Approaches
Ankle
- anterior
- anterolateral
- posterolateral
Hindfoot
- lateral
- Ollier's
Anterior approach to Ankle
Concept
Between EHL and EDL
Indications
- drainage of ankle joint
- ankle arthrodesis
- ORIF tibial plafond
- removal of loose bodies
Approach
Position
- supine / tourniquet
Incision
- 15cm longitudinal incision over anterior aspect of ankle joint midway between malleolus
Internervous plane
- no true internervous plane
- EHL / EDL define a clear intermuscular plane with anterior tibial vessels / deep peroneal nerve between them
Superficial dissection
- incise extensor retinaculum
- dissection in intermuscular plane between EHL / EDL a few cm above ankle joint
- identify anterior tibial vessels / deep peroneal nerve medial to EHL tendon
- retract EHL / NV bundle medially
Deep dissection
- incise anterior capsule ankle joint
- detach capsule from tibia or talus by sharp dissection
Dangers
- superficial peroneal nerve
- anterior tibial vessels / deep peroneal nerve
Extensile measures
- extended proximally to expose anterior compartment & proximal tibia between Tibia and T anteror
- distal extension rarely required onto dorsum of foot
Anterolateral approach to ankle and hind foot
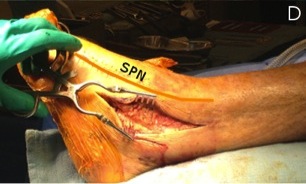
Concept
Between Peroneus Tertius and Brevis
Elevate EDB
Indications
- exposes AKJ / STJ / CCJ / STJ
- ankle fusions
- triple arthrodesis & pantalar arthrodesis
- talus excision
- open reduction of talar dislocations
Approach
Position
- supine with sandbag under hip to IR leg
Incision
- 15cm curved incision on anterolateral aspect of ankle joint.
- begin 5cm proximal to ankle joint
- 2cm anterior to fibular border
- crossing joint 2cm medial to lateral malleolus tip
- end over base of 4th MT
Internervous plane
- between peroneus tertius (DPN) and peroneus brevis (SPN)
Superficial dissection
- identify dorsal cutaneous branches of SPN
- incise superior (tibia to fibula) / inferior extensor retinaculum (calcaneum to MM and fascia)
- incise down to bone lateral to peroneus tertius / EDL
Deep dissection
- retract peroneus tertius / EDL medially to expose anterior ankle joint
- distally, expose origin of EDB on dorsum of calcaneus
- detach EDB by sharp dissection reflecting origin distally and medial
- this will involve division branches of lateral tarsal artery
- identify dorsal capsules of TN / Calcaneo-cuboid joints.
- mobilize fat pad in sinus tarsi to identify subtalar joint (preserve fat pad )
- open joints by forcefully plantar flexing and inverting foot
Dangers
- DPN
- Anterior tibial artery
Posterolateral approach Ankle Joint
Concept
Between Peroneals and Tendo achilles
Indications
- treat conditions of posterior aspect of tibia and ankle joint
- ORIF posterior malleolus
- removal benign tumors
- FHL tendonitis / Os trigonum
Approach
Position
- patient prone
Incision
- 10cm longitudinal incision
- halfway between posterior border of lateral malleolus and lateral border of T achilles
Internervous plane
- between PL and FHL tendon
Superficial dissection
- mobilize skin flaps
- identify peroneal tendons around back of lateral malleolus
- release fascia at posterior border of the peroneal muscle
- retract them anteriorly to expose FHL muscle at level of ankle joint
- FHL is most lateral of deep calf flexors and is still muscular at this level
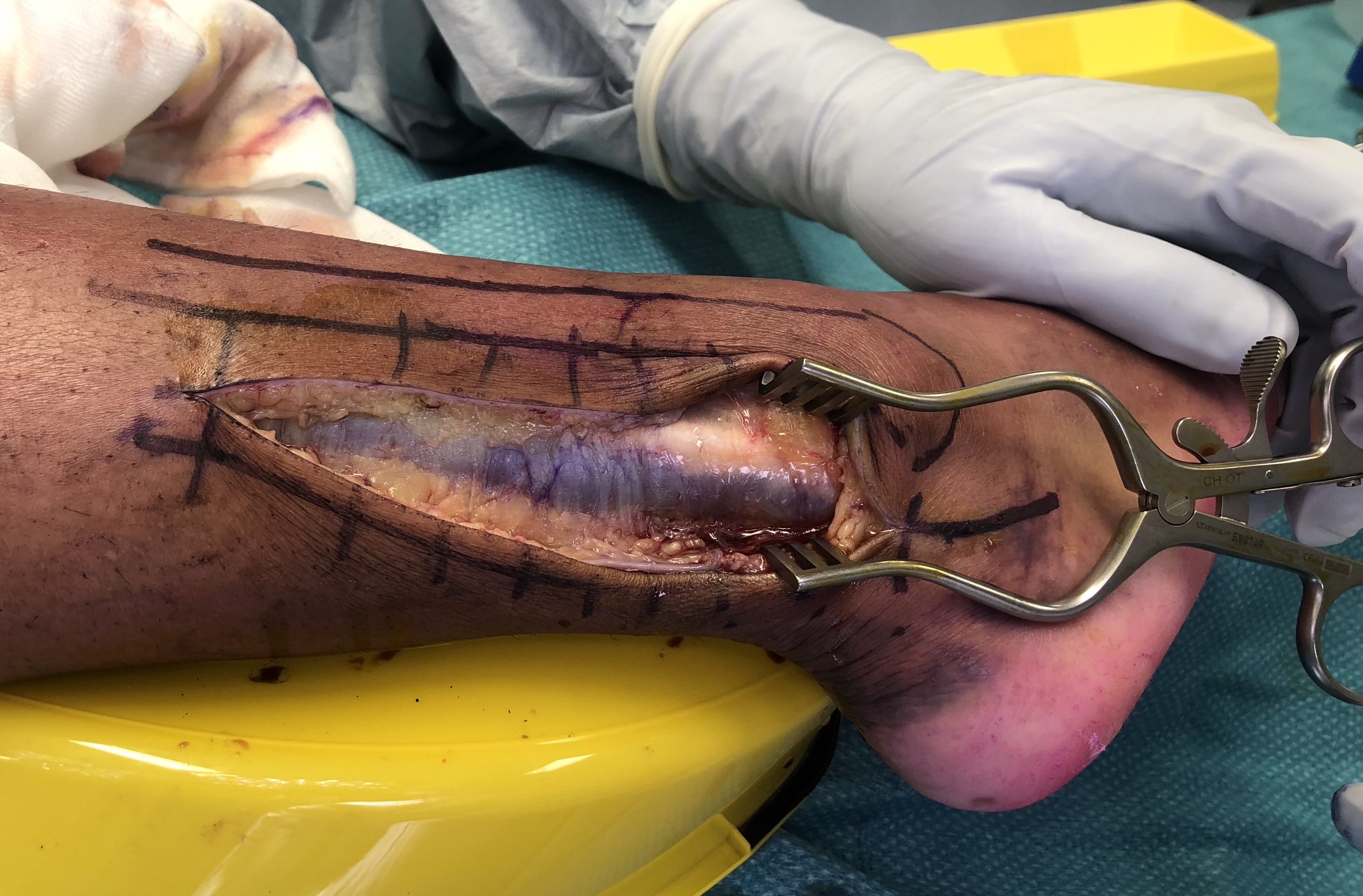
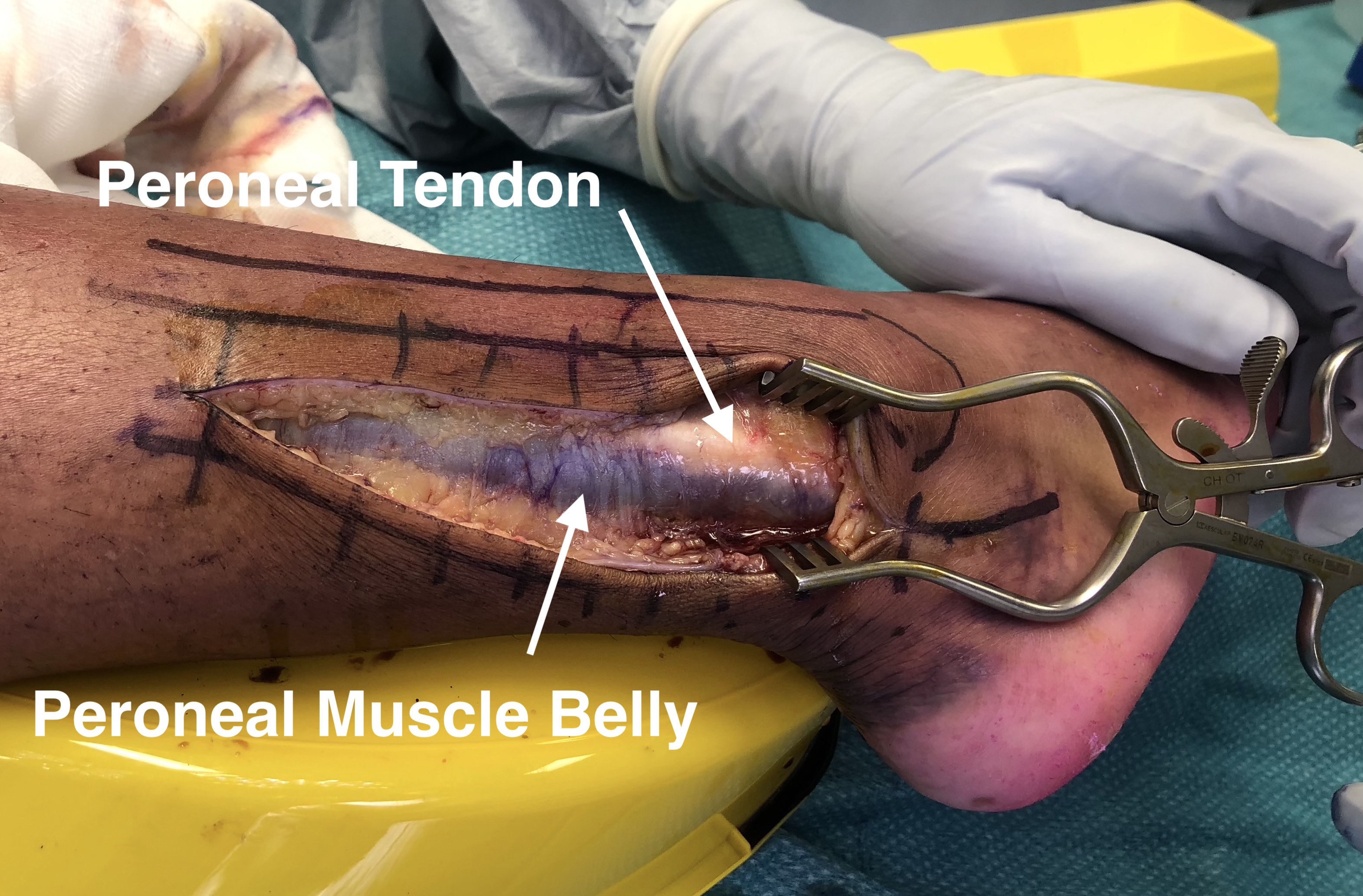
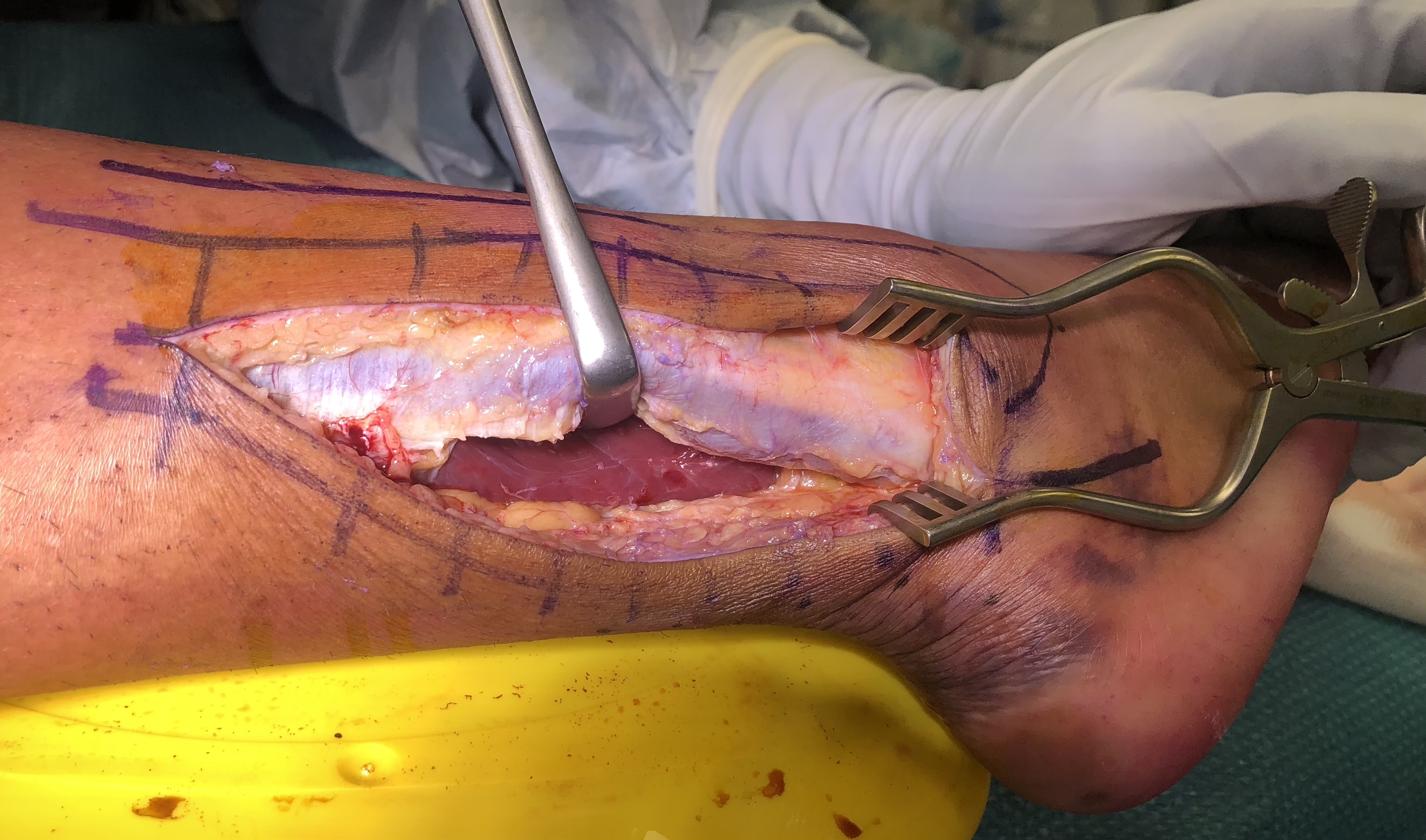
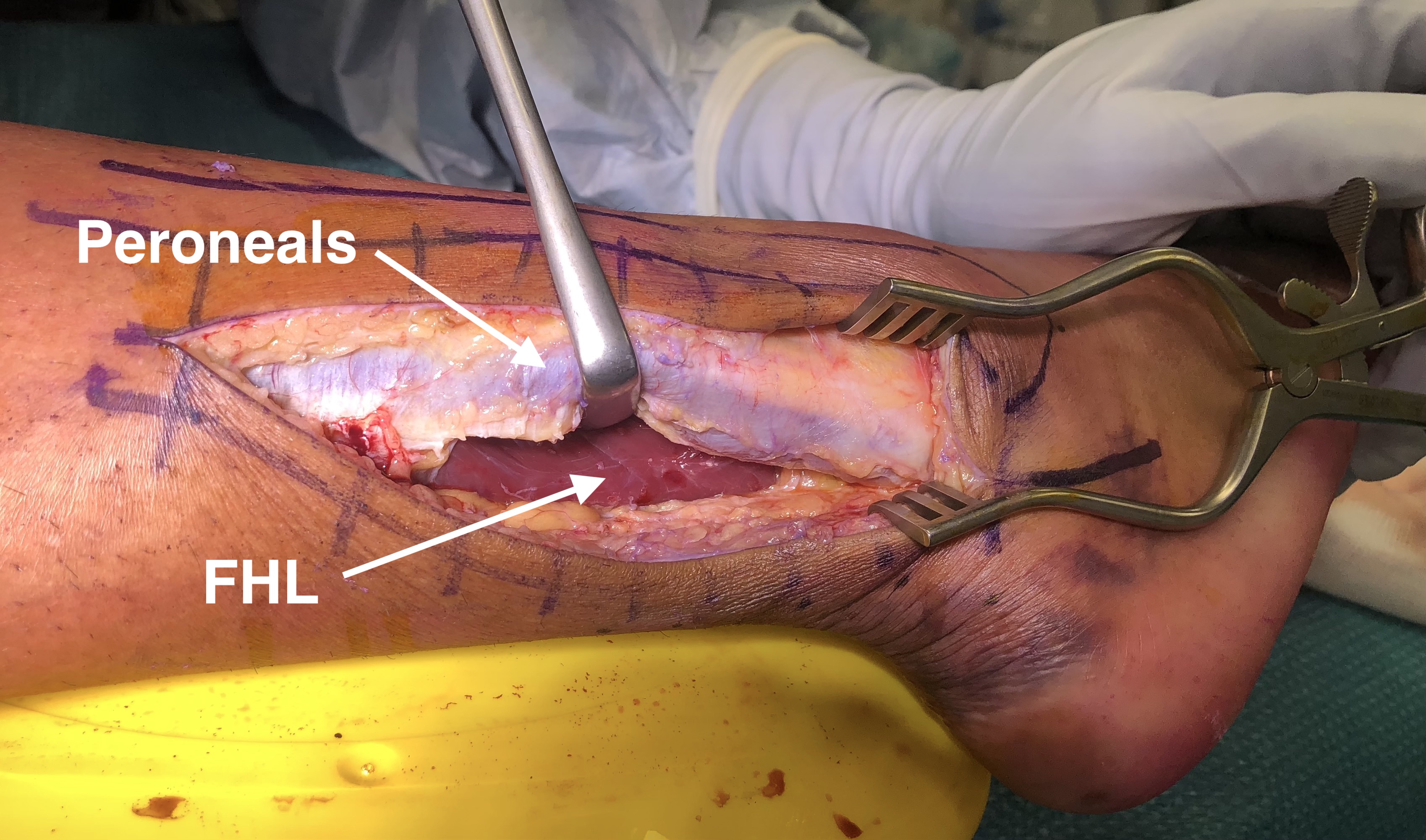
Deep dissection
- enhance exposure by making a longitudinal incision through lateral fibres of FHL origin on fibula
- retract FHL medially to expose posterior tibia & ankle joint
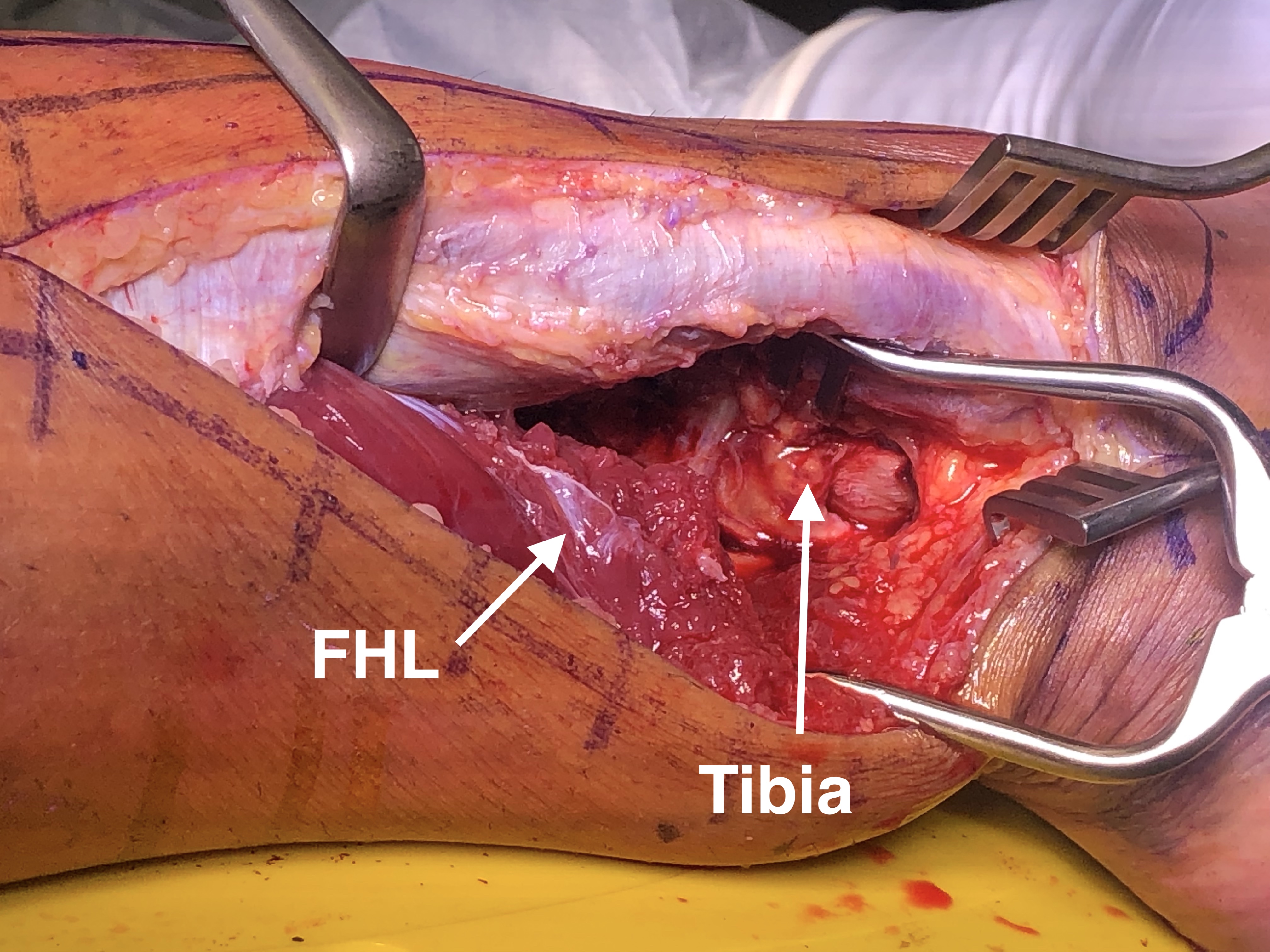
Dangers
- sural nerve and short saphenous vein
Extensile measures
- limited proximally by soleus
Lateral approach to STJ
Concept
Posterior / inferior to peroneal tendons
Indications
- STJ fusion
- ORIF calcaneal fracture
Approach
Position
- supine with sandbag under buttock to IR leg and bring hind foot forward
- place a support on opposite iliac crest, tilt table 20 - 30o away from surgeon to improve access
- or put patient on side
Incision
- along line of peroneal tendons
- 10-13cm curved incision, beginning 4cm above tip of lateral malleolus on posterior border of fibula
- follow posterior border of fibula to tip lateral malleolus
- curve incision forward, passing over peroneal tubercle
No Internervous plane
Superficial dissection
- avoid sural nerve and short saphenous vein behind lateral malleolus
- sural nerve posterior, superficial peroneal nerve anterior
- incise the separate sheaths of peroneus longus / brevis
- mobilize tendons anteriorly over distal end of fibula.
- ligaments of peroneal retinaculum must be repaired at the end to prevent anterior subluxation of tendons
Deep dissection
- identify and divide calcaneofibular ligament (part of STJ capsule)
- open STJ transversely to expose posterior facet of subtalar joint
- divide interosseous ligament for full exposure subtalar joint
Dangers
- sural nerve, short saphenous vein
Lateral approach to hind foot (Olliers)
Concept
Incision from lateral malleolus to TNJ
Between P. tertius and Peroneals
Indications
- exposes AKJ / STJ / CCJ / TNJ
- triple arthrodesis
- individual joint arthrodesis
- excision CN bar
Approach
Position
- supine with sandbag under hip to IR leg and bring hind foot forward
Incision
- curved incision
- commencing distal to lateral malleolus and slightly posterior to it
- continue distally along lateral side of hind foot & over the sinus tarsi
- curve medially ending over the dorsum of TNJ
Internervous plane
- between peroneal tendons (SPN) and peroneus tertius (DPN)
Superficial dissection
- do not mobilize skin flaps widely as large skin flaps may necrose
- identify and protect SPN
- incise deep fascia along incision
Danger
- Peroneus tertius / EDL tendons cross distal end of wound and retract medially
Deep dissection
- EDL and tertius medially, peroneals inferior
- mobilize fat pad in sinus tarsi to identify subtalar joint (preserve fat pad)
- expose origin of EDB on dorsum of calcaneus
- detach by sharp dissection reflecting origin distally and medial
- this will involve division branches of lateral tarsal artery
- identify dorsal capsules of TN medially / Calcaneo-cuboid joints laterally
- open joints by forcefully plantar flexing and inverting foot
- identify and open posterior talo-calcaneal joint / invert foot
Dangers
- skin flaps notorious for producing necrosis
- avoid stripping / retraction and sharp incision curves
- branches of SPN
Extensile measures
Proximal
- continue incision along posterior border of fibula
- dissect in plane between peroneal & flexor tendons
- exposing length of fibula (rarely required)
Posterior & proximal
- reach Achilles tendon
