Background
Epidemiology
Much less common than hip and knee OA
Patients tend to be younger


Much less common than hip and knee OA
Patients tend to be younger
National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center (2021) Facts and figures at a glance
- road traffic accident 40%
- falls 30%
- sports 10%
Chen et al Arch Phys Med Rehab 2016
- 80% male
- cervical (60%), thoracic (30%), lumbar (10%)
Congenital Talipes Equinovarus
Congenital abnormality of the foot characterised by
- hindfoot equinus & varus
- forefoot Adduction
- midfoot Supination
Latin: talus - ankle / pes - foot / equinus - horse like
Foot
- pipe stem calf
- short wide foot
- small heel
- curved lateral border
Host
Wound
Operating room environment
Antibiotics
Operative technique
Post operative
Immunocompromised
RA (0.9 v 2.2%)
Psoriasis
DM (6%)
Poor nutrition
Obesity
UTI
Prednisone
Previous operation
Previous infection
Age
To produce sufficient thrombin to rapidly convert soluble fibrinogen into insoluble mass of fibrin
Coagulation cascade must be localised & limited to site of tissue injury
1. Immediate Control of Blood Loss
Vascular Phase
- damage to blood vessel triggers reflex vasoconstriction
Platelet phase
Palmar Fibromatosis
AD with variable penetration
Murrell's Theory of Pathogenesis
1. Microvascular ischaemia
Accumulation of calcium salts in the soft tissues
- Dystrophic or Metastatic
Different from bone formation
- calcification is typically amorphous calcium crystals
- ossification has bone organic matrix (Osteoid) & cells
Dystrophic
Metastatic
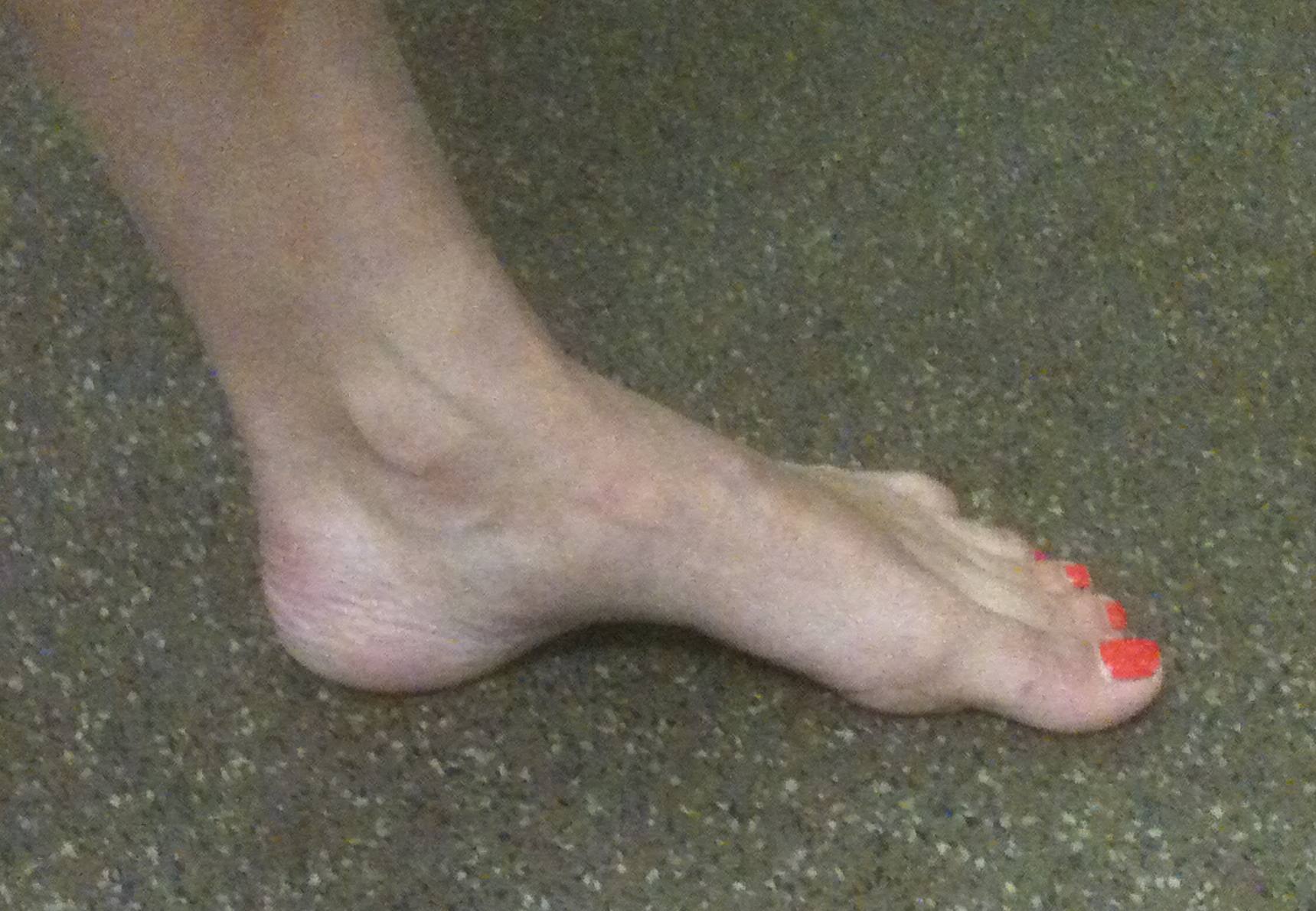
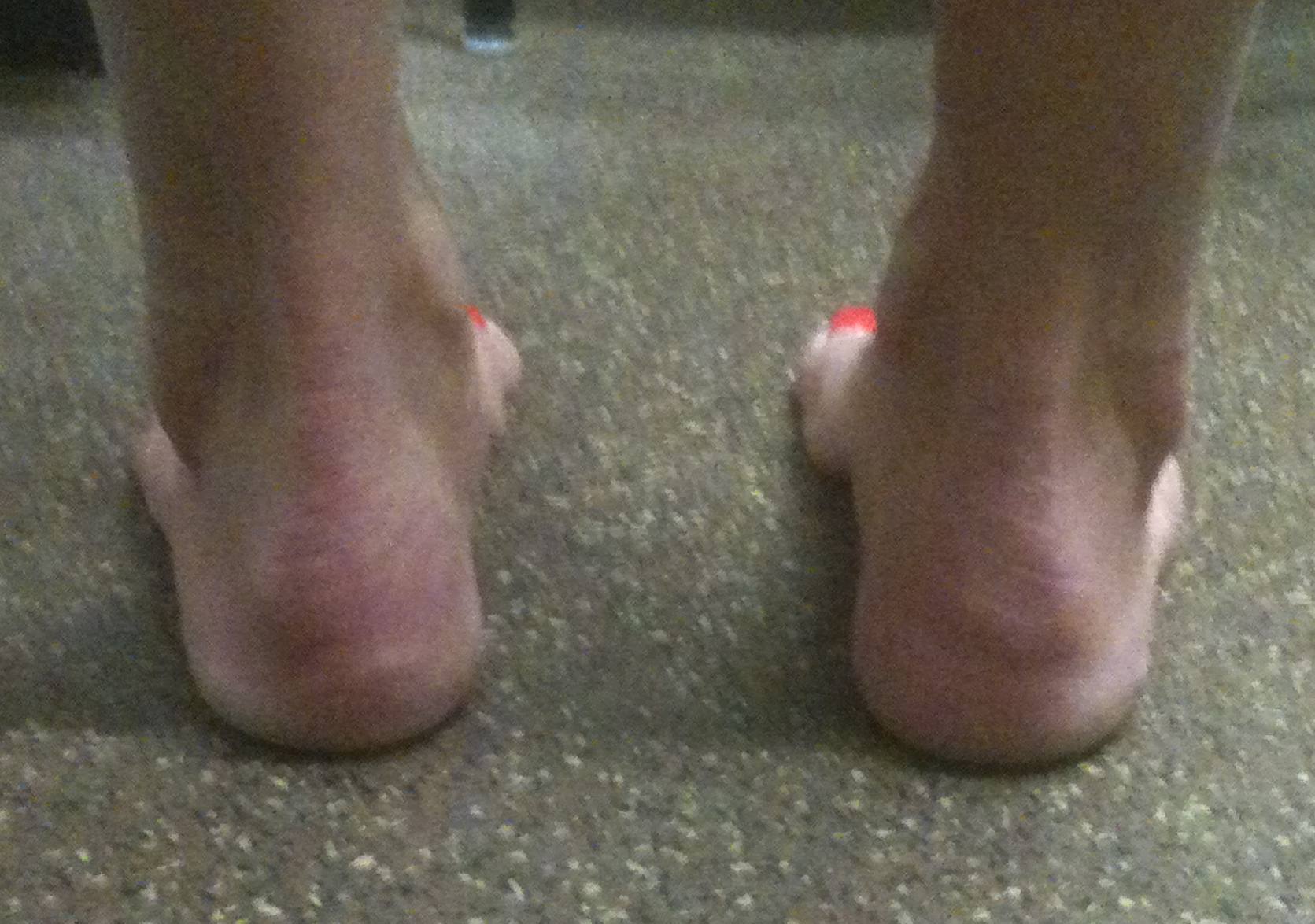
A fixed equinus deformity of the forefoot in relation to the hindfoot
- resulting in an abnormally high arch that fails to flatten with weight bearing
- deformity may be forefoot, hindfoot or combination