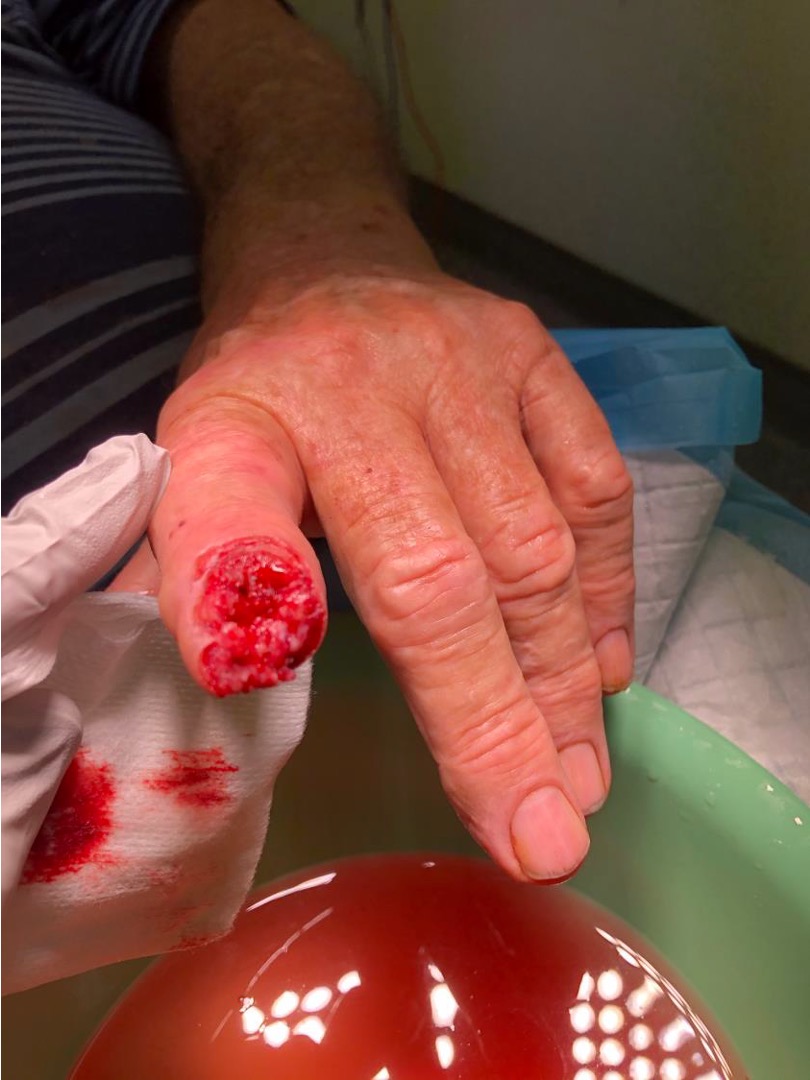
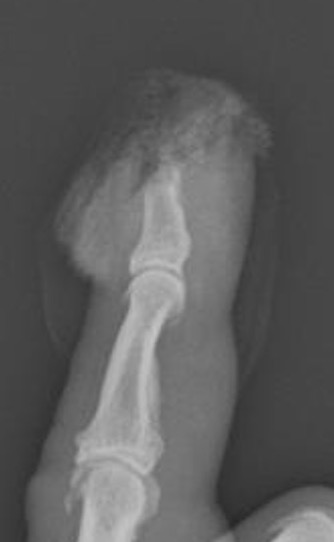
Detipping
Definition
Distal to insertion of flexor and extensor tendons
Anatomy
Thick skin
- fibrofatty tissue
- fibrous septa from dermis to periosteum
Tissue involved
Pulp only
Nail bed
Bone
Goals
1. Preserve functional length
2. Preserve useful sensibility
3. Prevent neuromas
4. Prevent joint contractures
5. Short morbidity with early return to work
Options
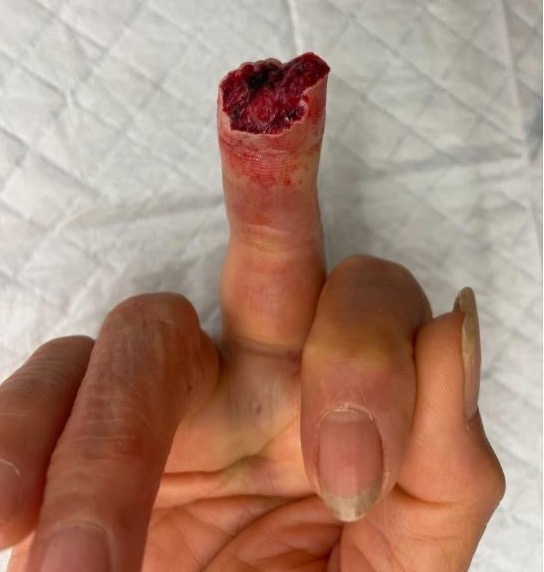
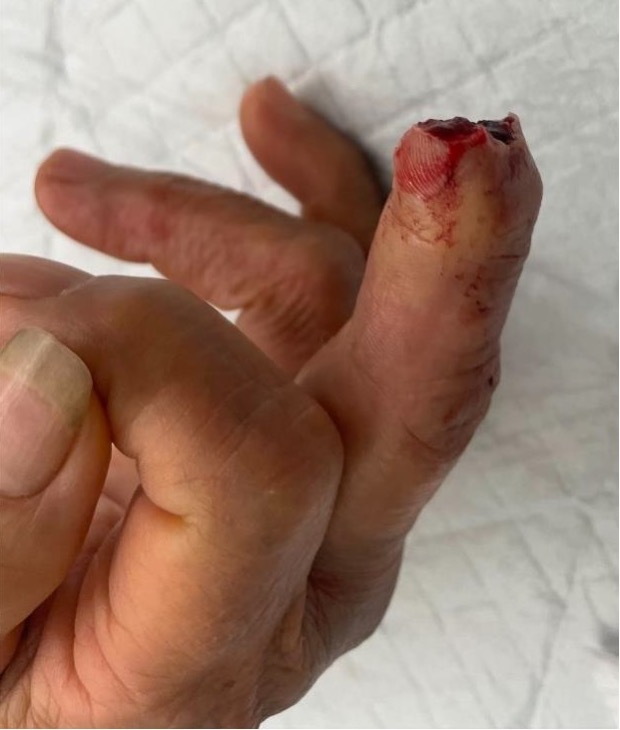
1. Primary suture and healing
2. Secondary healing (< 1 cm2 area)
4. Formalization
5. Flaps
Local flaps / VY flaps
Regional Flaps (Cross-finger / Thenar flap)
Formalization
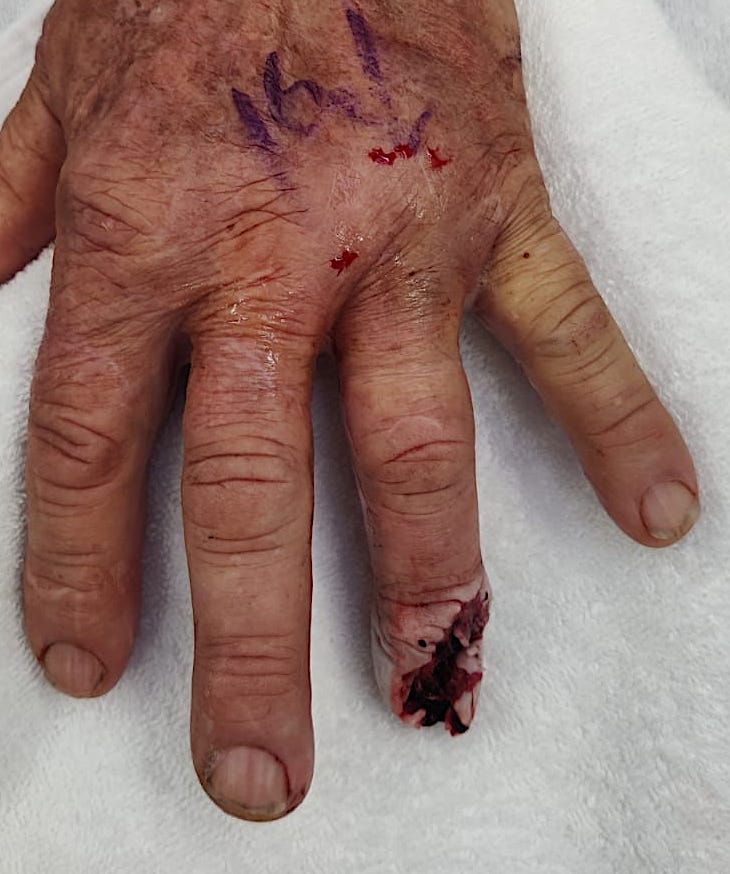
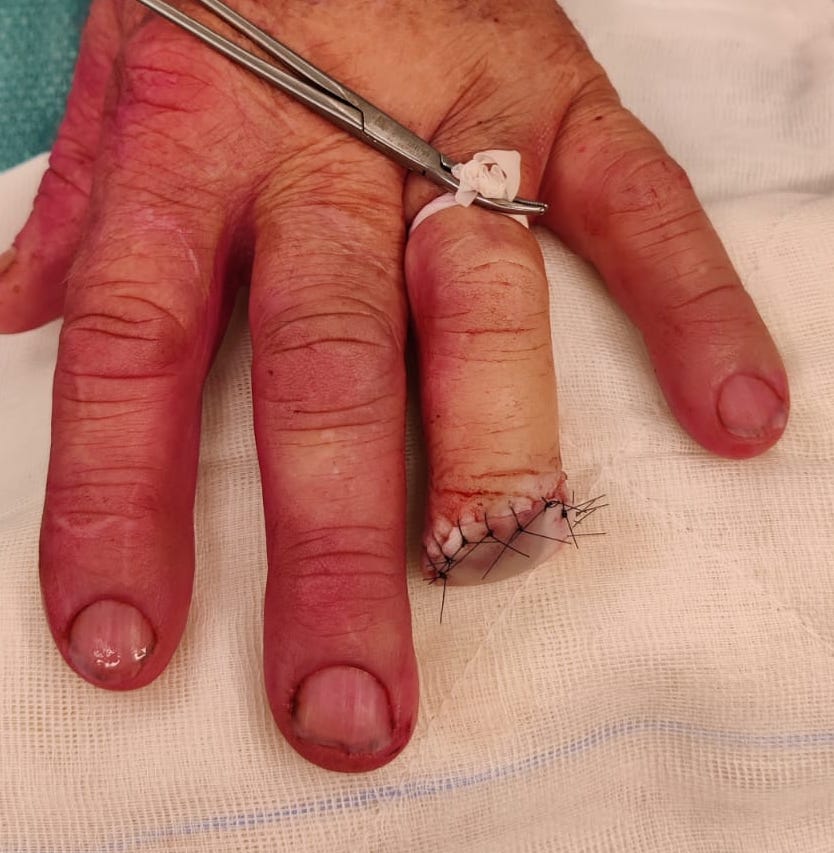
Technique
Remove nail bed in full (bilateral eponychial incisions)
Take bone to level distal to extensor / flexor tendons
Close using fishmouth flaps or volar flap
Local Flaps
Indications
Small defects < 1 cm2
Transverse or volar based defects
Results
Chakraborty et al World J Plast Surg 2021
- systematic review of 13 articles
- mean 2 point discrimination of 5 mm (c.f. 3 mm contralateral)
- minimal loss of ROM
- some cold intolerance
- risk of hook nail
1. Unilateral VY flap - Atasoy
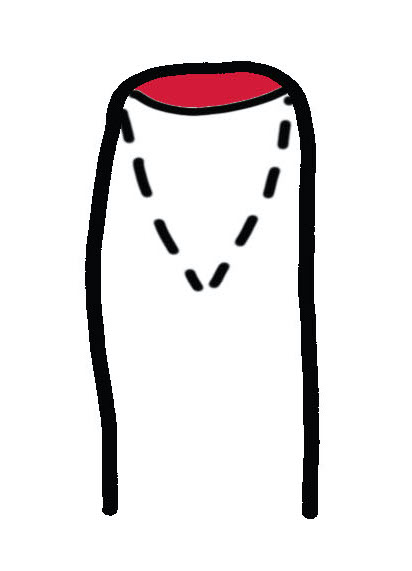
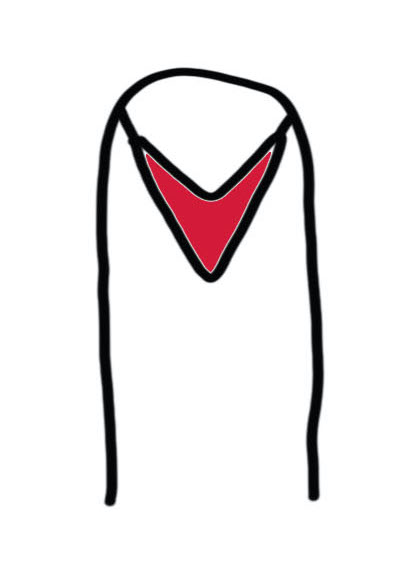
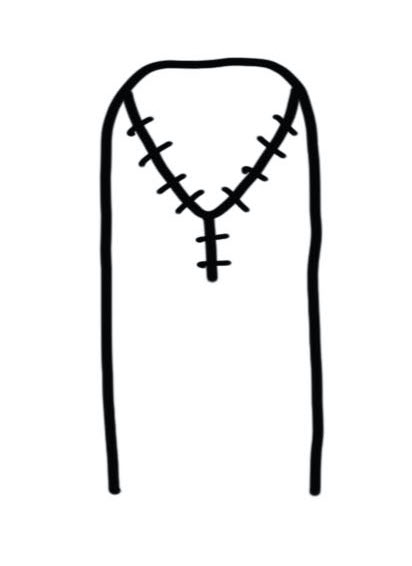
Volar VY Advancement flap
Technique
- nibble bone back
- incise skin in V
- ensure vase of flap is as wide as nail bed
- must release all fibrous septa to mobilize flap
- attempt to leave small vessels
- advance and suture to nail bed
- close in Y fashion
2. Bilateral VY flap - Kutler's
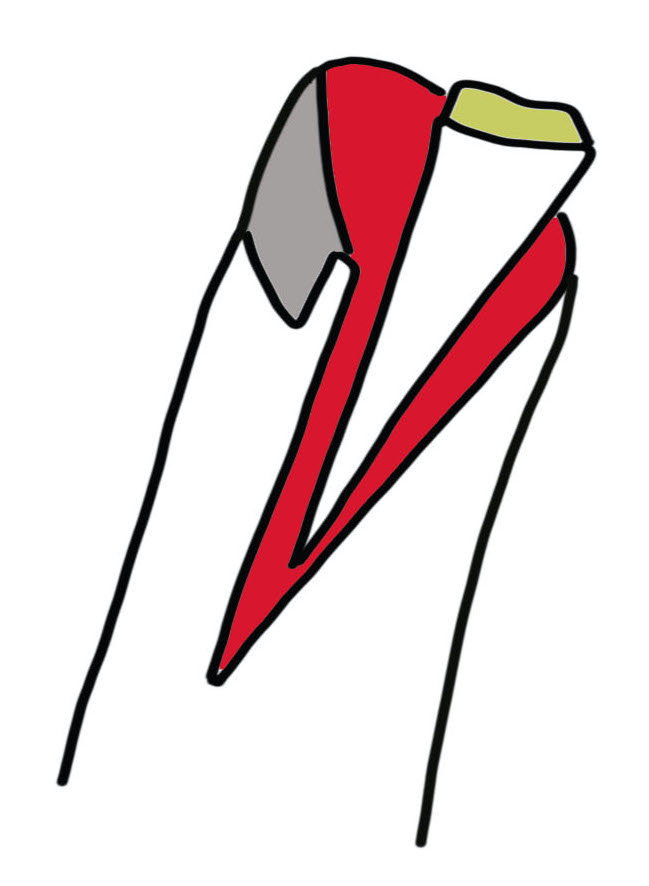
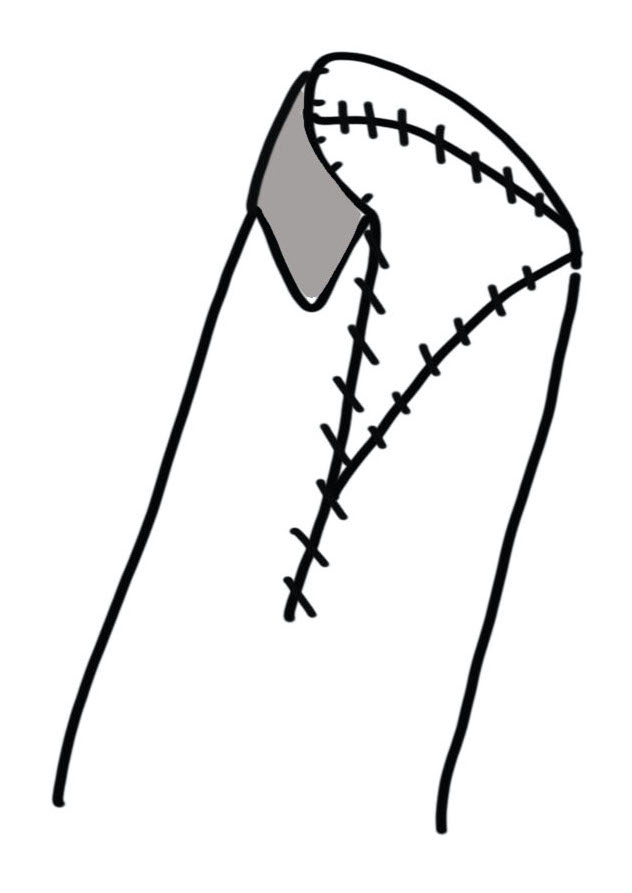
Technique
- triangular skin flaps on both sides of digit
- advanced to close transverse skin defect
- closed in Y patter
Regional Flaps
Advantages
Good quality skin
Good sensory outcome
Disadvantages
2 stage procedure
Longer period of recovery
Potential donor site morbidity
1. Cross finger flap
Indications
Volar based skin defects
Technique
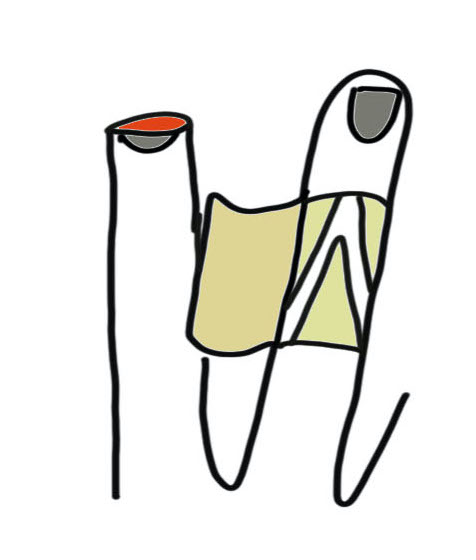
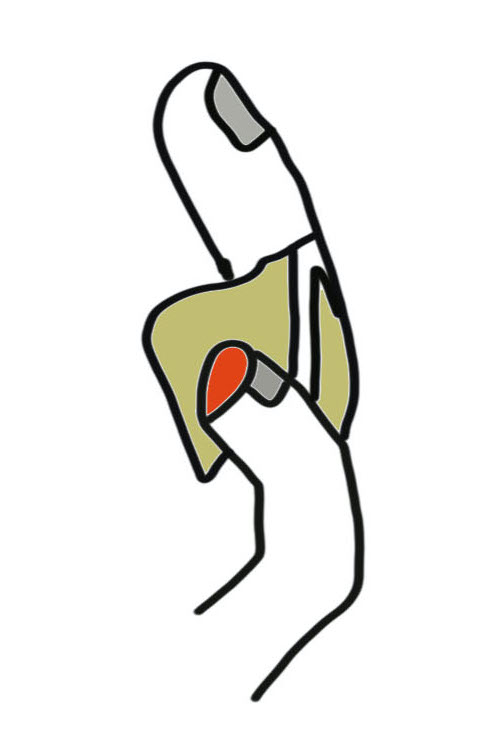
Rectangle of donor skin from dorsum of adjacent digit middle phalanx
- hinge is mid-axial line
- must preserve paratenon over extensor tendon to ensure take of the subsequent skin graft
- flap crossed onto distal finger pulp
Full-thickness skin graft to donor site from forearm
- must remove all fat from FT graft
- graft sutured 75% onto dorsum of donor finger
Divide flap under GA 3 weeks later
2. Reverse cross finger flap
Indication
Dorsal based skin defects
Complete nail bed defects
3. Thenar flap
Indications
2 cm2 defect of index / middle / ring finger pulp
Difficult to oppose little finger
Technique
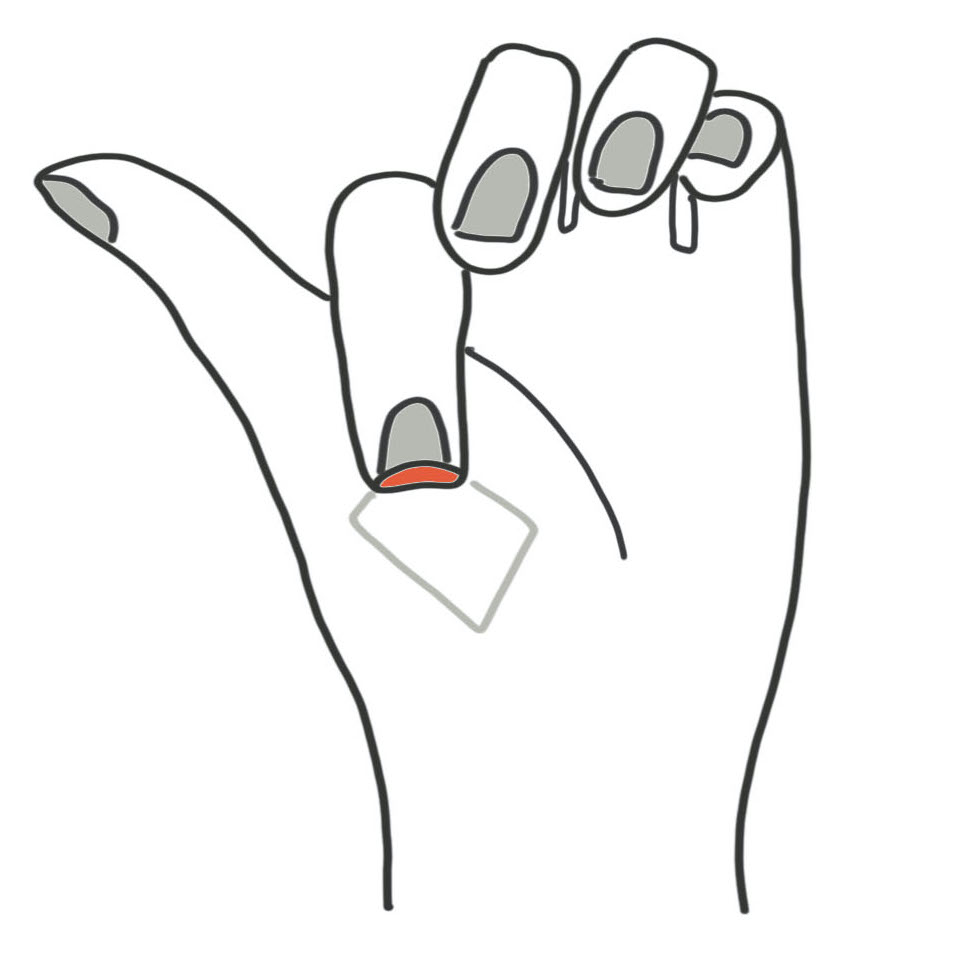
Most important point is site of flap
- if too distal and over webspace can endanger NV bundle to thumb
- needs to be over thenar eminence
Flex finger to identify donor site
- create distally based rhomboid flap
- suture to finger defect
Flap division 2 - 3 weeks later
- primary closure of thenar defect
3. Abdominal Flap
Suture finger to border between chest / abdomen
- release 3 weeks later
- primary closure of chest wound