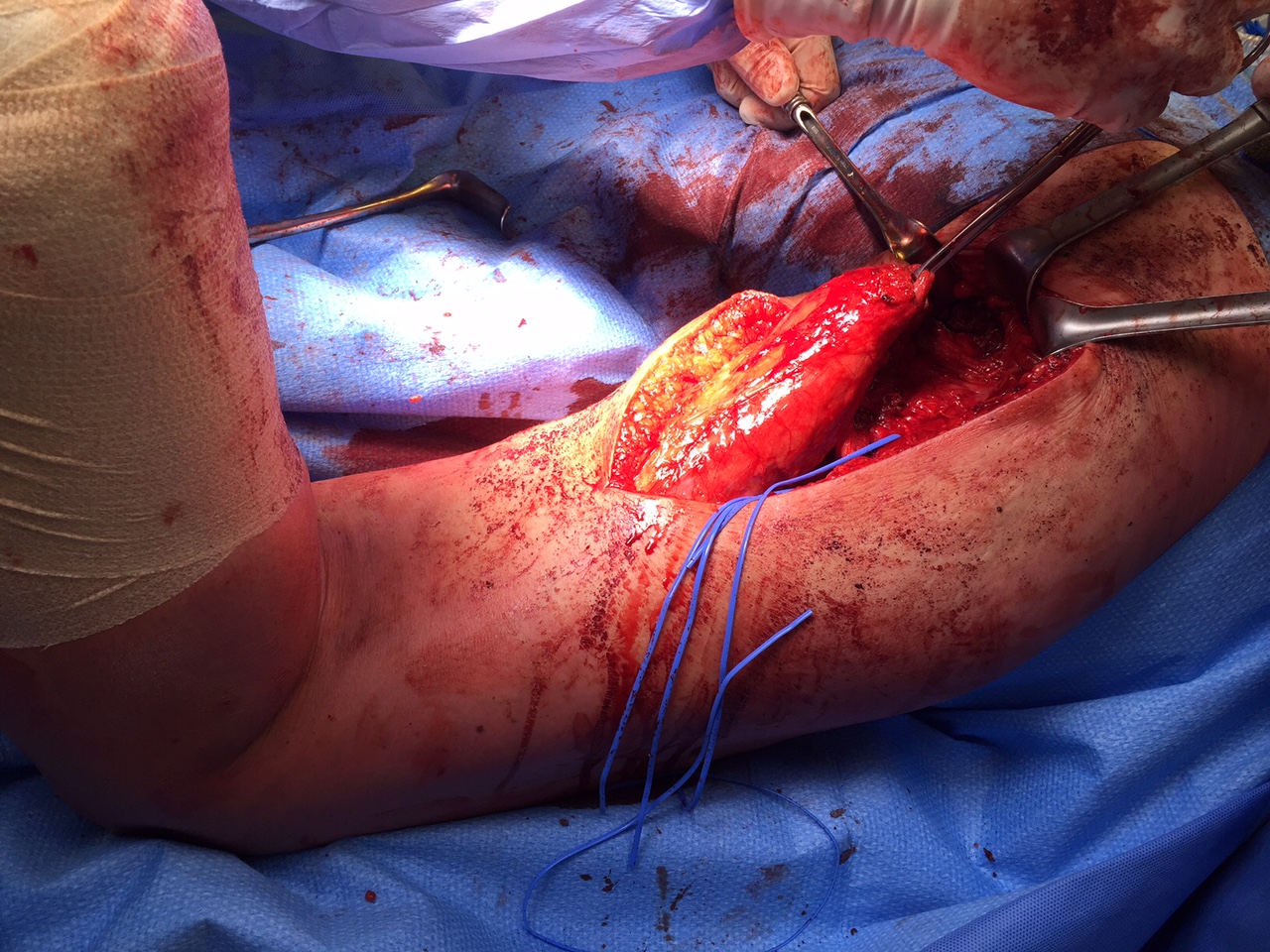
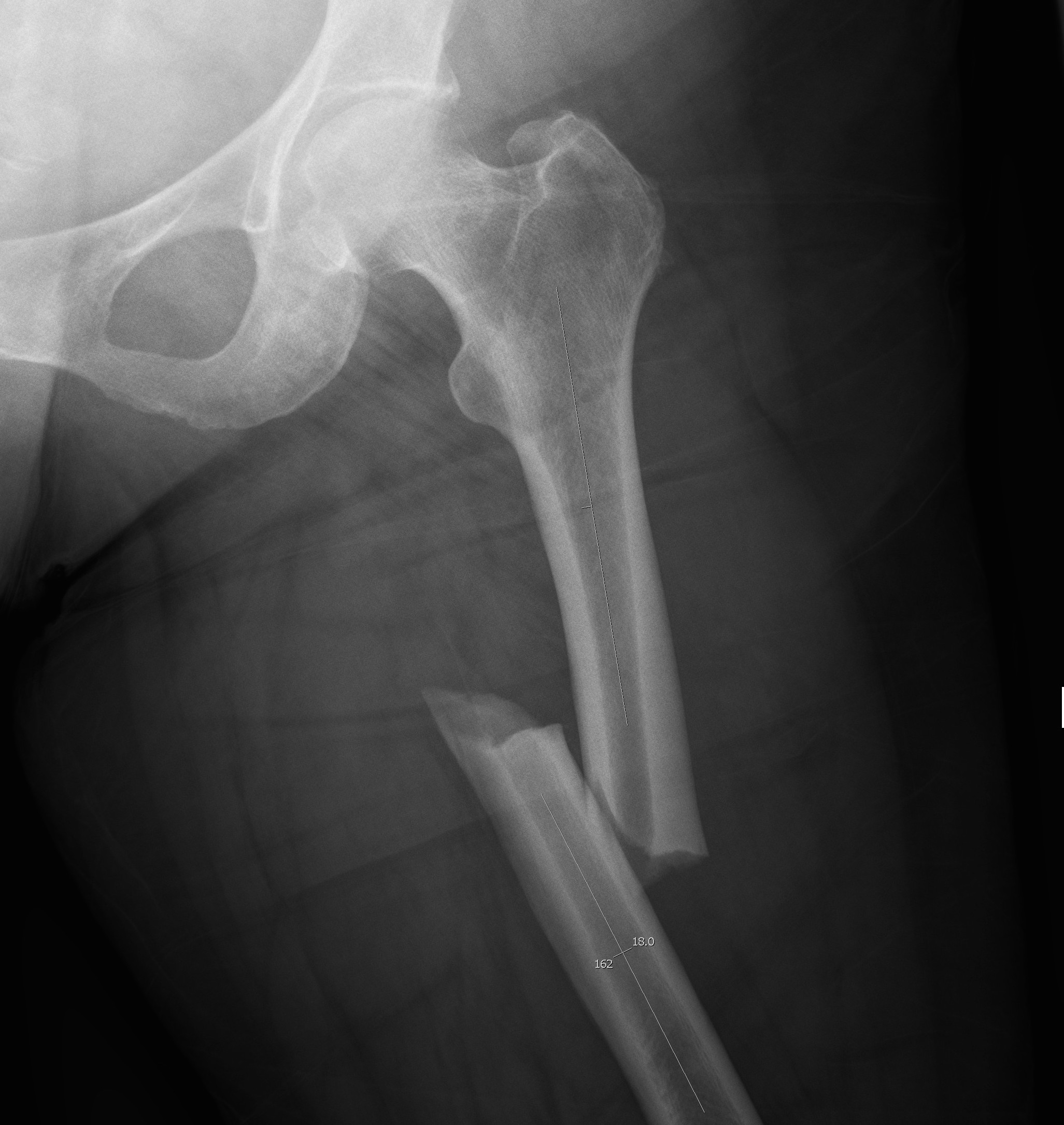
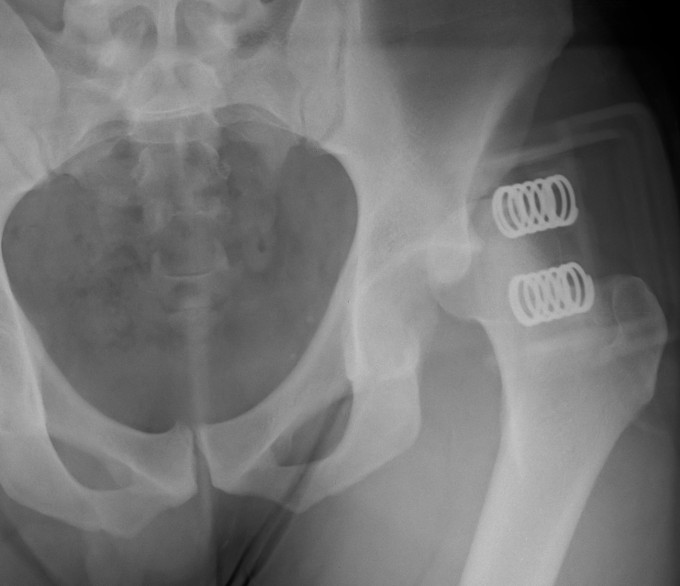
Sinus Tarsi Syndrome
Anatomy
Osseous canal between talus and calcaneum
- interosseous talo-calcaneal ligament
- cervical ligament
- joint capsule
- nerve endings / arterial anastomoses
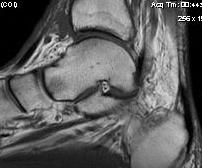
Aetiology
Flat foot / overpronation
Inversion / sprain
Pathology