Definition
Technetium 99m labelled MDP (Mono - diphosphonate)
Advantages
1. Pure gamma emitter
2. Half life only 6 hours
- limits radiation exposure
3. Localises in bone
- chemical interaction on the surface of the hydroxyapatite crystal of bone
- phosphorous component interacts with the endogenous calcium
- produces insoluble technetium calcium phosphate complexes.
Pharmocokinetics
50% goes to bone
50% in equilibrium throughout soft tissues
Excreted in urine
Uptake occurs in areas of
1. Increased blood flow
- e.g. hypervascular tumours, fractures, inflammatory process
2. Increased cellular activity and mineral turnover
- osteoblastic activity produces immature osteoid
- this has numerous binding sites for developing apatite crystals
- i.e. healing fractures, inflammatory foci, growth plates
- remodelling of trabeculae in response to stress
3. Metabolic bone disease
- where there may be abundant immature unmineralised collagen
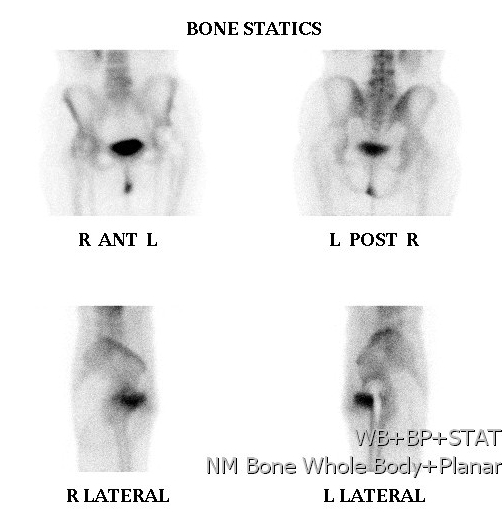
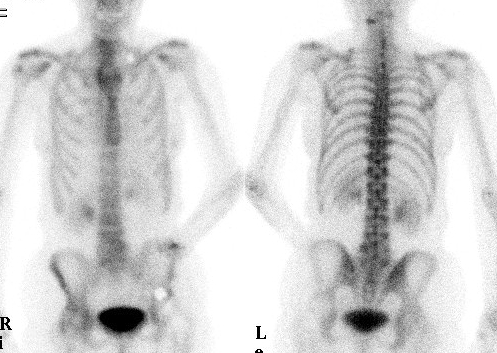
Imaging protocol
IV injection of 550 to 740 MBq of Tc 99 MDP
Patient encouraged to drink several glasses of water and micturate frequently
- dilute radiation dose to bladder wall
- accumulates in bladder
- a full bladder may obscure posterior abdominal wall
Gamma camera picks up emitted gamma rays
Anterior and posterior
- if just take anterior picture, posterior gamma rays will be absorbed by anterior body wall
3 phase scan
1. Flow phase
- patient positioned under camera
- images taken at 5 second intervals after injection into antecubital vein
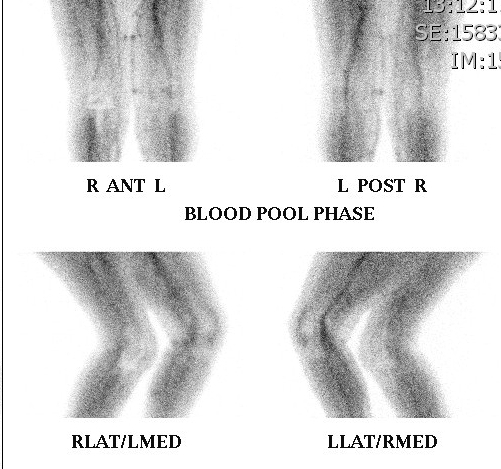
2. Blood pool phase
- within next 5 - 10 minutes
- shows extent of soft tissue and bone hyperaemia
- shows soft tissue component of lesions
- i.e. cellulitis around osteomyelitis, soft tissue extent of bony tumours
- synovial hyperaemia in inflammatory arthritis
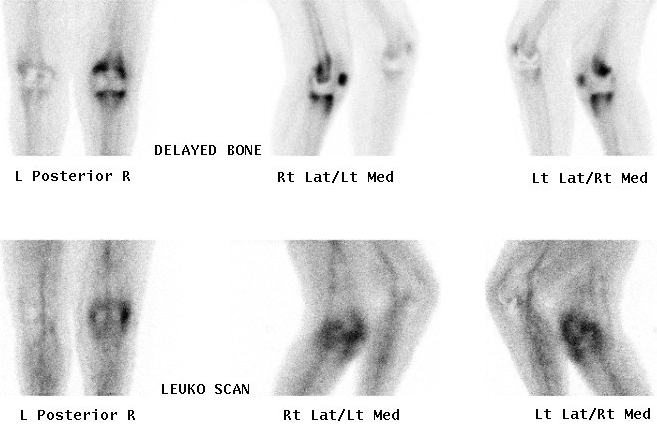
3. Delayed scan
- 2-4 hours later
- soft tissue activity has cleared
- skeletal structures demonstrated
- separate anterior + posterior scans obtained
- takes 15-30 minutes
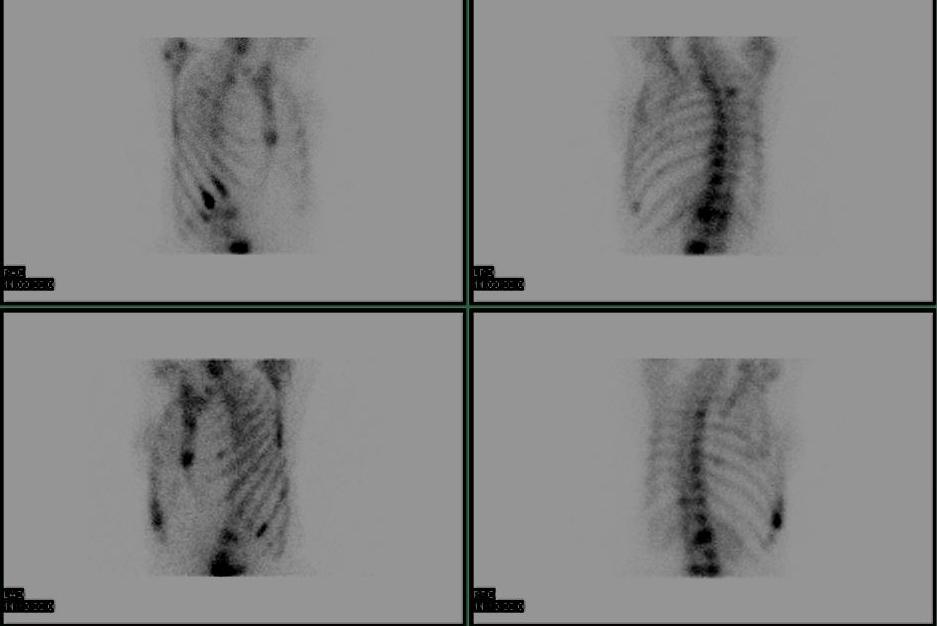
SPECT (Single photon emission CT)
Tomographic examination
- rotate gamma camera around the patient
- creates CT like slice
- useful in spine i.e. spondylysis
Normal scan
Children
- overall very active
- hot symmetrical epiphyseal growth zones
Adults
- slightly hot at ends of long bones, SI joints, tips of scapulae, nasal cavity
- age related changes (ACJ, DDD)
Hot Lesions on Bone Scan
Metastasis
Primary Malignant Bone Tumour
Osteomyelitis
Trauma / Stress Fracture
Osteoid Osteoma
Paget's
Fibrous dysplasia
Arthritis
Locally increased blood flow
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Renal osteodystrophy
Specific Conditions
1. Investigation for bony metastases
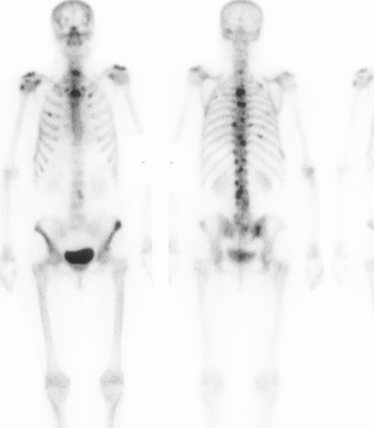
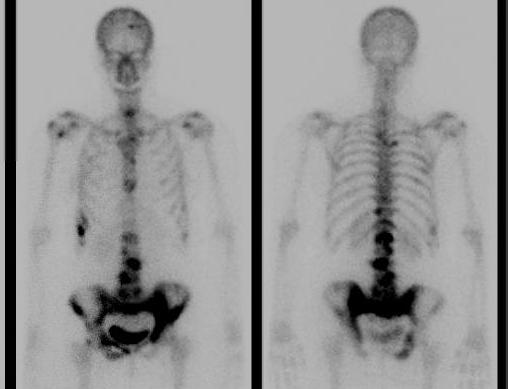
95% sensitivity
- multiple scattered focal hot spots in axial skeleton
'Superscan'
- can occur if metastases coalesce
False Negative Bone Scan
- osteolytic and osteoblastic components are balanced
- multiple myeloma, melanoma, renal cell carcinoma
2. Primary malignant bone tumours
Indication
- detects metastasis
- detects extent of lesion for resection / skip lesions
3. Benign bone tumours
Most show low grade uptake
Giant cell tumours / osteoid osteomas
- have intense uptake
4. Fractures
Uses
- detection of stress fractures
- scaphoid fractures
- myositis ossificans
Findings
- initially blood flow & blood pool phases hot
- then only delayed scan positive which remains hot for several months
- when a fracture fails to unite, blood pool phase negative with delayed scan mildly positive
Sacral insufficiency fracture
- H / Honda sign
- bilateral linear uptake in sacral alar
- transverse uptake in mid sacrum
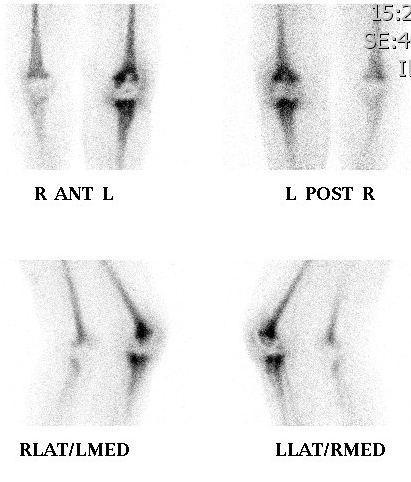
5. Infection
Cellulitis
- Hot flow and pool phases, negative delayed scan
Osteomyelitis
- All 3 phases positive
6. Investigation of pain around prostheses
Bone scan becomes normal at 12 months
- persistently positive scan means loosening or infection
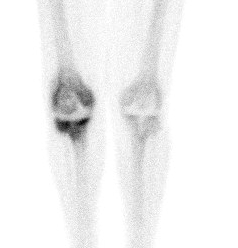
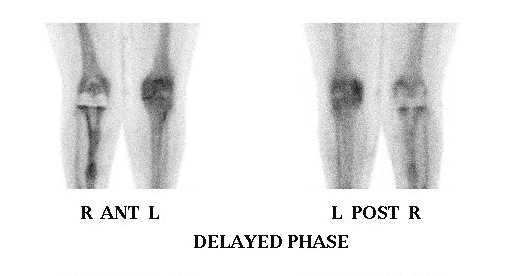
7. Arthritis
Can differentiate between degenerative + inflammatory arthritis
Degenerative
- negative blood pool phase, positive delayed scan
Inflammatory
- all three phases positive
8. Avascular necrosis
Ischaemic bone cold, surrounding bone hot
- doughnut appearance in hip
9. Paget's disease
Intensely hot on all three
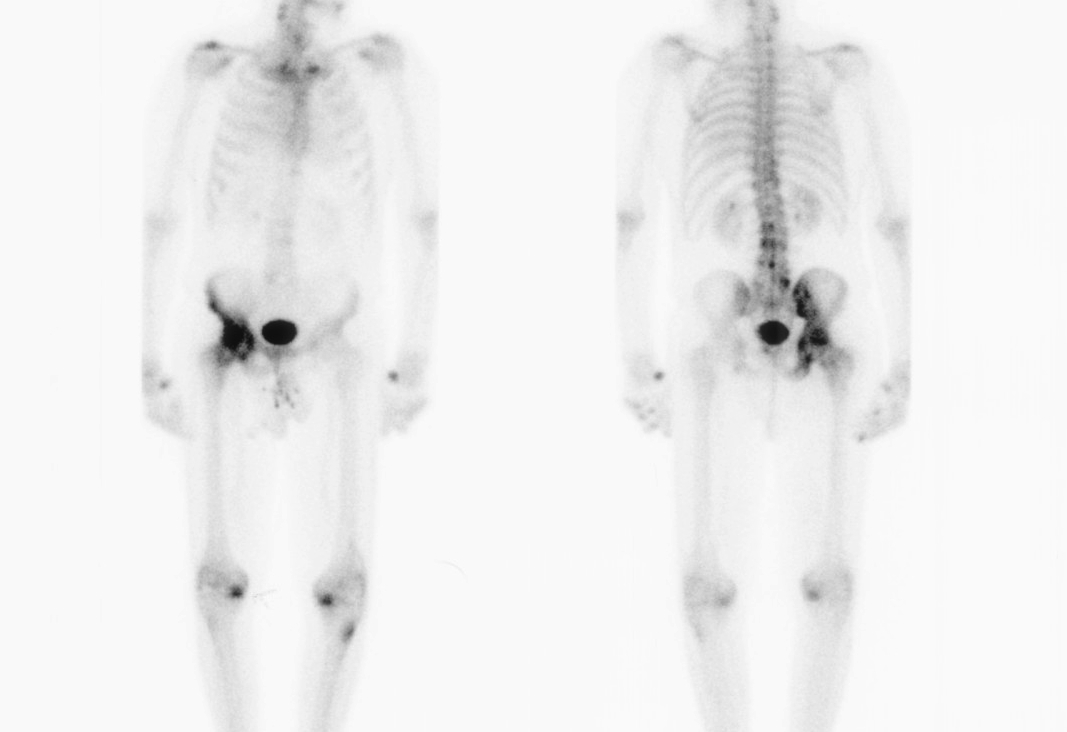
10. Fibrous dysplasia
11. Superscan
Metabolic bone disease
- osteomalacia
- hyperparathyroidism
- enal osteodystrophy
Myelofibrosis
Disseminating coalescing metastasis
12. Undiagnosed bone pain
May reveal an osteoid osteoma / unsuspected AVN / microfractures / low grade osteomyelitis
Gallium Scan
Gallium
Gallium 67 citrate
- localises in areas of inflammation and neoplasia
- due to exudation of labelled serum proteins
Technique
Delayed imaging at 24-48 hrs
Frequently used in combination with a technetium bone scan
- a double tracer technique
Less dependent on vascular flow than technetium
Difficulty in distinguishing between cellulitis and osteomyelitis
Technetium or Indium 111-Labelled White cell scan
Technique
Label patients own WBC's with radioactive tracer
Labelled white cells accumulate in areas of inflammation but not in areas of neoplasia
Useful in diagnosing osteomyelitis or infection around joint replacement
Unlike gallium also useful in the presence of pseudarthrosis