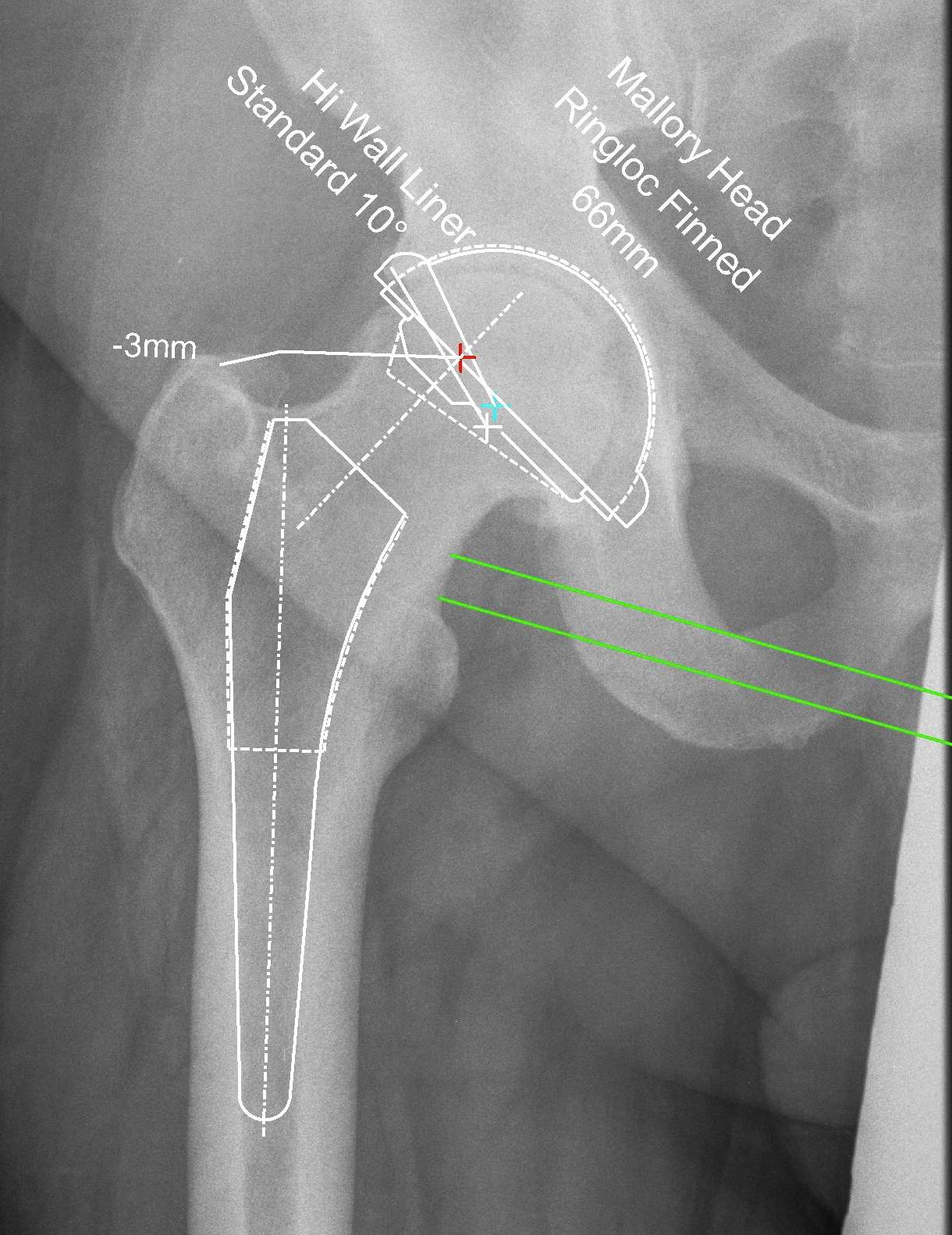
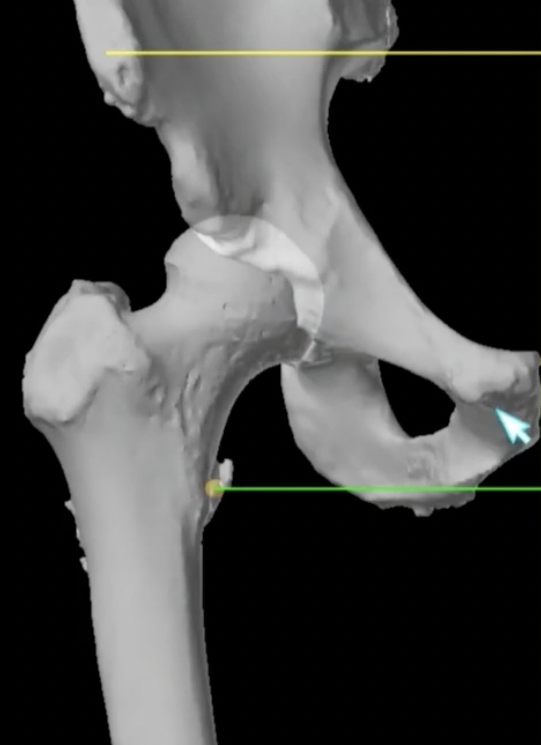
Aim
Reproduce
- anatomical center of rotation
- offset
- neck-shaft angle
- leg length
- femoral osteotomy
- femoral implant size and anteversion
- acetabular size and orientation
Pre-operative options
1. 2D xray
2. 3D EOS xray templating
3. CT templating
Results
Bishi et al EFORT Open Rev 2022
- meta-analysis
- 3D more accurate than 2D
- CT most accurate
X-ray
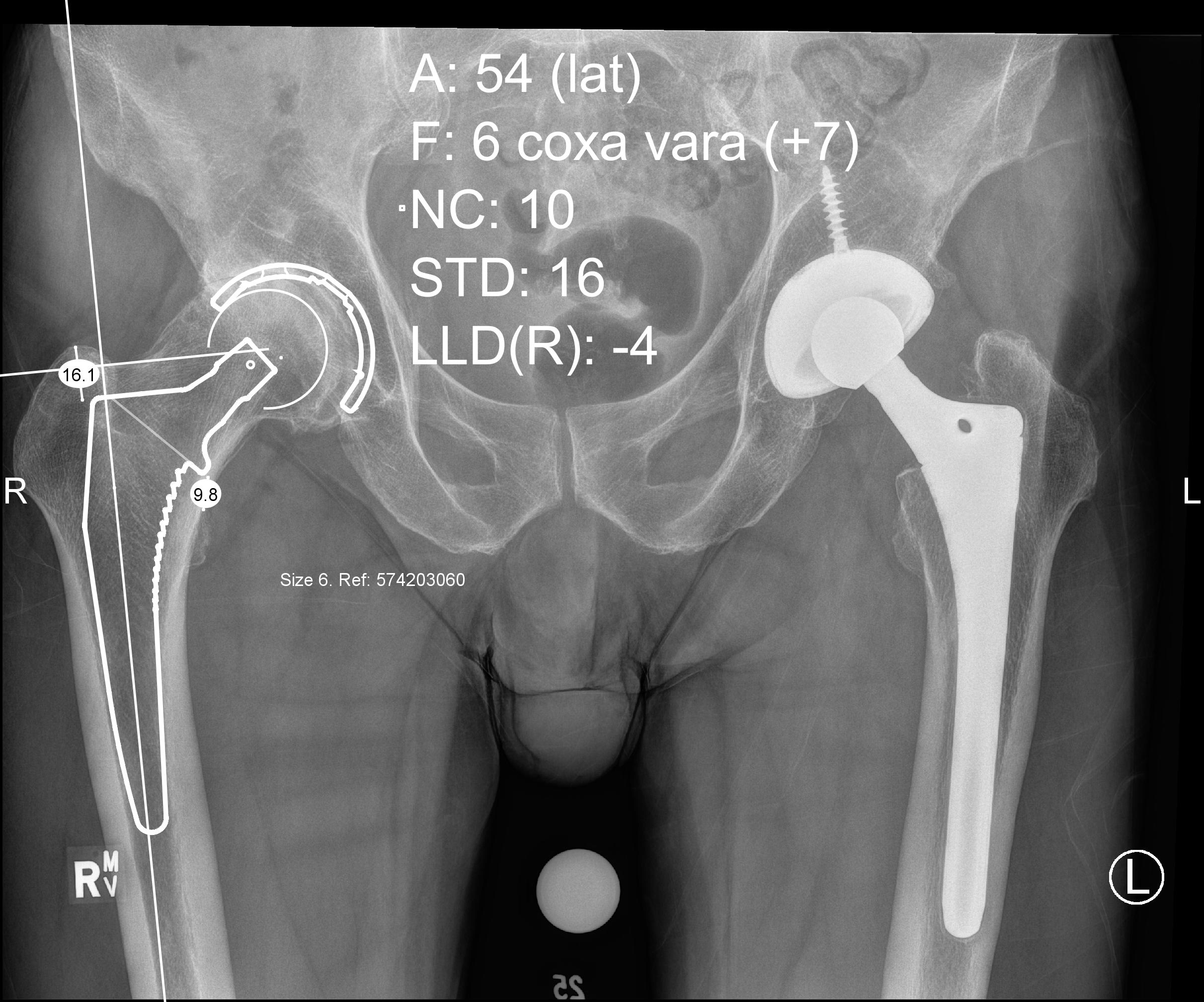
Requirements
1. AP pelvis
2. Lower extremities internally rotated 15° to 20°
- accounts for femoral anteversion
- allows offset templating
3. Magnification marker
- degree of magnification directly related to distance from bone to cassette
- typical magnification of 15% to 20%
- also varies with patient size
- larger patients increased magnification, smaller patients reduced magnification
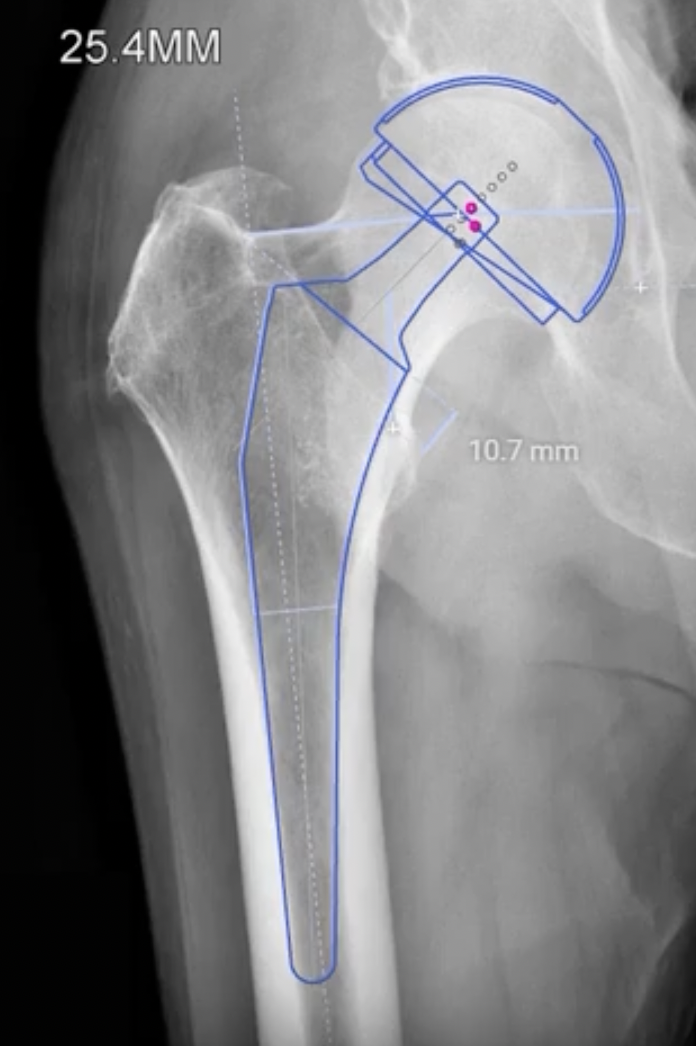
Zimmer Online One Planner
Accuracy
Holzer et al Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2019
- 632 uncemented THA with digital templating of xrays
- implant size predicted correctly 42% femur and 37% acetabulum
- accurate within implant size within 1 size 87% femur and 78% acetabulum
- less accurate with overweight patients
EOS xray imaging


Technique
- low dose biplanar digital xrays
- two orthogonal xrays obtained simultaneously
- recreate 3D image
Advantage
- lower radiation than both CT and xray
- includes spinopelvic anatomy
Disadvantage
- not offered in all centers
Accuracy
Buller et al J Arthroplasty 2021
- EOS imaging in 43 THA
- implant size predicted correctly 66% femur and 71% acetabulum
- accurate within implant size within 1 size 98% femur and 98% acetabulum
CT templating
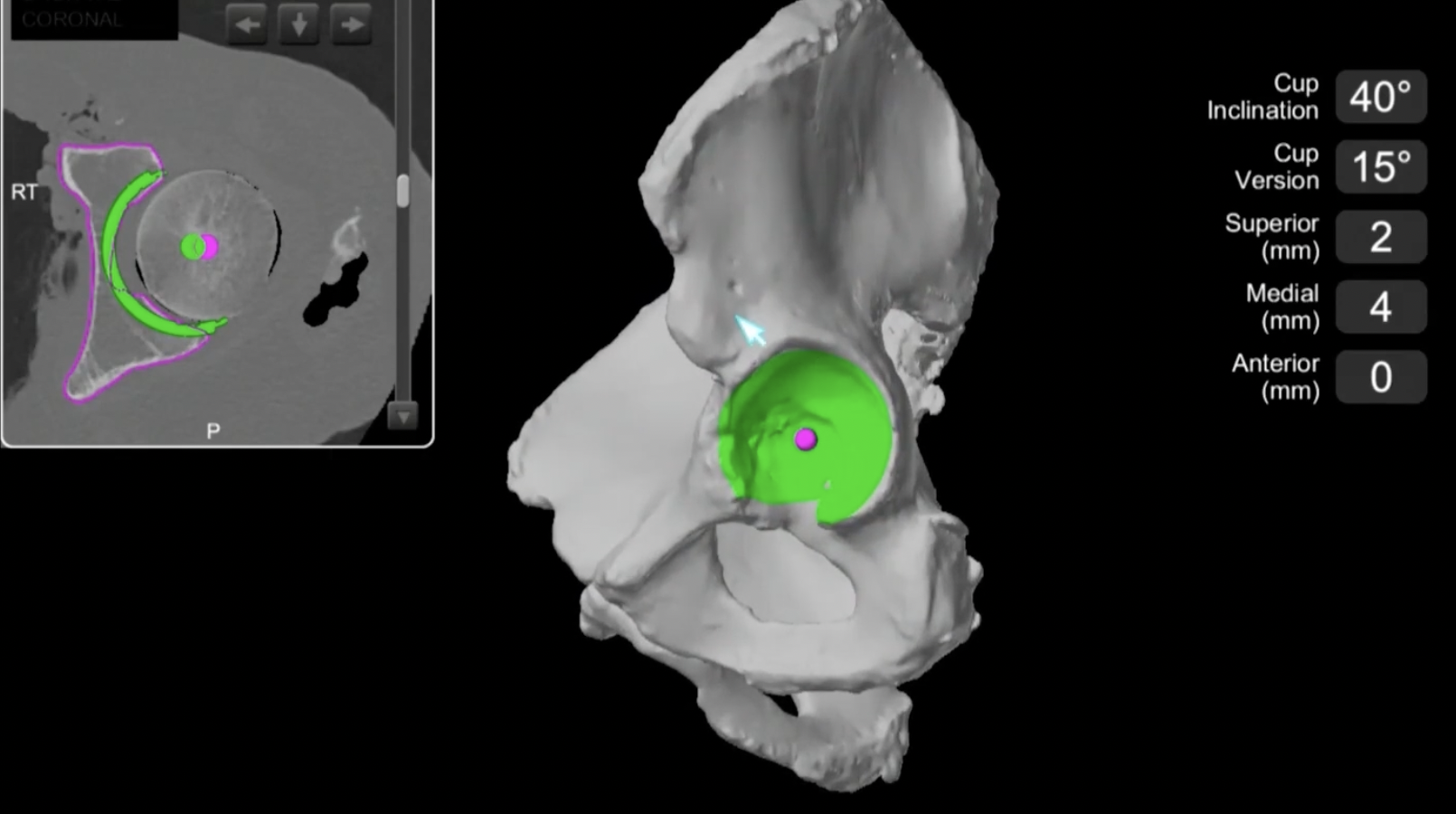
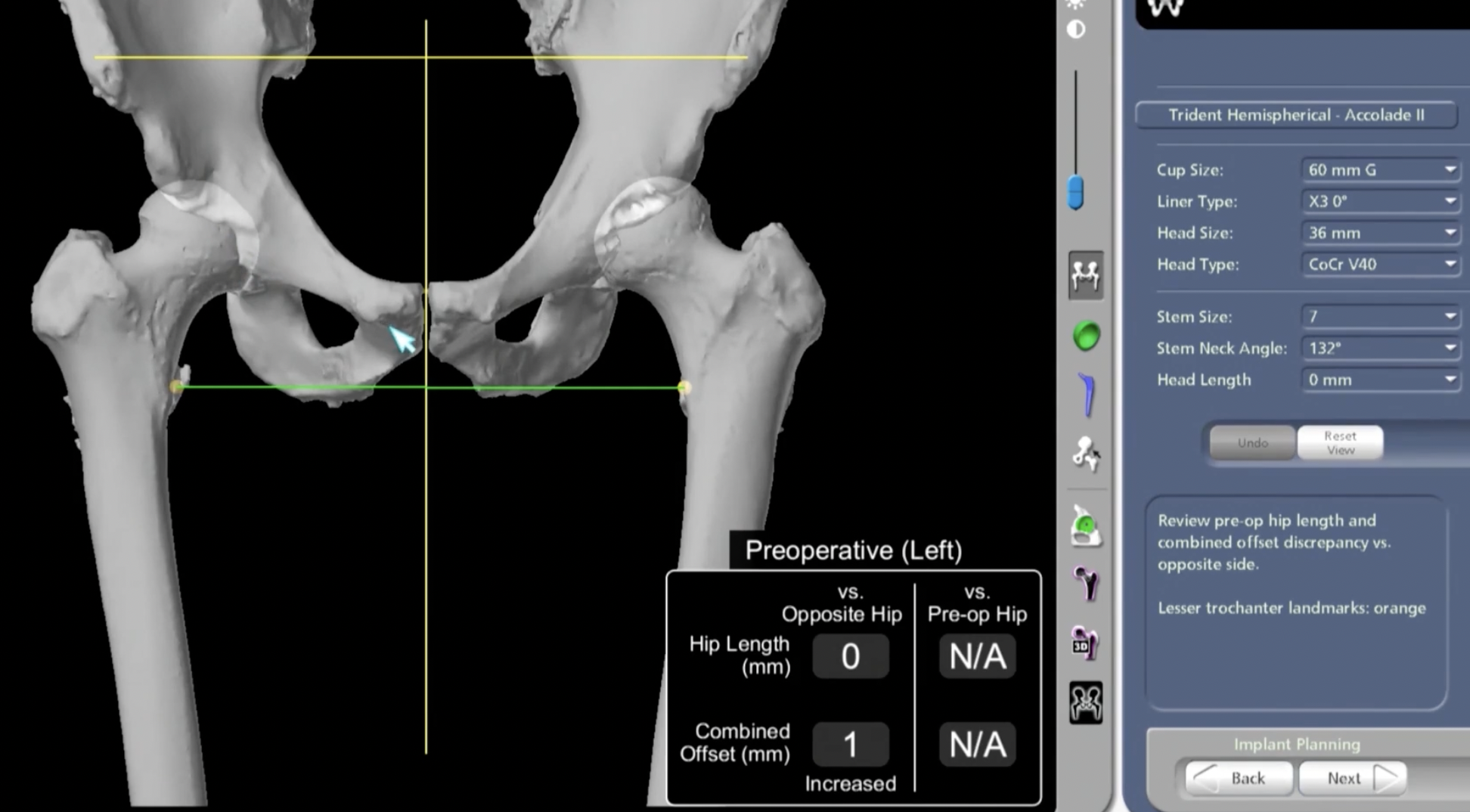
Advantage
- extremely precise especially with femoral anteversion / cup inclination and anteversion
- evaluates bone stock
- identify osteophytes
Disadvantage
- radiation
Accuracy
Hassani et al J Arthroplasty 2024
- preoperative CT templating in 50 uncemented THA
- 100% accurate femoral stem stize
- 94% accurate acetabular size
