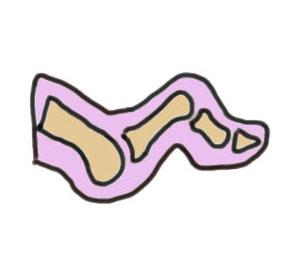
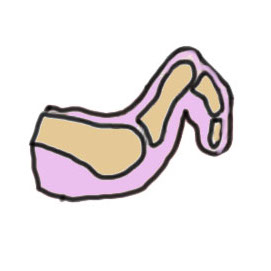
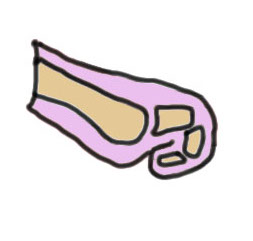
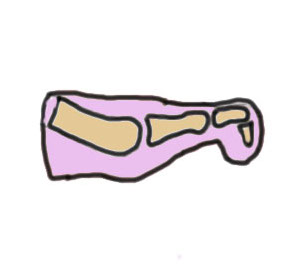
Deformities
| Hammer | Claw | Curly toe | Mallet |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PIP flexion DIPJ neutral / extended |
PIPJ and DIPJ flexed MTPJ hyperextended |
PIP and DIP flexion |
DIP flexed MTP / PIPJ neutral |
|
Hallux valgus Tight shoes |
Multiple toes affected Neuromuscular conditions Cavus foot |
Pediatric 3rd toe Under-riding Usually resolves |
Pediatric 2nd toe |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Claw toe v hammer toe
1. Claw toes often affects all toes
- frequently are caused by neuromuscular disease
- in hammer toe deformity only one or two toes are involved
2. Claw toes always have extension deformity at the MTPJ
- in hammer toe MTPJ may or may not be present
3. Claw toes have a flexion deformity DIPJ
- this usually does not occur in hammer toes
Issues
Shoe wear difficulty
Painful calluses
Metatarsalgia
Anatomy
| EDL | EDB | FDL | FDB |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Divides into 3 slips over P1 - middle to P2 - side slips to P3 - no insertion to P1 |
4 tendons - P1 great toe - side of EDL tendon toes 2 - 4 |
Passes between 2 slips of FDB Inserts P3 |
Splints into 2 Inserts into side of P2 |
| Extends P1 | Flexes DIPJ | Flexes PIPJ |
Claw Toes

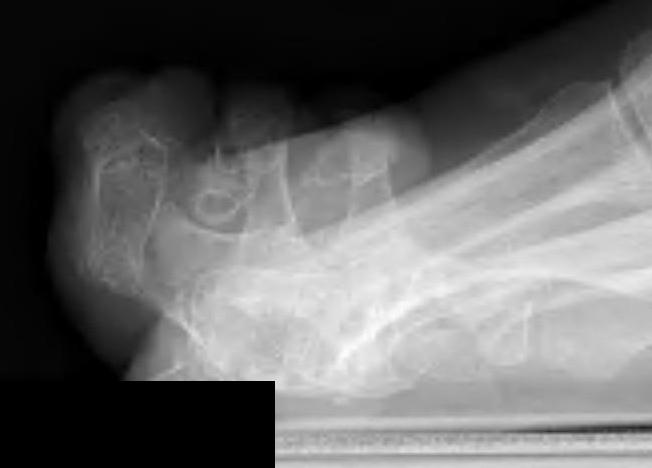
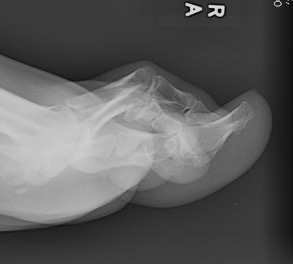
Definition
Hyperextension of MTPJ
PIPJ / DIPJ flexion
Usually all toes affected
Associations
Cavus foot
Neuromuscular conditions
Compartment syndrome
Diabetic neuropathy
Rheumatoid arthritis
Pathology
Imbalance between intrinsics and extrinsics
- intrinsics weak
- extrinsics strong - MTPF extension / IPJ flexion
P1 subluxes dorsally
Metatarsal head more plantar - metatarsalgia
Cavus foot
- claw occurs not only due to intrinsic weakness but because of plantar flexed metatarsals
Examination
Hindfoot - cavus / coleman block
Forefoot - all toes / extended MTPJ / flexed IPJ
Calluses - dorsum PIPJ / bleow MTPJ
Flexible deformity
- claw toes disappears with ankle planar flexion
- claw toes return with ankle dorsiflexion
- tight long flexors
Operative Management
Significant deformity of the hindfoot ± a cavus foot should be addressed first if symptomatic
Surgical Algorithm
1. Flexible Deformity PIPJ / MTPJ
FDL transfer - flexor tenodesis to base of P1
+/- extensor tenotomy & dorsal MTPJ capsulotomy
2. Fixed PIPJ Deformity / Flexible MTPJ
Extensor tenotomy + PIPJ Fusion
+/- dorsal MTPJ capsulotomy
3. Fixed PIPJ / Fixed MTPJ
Extensor tendon tenotomy + PIPJ fusion +
Dorsal MTPJ capsulotomy +
Distal metacarpal shortening osteotomy (Weil)
Hammer toe
Definition
Plantar flexion deformity PIPJ with dorsiflexion of the MTPJ

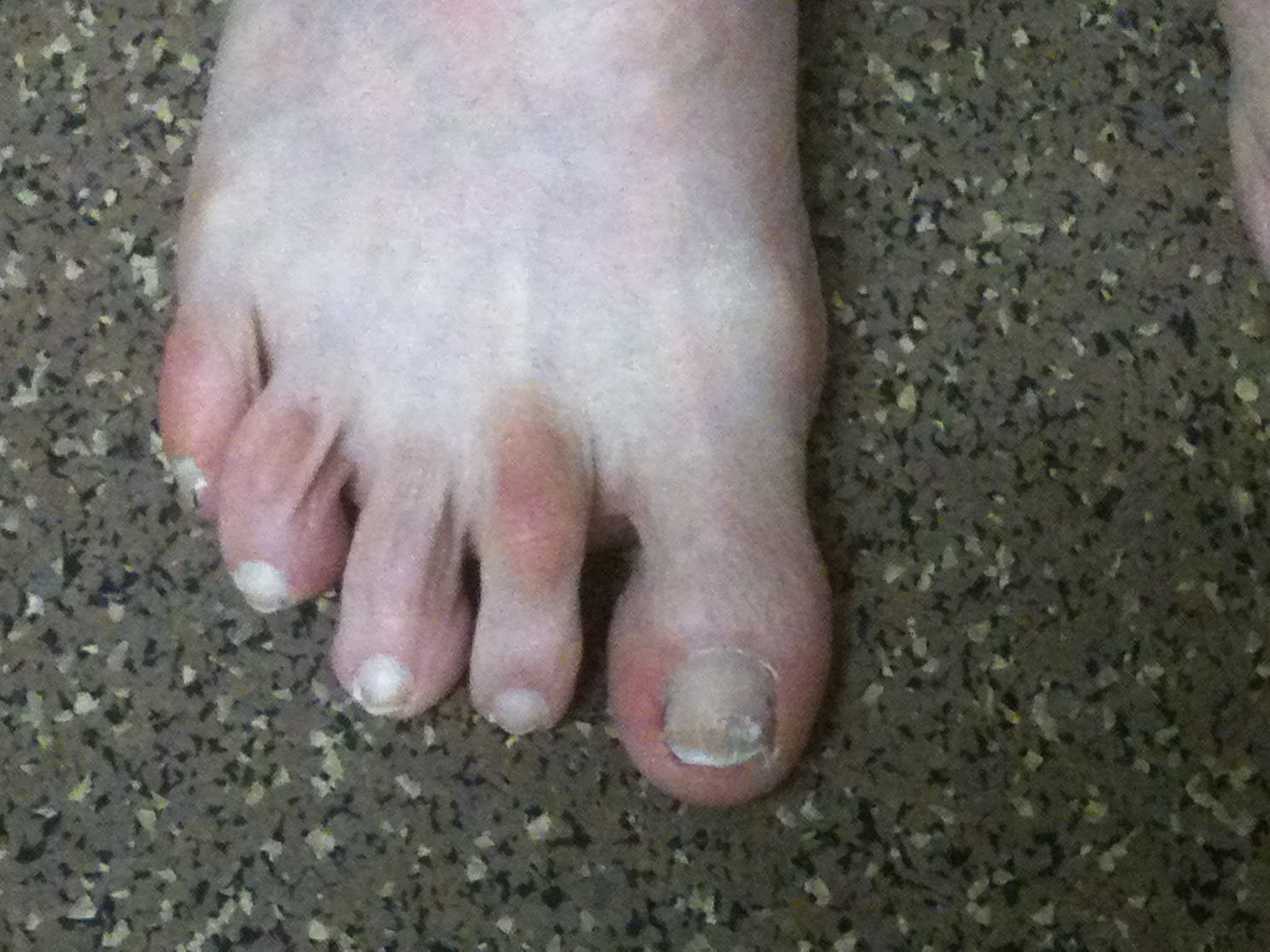
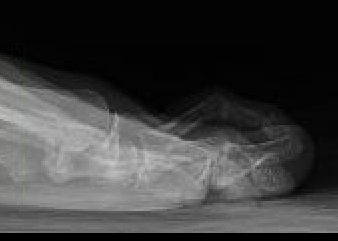
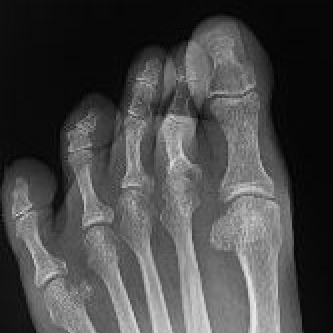
Etiology
Uncertain - long second toe / metatarsal & tight shoes
Associated with Hallux valgus
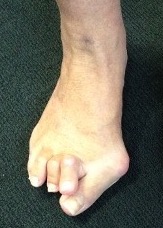
Hammer toe associated with severe hallux valgus
Examination

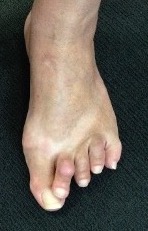
Dorsal callous over PIPJ second hammer toe
Operative management
1. Flexible Deformity PIPJ / MTPJ
FDL transfer - flexor tenodesis to base of P1
+/- extensor tenotomy & dorsal MTPJ capsulotomy
2. Fixed PIPJ Deformity / Flexible MTPJ
Extensor tenotomy + PIPJ Fusion
+/- dorsal MTPJ capsulotomy
3. Fixed PIPJ / Fixed MTPJ
Extensor tendon tenotomy + PIPJ fusion +
Dorsal MTPJ capsulotomy +
Distal metacarpal shortening osteotomy (Weil)
Mallet toe

Definition
Flexion deformity of DIPJ usually of 2nd toe
Young children
Etiology
Long second toe / metatarsal / constrictive footwear
Operative management
1. Flexible - percutaneous FDL tenotomy
2. Fixed - FDL release + DIPJ fusion
Curly toe

Definition
Under-riding toe
- toe lies beneath adjacent toe
- congenital deformity
Management
Most don't require treatment and most non symptomatic and 25% improve spontaneously
- 2 year old with curly toe
- most will improve
- give parents stretches
1. Flexible deformity 4 - 12 year old
- flexor tenotomy thru plantar skin
2. Fixed deformity > 12 years old
- resection / arthrodesis of IPJ
Case scenario
- 2 year old with curly toes
- nil other abnormality
- vast majority will improve
- give stretches for parents to do
- only if continual problem, do FDL release
