Definition
Cavus
- fixed equinus deformity of the forefoot in relation to the hindfoot
- abnormally high arch that fails to flatten with weight bearing
Varus hindfoot
Etiology
Neuromuscular - two thirds of condition with Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) most common
Congenital - congenital cavo-varus, residual club foot, arthrogryposis
Traumatic - compartment syndrome, foot fracture malunion
Degenerative - arthritis of hindfoot
Idiopathic
Neuromuscular causes
| Central | Spinal cord | Anterior horn cell | Peripheral nerves | Muscle disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Friedreich's Ataxia Cerebral Palsy Hydrocephalus |
CMT type 2 Spina bifida Syringomyelia Spinal cord tumours
|
Polio SMA |
CMT type 1 |
Muscular dystrophy
|
Charcot-Marie-Tooth
Hereditary Motor sensory neuropathy
- affects 1 in 2500 persons
- most common inherited neurological disorder
- characterised by weak muscles and abnormal sensation
- heterogenous group
- foot deformity often doesn't present until adolescence
| CMT Type 1 | CMT Type 2 |
|---|---|
|
Demyelinating disorder of peripheral nerve roots |
Degeneration of spinal axons Primary axonal neuropathy |
| Most common 80% | Second most common 20% |
|
Glove and stocking parasthesia Absent reflexes Claw toes, cavus feet, stork legs Loss of intrinsics in hand |
Reflexes intact |
Deformity
Rang Tripod concept
Heel, 1st MTPJ and 5th MTPJ must all touch the ground
If 1st MTPJ plantaflexed the heel must move into varus
Imbalance is the key to understanding
| Cavus foot | Varus hindfoot | Clawed toes |
|---|---|---|
|
Weak Tibialis anterior |
Strong Tibialis posterior |
Weak intrinsics |
|
EHL / EDL plantar flex first metatarsal Equinus forefoot |
Brings heel into varus Allows lateral column to sit on floor |
MCPJ hyper-extended Toes flexed |
|
Plantar fascia contracts Fixed cavus deformity |
History
Metatarsalgia
Lateral ankle instability - weak P brevis / hindfoot varus
Pain from claw toes
Foot numbness
Difficulty shoewear
Neurological examination
CMT - stork legs, high stepping gait, abnormal sensation, reflexes
Spina bifida - examine spine


Stork legs of CMT
Examination

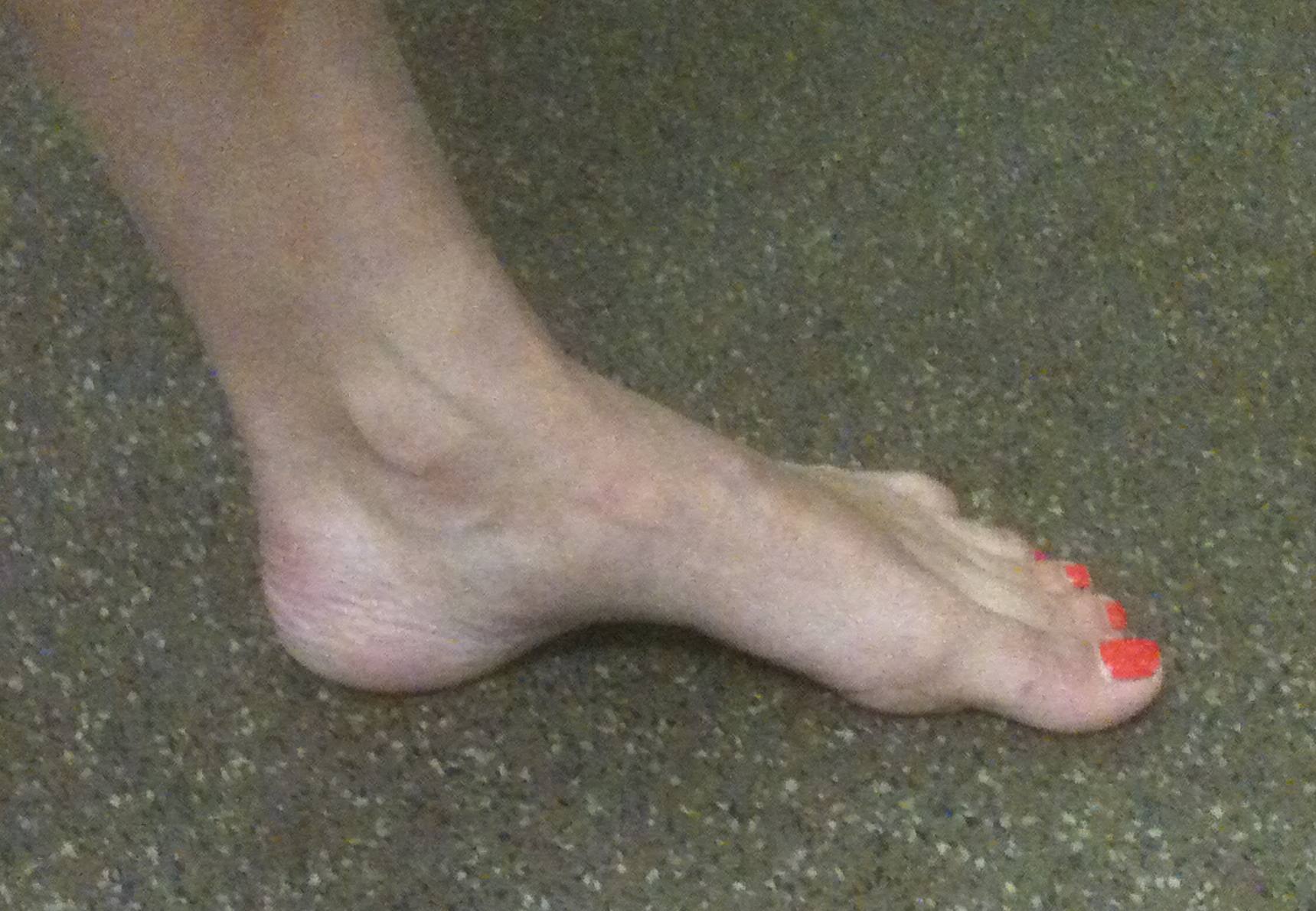

Cavus foot
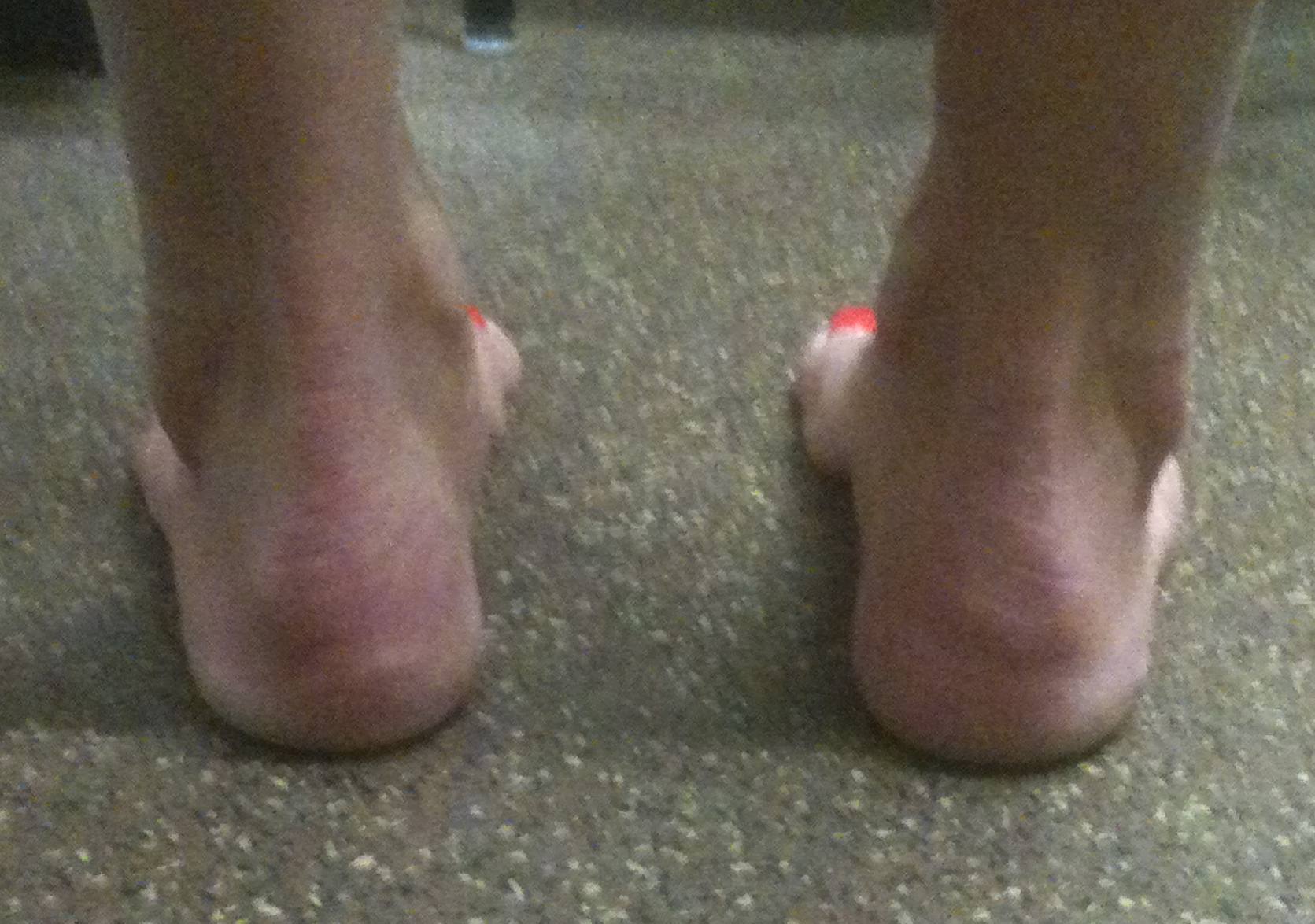
Varus hindfoot
Aim is to determine stage
1. Flexible cavus / flexible 1st metatarsal
2. Fixed 1st metatarsal equinus / mobile hindfoot varus
3. Fixed hindfoot varus
4. Bony changes
Flexible / correctable cavus / plantaflexed first metatarsal
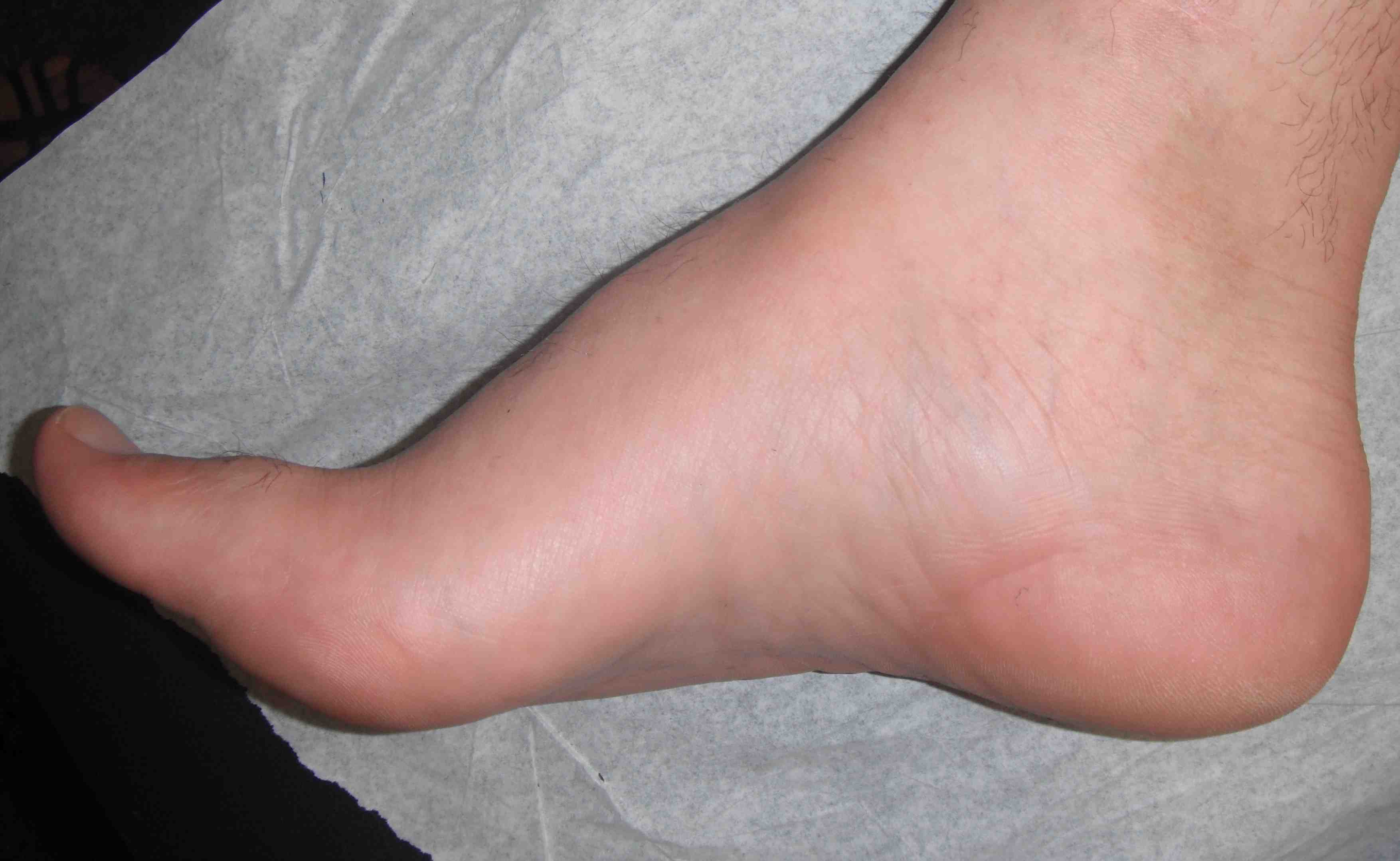
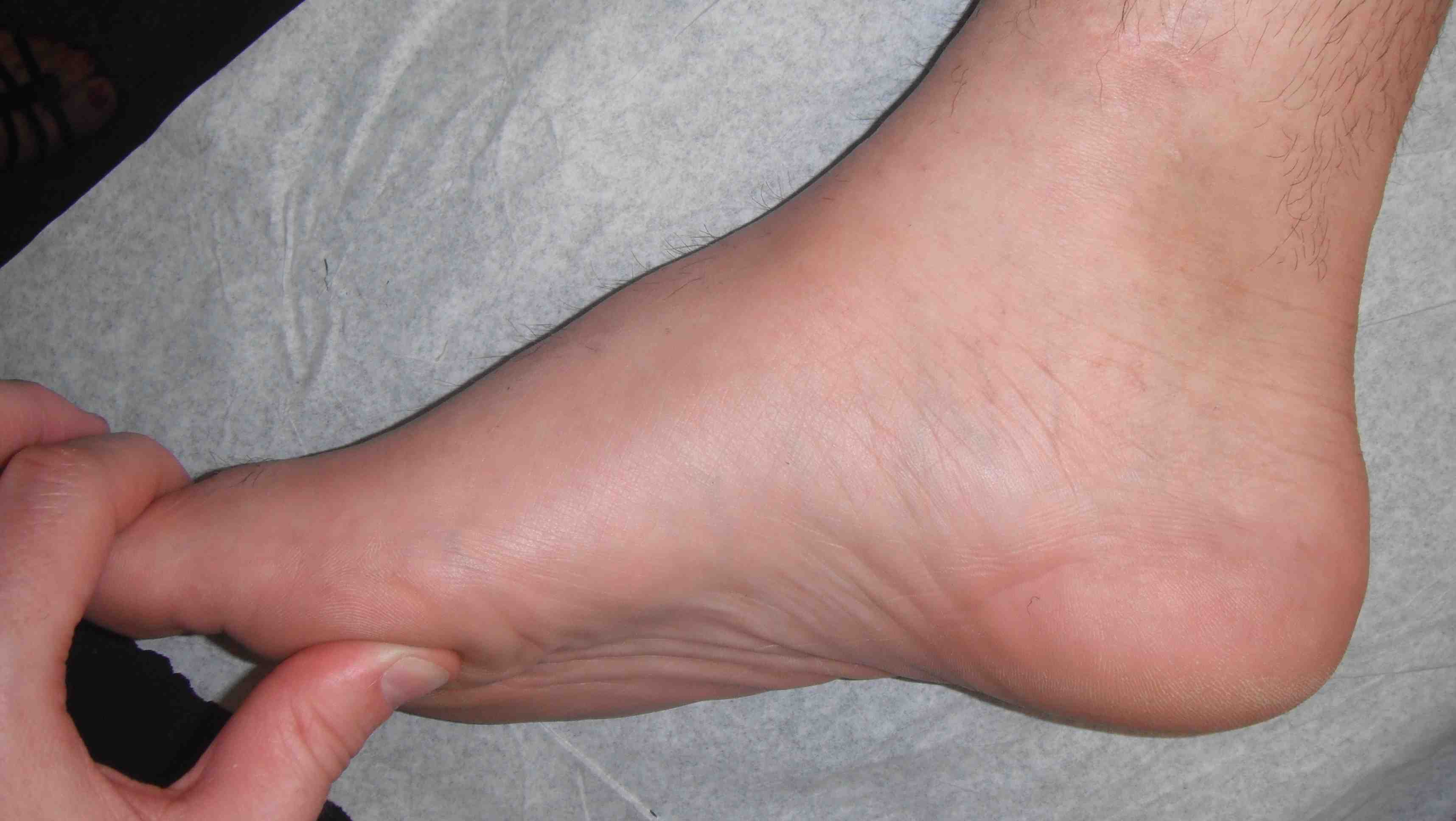
Plantarflexion corrects with pressure on 1st metatarsal
Flexible / correctable hindfoot varus
Coleman Block / Lateral Block Test
- block under lateral foot so first ray touches the ground
- eliminates forefoot deformity
- if hindfoot corrects the hindfoot is flexible



Correctable hindfoot
Differential diagnosis
| Bilateral | Unilateral | Calcaneocavus |
|---|---|---|
| Central | Peripheral / local | Calcaneum is dorsiflexed |
|
Spina bifida Spinal cord tumour |
Polio Clubfoot Incomplete spinal cord Compartment syndrome |
X-ray
Meary's angle
- longitudinal talus axis - 1st metatarsal angle
- normal 0o
- cavus > 30o


Calcaneal Pitch
- normal 20o or less
- > 30o abnormal


MRI spine
Exclude spinal dysraphism
NCS
Can help diagnose CMT
Nonoperative Management
Options
Metatarsalgia - premetatarsal dome
Claw toes - wide deep toe box
Varus - lateral heel wedge / AFO (flexible) / medial iron with lateral T strap