Background
Definition
Multi-ligament knee injury (MLKI)
- 2 or more ligaments disrupted
Knee dislocation
- ACL + PCL + one of collaterals
Mechanism of injury
High energy (MVA)
Low energy (sport)
- low energy has 5% arterial injury

Multi-ligament knee injury (MLKI)
- 2 or more ligaments disrupted
Knee dislocation
- ACL + PCL + one of collaterals
High energy (MVA)
Low energy (sport)
- low energy has 5% arterial injury
Patella may develop from one or multiple ossification centres at 3 years
Failure of centres to fuse may produce bipartite or tripartite patella
- usually bilateral and painless
Classically superolateral
I Inferior Pole 5%
II Lateral 20%
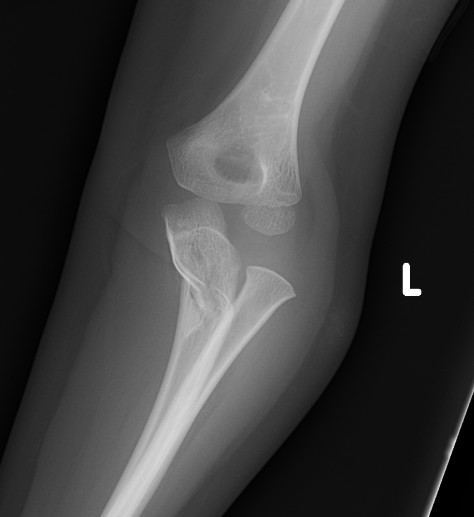
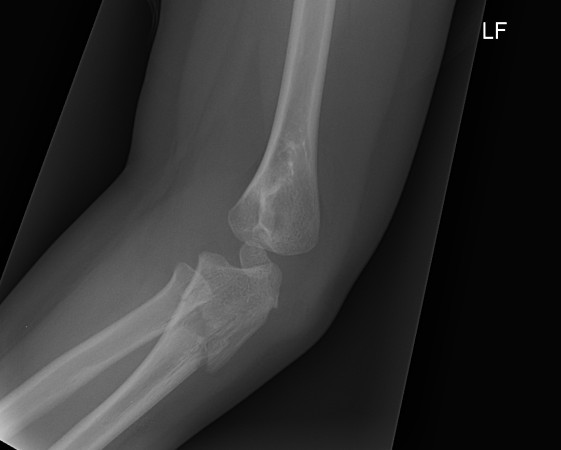
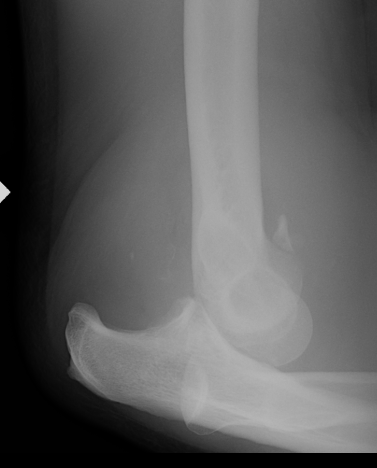
Fracture / plastic malformation of proximal ulna with dislocation of radial head
Radio-capitellar line disrupted
Second most common hindfoot after calcaneal fractures
Aviators Astragalus
Fall from height
- hyper-dorsiflexion injury
- neck of talus strikes the anterior tibia
More than half surface covered by articular cartilage
- medial articular wall straight
- lateral articular wall curves posteriorly
Hyper-dorsiflexion injury to 1st MTP joint
Grade 1 - Mild sprain
Symptoms
- minimal swelling / ecchymosis
Management
- return to play immediately
- RICE / NSAIDS
Grade 2 Partial tear plantar plate
Symptoms
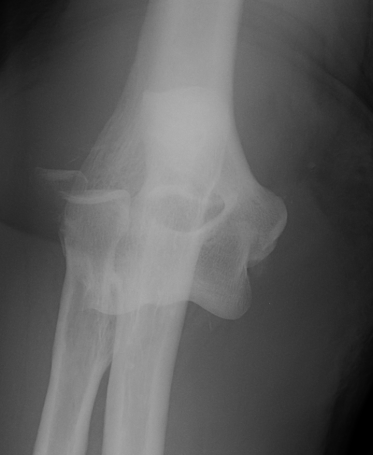
6 /100 000
- second most common dislocation after shoulder
FOOSH
Young men
FOOSH
- axial load, dorsiflexion and radial deviation
DISI occurs in ulna deviation
Type A Stable acute fracture
A1 Tubercle
Scaphoid non union advanced collapse
Xray / CT
- non union of scaphoid
- radio-scaphoid OA
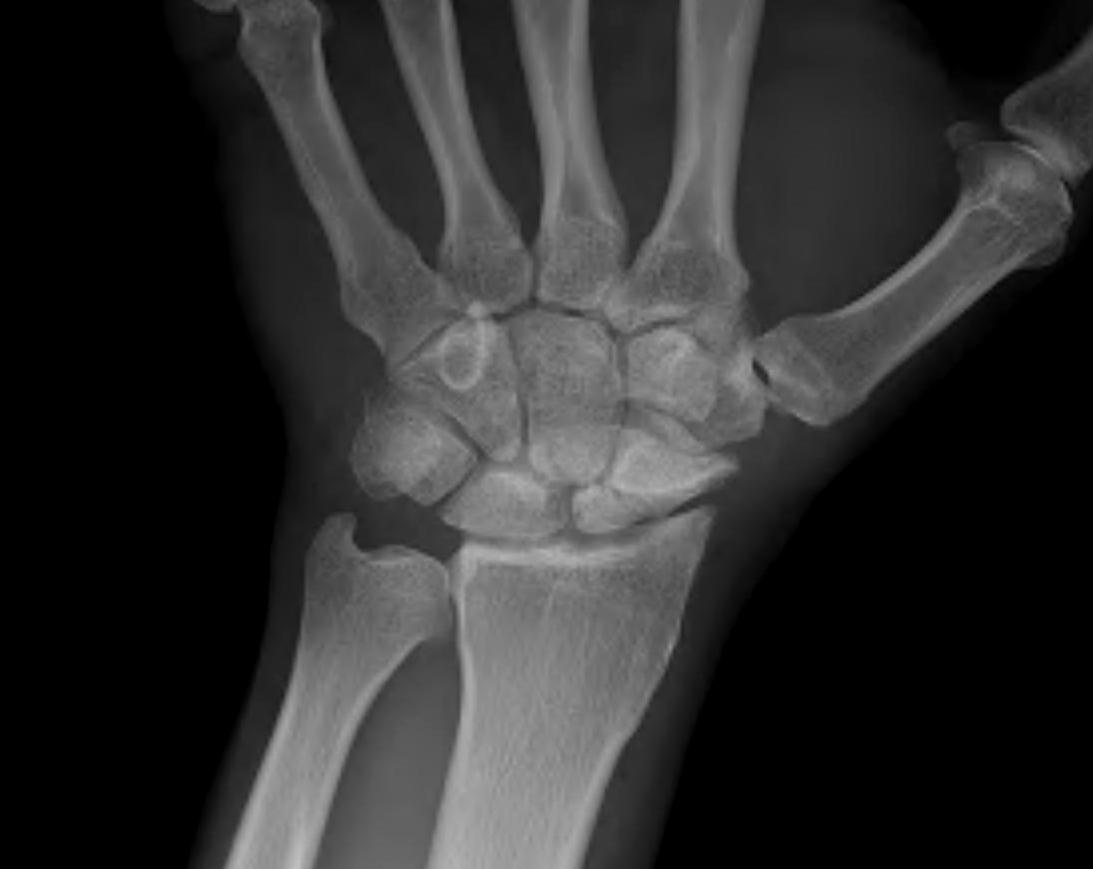
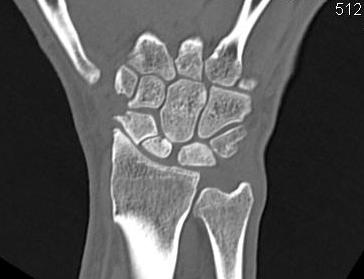
2 groups
1. Elderly
- low velocity injury
- osteoporotic
- need to start bisphosphonates
2. Young patients
- high velocity injury
Distal Radius Angles
- radial volar tilt 11°
- radial inclination 22°
- radius is 11 mm longer than ulna
- ulna variance 2mm positive on average
Avascular necrosis & subsequent disintegration of lunate
50-75% history of trauma
Occasionally seen in sickle cell / steroid use
Trauma disrupting vascularity
- single incident with disruption of blood supply