Creation of images
Placing patient into a strong magnetic field
- 30 000 x stronger than the earth's magnetic field
Stronger magnets, better images, shorter times
- 1.5 Tesla
- 3 Telsa
The nuclei of elements with odd numbers of protons line up
- i.e. hydrogen atoms
- hydrogen is plentiful in fat and water
A radiofrequency is then applied, exciting the protons
- as the excited protons relax back into equilibrium, a RF signal is emitted
- a receiver coil or antenna listens for an emitted radiofrequency signal
- the method and timing of the application of the radiofrequency signal can be varied
- T1 / T2 weighted, fast spin echo, fat suppressed or a gradient echo sequences
TE / time echo
- time for 90o RF to echo from tissue
- vary the time to detect the signal
TR / time repetition
- time between 90o RF
The hydrogen atoms return to a relaxed state by two mechanisms
- T1 relaxation
- T2 relaxation
- these are dependent on molecule size and binding to larger macromolecules
- all tissues have different T1 and T2 relaxation times
Liquids
- long T1 and T2 values
Fat
- short T1 and T2 values
By varying TE and TR can weight the sequences as T1 or T2
- if increase TE and TR
- produce T2 weighting
- sensitive for fluid i.e. oedema and inflammation
Contraindications
Absolute
Intracerebral aneurysm clip
Cardiac pacemakers
Automatic defibrillators
Implanted infusion devices
Internal hearing aids
Metallic orbital foreign bodies
Dorsal column stimulators
Vascular clips anywhere less than 2 weeks after insertion unless proven to be MRI compatible
Relative
- 1st + 2nd trimester of pregnancy
- middle ear prosthesis
- penile prosthesis
- internal orthopaedic hardware is safe but can create local artefact
- Claustrophobia
Disadvantages
Expensive
Can be claustrophobic
Very loud
- difficult for young children to cooperate, need sedation
Advantages
No radiation used
When to use which sequences in the musculoskeletal system
Types of images / Sequences
T1
Low TE/TR
- TE < 60 ms
- TR < 1000ms
- T1 relaxation - 1s
T1 weighted films
- fat has a bright signal e.g. bone marrow
- those tissues with little fat or water e.g. cortical bone, tendons, ligaments are dark in both T1 & T2
Standard workhorse for anatomy
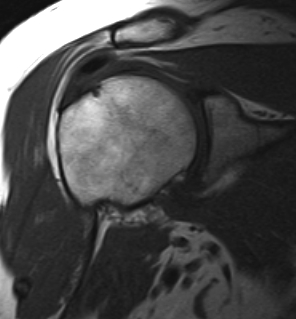
Options
- post gadolinium
- spin echo
- gradient echo
- fat saturation (important to improve contrast when using gadolinium)
Gadolinium usually performed in T1 with STIR to determine if patient has abscess
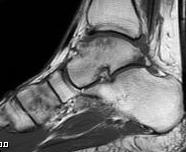
T2
High TE/TR
- TE > 60 ms
- TR > 1000 ms
- T2 relaxation - 40 ms
T2 weighted films
- fluid has a bright signal
- Highlights pathology / fluid
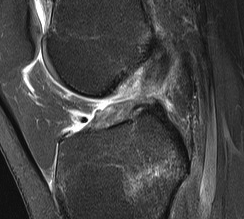
Options
- spin echo (SE)
- gradient echo (GE)
- turbo / fast spin echo (TSE/FSE)
STIR
A method for fat suppression
- very important for TI and gadolinium
- changing the appearance of fat from white to black
- important for T2 to highlight fluid
Proton density
Intermediate between T1 and T2
- fat is high signal intensity
- oedema is high signal intensity
Usually done as part of a standard T2 spin echo image
Long TR / Short TE
- TR > 1000 ms
- TE < 60 ms
Can be useful on its own to look at the anatomy of tendons and ligaments
- good for menisci
- good for cartilage
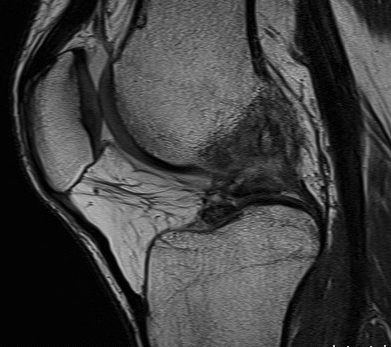
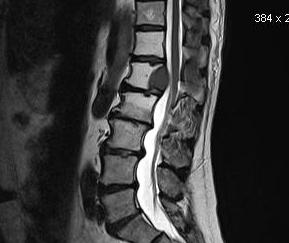
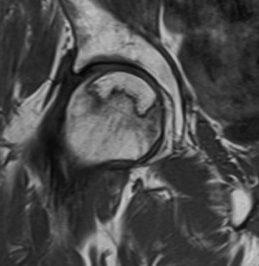
Gradient echo
Accelerated T2 sequence
- very good for ligaments and articular cartilage
Images are fast but very susceptible to chemical shifts which can produce artefacts
Shows cancellous bone as black which can be helpful
Spin echo (SE)
A spin echo is a 90o RF followed by 180o RF
Turbo spin echo or fast spin echo
- faster than standard spin echo
- an accelerated way of acquiring T2 and PD images
Fat remains bright
- cannot differentiate between water and fat
- therefore fat suppression is required & can be performed using STIR
Can reduce metal artefact
OOPS (Out of Phase Sequence)
A technique for separating water and fat
- useful if there is watery fat or fatty water in two adjacent structures
Magic angle effect
When collagen bundles are 55o to the magnetic field
- artifactual high signal on T2
- reduce with STIR
- i.e. PD show increased peroneal signal, but not seen on T2
- therefore is due to magic angle
