![]()
AO Classification
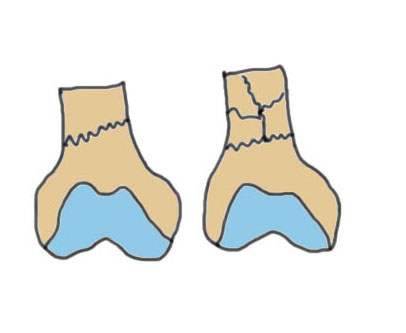
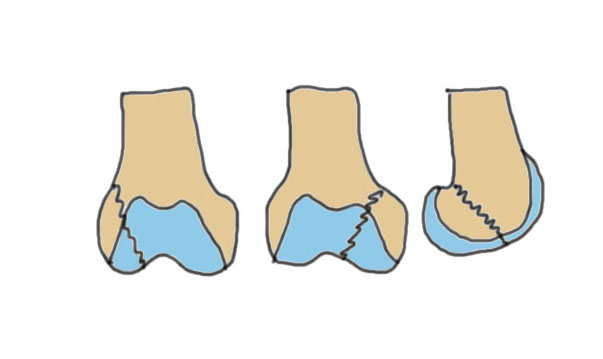
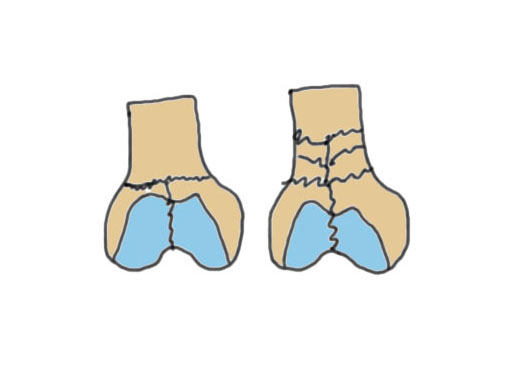
Types
| Type A: Supracondylar | Type B: Partial articular | Type C: Complete articular |
|---|---|---|
|
A1: Minimal comminution A2 / 3: Increasing comminution |
B1: Sagittal lateral B2: Sagittal medial B3: Coronal plane / Hoffa |
C1: Minimal comminution C2 / 3: Increasing comminutioin |
 |
 |
 |
|
Lateral plate IM nail Dual plate if highly comminuted |
ORIF + lateral plate for sagittal plate Cannulated screws for coronal plane |
Dual plate Plate + nail Distal femoral replacement |
 |
|
 |
Operative Management
Options
1. Retrograde nail
2. Lateral Plate
3. Dual plating
4. Plate / nail combination
5. Distal femoral replacement
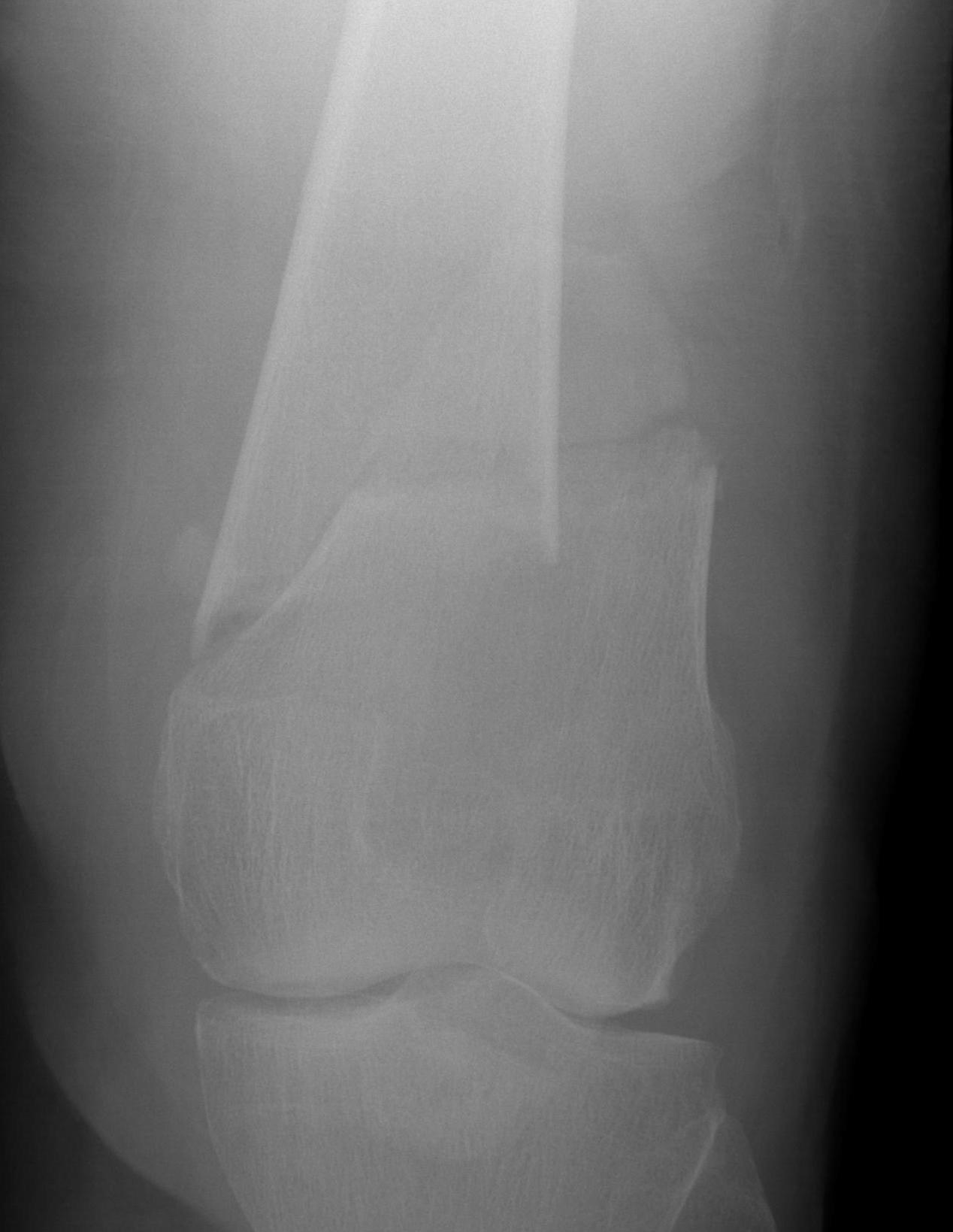
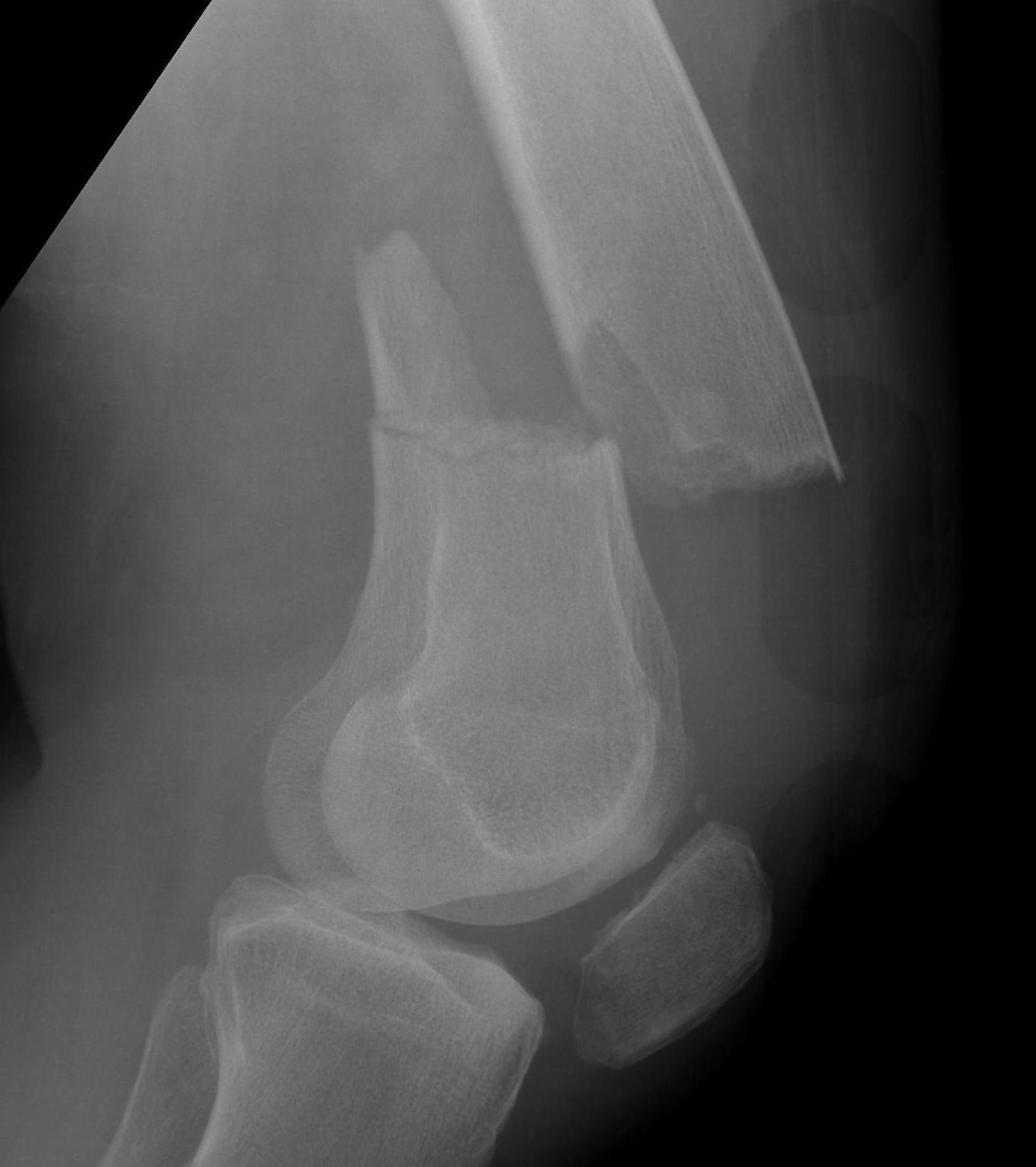
AO Type A: Supracondylar / Extra-condylar
Xray
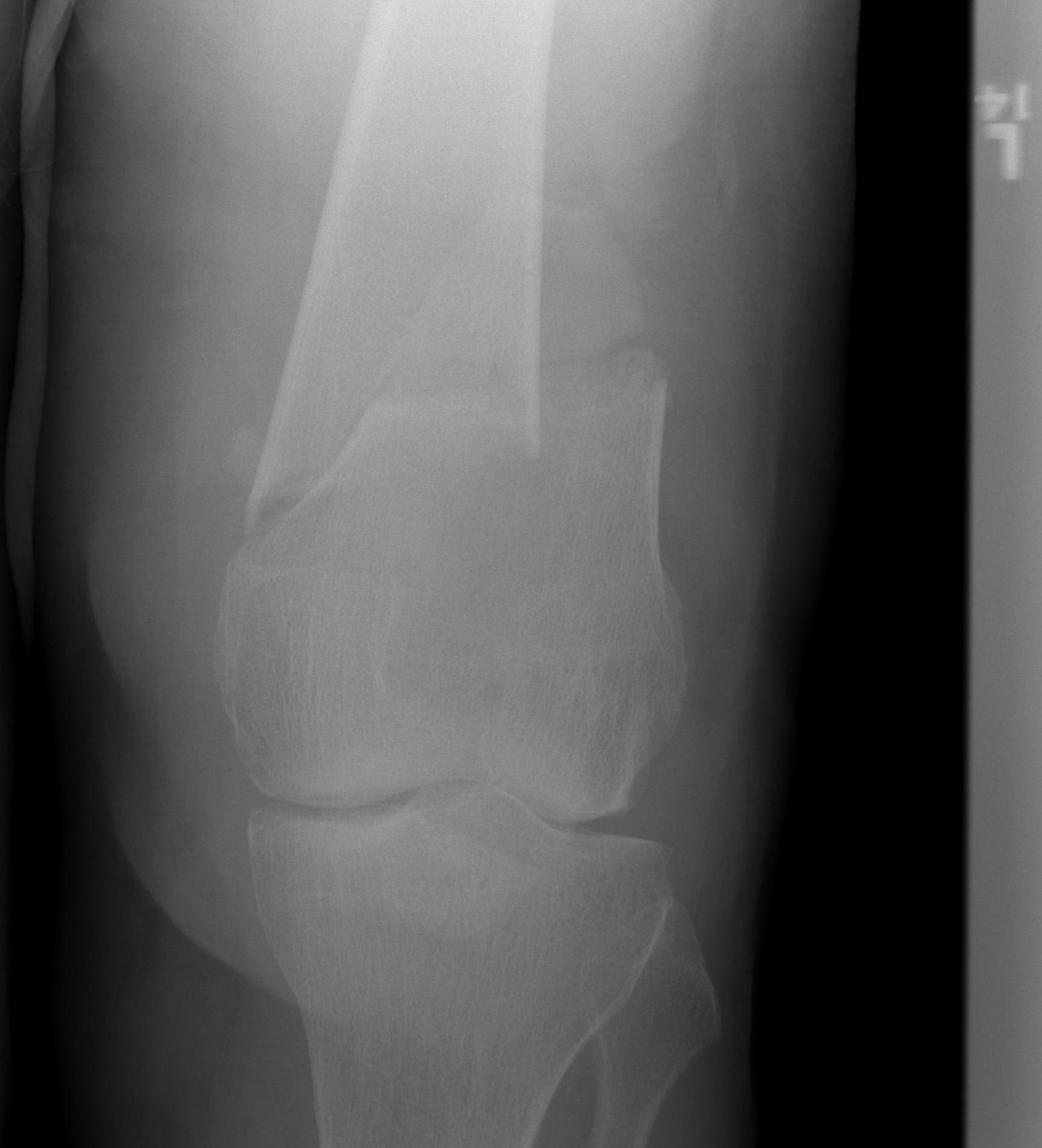
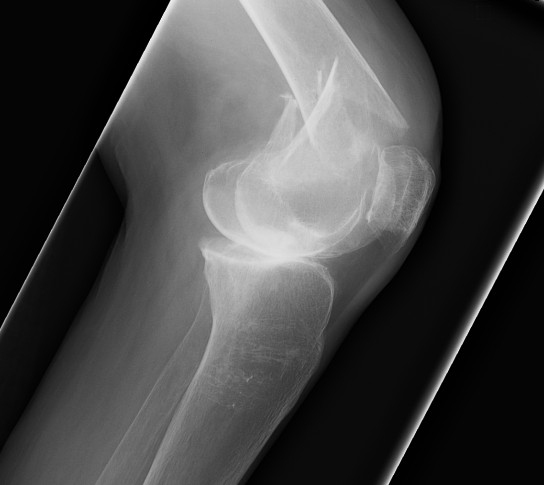
Options
Lateral plate
Retrograde IM nail
Results
Plate v Nail
Kim et al Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2024
- IMN versus plate for distal femur fractures
- 33 studies and 2400 patients
- shorter time to union and lower infection rate with nail
- fracture treatment needs to be dictated by fracture pattern
Nail
Iannacone et al J Orthop Trauma 1994
- 41 distal femur fractures treated with retrograde nail
- 4 non unions requiring revision fixation
- 4 fatigue fractures of the IMN; changed to using minimum 12 and 13 mm rods
Plate
Schutz et al Arch Orhop Traum Surg 2005
- 62 patients average age 52 years treated with LISS plate
- union achieved in 85% patients
- 6 required bone grafting, 3 required revision of components
Retrograde Nail
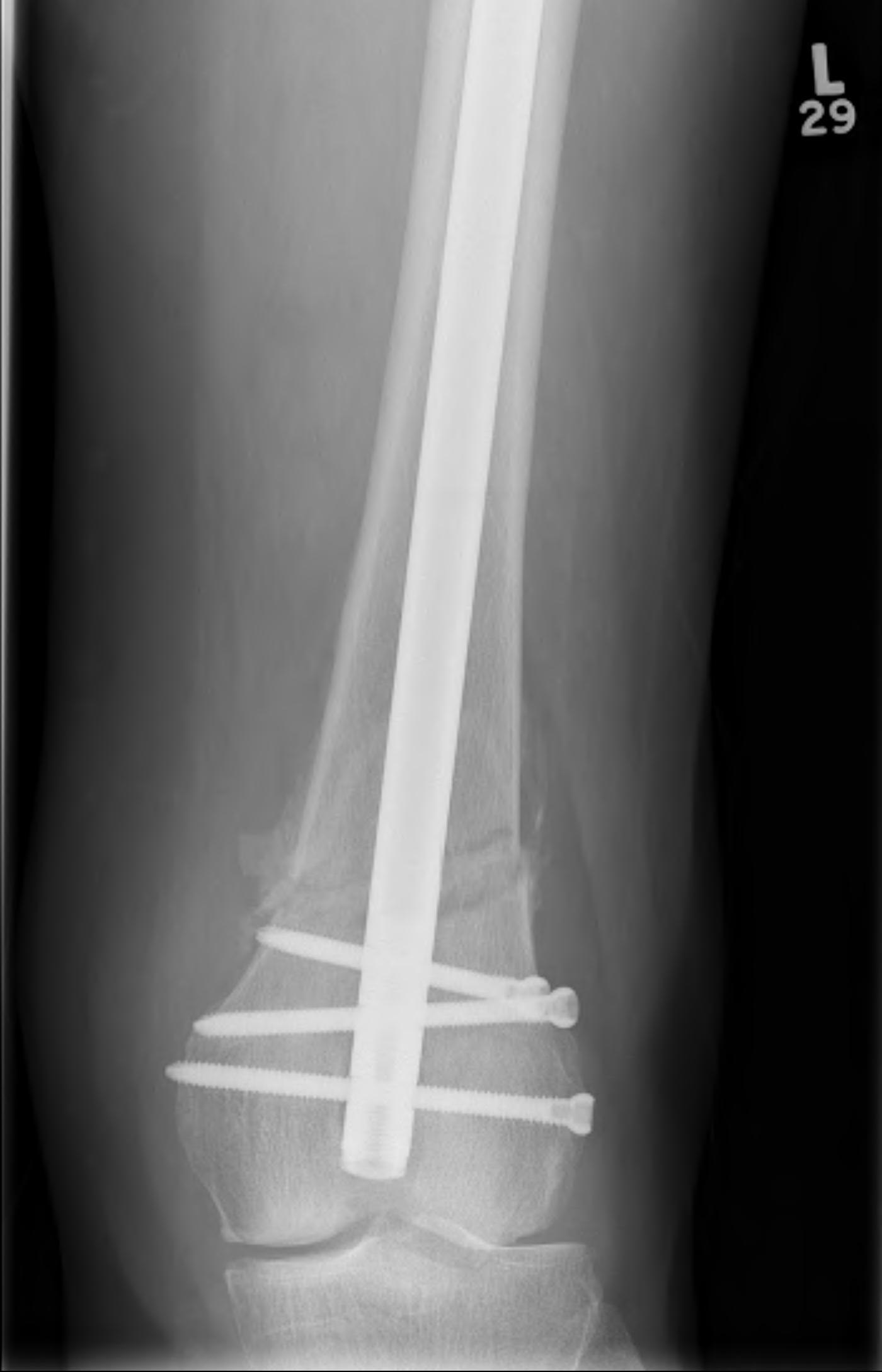
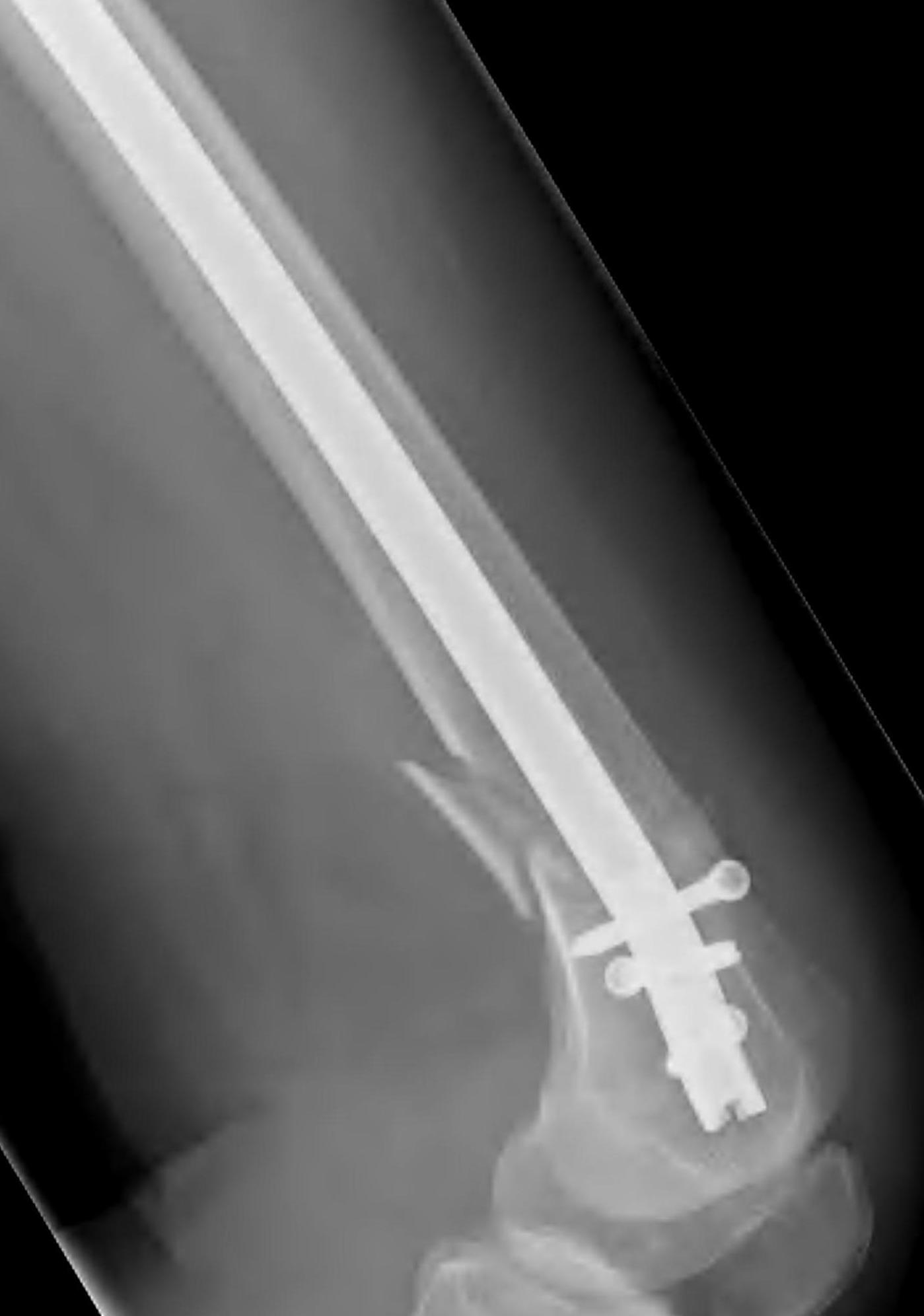
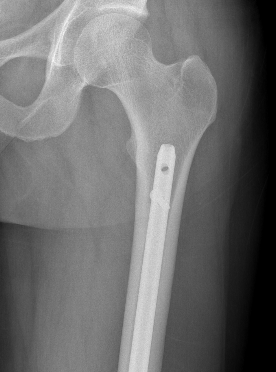
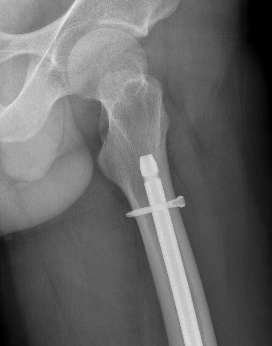
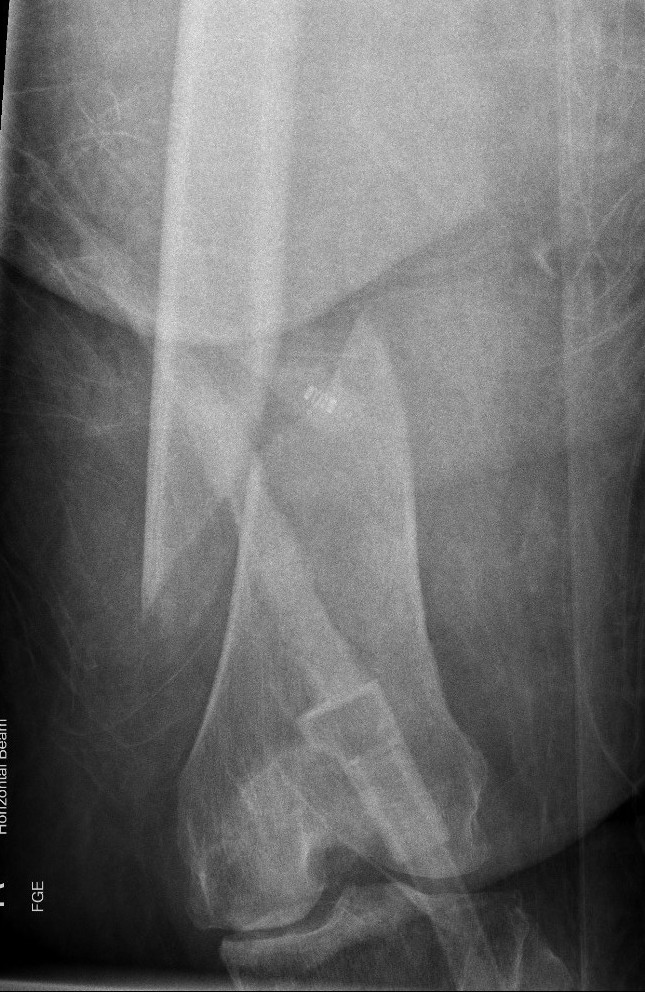
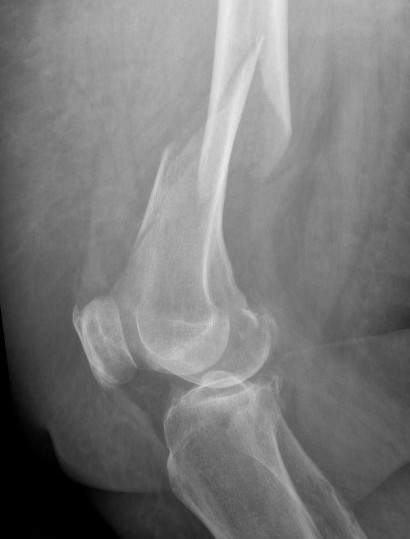
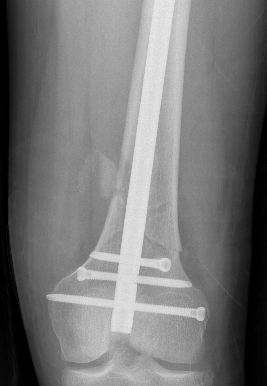
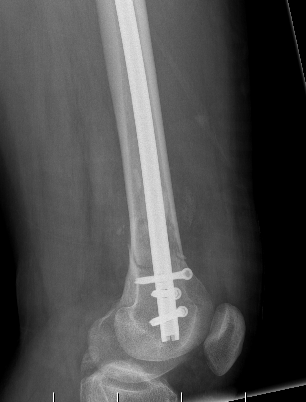
Surgical Technique
Synthes retrograde nail technique guide
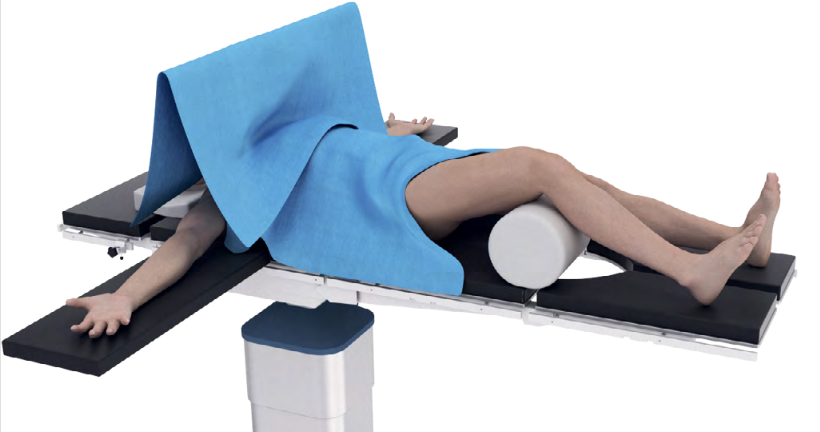
Set up
- patient supine on radiolucent table
- ensure xray imaging for AP and lateral of knee
- ensure AP of hip for proximal locking screw
- elevate knee over radiolucent triangle / bundle of gowns
- flex knee to allow entry to knee and detension gastrocneumius
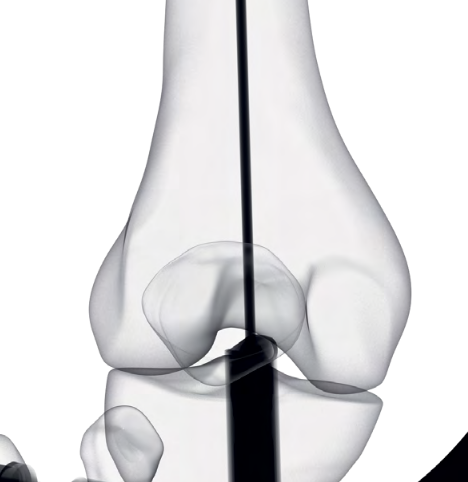
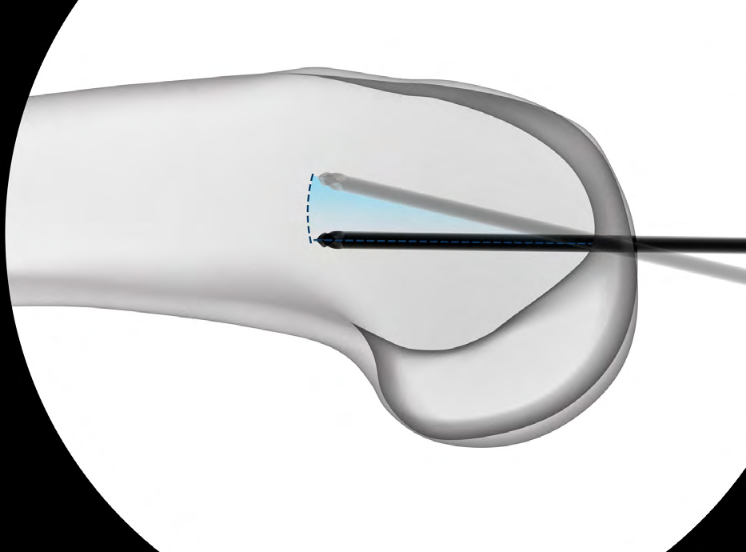
Entry point
- medial parapatella approach
- entry above notch slightly medial
- slightly anterior and lateral to femoral attachment of PCL
- central in AP and lateral of the distal fragment
- awl / 3.2 mm guide wire
- ream for enlarged end of retrograde nail
Pass guide wire
- consider blocking screws to aid reduction
- can use femoral distractor
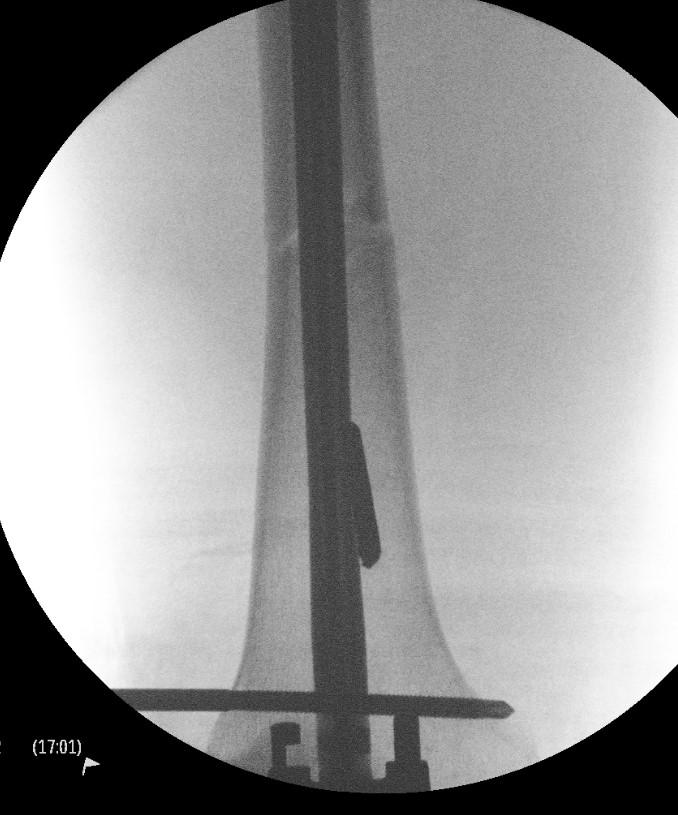
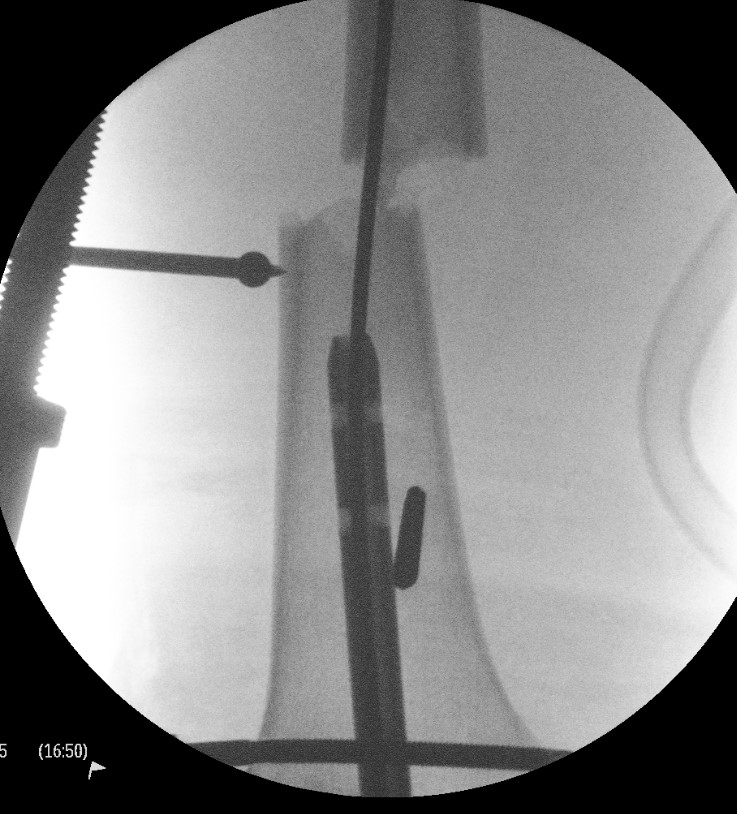

Blocking screws
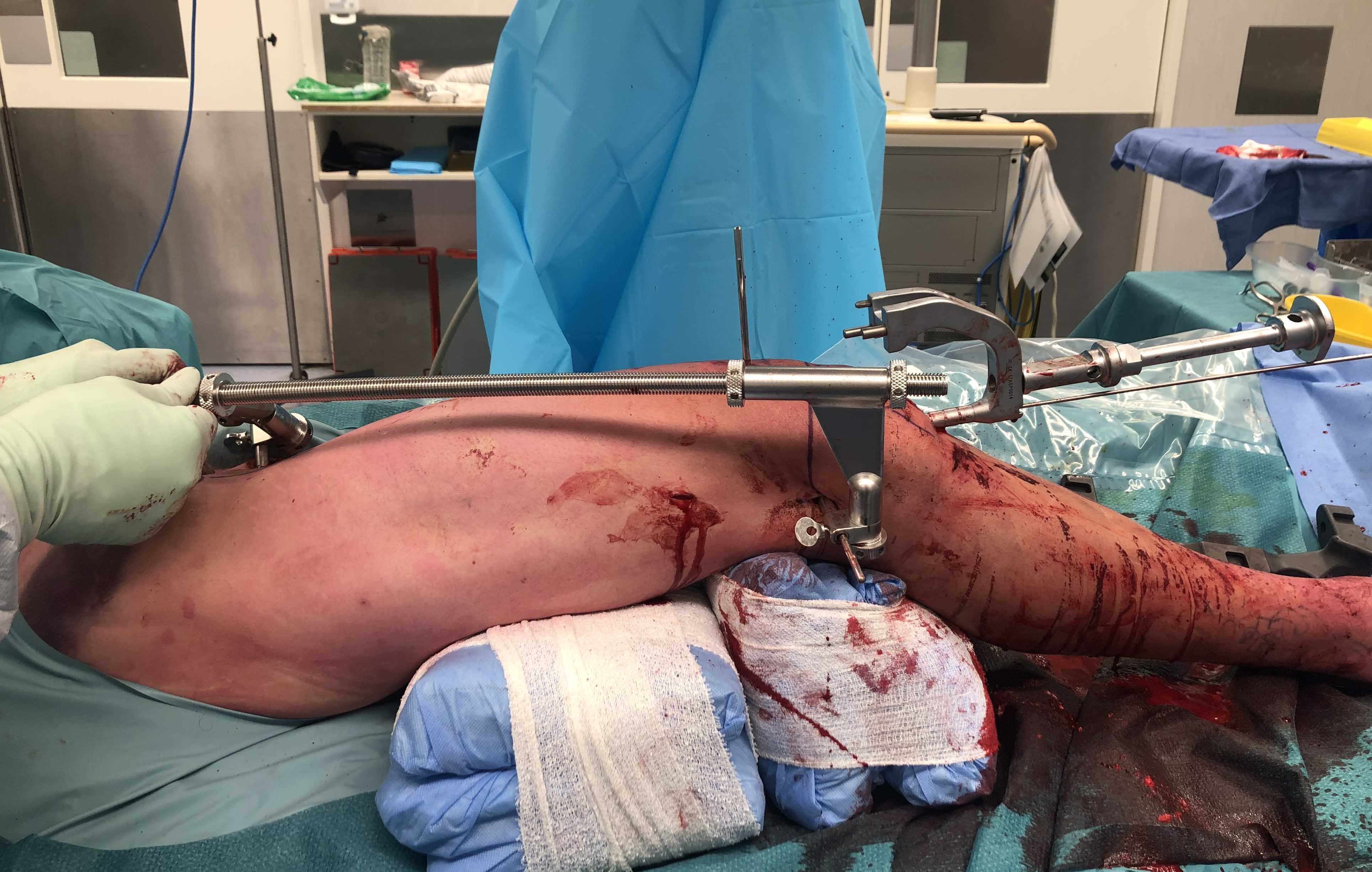
Femoral distractor and retrograde nail
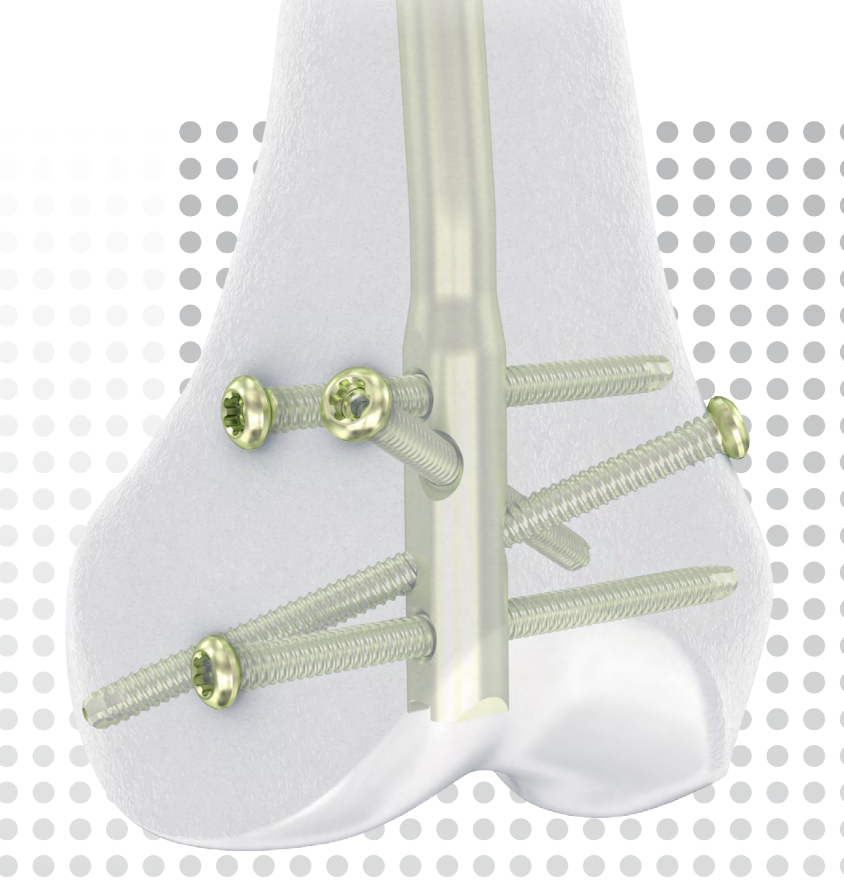
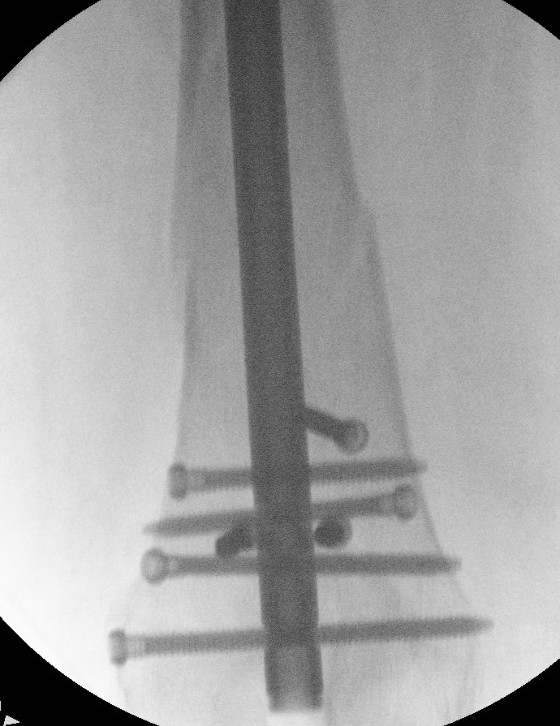
Locking screws
- distal locking performed with jig
- proximal AP locking under xray control
Lateral Plate
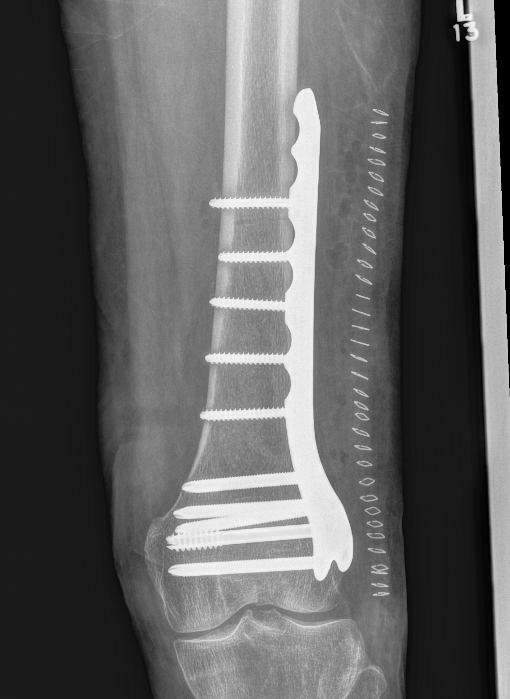
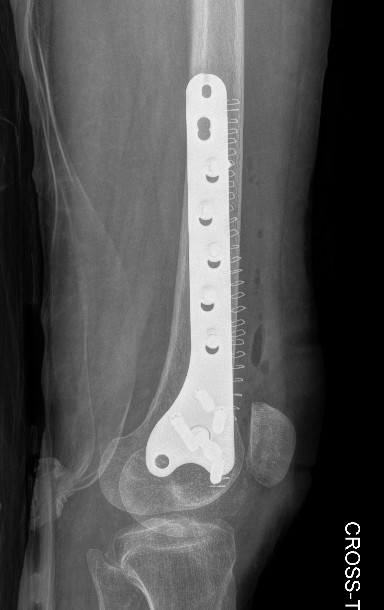
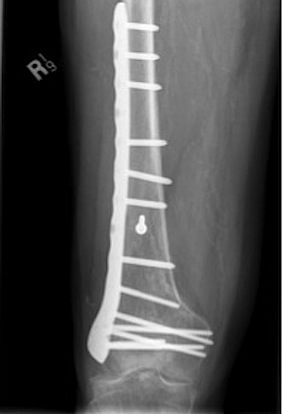
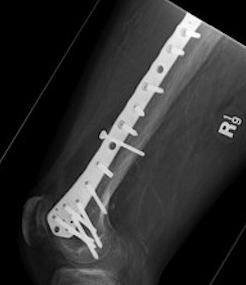
Surgical Technique
Vumedi video lateral plating distal femur
Synthes LISS Plate surgical technique guide
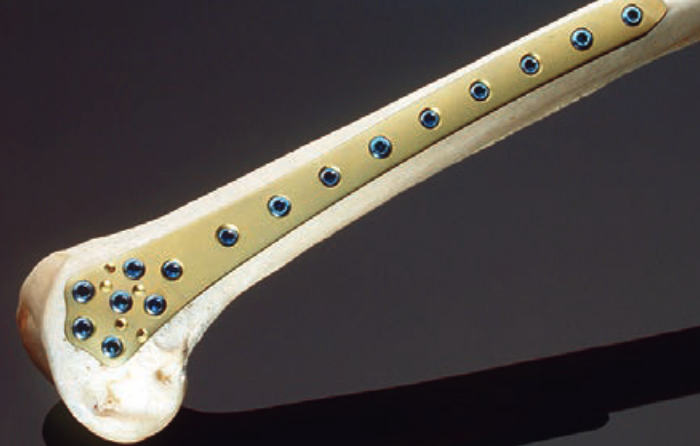
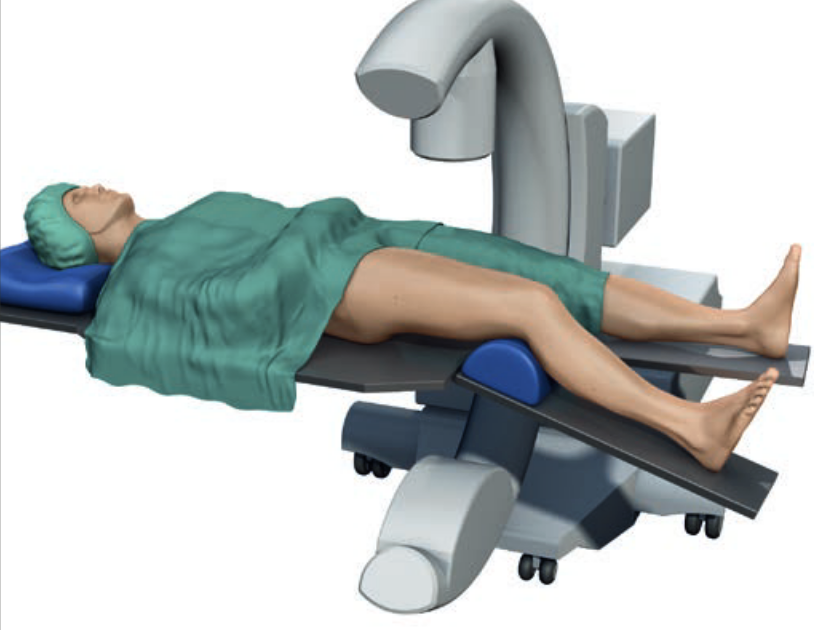

Position
- patient supine on radiolucent table with image intensifer
- elevate femur to obtain lateral image without interference from other leg
- flex knee to detension gastrocnemius, aiding fracture reduction
Approach
A. Lateral anterolateral approach
- longitudinal incision over lateral distal femoral condyle
- split ITB
- elevate vastus lateralis and cauterize perforators
B. Lateral parapatella approach
Reduce intra-articular portion if required
- compress with bone reducing forcep
- cannulated screws
- anterior / posterior / distal to plate
Apply plate distally
- length, valgus alignment, rotation restored
- ensure screws not in joint / above blumensaat's
- ensure screws not in PFJ (distal femur is trapezoidal)
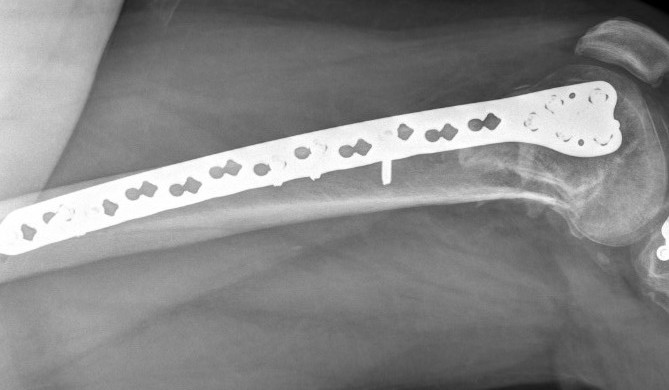
MIPO plate technique
- percutaneously elevate muscle off femur with elevator
- insert appropriate length plate (4 bicortical screws above)
- second proximal incision
- obtain indirect reduction
- attach plate with screws
Tips
- longer plate better
- titanium plate better
- reduce rigidity better - proximal screws away from fracture
- cortical non locking screws in proximal plate
Issue
Malreduction significant medial comminution - can lead to nonunion
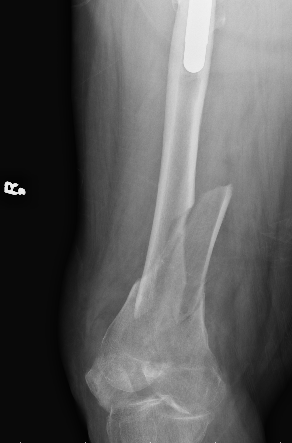
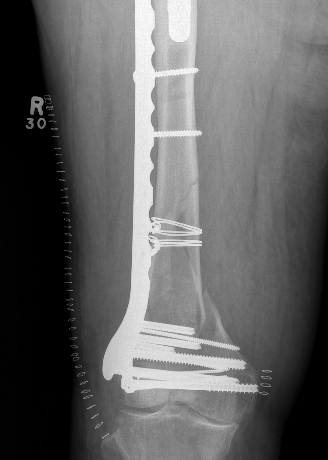
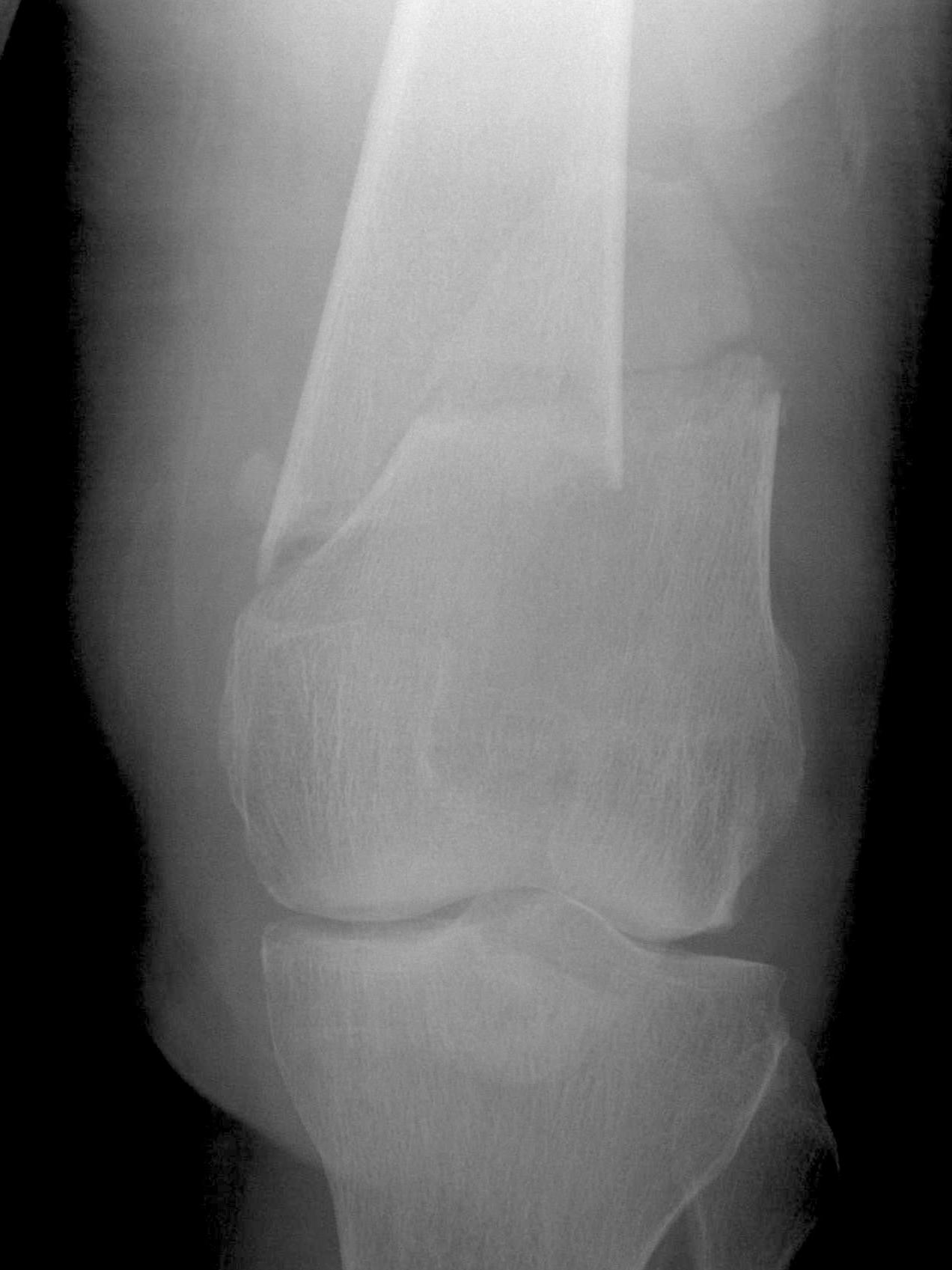
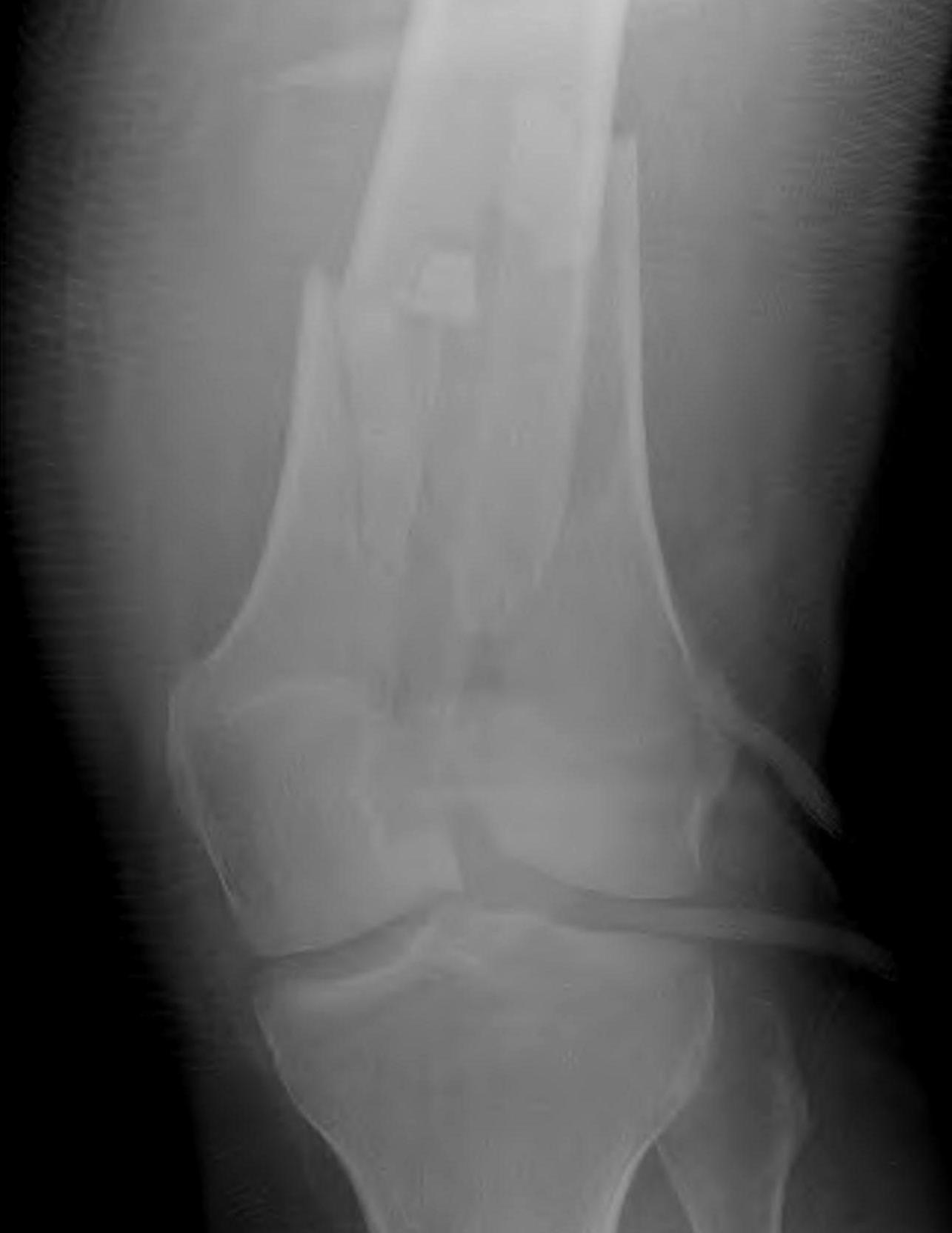
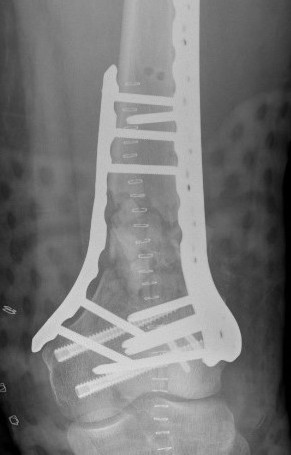
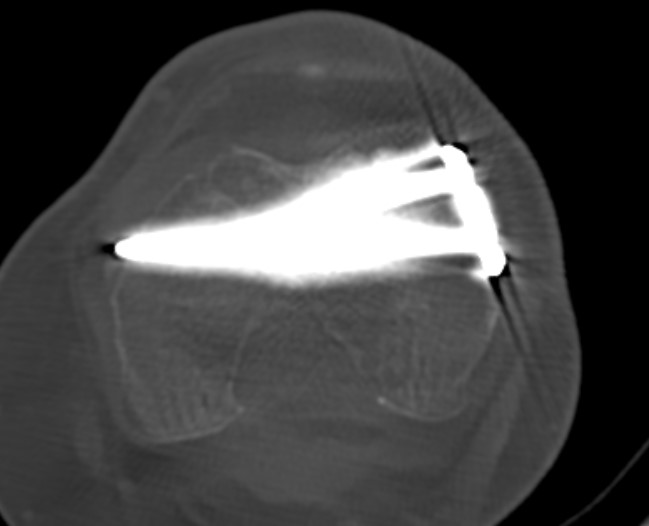
AO Type B1 & B2: Partial articular
![]()
![]()
Definition
Medial or lateral sagittal split
Technique
ORIF
- medial or lateral approach based on fracture location
- reduce articular split and fix with screws
- medial or lateral buttress plate
![]()
![]()
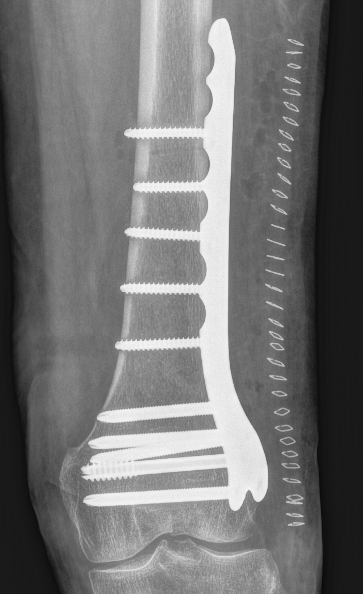
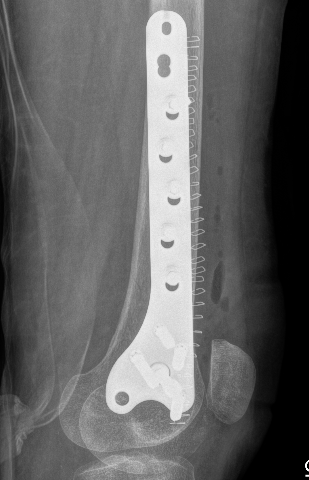
Lateral split fracture distal femur
Coronal plane / Hoffa fracture: www.boneschool.com/hoffa-fracture
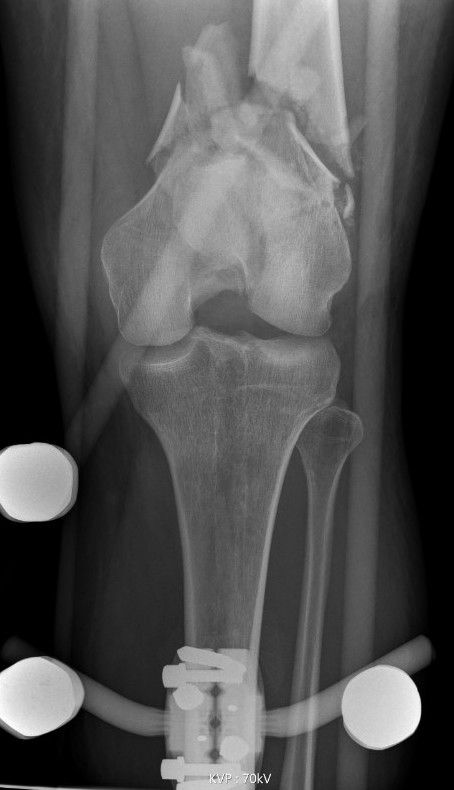
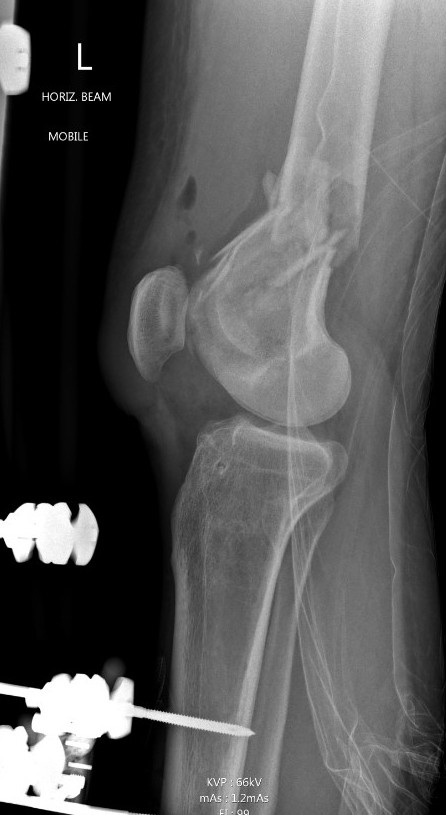
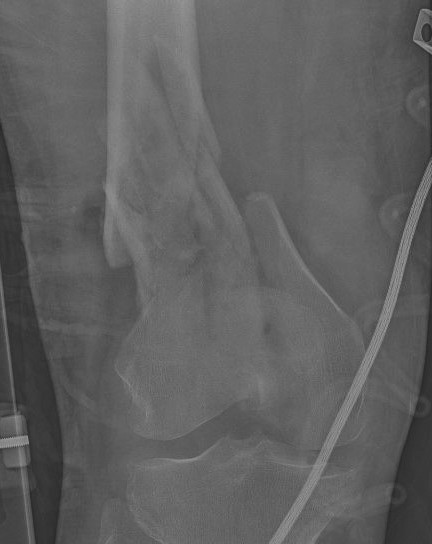
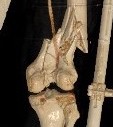
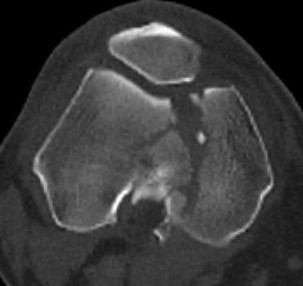
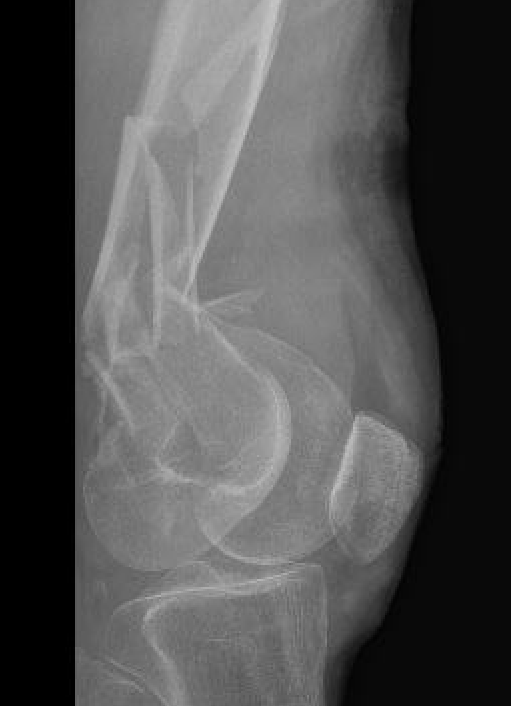
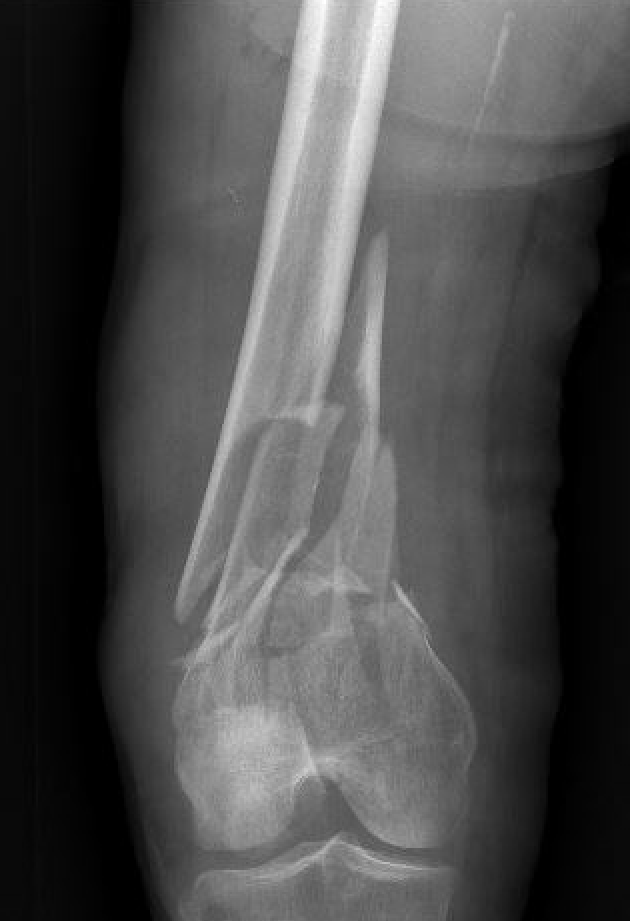
Type C: Complete articular
Xray / CT
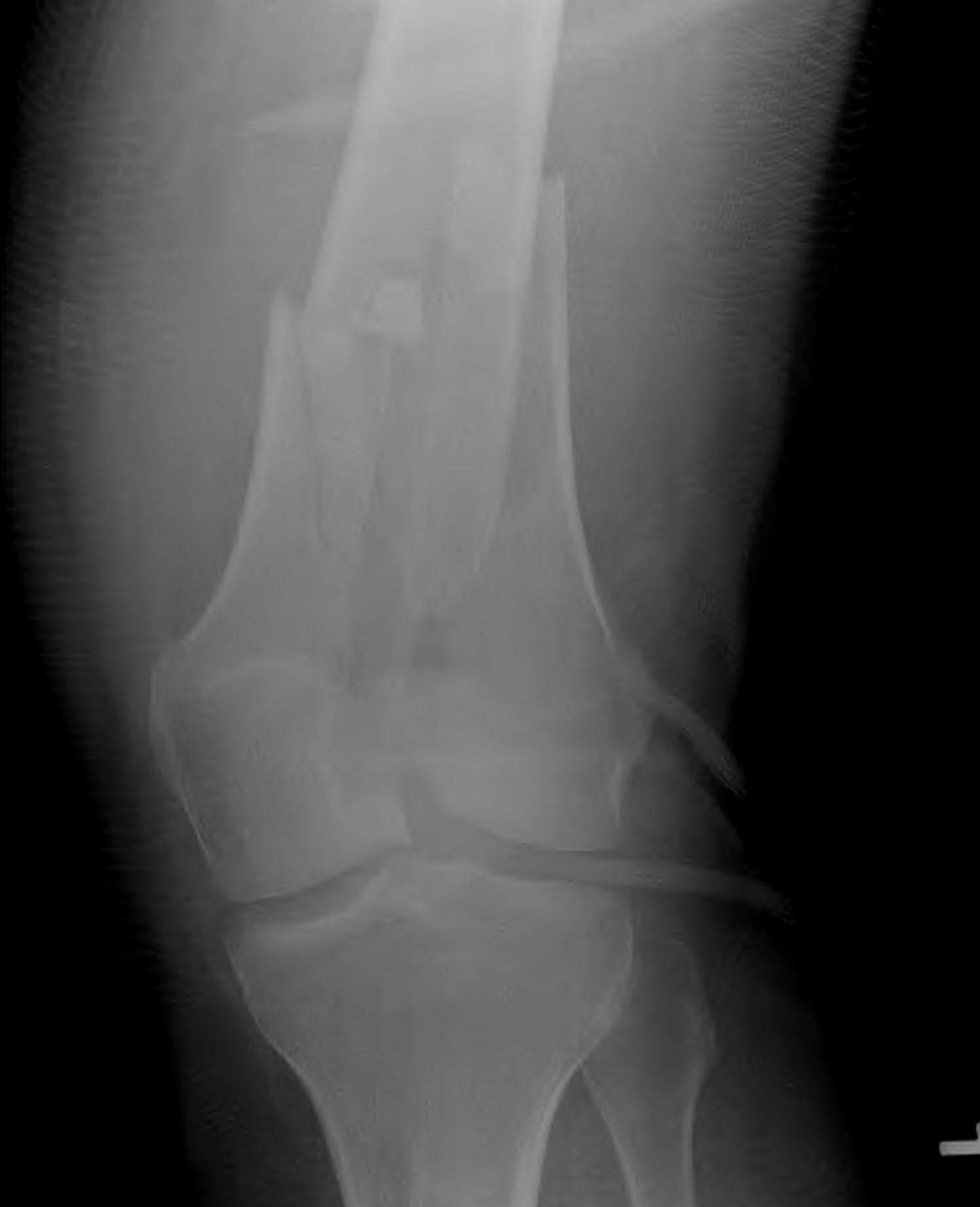
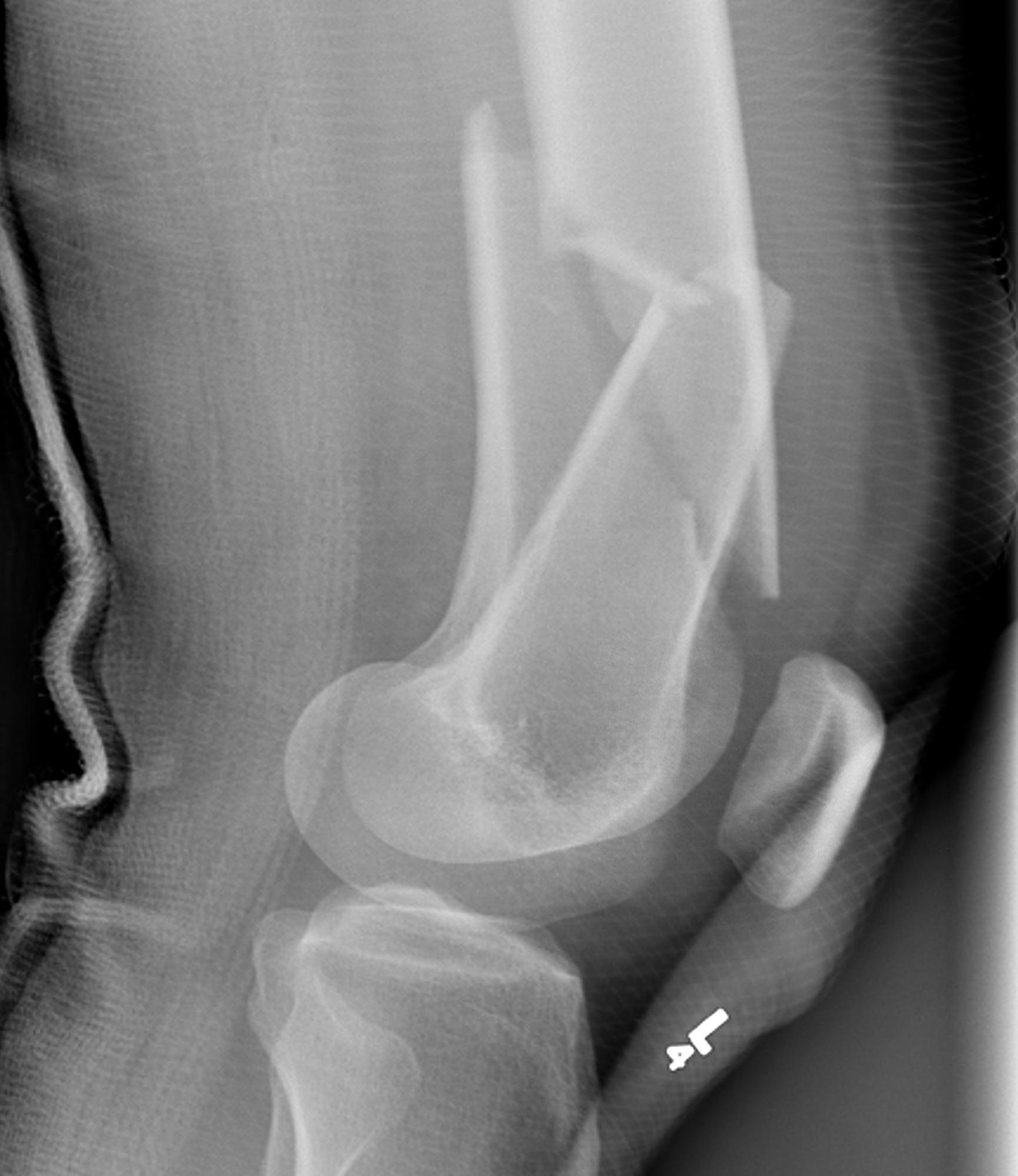
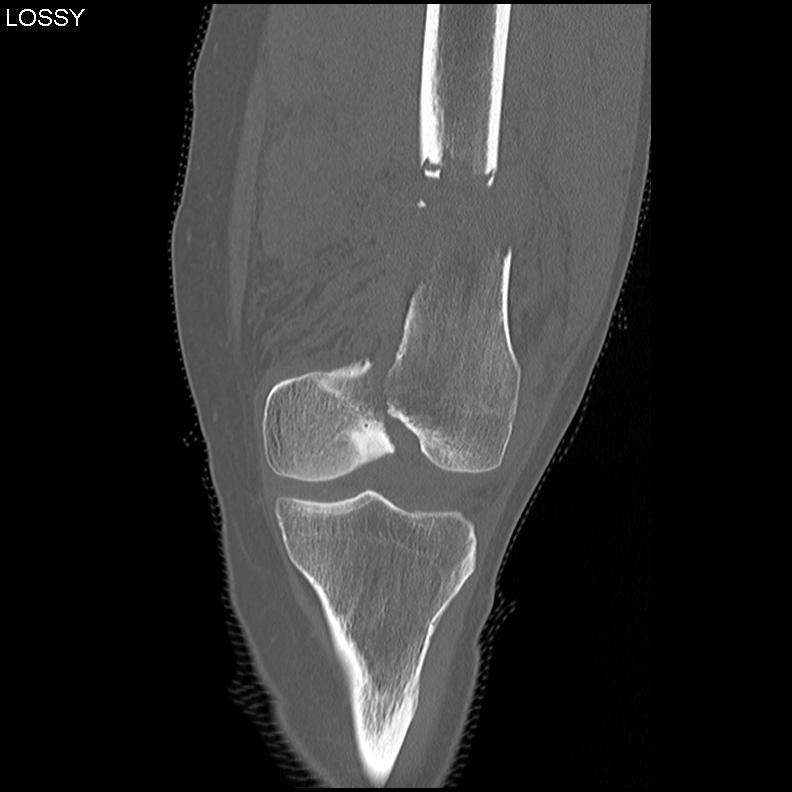
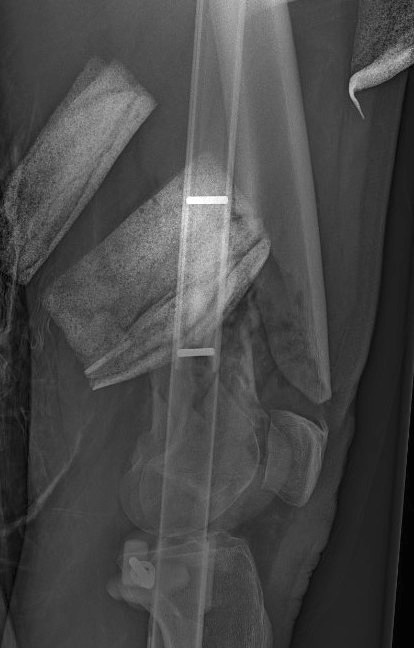
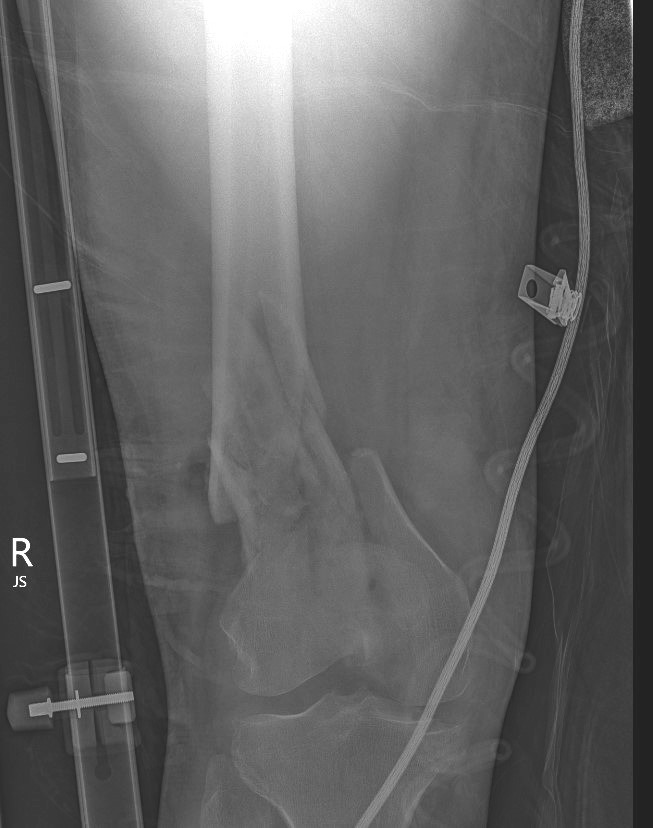
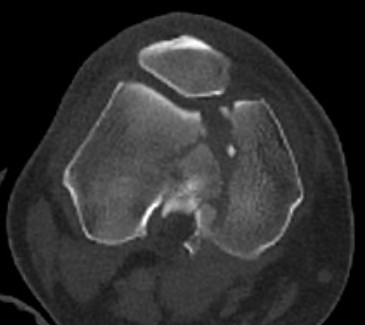
Options
Dual Plate
Plate + Retrograde nail
Distal femur replacement
Bridging External Fixation
Indications
- compound wound
- damage control orthopedics
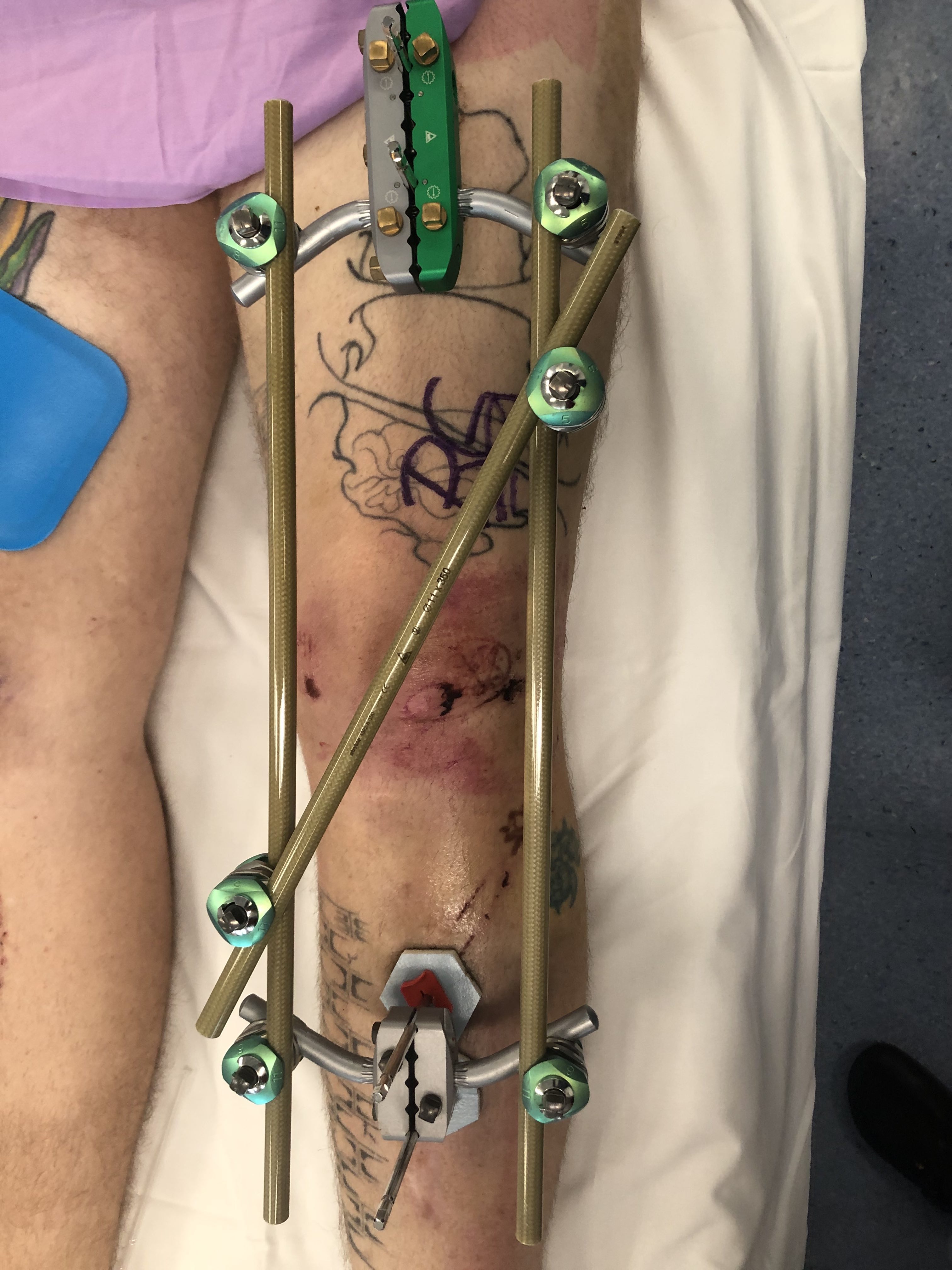
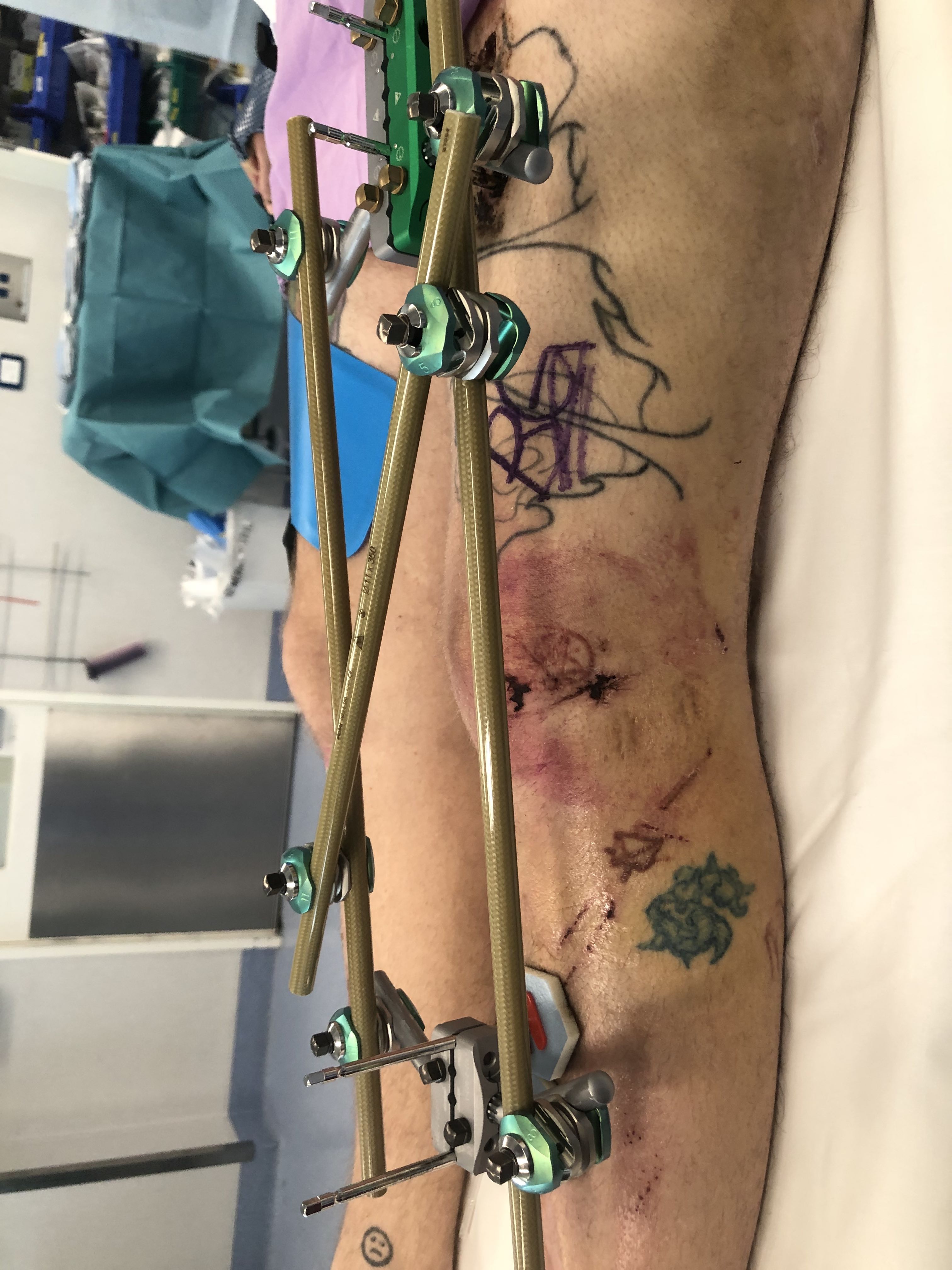
Dual plate
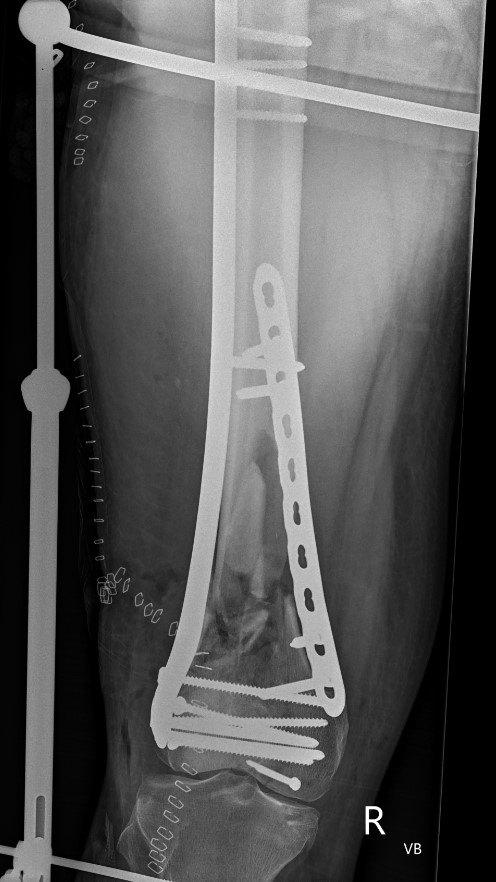
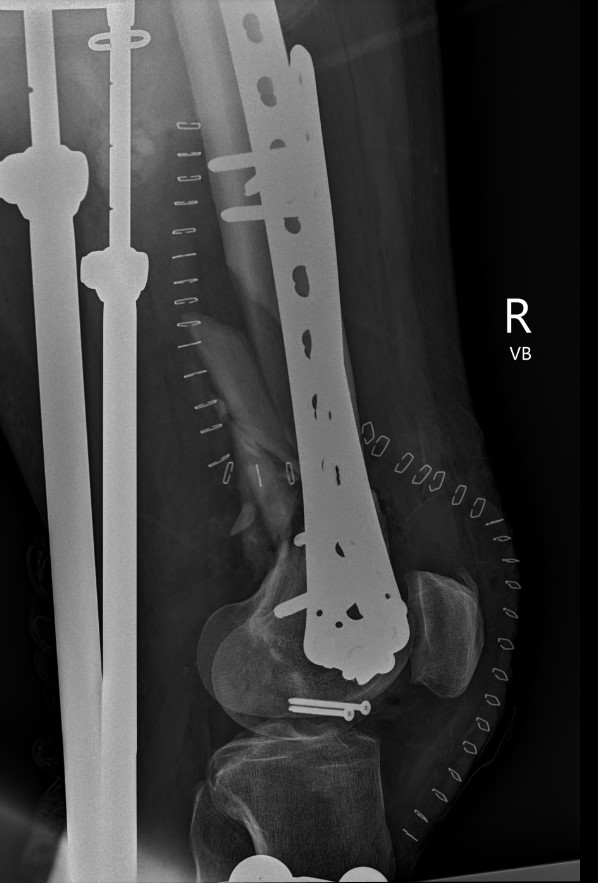
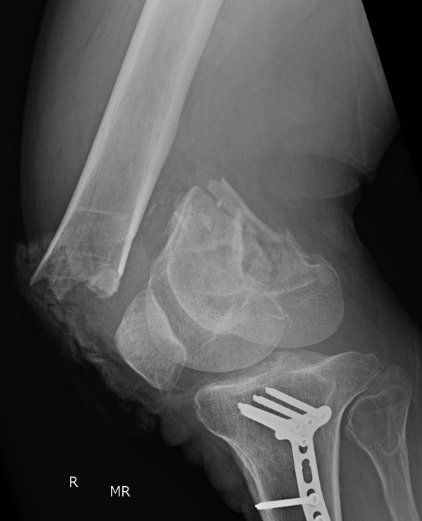
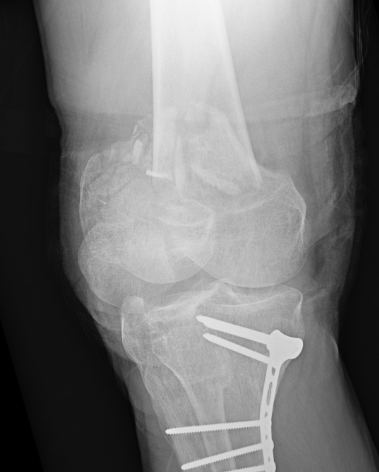
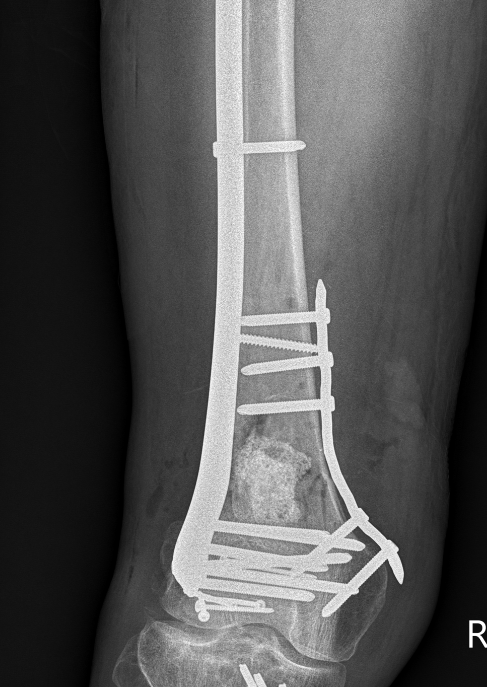
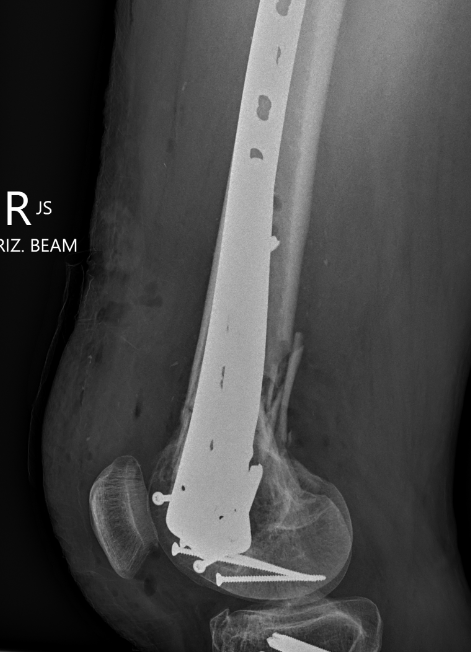
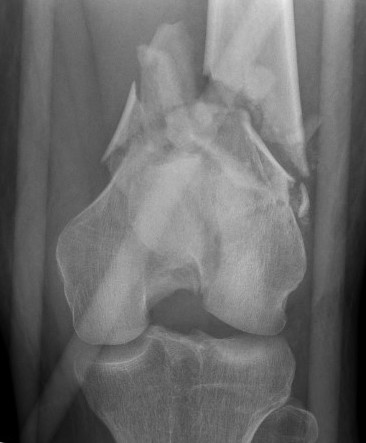
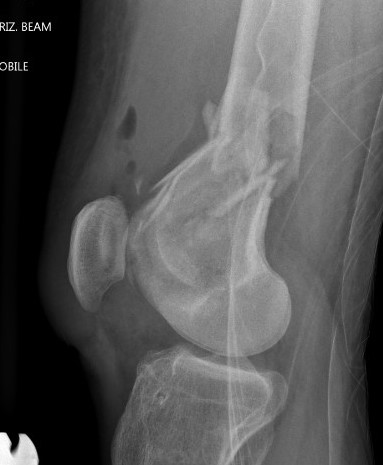
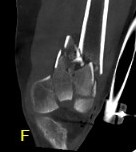
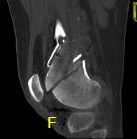

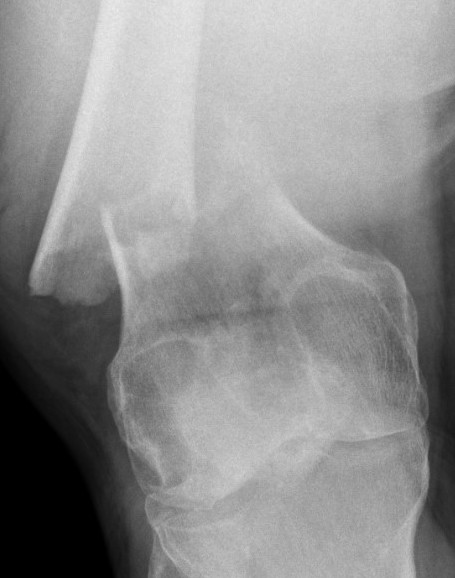
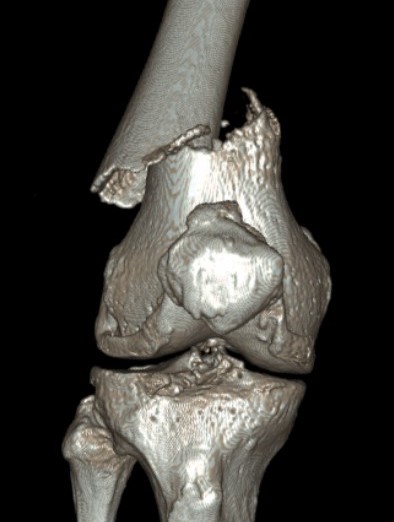
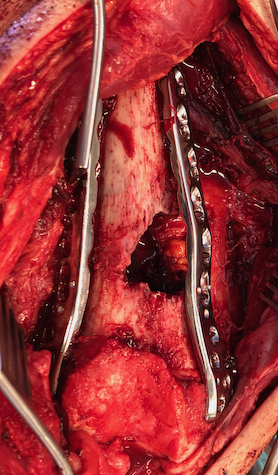
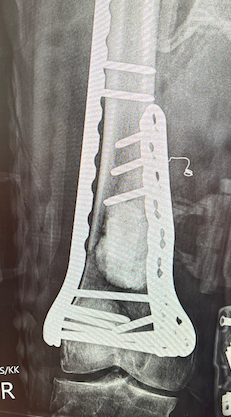
Indications
Significant comminution
Loss of medial cortical buttress
Approach
1. Dual incision
- medial + lateral approach
- midlateral appraoch - split ITB, elevate vastus lateralis
- medial subvastus approach
AO surgery reference lateral approach distal femur
AO surgery reference medial approach distal femur
2. Single anterior incision
- extensile medial parapatella approach
Vumedi extensile medial parapatella approach
Technique
Results
- 21 comminuted distal femur fractures
- increased union rates with double v single plate
- increased revision rate with single plate
Plate + Nail
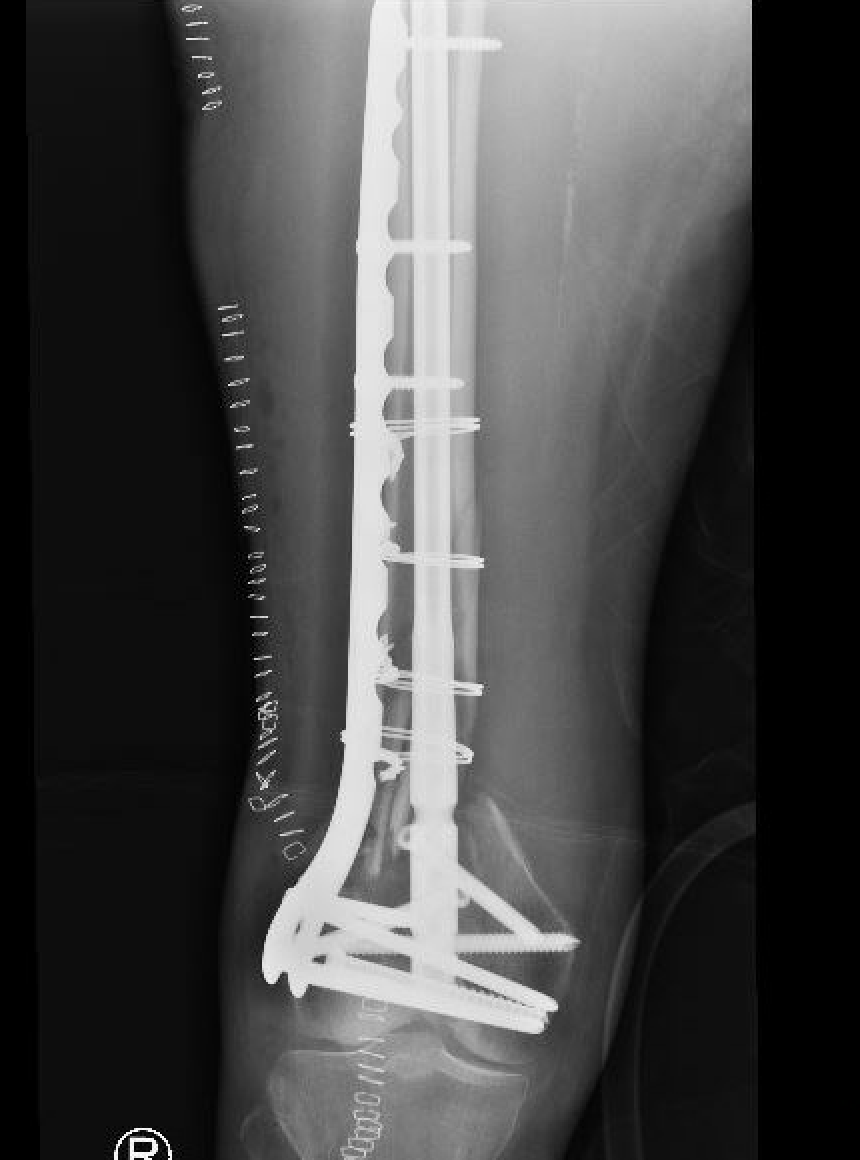
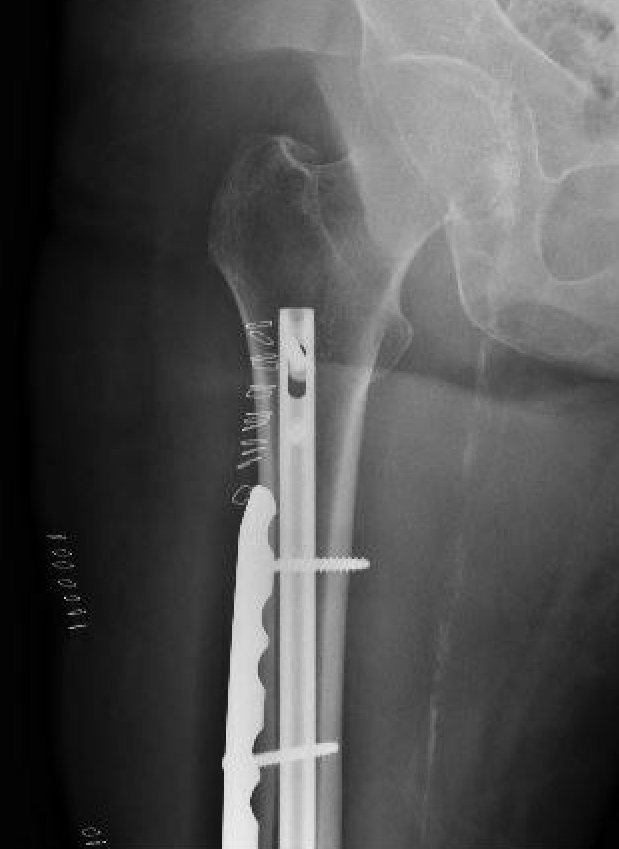
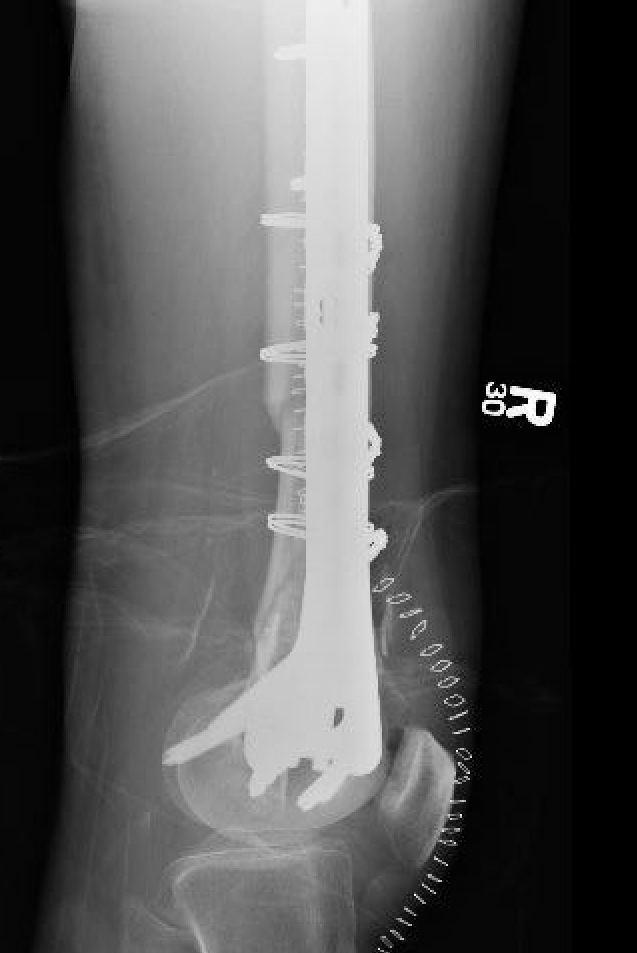
Distal Femoral Replacement
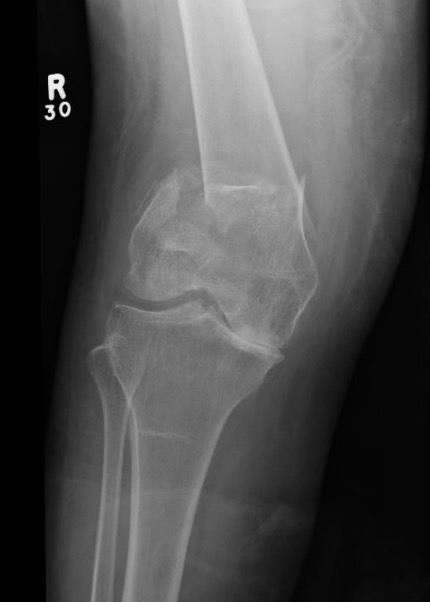
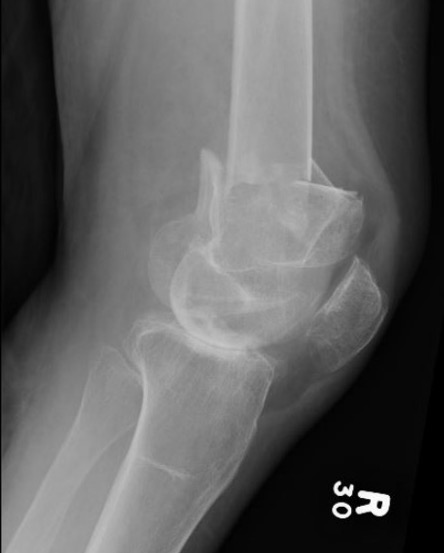
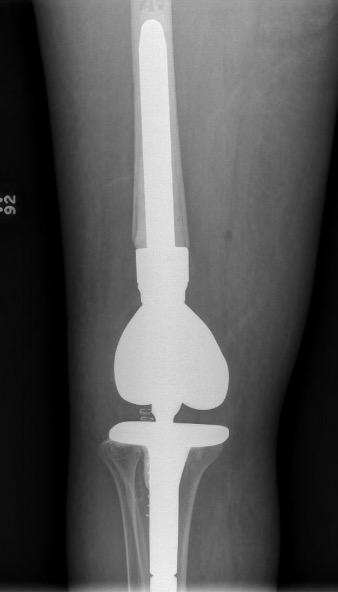
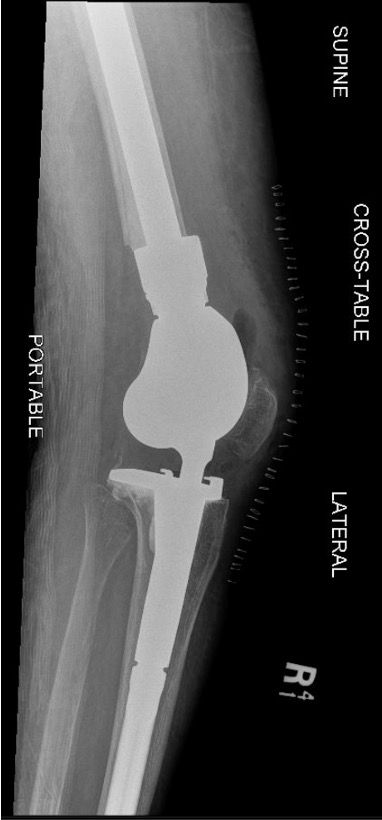
Indications
Elderly osteoporotic patient
Unreconstructable distal femur
Multiple co-morbidities
Difficulty non weight bearing
Results
Hart et al. J Arthroplasty 2017
- ORIF v distal femoral replacement in patients > 70 years old
- reoperation rate 10% in both groups
- 20% non union in ORIF
- at one year, 1/4 ORIF patients wheelchair bound, all DFR patients ambulatory
Complications
Nonunion
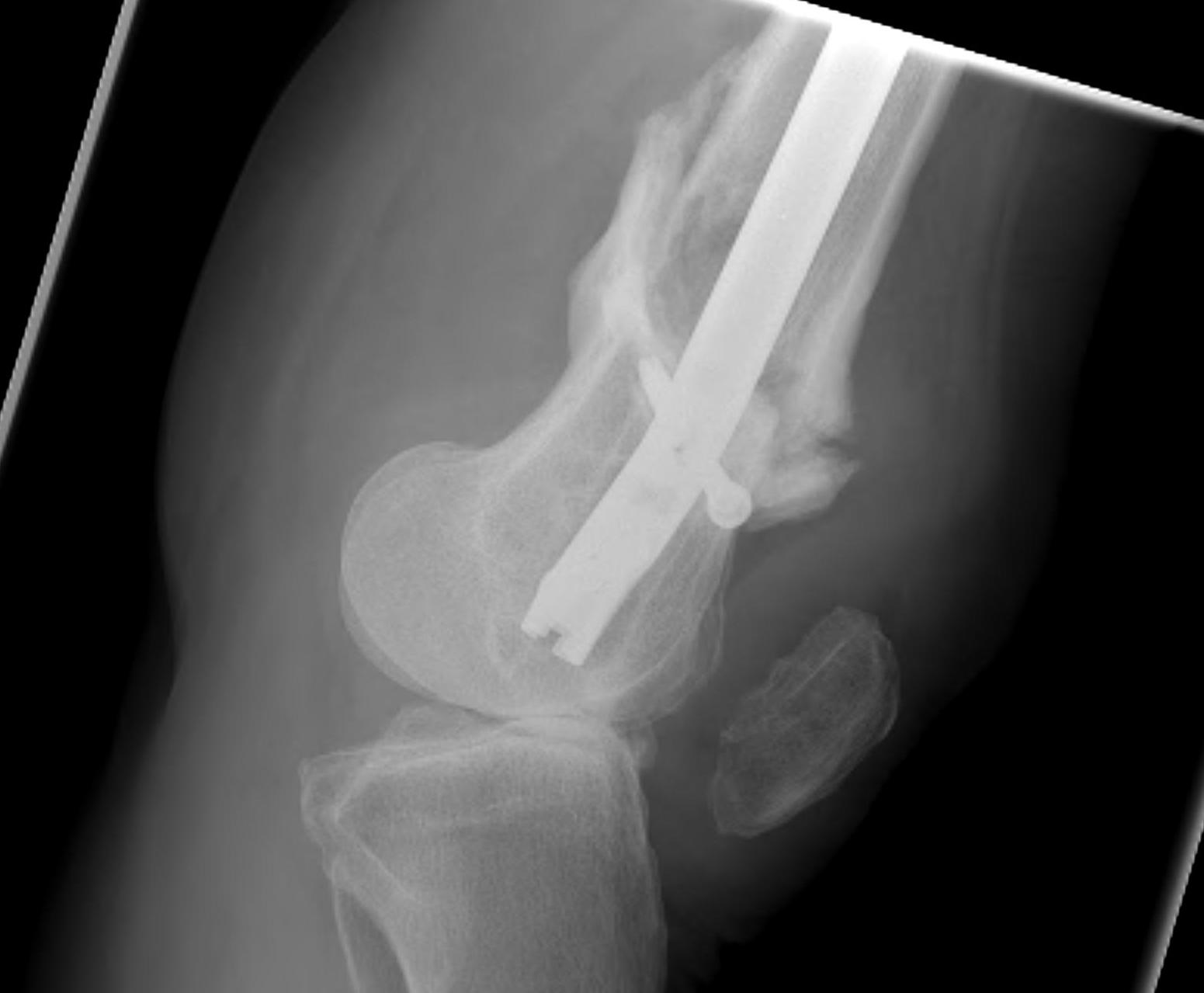
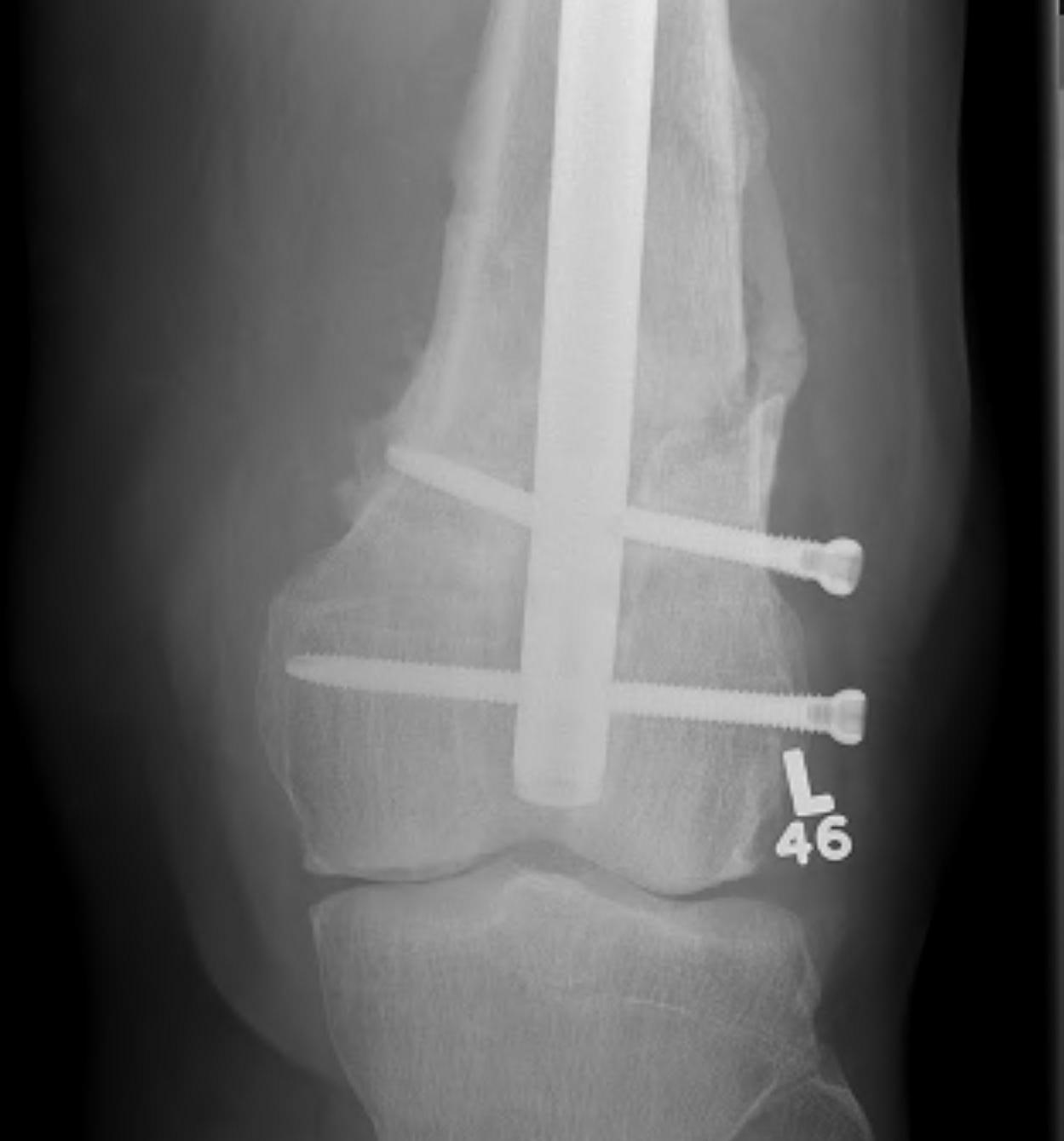
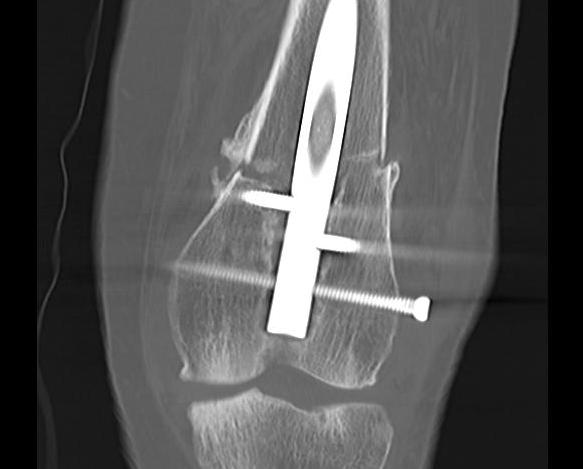
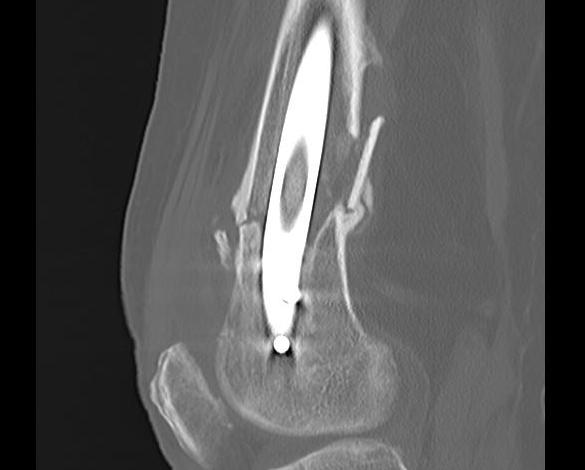
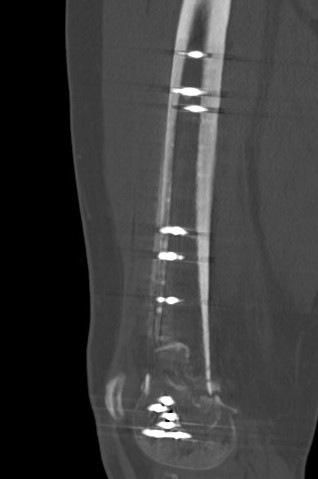
Incidence
Yoon et al. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2021
- meta-analysis
- 166/2156 nonunion (5%)
- no difference nail v plate
Risk Factors
- nonunion associated with obesity / open fracture / infection / stainless steel plates
Kiyono et al. J Orthop Surg Res 2019
- increased nonunion with medial fracture gap > 5 mm
- 96 patients
- more rigid plate screw constructs associated with nonunion
- avoid locking screws in the diaphysis
- 271 patients
- increased non union stainless steel plates compared with titanium plates
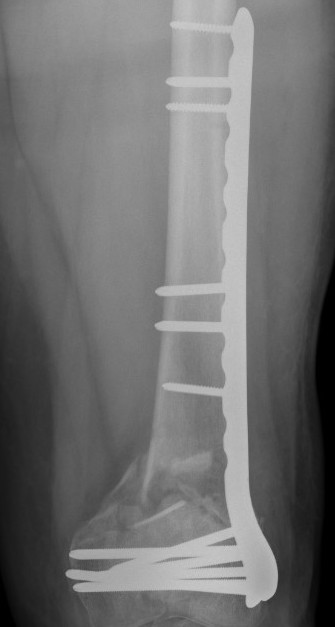
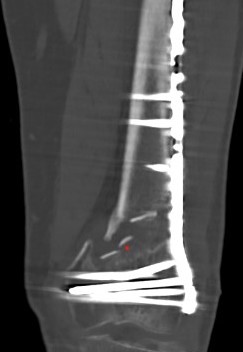
Management
Options
1. Medial plate + bone graft
2. Medial allograft cortical strut + bone graft
3. Distal femoral replacement
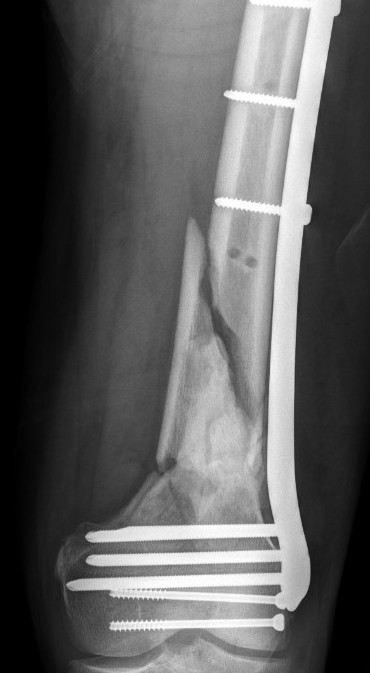
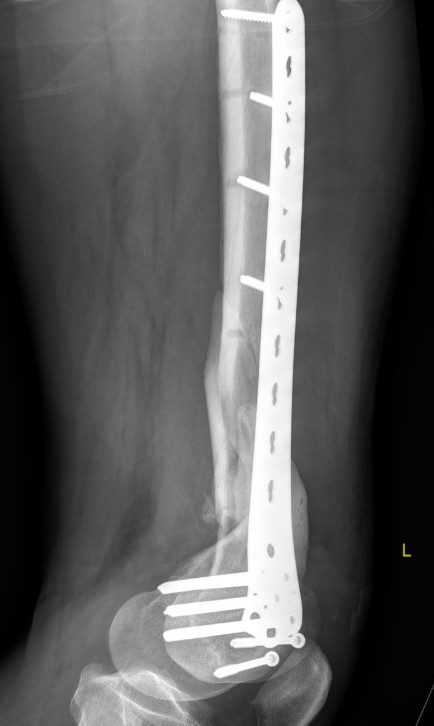
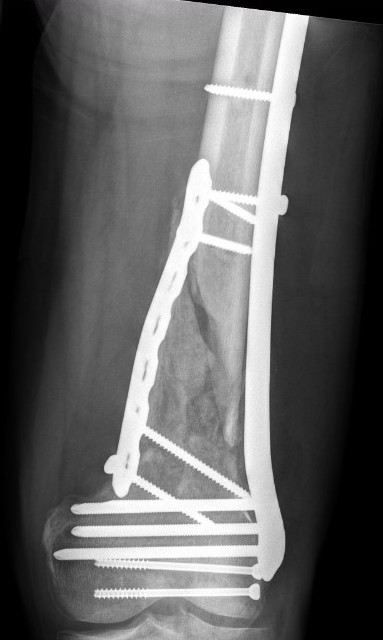
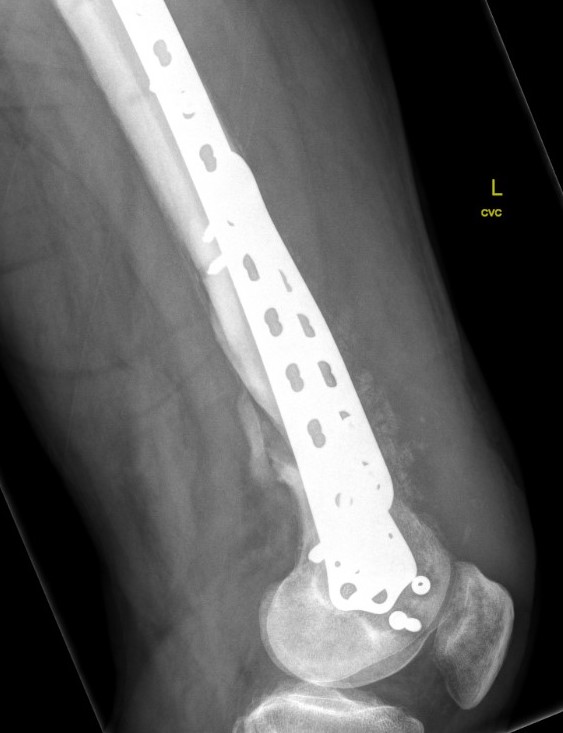
Revision medial plate + bone graft
Results
- cortical allograft strut with autograft and lateral plate
- addition of medial plate with autograft if lateral plate intact
- 16 nonunions
- all achieved union
