Classification Leffert "OCRO"
I Open
II Closed
A Supraclavicular
- Preganglionic / Avulsion of Roots
- Postganglionic / Rupture of Trunks
B Infraclavicular
- cords & branches
C. Post anaesthetic
III Radiation / Other
Tumour
Iatrogenic e.g. patient positioning
Other
IV Obstetric
A Erb C5/6
B Klumpke C7/8 T1
C Mixed
Narakas Rule of 7's
70% MVA
70% of these MBA
70% associated injuries
70% supraclavicular
70% root avulsions
70% C8/T1 involvement
70% persistent pain
Aetiology
MBA most common
Gunshot Injury
- deficit 2° nerve concussion
- usually improves
- observe for 3 /12
- explore if no improvement / large residual deficit
Position of arm
- abducted above horizontal (lower lesion)
- abducted below horizontal (upper lesion)
Associated Injuries
Axillary / subclavian artery 10-20%
Fracture humerus / clavicle / scapula / ribs
Dislocations GH / AC / SC joints
Rotator cuff tears
Patterns
Supraclavicular preganglionic (nerve root patterns)
Supraclavicular postganglionic (trunks)
Infraclavicular (cords)
Can be mixed
- 2 patterns can occur in one nerve root
Supraclavicular Preganglionic / Root avulsion
Clinical
Severe pain in anaesthetised arm
- starts day 1 in 50%
- constant burning + superimposed `lightning shocks`down limb
Tender & swollen in posterior triangle
- pseudomeningocoeles
Tinel's negative
- dorsal root ganglion intact so no wallerian degeneration of sensory nerve
Horner's if T1
Evidence of injury to branches from roots
- long thoracic / serratus anterior
- dorsal scapular / rhomboids
Investigations
NCS
- SNAP normal (as fibres in continuity with DRG)
- abnormal sensation
EMG
- denervation dorsal neck muscles (posterior rami)
Diaphram paralysis
- high nerve root lesion / phrenic nerve
MRI Neck
- pseudomeningocoeles
- empty root sleeves
Patterns
1. Erb's Palsy
C5 & 6 +/- 7
- also lose branches from roots and trunk
- long thoracic / dorsal scapular / suprascapular
Clinical
- shoulder adducted & internally rotated
- elbow extended
- forearm pronated
- waiter's tip
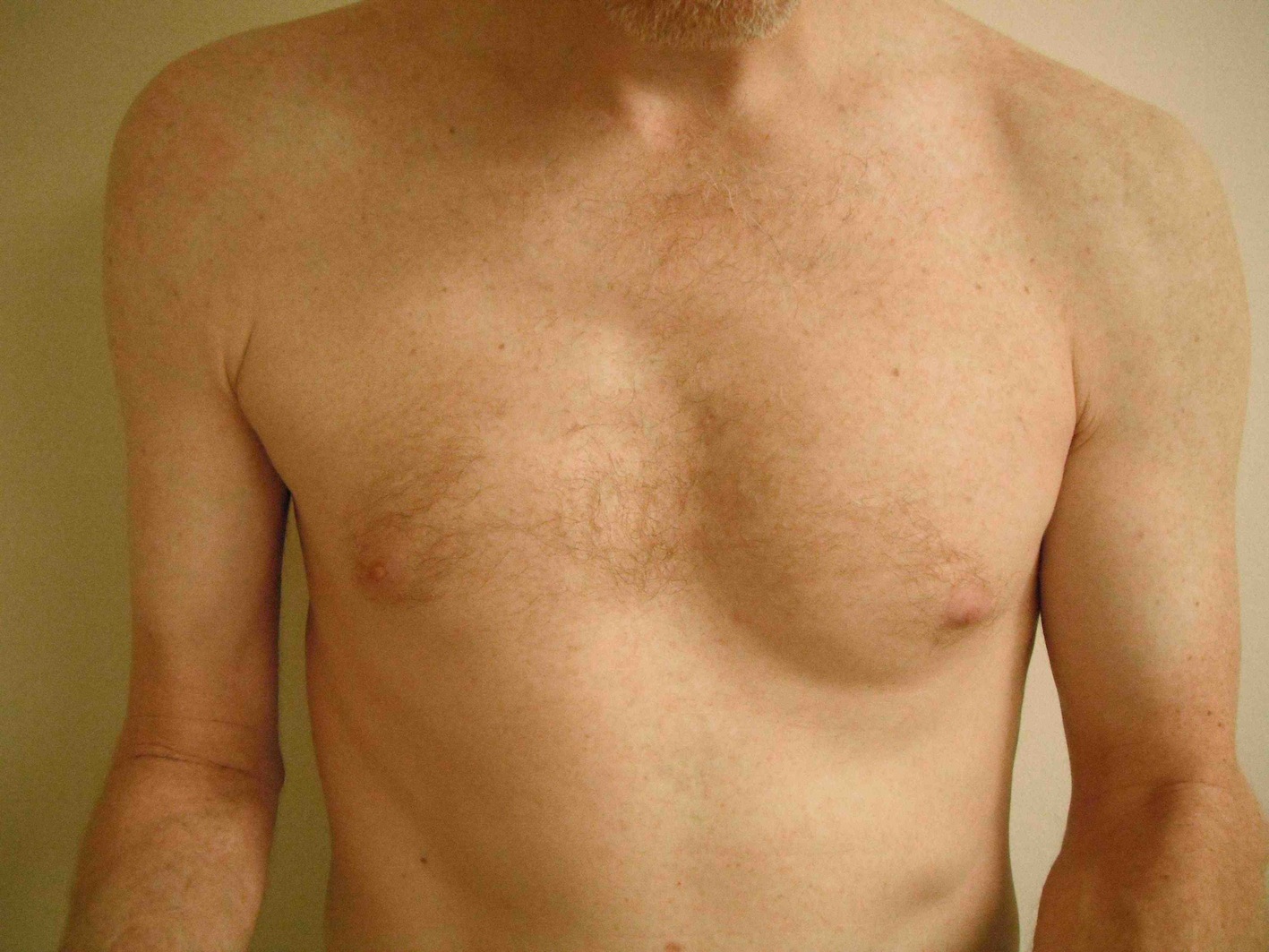
Paralysis of
- deltoid / abductors
- SS / abductor
- IS / external rotator
- biceps / supinator and elbow flexor
Sensory loss
- lateral shoulder
- lateral forearm and hand
2. Klumpke's palsy
C8 & T1 lesion
- paralysis intrinsics, wrist and finger flexors
- sensory changes medial hand and forearm
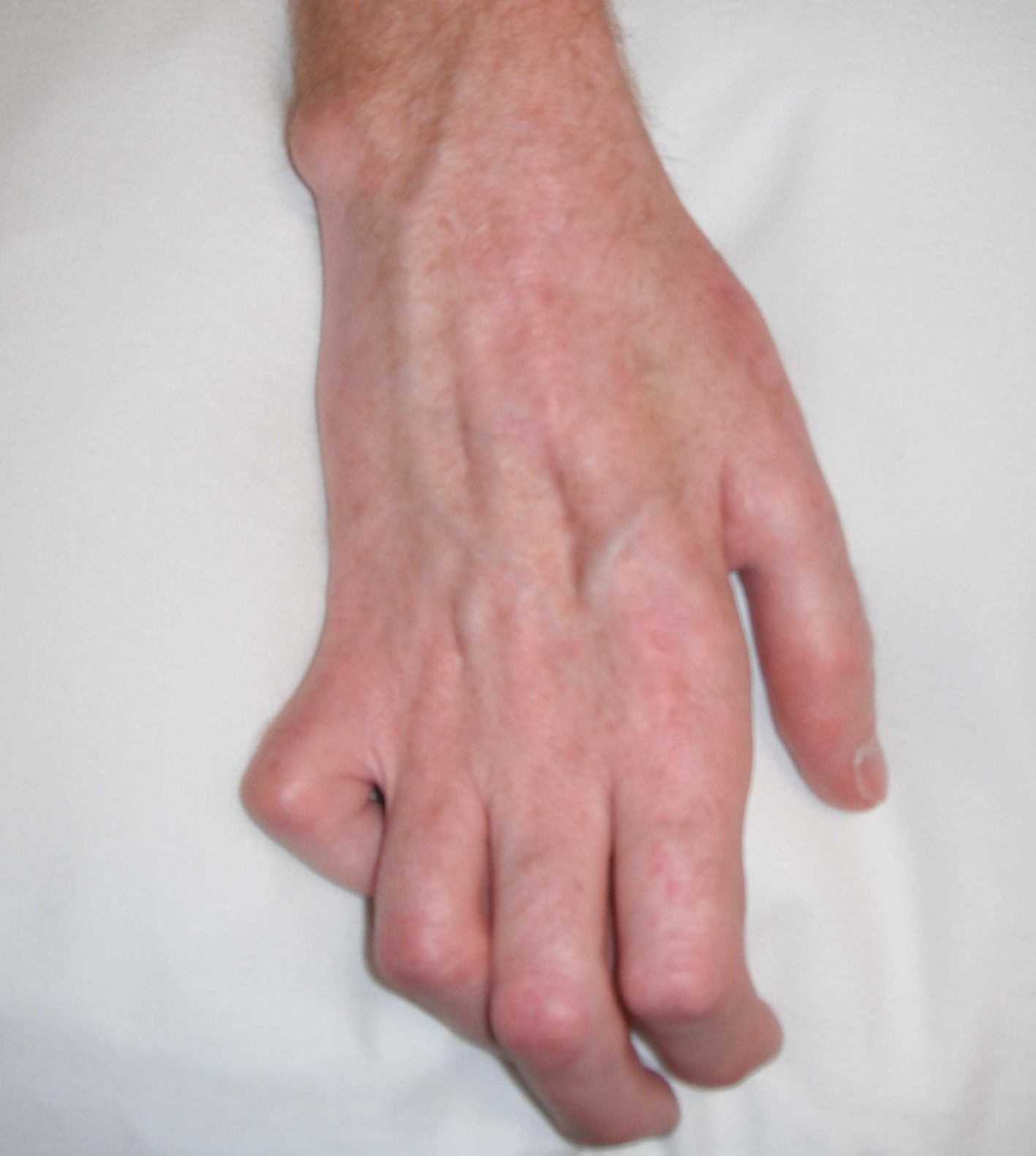
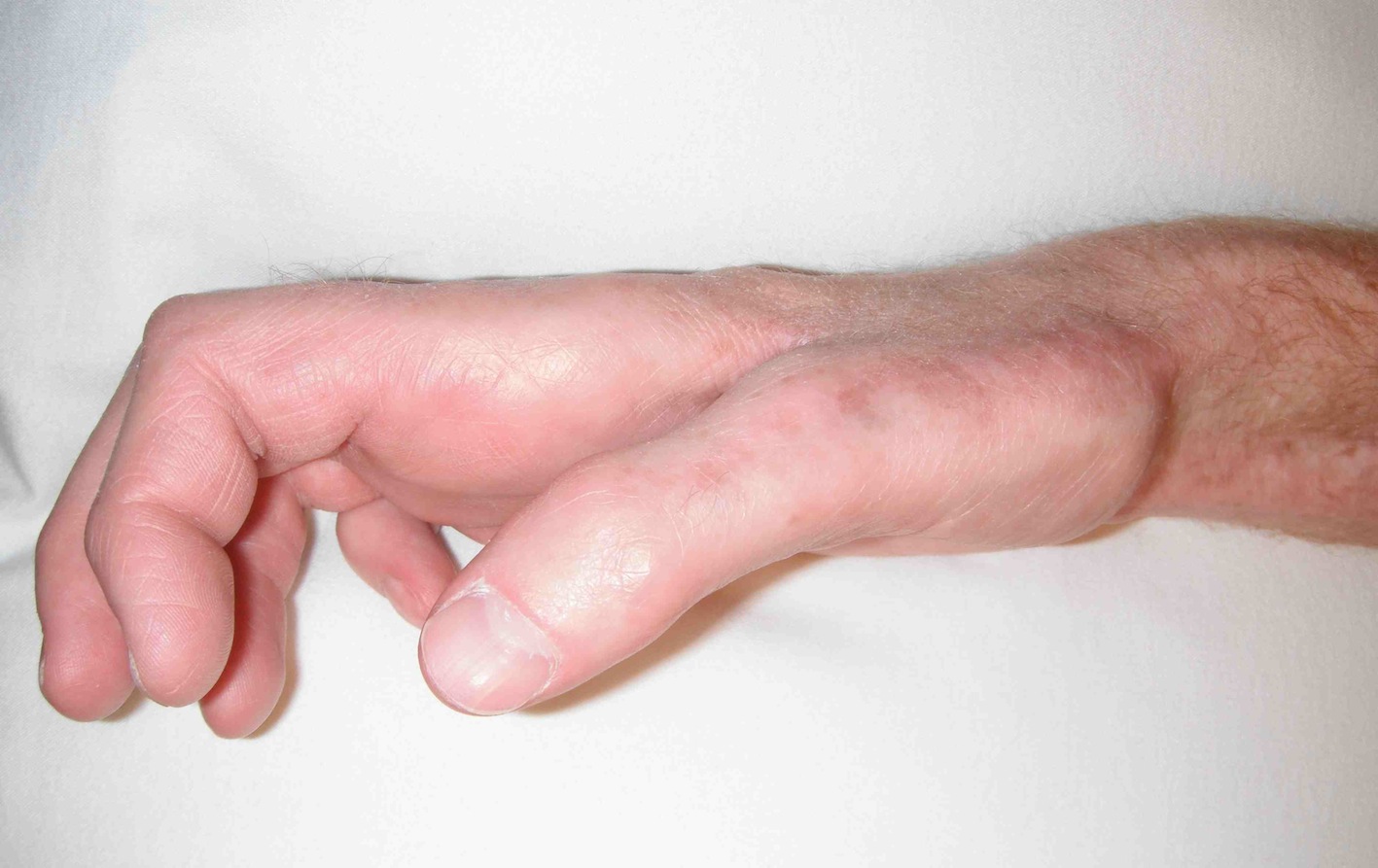
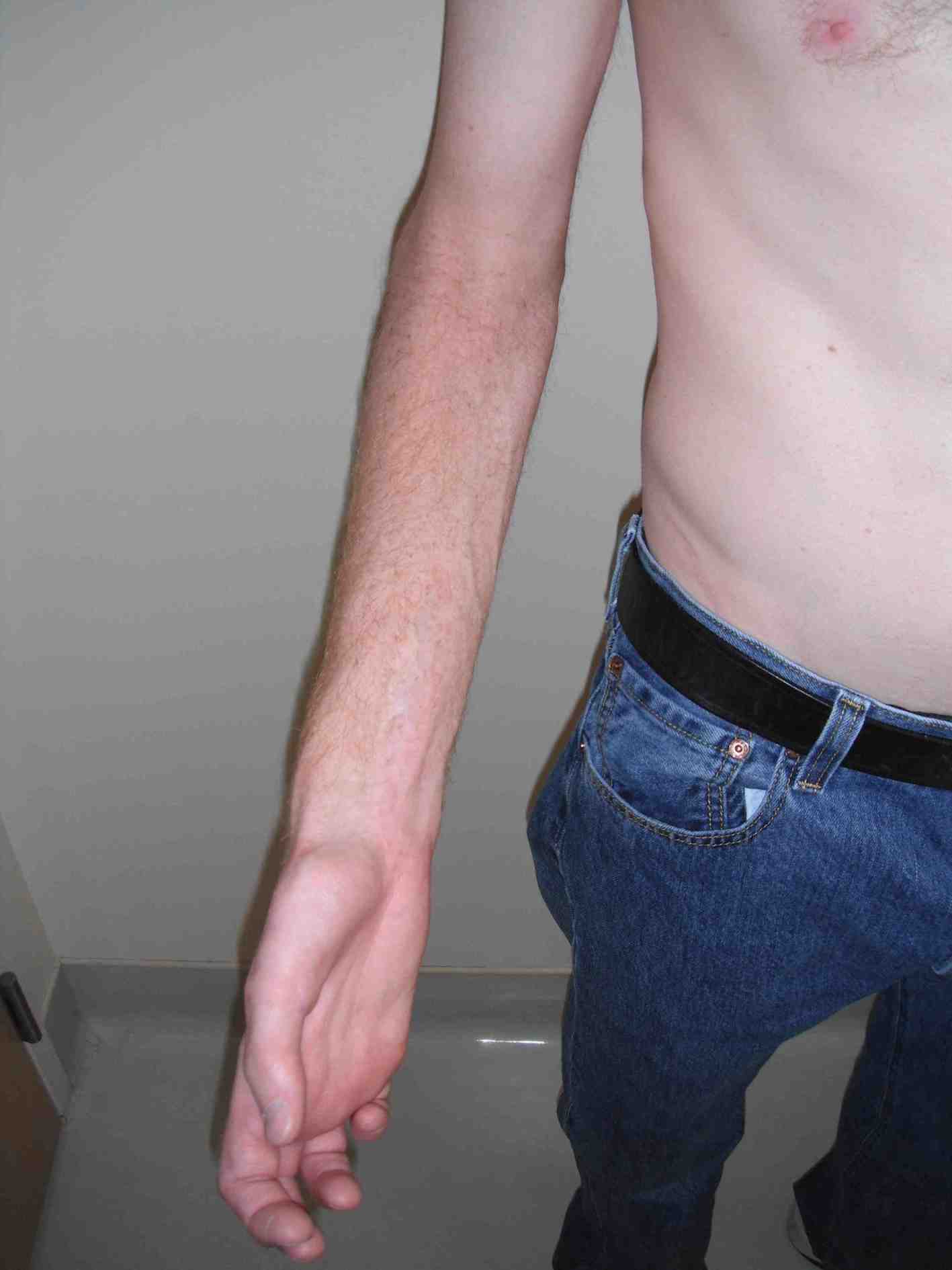
Horner's
- ptosis (drooped)
- miosis (small)
- anhidrosis (dry)
- enophthalmos (sunken)
Supraclavicular Postganglionic (trunks)
Diagnosis
Tinel's positive
SSN / DSN / LTN intact
No Horners
Patterns
Erb's Palsy
Klumpke's Palsy
- no Horner's
Infraclavicular
Peripheral nerve patterns
A. Lateral cord weak (C5,6,7)
MCN
- biceps (C5)
Lateral cord median
- FCR (C6)
- PT (C6)
Lateral pectoral nerve
- clavicular head
B. Posterior cord weak (C5-T1)
AXN (C5)
- deltoid
Radial nerve
- triceps (C7)
- ECRL / ECRB (C8)
- EDC (C8)
- EPL (C8)
Upper and lower SCN (C5,6)
- SSC, T major
LTN (C5,6,7)
- latissimus dorsi
C. Medial cord weak
Ulna nerve (C7,8 T1)
- FCU (C8)
- LF FDP (C8)
- interossei (T1)
Medial median Nnerve
- FDP IF / MF
- FPL
- Thenar / APb
Medial pectoral
- sternocostal P. major
X-rays
CXR
- elevated diaphragm (phrenic nerve injury)
- fractured 1st rib
- suggests root avulsion
C spine Xray
- avulsion of C7 TP
- suggests root avulsion
Shoulder Xray
- fracture clavicle / Scapula / GHJ / ACJ / SC
NCS / EMG
Takes 3 weeks for Wallerian degeneration / denervation to occur
EMG
- muscle sample of specific groups of interest
- denervation / sharp waves & fibrillation potentials
- re-innervation / polyphasic AP on volitional activity
Preganglionic lesion
NCS
- Skin Anaesthetic
- SNAP persist because of DRG
EMG Denervation in
- paravertebral muscles
- serratus anterior
- rhomboids
Postganglionic lesion
NCS
- skin anaesthetic
- no SNAP as due to wallerian degeneration
MRI
MRI C Spine
Nerve root avulsion
- displacement or oedema spinal cord
- empty foramen
- pseudomeningocoeles (takes 5 days to develop)
MRI Shoulder
Difficult to correctly image trunks and cords
- high amount of oedema / hard to define severity of injury
Hems et al J Hand Surg Br 1999
- some usefulness in identifying level of injury in postganglionic
Prognosis
1. Infraclavicular > Supraclavicular
2. Upper trunk > Lower trunk
3. Better in children and young adults
