Types
Dorsal
- most common
Volar
Causes
1. Acute traumatic peripheral tear TFCC with DRUJ dislocation
- usually major trauma
- dorsal or volar
2A. Distal radial fracture
- Galleazzi fracture
- sigmoid notch fracture
2B. Radial Malunion
3. Ulna styloid fracture
4. Essex Lopresti
- fracture radial head with dislocation DRUJ
Diagnosis
Xray
- need true lateral
- ensure radial styloid overlies proximal scaphoid / lunate / triquetram
CT
- Axial view shows DRUJ incongruency
1A. Dorsal Dislocation DRUJ
Mechanism
- hyperpronation
- tear of dorsal distal RUJ ligament
- with partial or complete TFCC tear
Clinically
- dorsal prominence
- forearm locked in pronation
- attempted supination painful
CT scan
Management
1. Closed reduction
- maintain in supination 4/52
2. Open reduction
- rarely needed
- failure closed reduction (ECU incarceration)
- chronically dislocated
- may require acute repair TFCC +/- K wires
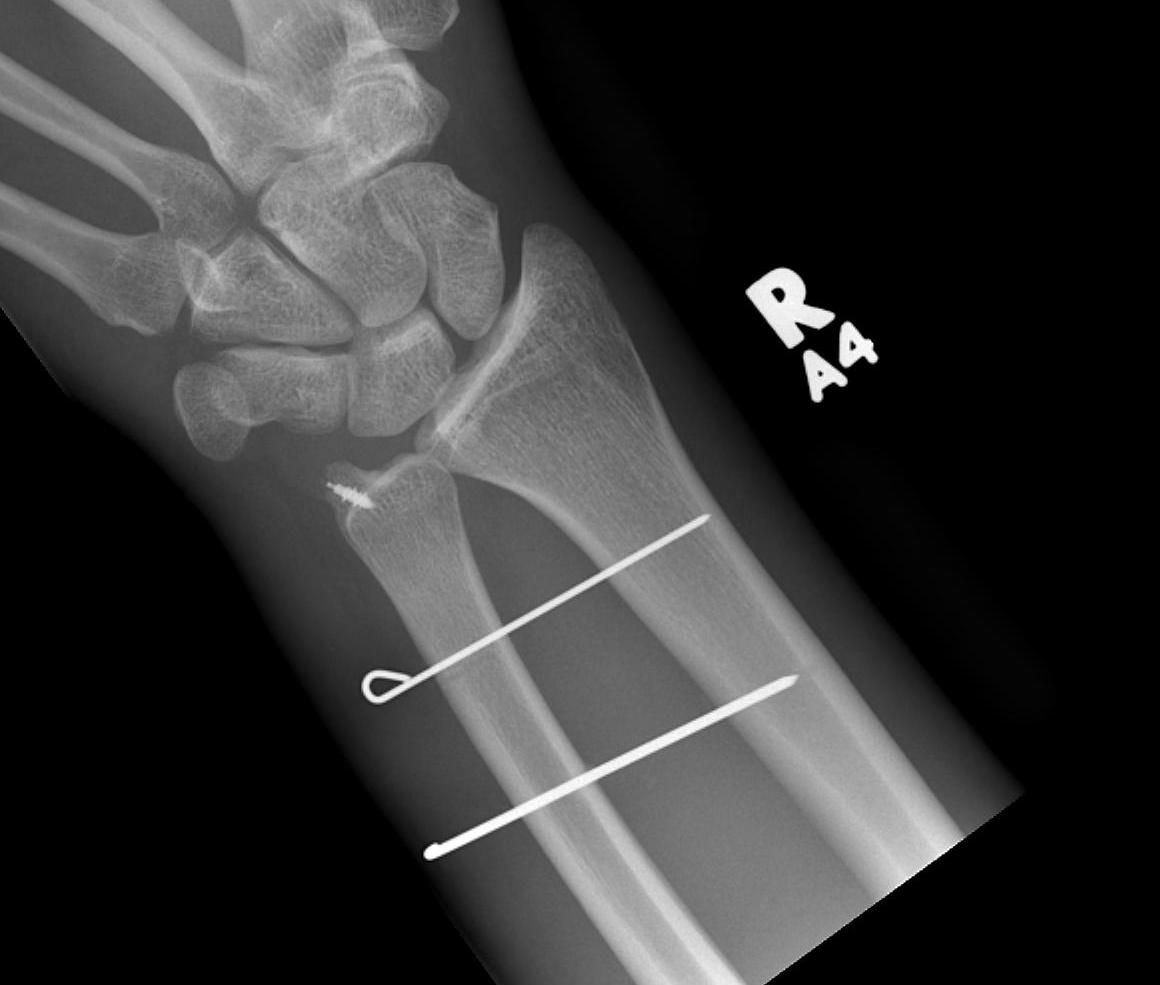
1B. Volar Dislocation DRUJ
Mechanism
- forced supination
- usually complete tear TFCC
Clinically
- arm locked in supination
CT scan
Management
- closed reduction
- maintain in pronation 4 weeks
- rarely need open reduction or in chronic cases
2A. Acute Distal radial fracture / Galleazzi
Incidence
- up to 60%
Treatment
- Anatomical reduction of radius
- usually makes DRUJ stable
- rarely need to repair TFCC / K wire for stability
2B. Radial malunion / Non anatomical ORIF
A. Short radial fracture
- lengthening radius difficult
- ulna shortening
B. Angulation / rotation
- radial osteotomy
- TFCC repair
- +/- TFCC reconstruction with strip ECU
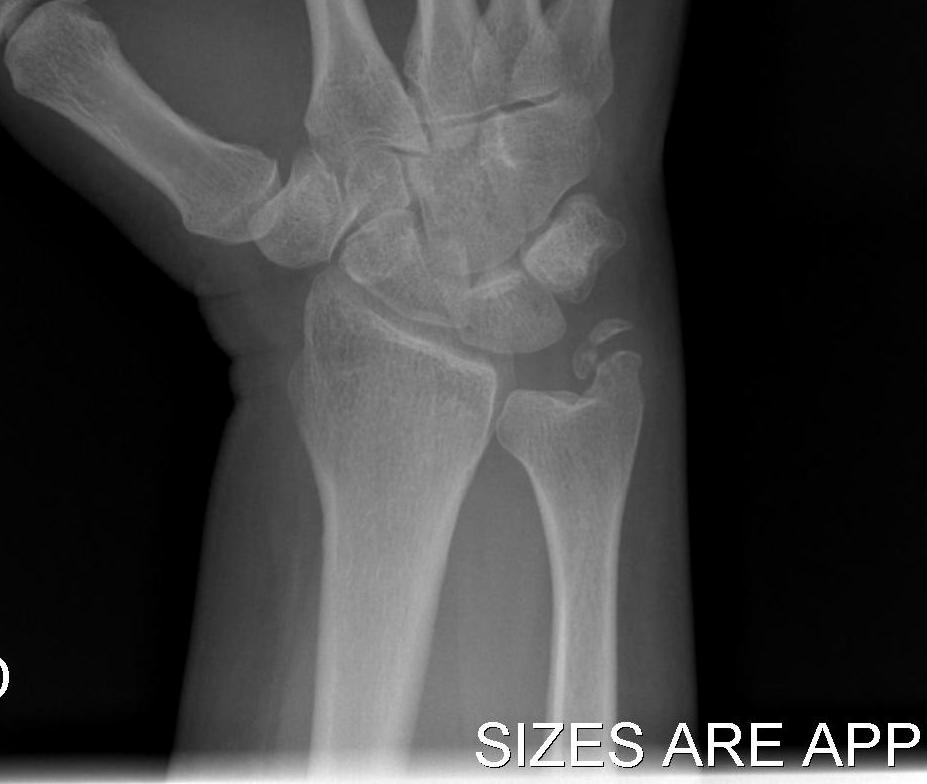
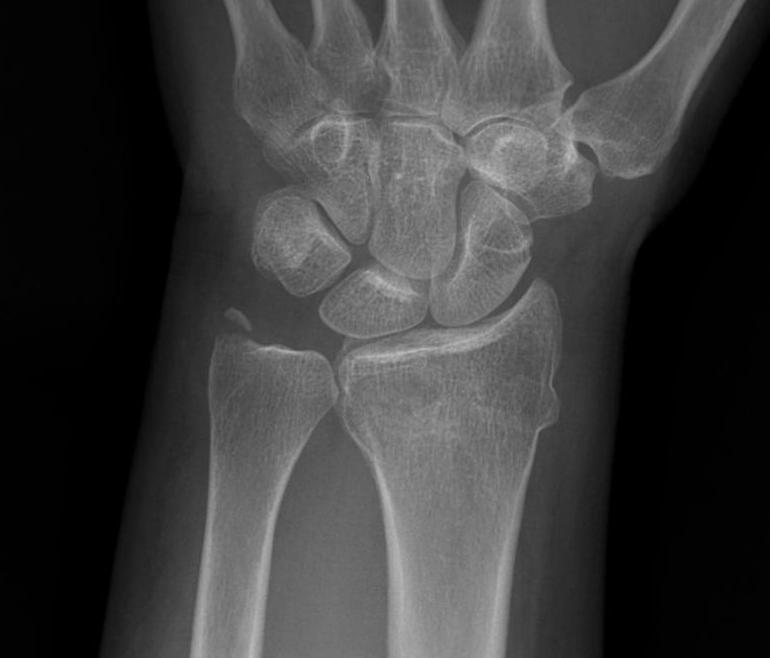
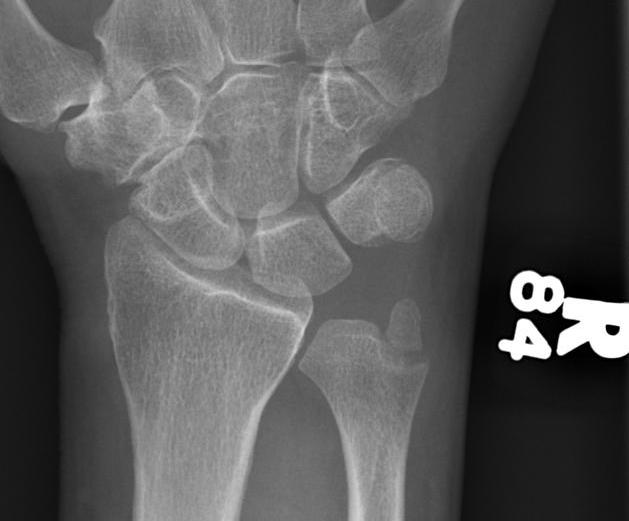
3. Displaced ulna styloid
Classification
Type 1
- tip fracture
- stable DRUJ
Type 2
- base fracture
- unstable DRUJ
Management
POP immobilisation in neutral rotation and UD for 6/52
- ensure DRUJ remains located
Rarely need ulnar styloid ORIF if displaced and DRUJ unstable
4. Essex-Lopresti injury
Definition
- fracture radial head with dislocation DRUJ
- Essex-Lopresti variant - radial neck fracture with dislocation DRUJ
Type 1
- acute radial head fracture
Management
- reconstruct or replace radial head
- assess stability in supination
- occasionally need TFCC repair +/- K wire
Type 2
- late
- following excision of radial head with injury to interosseous membrane
- usually occurs within first two years following injury
Management
Nil degenerative changes
- ulna shortening with plate to reduce DRUJ
- radial head replacement to prevent recurrence
Degenerative changes
- Hemiresection / Darrach's / Kapandji
