operative options
Sportsman's Hernia
Definition
Groin pain in athletes
- secondary to tear in external oblique fascia
Epidemiology
Sports with aggressive adduction
- hockey / soccer
Pathology
Tears in external oblique fascia
- tend to be central
- around spermatic cord and ilioinguinal nerve
- pain may be from nerve entrapment
DDx
Adductor Longus Tear
Management
Non Operative
Options
Metatarsalgia
- preMT dome
Claw toes
- wide deep toe box
Foot drop
- AFO
Insensate foot
- custom orthosis
Varus
- lateral heel wedge
- AFO (flexible)
- medial iron with lateral T strap
ITB Friction Syndrome
Pathology
ITB rubbing on LFC
- long distance runners (slow running more at risk than fast)
- cyclists (seat too high, improper technique)
ITB becomes tight, especially posterior portion
Develop inflammed tissue under ITB
- synovium
- bursa
Aetiology
Overuse
- sudden increase in distance
- hill running
- genu varum
- improper shoe wear
Intertrochanteric Fractures
Definition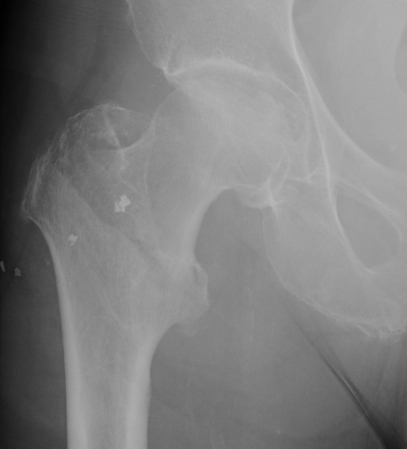
Fracture which extends between the trochanters of the proximal femur
- lower limit is inferior border of lesser tuberosity
Anatomy
Extra capsular / well vascularized
The key to stability is the posteromedial cortex
Subtrochanteric Fractures
Definition
Fracture below lesser trochanter / proximal 5 cm femur
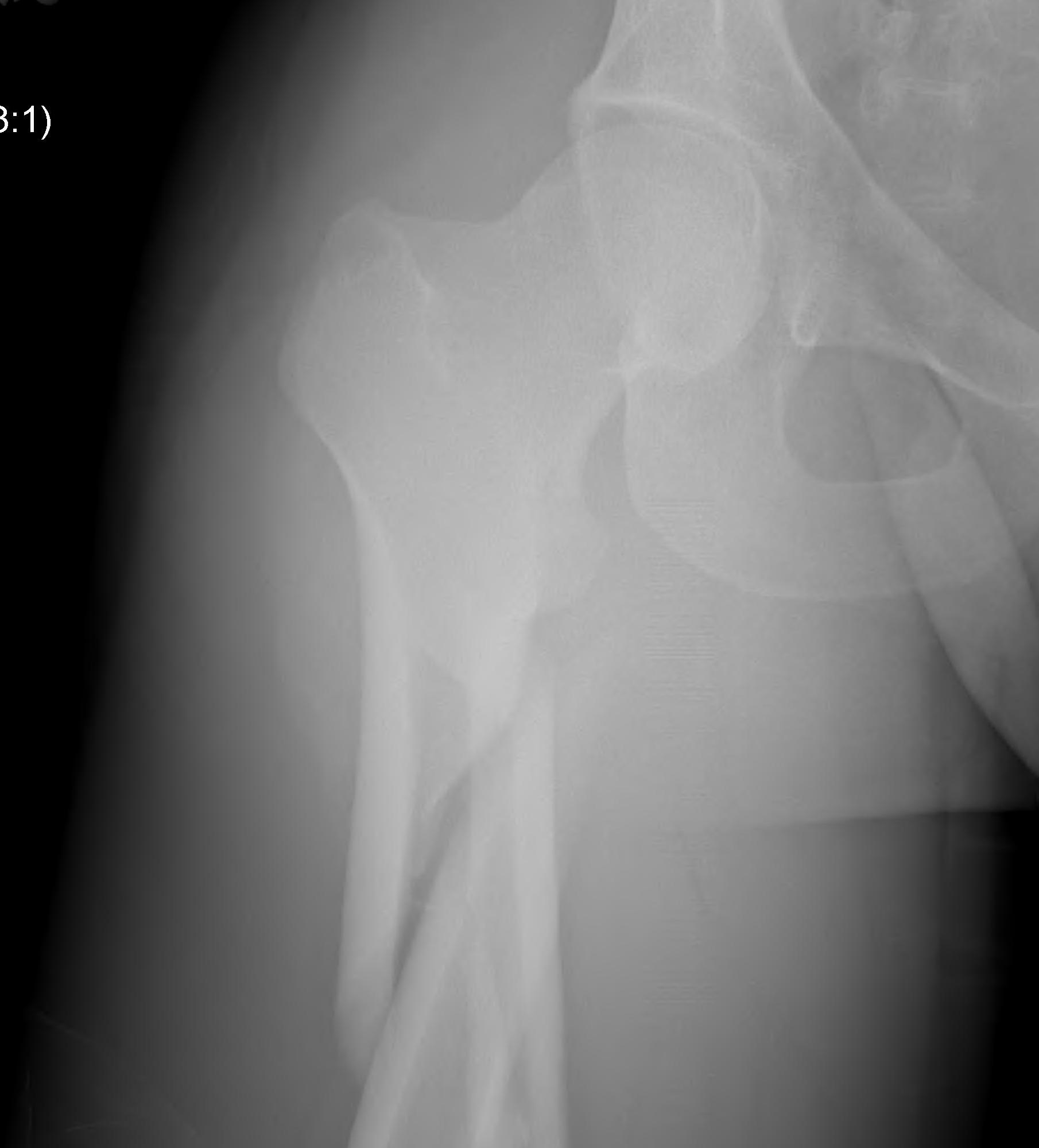
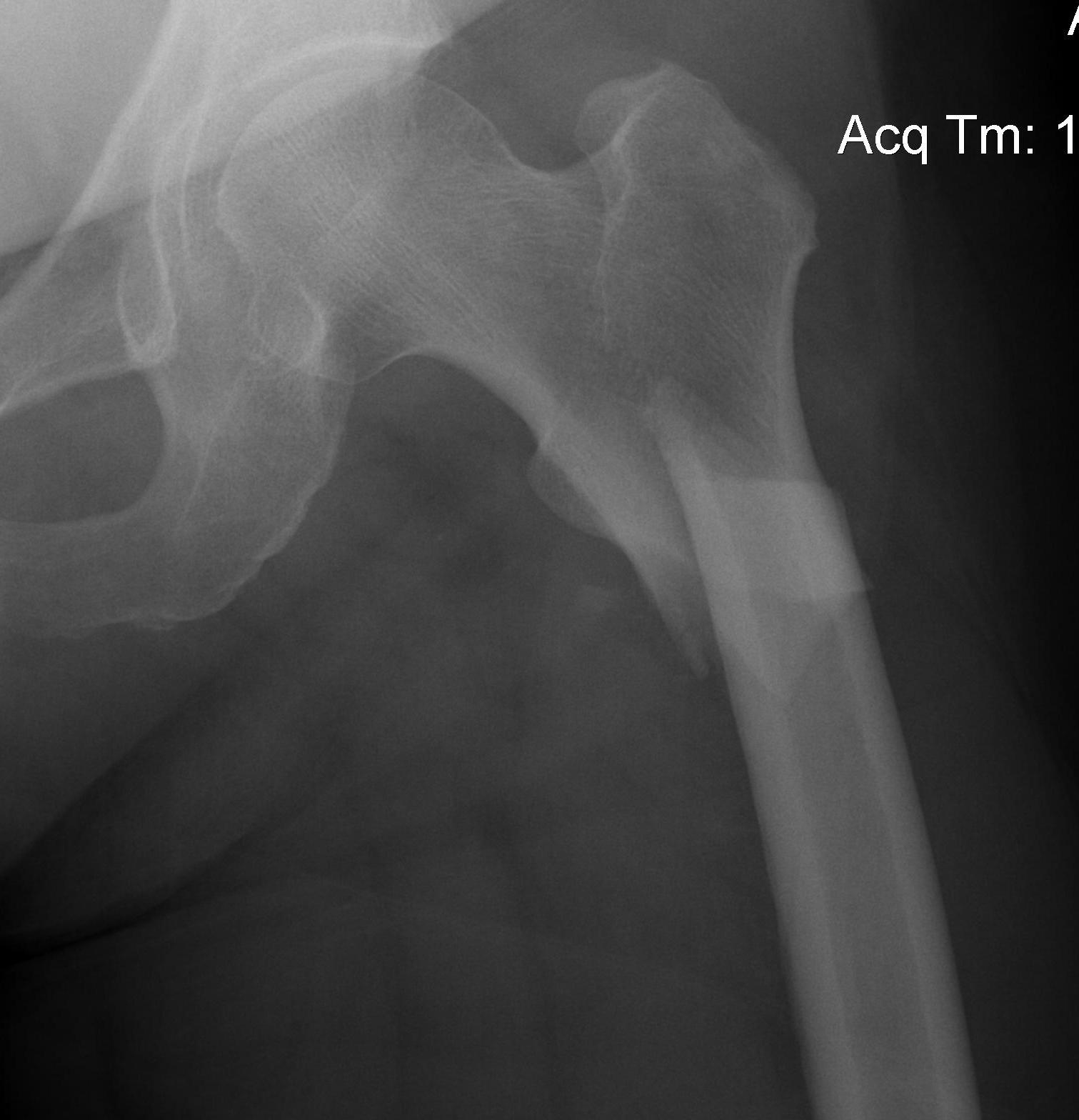
Aetiology
Young patients / high velocity injuries
Old patients / osteoporosis
Forefoot
Issues
1. Painful Bunion / Hallux valgus
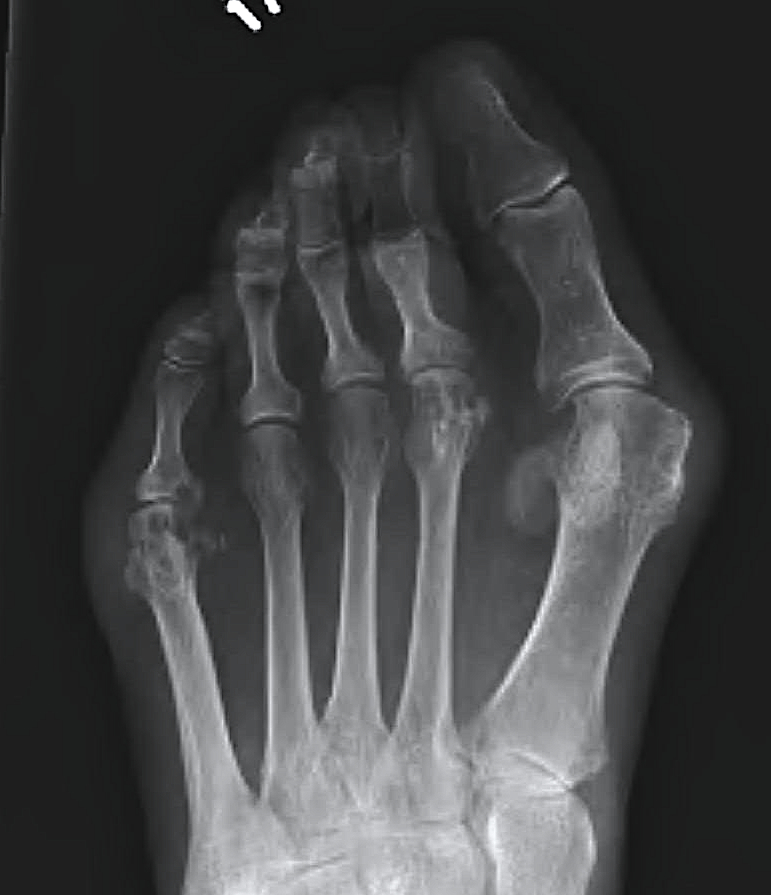
2. Metatarsalgia / MTPJ dislocation
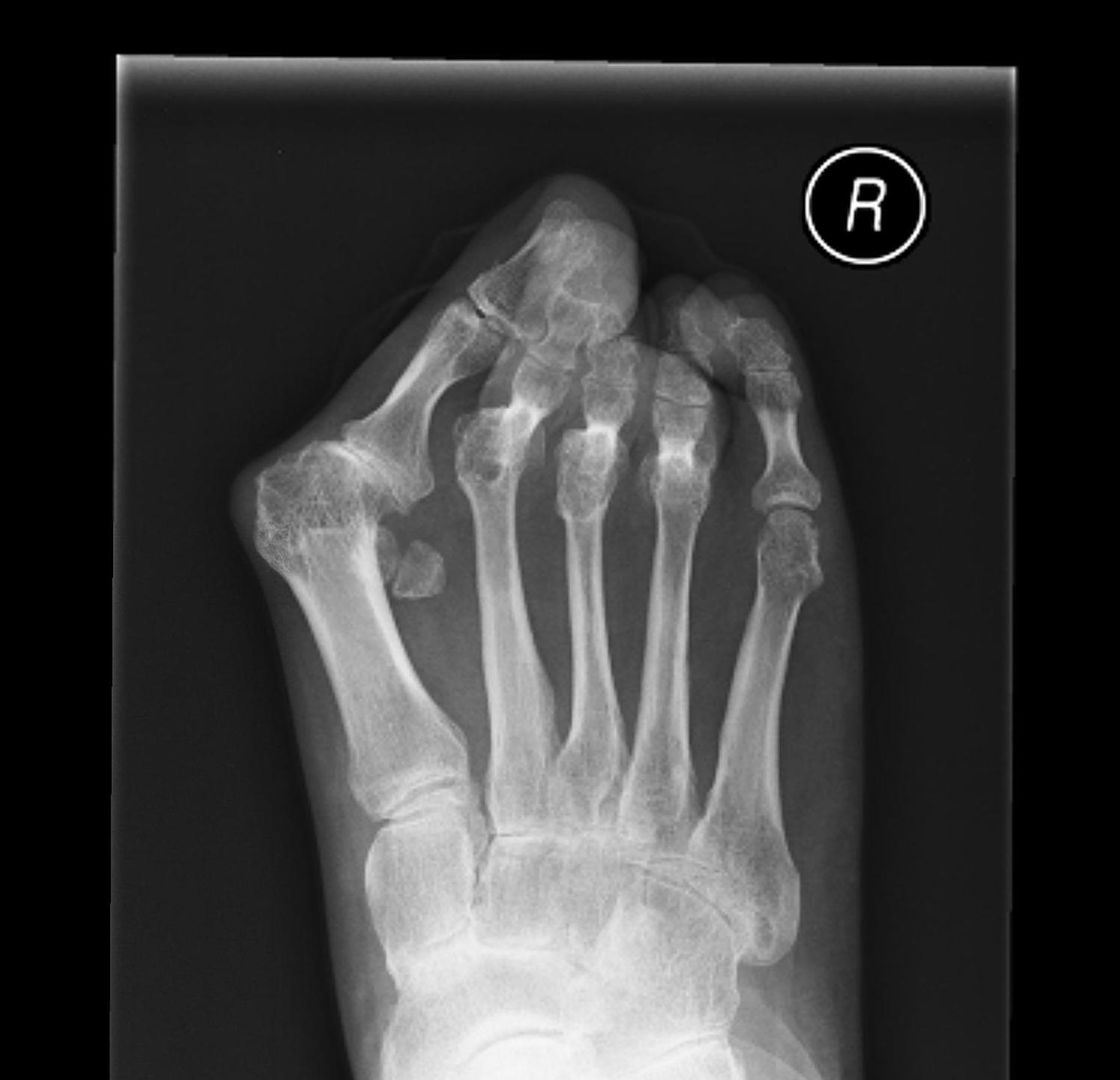
3. Claw toes
Flexible Flat Feet
Symptoms
Complain of pain with prolonged standing
Complain feet tire easily
Examination
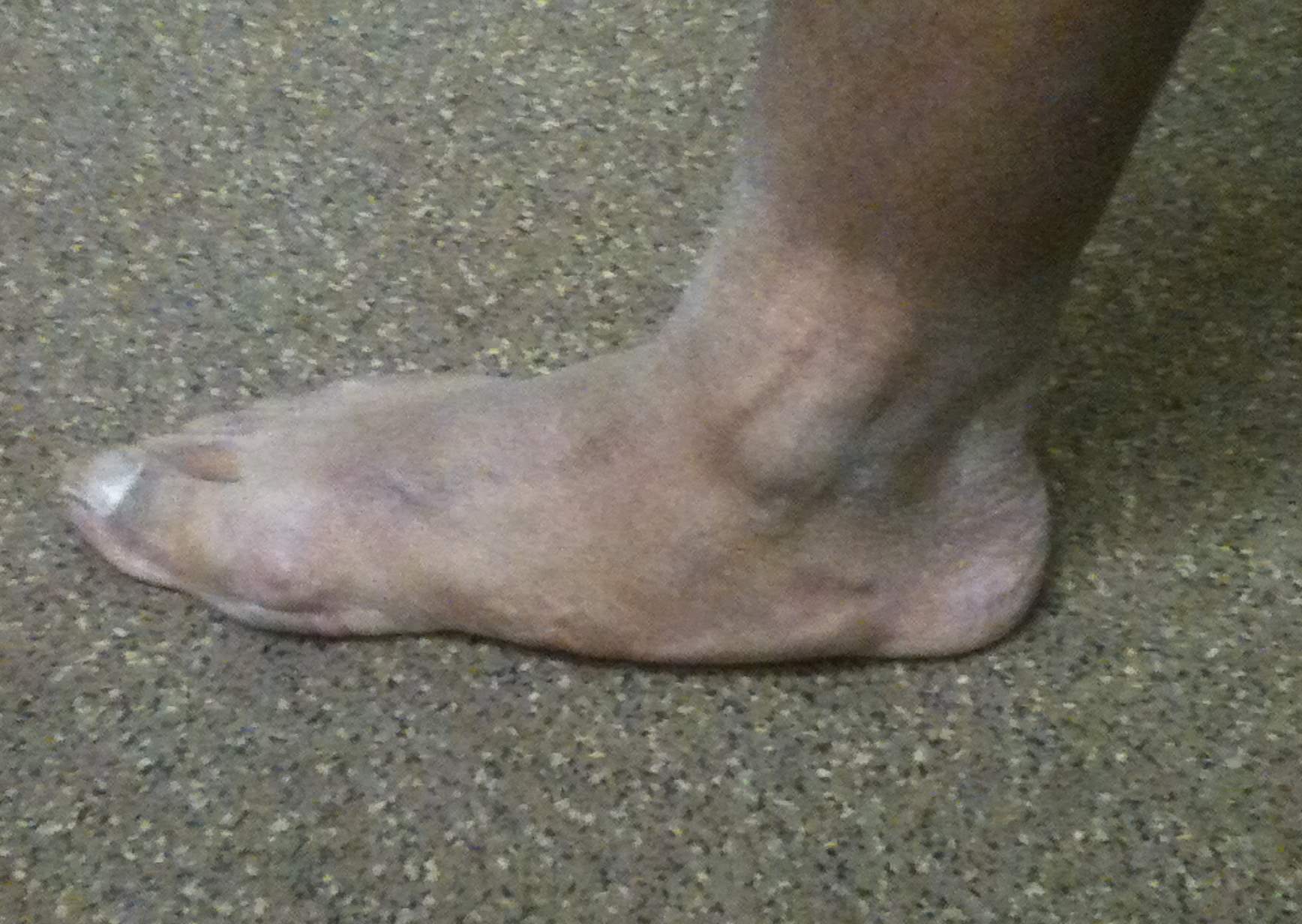
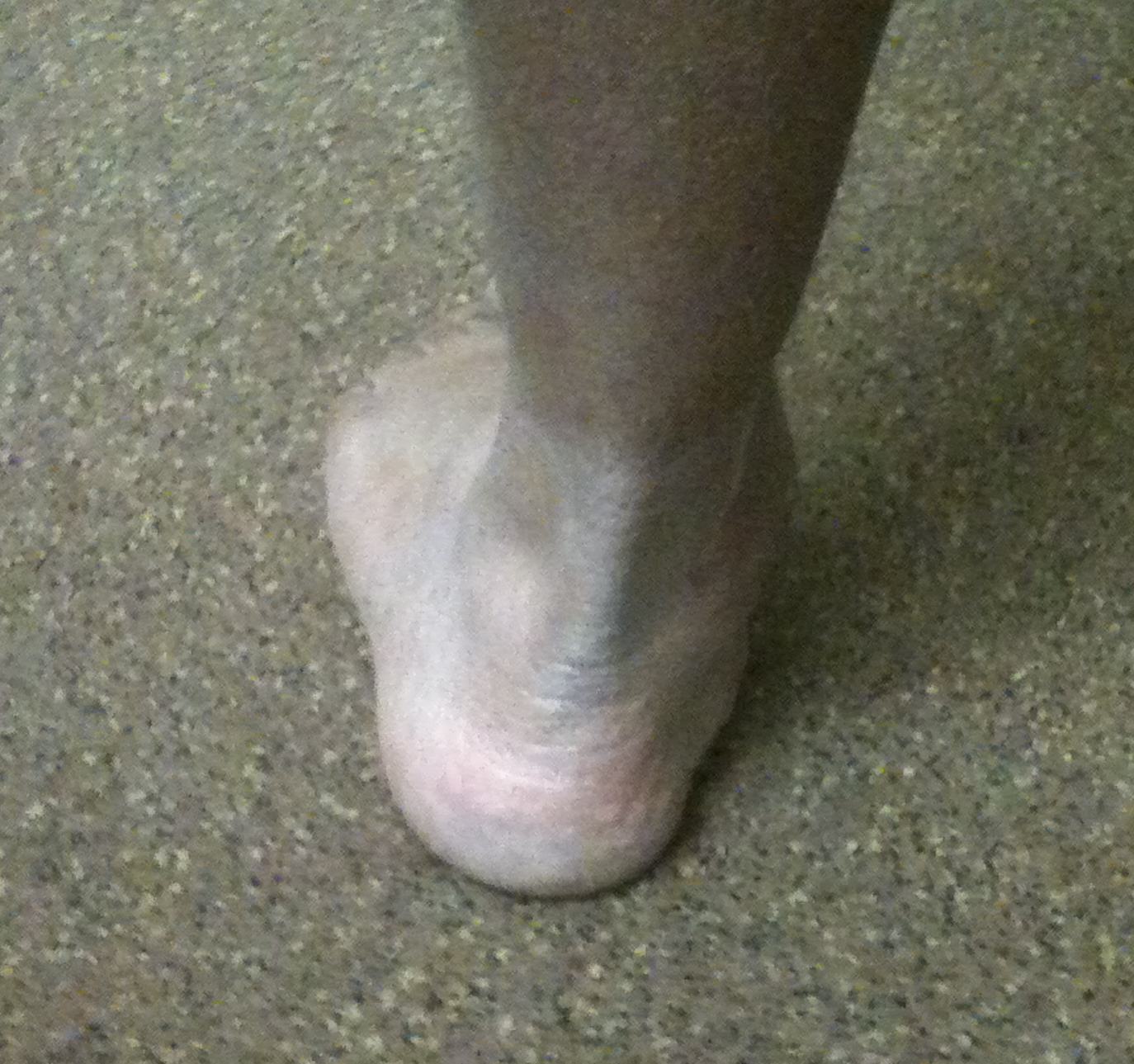
Overall alignment
Heel raises
Bunionette
Definition
Painful prominence of lateral eminence of 5th metatarsal head
Coughlin Classification
Type I deformity
- prominent lateral condyle 5th metatarsal head
- lateral condylectomy
Type II deformity
- lateral bowing of 5th metatarsal
- chevron osteotomy
Hallux Rigidus
Definition
Painful restriction of dorsiflexion of the great toe
- secondary to degenerative changes in MTPJ
- initially pain and synovitis
- osteophytes don't form medially or on plantar aspect
Epidemiology
Two peaks
1. Adolescence F > M
2. Middle Age M > F
Aetiology
Often Idiopathic
Trauma
