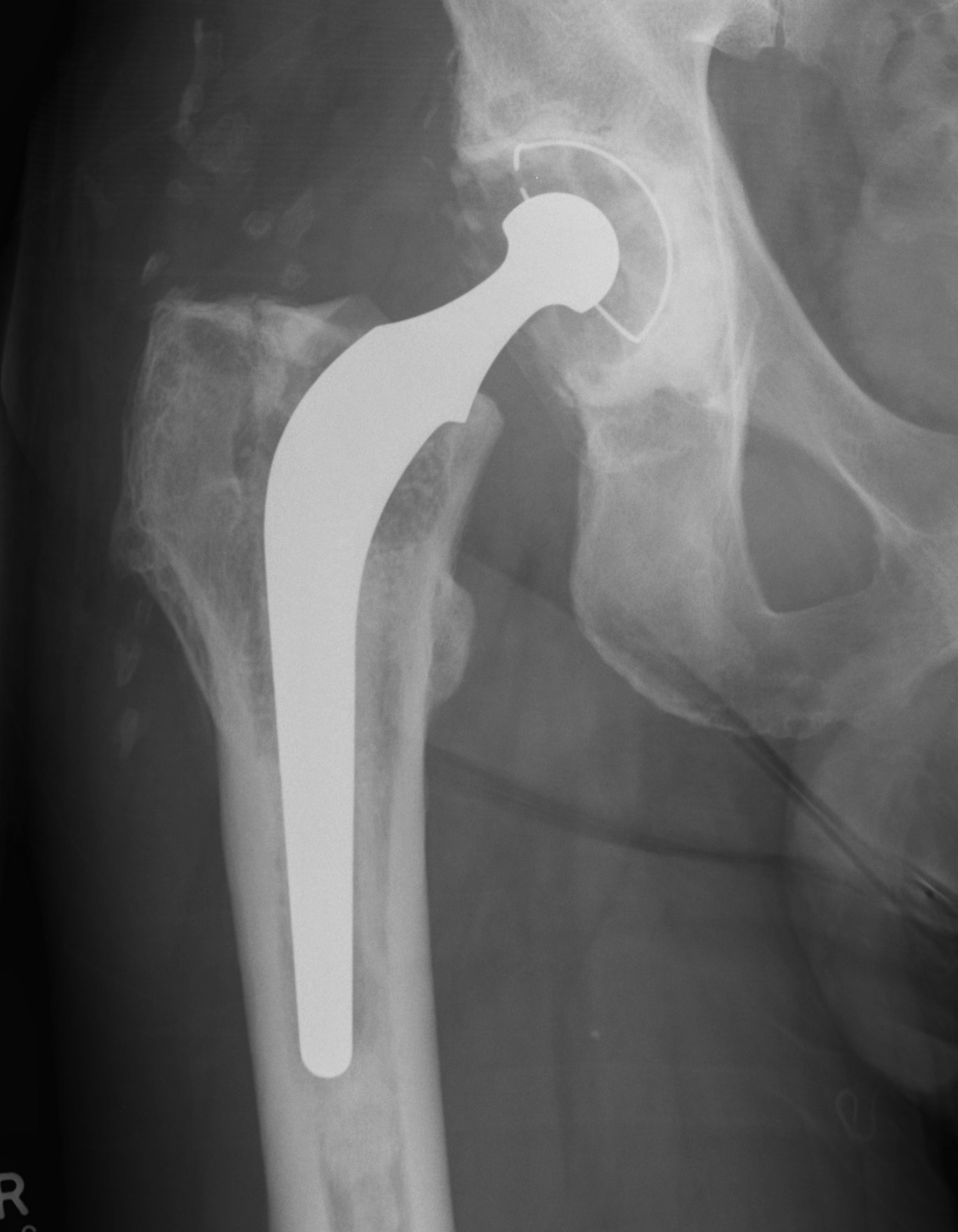
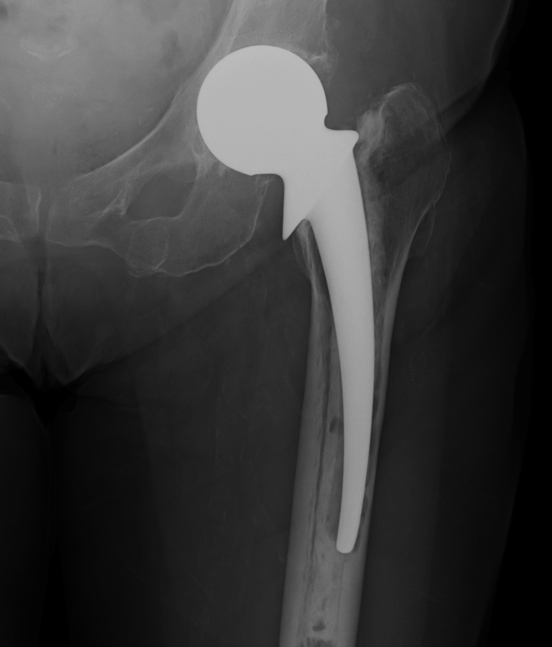
IIIA Metaphysis severely damaged / > 4cm diaphyseal bone for distal fixation
- grossly loose femoral component
- first generation cementing techniques
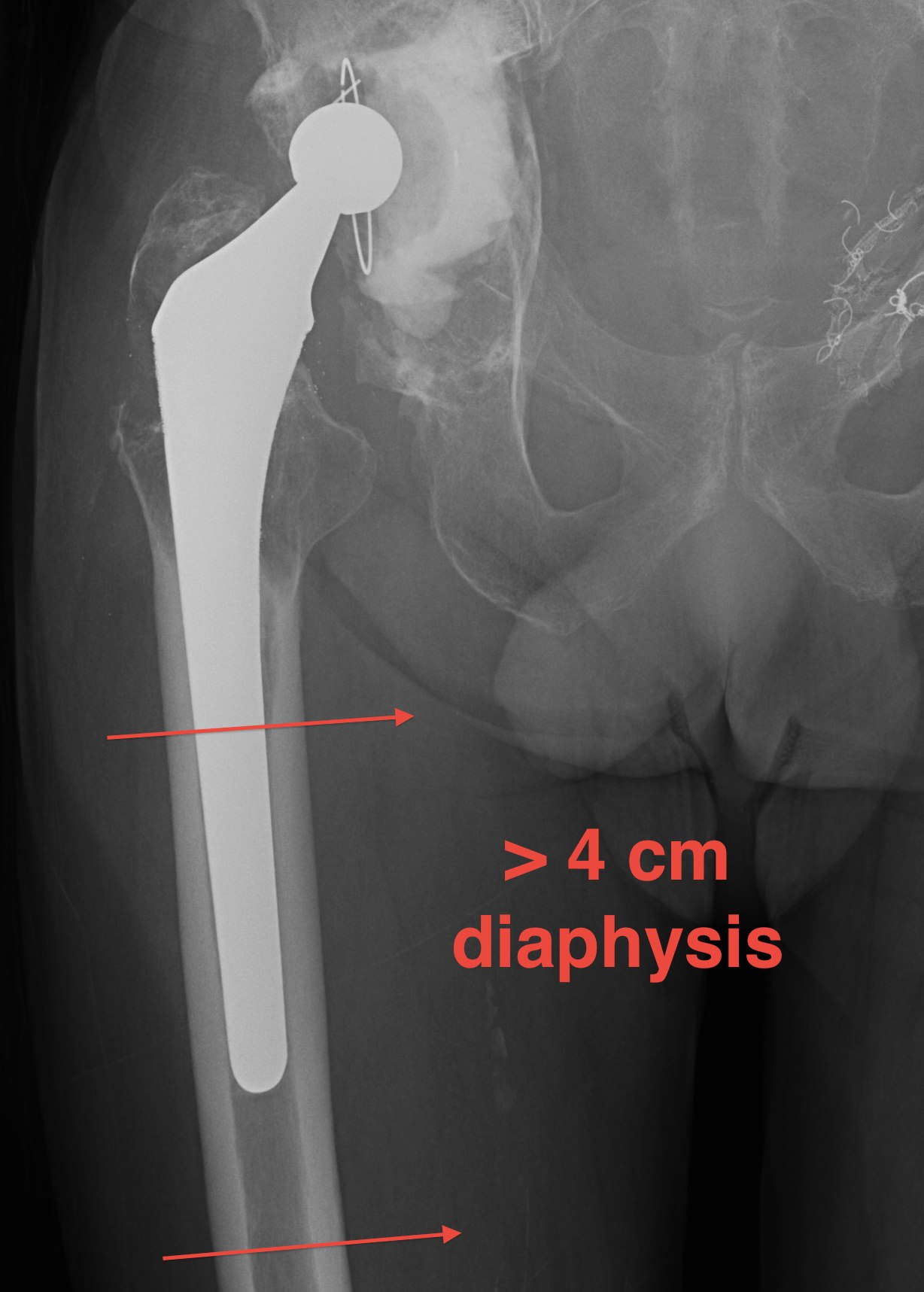
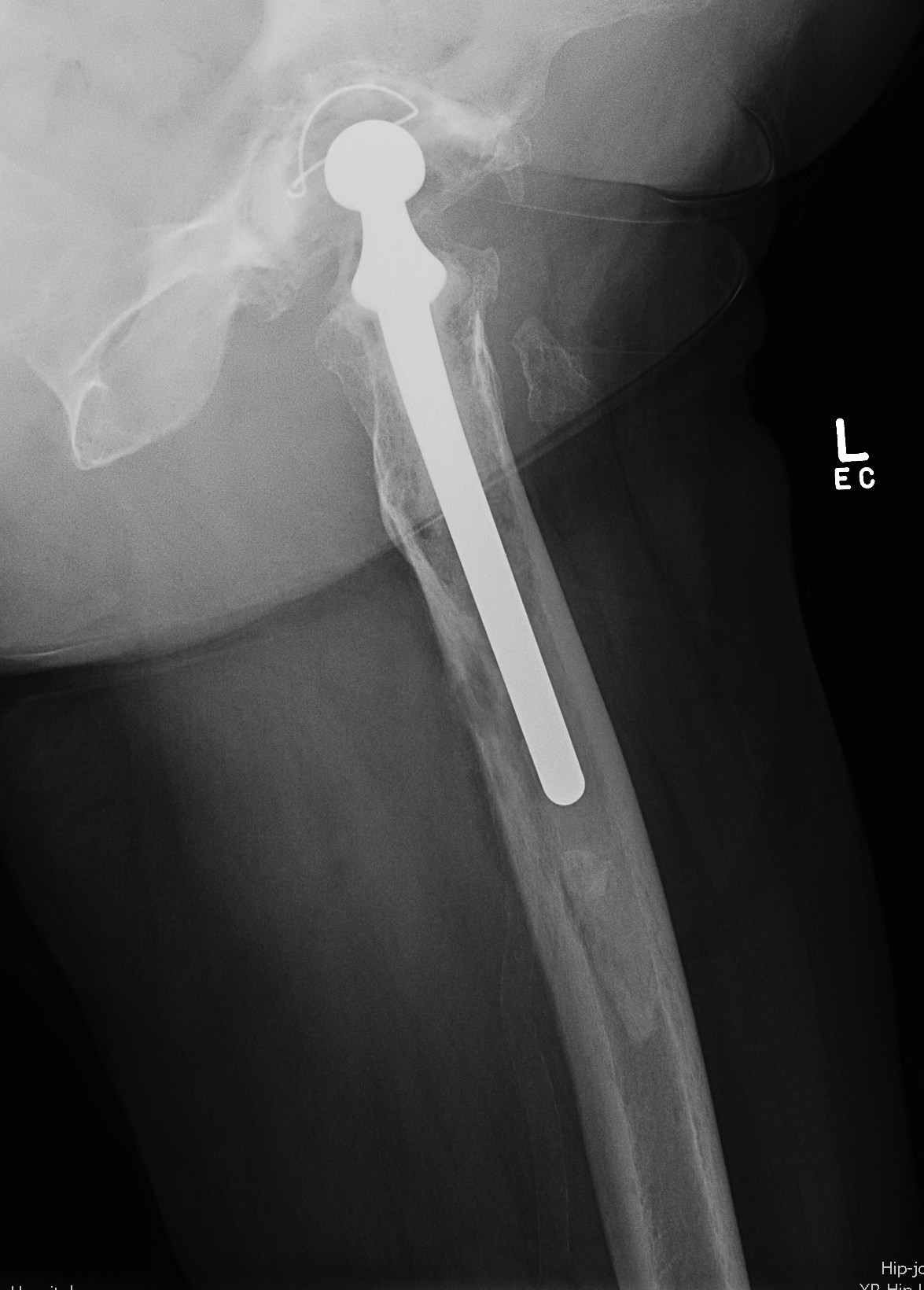
IIIB Metaphysis severely damaged / < 4cm diaphyseal bone for distal fixation
- cemented with cement restrictor
- uncemented with substantial distal osteolysis
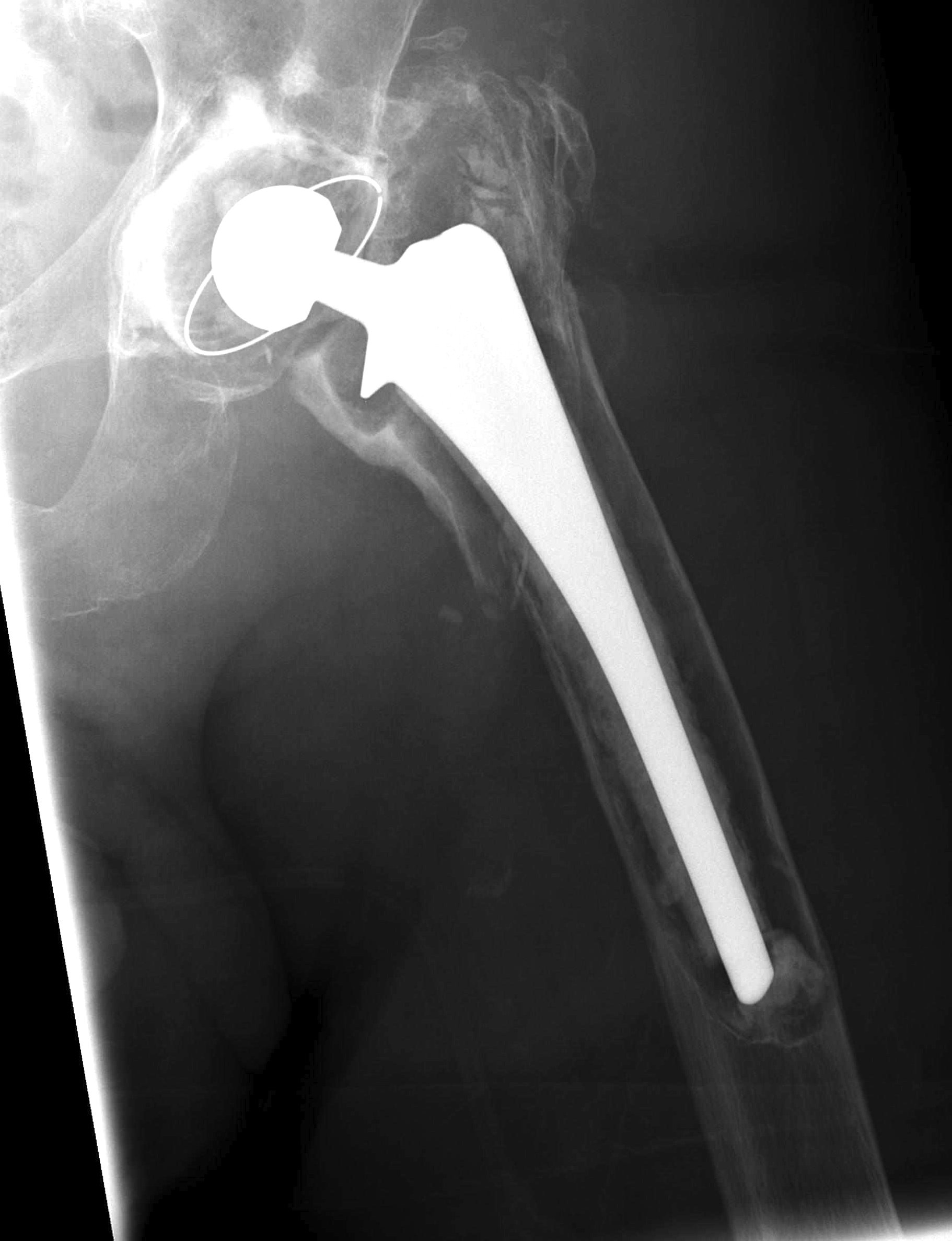
IV Extensive metaphyseal and diaphyseal bone loss / isthmus non supportive
AAOS Classification
I Segmental
- proximal (partial or complete)
- intercalary
- greater trochanter
II Cavitary
- cancellous
- cortical
- ectasia (dilatation)
III Combined segmental and cavity
IV Malalignment
- rotational
- angular
V Femoral Stenosis
VI Femoral Discontinuity
Acetabular Bone Loss
AAOS Classification
Type I Segmental deficiencies
Peripheral - superior / anterior / posterior
Central - medial wall absent
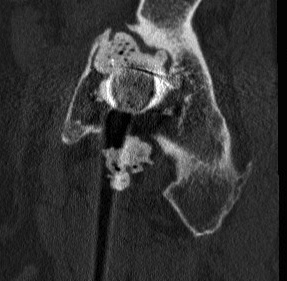
Type II Cavitary deficiencies
Peripheral - superior / anterior / posterior
Central - medial wall intact
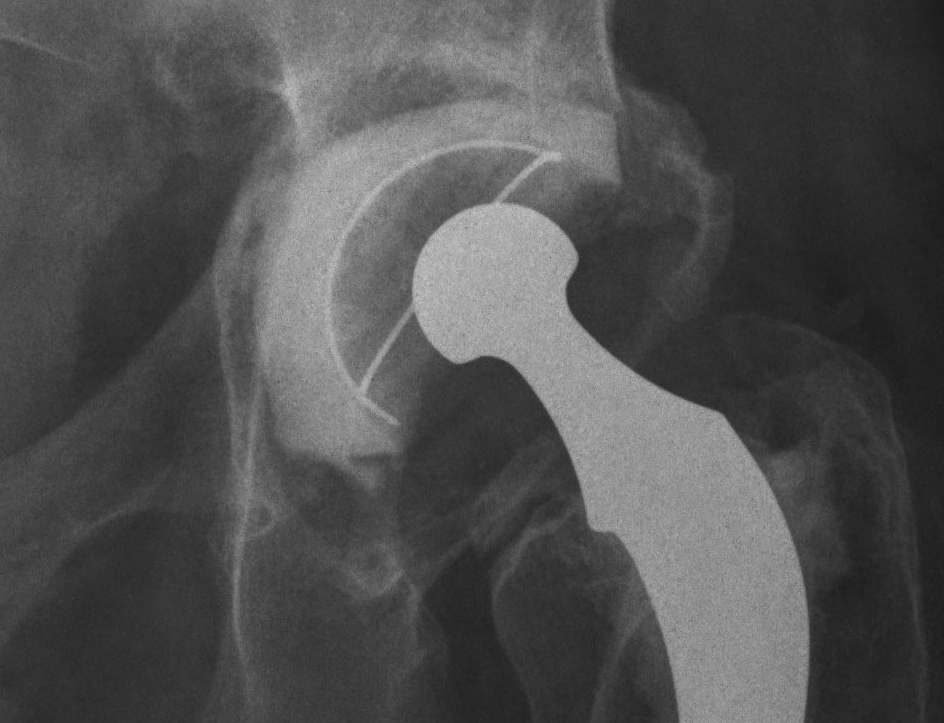
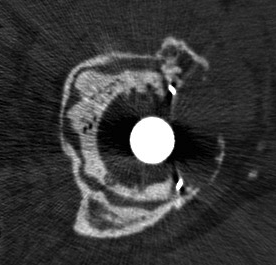
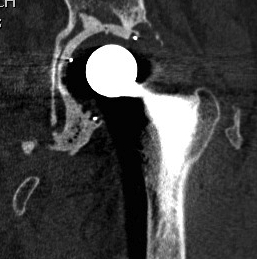
Type III Combined deficiencies
Type IV Pelvic discontinuity
Separation of anterior and posterior columns
Type V Arthrodesis
Paprosky Classification
Based on ability of the remaining host bone
- to provide initial stability to a hemispherical cementless acetabular component
- until ingrowth occurs
Type 1
Undistorted rim
- anterior and posterior columns intact
- no superior migration
- may have some contained deformities
- ishium, teardrop and Kohlers line intact
Type 2
Distorted but intact rim
- can support a hemispherical cementless implant
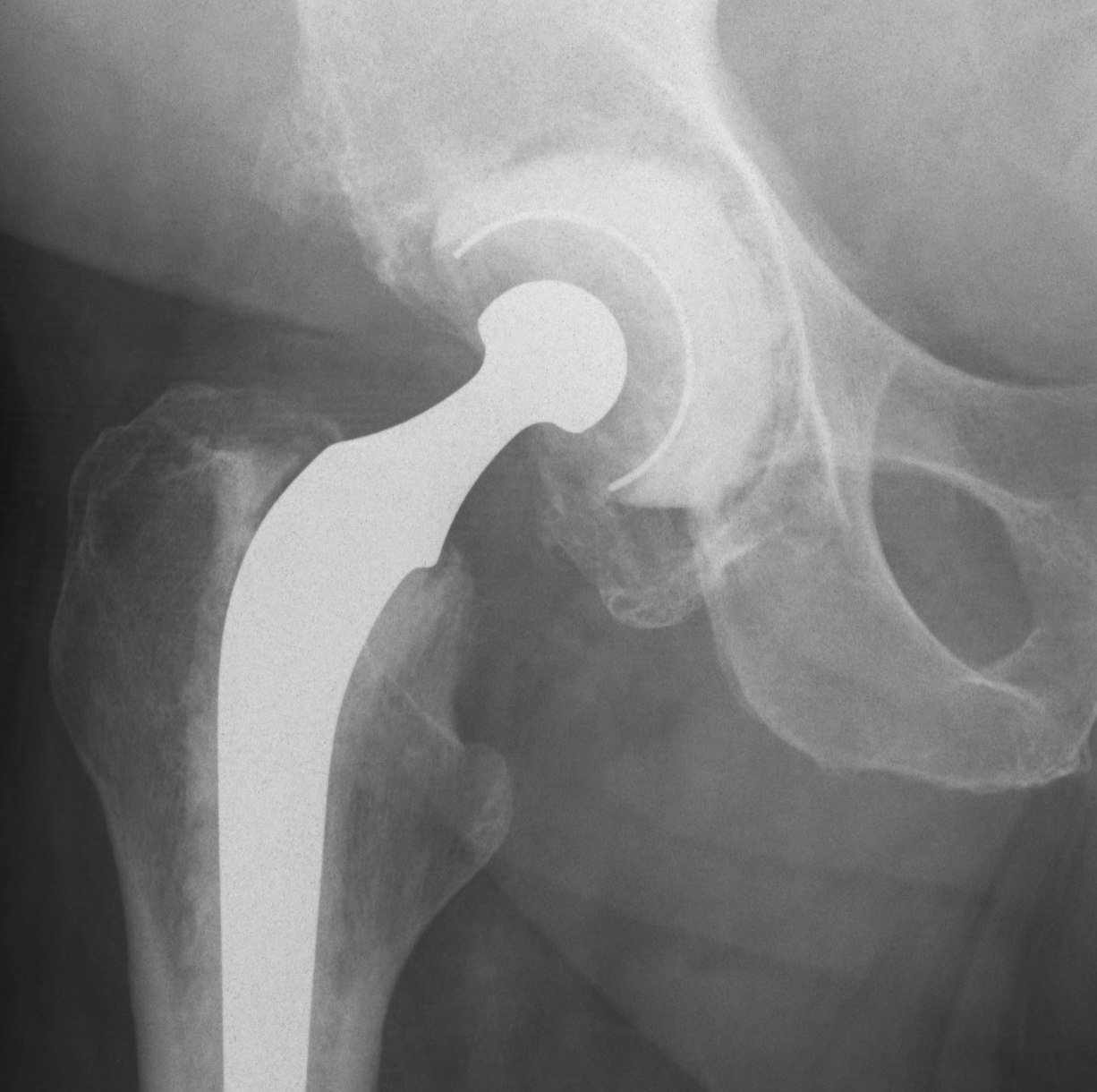
Some distortion, minimal superior migration
- at least 50% good support by host bone
- anterior and posterior columns intact
- no substantial osteolysis of ischium or teardrop
2A
- superomedial migration but superior rim intact
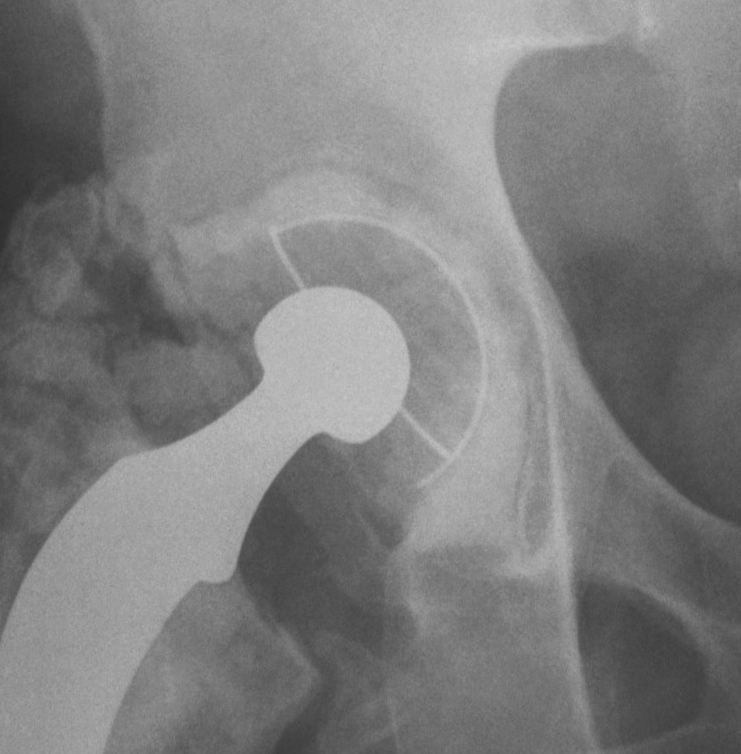
2B
- < 1/3 superior deficit
- remainder is still supportive
- replace with allograft for bone stock
2C
- medial migration to Kohlers, but wall intact
- rim is supportive
- manage as for protrusio
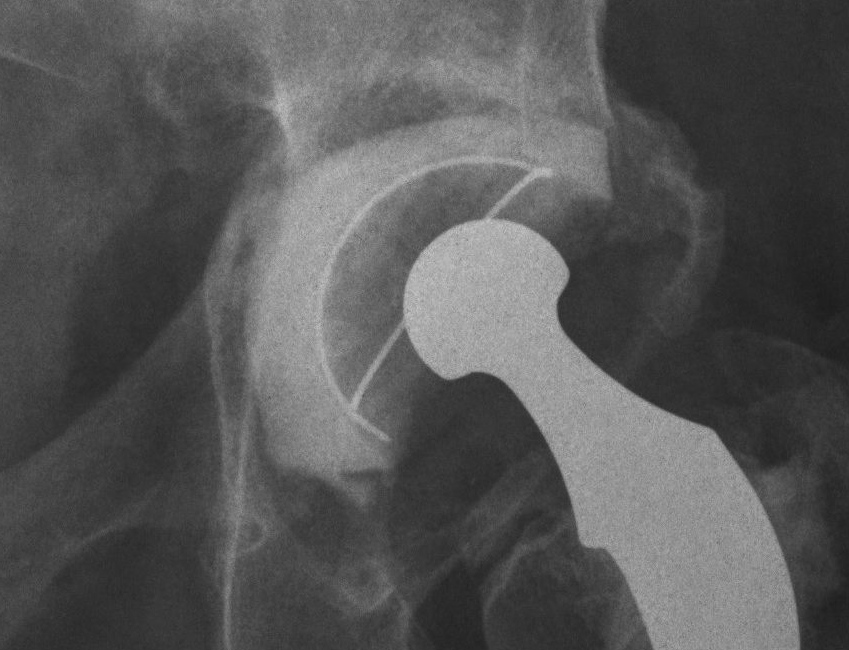

Type 3
Non supportive rim
- columns not supportive, superior migration> 3 cm
- require structural allograft for support
4 radiographic criteria
1. Superior migration of the hip centre
- indicates damage to anterior and posterior columns
- supero-medial indicates greater damage to anterior column
- supero-lateral indicates greater damage to posterior column
2. Ischial osteolysis
- bone loss inferior posterior column
3. Teardrop osteolysis
- inferior anterior column and medial wall
4. Position of the implant relative to Kohler’s line
- deficiency of anterior column
3A
- > 40% host bone contact
- < 50% rim missing
3B
- < 40% host bone contact
- > 50% rim missing
