Background
Trauma is 3rd most common cause death in all age groups
- number one in young adults < 44 years
Death
Death occurs in 3 time periods
1. First few minutes
- death secondary aortic rupture or severe head injury
- 50% die in this period
- only a few survive
- only if rapid transport
2. Golden Hour
- major head injury (Haematoma)
- chest injury (Pneumothorax)
- abdominal injuries (Ruptured viscus)
- major fracture (Pelvis, Long bone)
- 35% of deaths
- high salvage rate
3. Late death
- days to weeks later
- brain death / multiorgan failure / sepsis
Management priorities
1. Life threatening injuries
2. Limb threatening injuries
Assessment & Management
1. Preparation
A Pre-hospital
B In-hospital
2. Triage
3. 1° Survey
4. Resuscitation
5. 2° Survey
6. Continue post resuscitation monitoring & re-evaluation
7. Definitive Care
Can occur simultaneously or parallel
Preparation
A. Pre-hospital
Co-ordination between Ambulance & hospital
Aims
1. Airway control
2. Stop bleeding
3. Immobilize patient
4. Rapid transport to appropriate facility
5. Obtain history
B. In-hospital
1. Prepare trauma area
- 1 nurse to take observations on arrival and every 2 minutes
- 1 nurse to record
- cannulas / IDC / chest tube
- suction / intubation
2. Notify trauma team
- general surgery / cardiothoracic aware and available
- anaethetist aware and available
3. Notify lab
- O negative blood available
- ready to process emergency blood tests / cross match
4. Radiology
- technician to take C spine / CXR / pelvis
Triage
Sorting of patients based on treatment needs
Two scenarios
Multiple
- patients don't exceed treatment maximum of hospital
- treat life threatening pathology first
Mass
- patients exceed treatment maximum of hospital
- treat those who will survive if simple intervention
Primary survey
Life threatening conditions are diagnosed and treated simultaneously
A. Airway Maintenance and Spinal Precautions
A patient who can respond verbally to "How are you?" is conscious and has a clear airway
Assume spinal fracture
- hard cervical collar with sand bags and tape
- spinal board
- log roll
Monitoring / 2 x large bore 16G cannulas / bloods
- simultaneously attached
- 02 / ECG / blood pressure
- CBC / Renal and liver function / coags / Group and hold / cross match / BHCG
Immediate management
- jaw thrust and chin lift
- clear FB / blood etc
- apply oxygen
Indications intubation
- GCS < 8
- maxillofacial fractures
- laryngeal trauma / stridor
Intubation Adult
- guedel airway / preoxygenate 100% oxygen
- inline traction / protect spine at all times
- rapid sequence induction / cricoid pressure
- xylocaine spray 10%
- fetanyl (1 mcg / kg, 50 - 100 mcg)
- midazolam (0.05 - 0.1 mg / kg, 5 - 10 mg)
- avoid muscle relaxants if possible (succinylcholine 1 mg / kg, usually 100mg)
- avoid propofol if possible / causes hypotension (10mg / ml, give 2.5 mg / kg to maximum 250 mg)
Intubation Paediatric Patient
- use Broselow Paediatic Emergency Tape for weight and medications based on heights
- preoxygenate
- atropine 0.02mg / kg or 0.1 to 1 mg given 2 minutes before intubation
- this prevents excessive vagal response and dries secretion
- sedate midazolam 0.1 - 0.3 mg / kg
- cricoid pressure
- paralyse succinylcholine 2mg / kg < 10 or 1 mg / kg > 10
- ETT based on size little finger
- trachea short (5 - 7cm in infant) and very anterior
- set tidal volumes at 6 - 8 ml / kg and RR 40/min infant and 20/min older child
Unable to intubate
1. Jet insufflation cricothyroidotomy
- prep / LA
- small incision often required
- insert 12 or 14 G plastic cannula through cricothyroid membrane
- attach to syringe / angle 45o caudal
- aspirate as insert / stop when aspirate air / advance cannula over needle
- connect to 15 L minute oxygen
- have Y connector or cut side hole in tubing
- intermittitent insufflation 1 second on and 4 seconds off with thumb over hole
- suitable for 30 minutes
2. Surgical cricothyroidotomy
- prep / LA
- horizontal incision between thyroid and cricoid cartilage
- horizontal incision between thyroid and cricoid / don't cut either cartilage
- open with artery forceps
- insert size 5, 6 or ETT, inflate and secure
- not suitable in children under 12 as cricoid is very important
Gastric distention / NGT
- can cause hypotension or aspiration
- very common in trauma / children / forced ventilate with bag and mask
- insert NGT as soon as able
- insert through mouth if facial trauma / avoids intracranial penetration
B. Breathing
Immediate management
Apply oxygen
- 12 L/min
- check RR (> 20 / minute worrying)
- check oxygen saturations
- apply ECG monitoring
Examination
Expose chest
- look / feel for flail segment
- symmetrical motion
Auscultate
- symmetrical breath sounds
- hear sounds
Palpate
- trachea midline
- heart apex
- rib fractures
Diagnosis
Pneumothorax / haemothorax
- decreased breath sounds
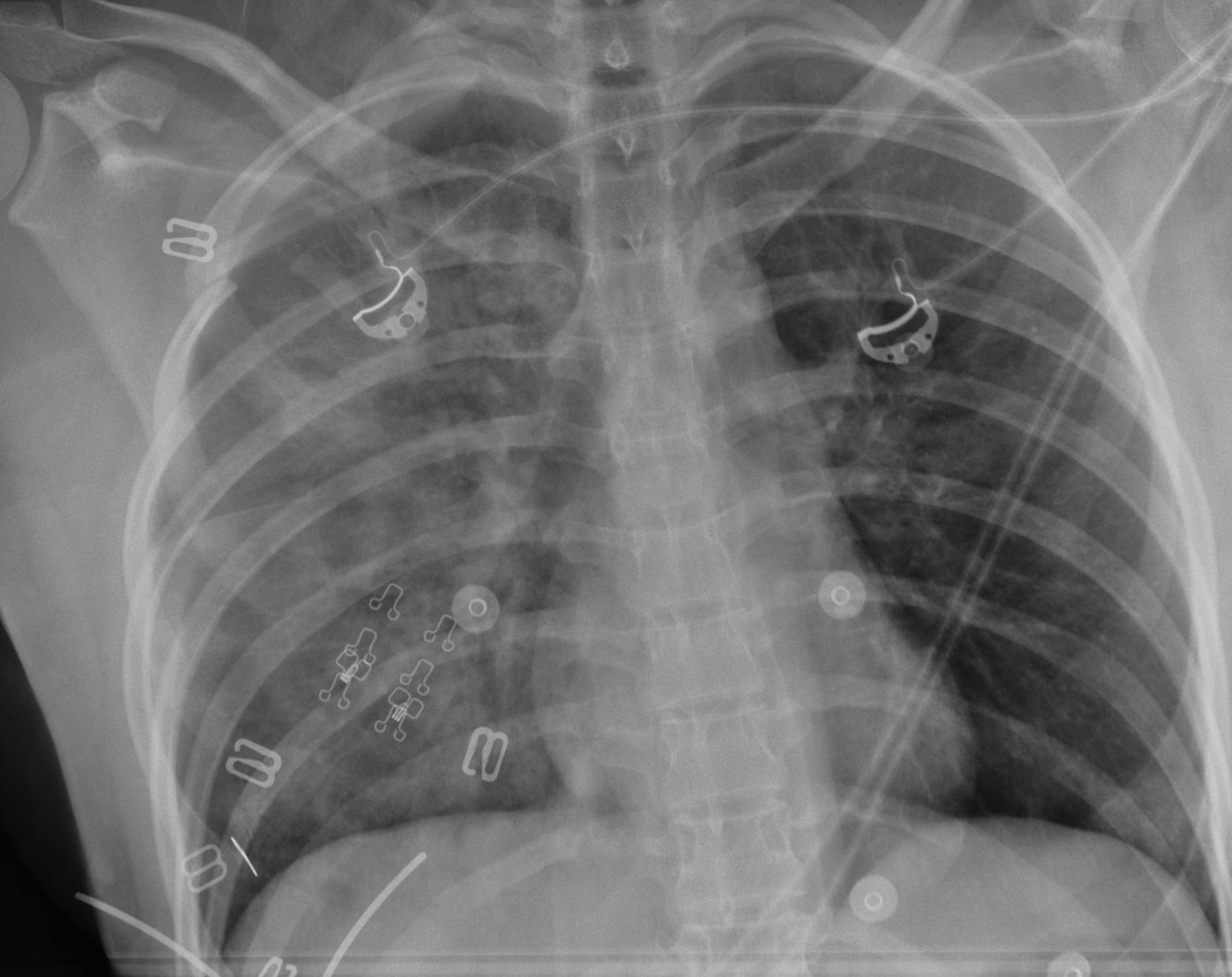
Tension pneumothorax
- heart apex and trachea displaced
- heart sounds (muffled + distended neck veins = cardiac tamponade)
Tension Pneumothorax / Needle thoracostomy
- second intercostal space in midclavicular line
- large gauge needle / 16G
- will hear hiss if tension
- need to place ICC
Pneumothorax / Hemothorax / Intercostal Catheter
- 5th intercostal space just anterior to midaxillary line
- need to avoid spleen / liver
- level with nipple
- use larger tube if for haemothorax
- gown and glove, prep, LA down to pleura
- scapel incision, artery forcep down through pleura
- blunt dissection
- insert 32 F gauge tube without stylet aiming posteriorly and superiorly
- connect to underwater suction drain at -20 cm H2O
- suture and tape in (no 1 suture purse string, standard dressing, sleek)
- ensure drain is swinging
Open chest wound
- taped on 3 side flutter dressing intially
- allows air out with expiration
- convert to occlusive dressing only after insertion of ICC
- ICC in 5th intercostal space
- otherwise risk tension pneumothorax
Cardiac Tamponade / Pericardiocentesis
- 20 ml syringe and 18G spinal needle
- aseptic technique
- insertion point between xiphisternum and left sternocostal margin
- can fill with some saline and inject 1ml periodically to prevent blockage of tip
- angle 45o to abdominal wall, 45o to sagittal plane
- aim for tip of left scapula
- insert up to 5 cm watching for ECG changes, aspirating as advance
- if patient truly has cardiac tamponage, insert drainage catheter using seldinger technique
- best done under echo guidance if possible
Hemothorax / Indications for thoracotomy
- > 1500 mls blood
- > 250 mls per hour for 4 hours
Flail chest
- no specific management required
- management of underlying lung injury
- may require mechanical ventilation / epidural
C. Circulation
Stages of Shock
| Stage I | Stage II | Stage III | Stage III | |
| Blood loss | < 750 | 750 - 2000 | 1500 - 2000 | > 2000 |
| % blood volume | 15% | 30% | 40% | > 40% |
| PR | < 100 | > 100 | > 120 | > 140 |
| BP | Normal | Decreased | < 90 | < 70 |
| Pulse Pressure | Normal | Decreased | ||
| RR | Normal | 30 - 40 | > 35 | |
| Urine output | > 30 | Slightly reduced | Negligible | |
| GCS | Anxious | Anxious | Confused | Lethargic |
Immediate Management
Stop external bleeding / pressure
IV cannulas x2 16G
Send off FBC / ELFT / glucose / Toxicology / Xmatch / pregnancy test
Resuscitate with isotonic crystalloid
- 2 litres then
- blood (O negative / type specific / cross matched)
Children 20 mls / kg bolus
- repeat x 3 then consider blood
- blood 10mls / kg type specific or O negative
- any hypotension in child indicates severe blood loss / > 45%
- can provide via intraosseous tibial infusion in < 6 hours
- anteromedial tibia below tibial tubercule / aim away from knee
- maintenance 4 / 2 / 1 rule per hour
Burns
- rule of 9's to calculate % BSA
- 2 - 4 mls RL per kg per % BSA first 24 hours
- half in first 8 hours, remainder in last 16 hours
Pelvic immobiliser / strap / sheet if any signs pelvic injury
ECG
- premature ventricular contractures
- lidocaine 1 mg / kg
Causes
Lung - tension pneumothorax / hemothorax
Heart - cardiac tamponade / aortic dissection
Abdomen - intra-abdominal bleeding
Pelvis - pelvic fractures
Long bone fracture
Spinal injury
External bleeding
Corticosteroid deficiency
Examine
- signs chest trauma / reduced breath sounds
- muffled heart sounds / distended neck veins
- abdomen exam - tenderness / rigidity
- pelvis - tender / mobile
- femoral deformity / long bone fracture
- external bleeding / scalp laceration
Investigations
- abdomen (Fast scan / DPL / CT scan)
- pelvis (Xray)
- CXR (hemothorax / widened mediastinum)
- echo / CT chest
DPL
Technique
- LA
- decompress bladder with IDC
- decompress stomach with NGT
- incision supraumbilical if pelvic fracture / infraumbilical otherwise
- dissect down to peritoneum
- insert peritoneal dialysis catheter and aspirate
- if aspirate negative, infuse 1L crystalloid
- lavage , then aspirate 250 mls
- send to lab for analysis
Results
1. Initial aspiration
- > 10 mls frank blood or obvious bowel contents
2. Post lavage
- labs analysis: > 100 000 RBCs or > 500 WBC / ml, or positive gram stain
Hypotensive / Bradycardia
- suspect spinal injury
- trial 2L fluid
- atropine: 0.5 - 1 mg IV as push / maximum 3 mg
- noradrenalin: 0.1 - 2 mcg / kg / min up to maximum 30 mcg/min
- dopamine: 10 mcg / kg / min
IDC
- as soon as patient stable enough
- enables monitoring of resuscitation
- adults 0.5 mls / kg / hour
- paeds 1 ml / kg / hr (2mls if < 1 year)
D. Disability
GCS / Pupils
GCS = MVE
Severe HI <9
Moderate HI 9-12
Minor 13-15
Best eye response (E)
1. No eye opening
2. Eye opening in response to pain
3. Eye opening to speech
4. Eyes opening spontaneously
Best verbal response (V)
1. No verbal response
2. Incomprehensible sounds
3. Inappropriate words
4. Confused
5. Oriented
Best motor response (M)
1. No motor response
2. Extension to pain
3. Abnormal / decorticate flexion to pain
4. Normal flexion / Withdrawal to pain
5. Localizes to pain
6. Obeys commands
Head Injury < 9
Intubate
CT Head
Neurosurgery consult
Oxygenate
Avoid hypotension
Maintain low ICP
Low ICP
Maintain BP
- avoid glucose containing fluids
- Ringer's lactate or N/S
Hyperventilation
- low CO2 can cuase cerebral ischaemia
- keep CO2 at 35 mmHg
- can lower CO2 to 30 mmHg in acute deterioration
20% Mannitol
- indicated for acute neurological deterioration in patient without hypotension
- 1g / kg IV as bolus over 5 minutes
Seizures
Diazepam 0.2 mg / kg at rate 5 mg / minute
- so maximum dose 20 mg in 100 kg man
Phenytoin
- loading dose 1g IV at 50mg / minute
- maintenance dose then 100 mg / 8 hours
- titrate based on serum levels
E. Exposure
Suitably undress
Avoid hypothermia / keep warm
Do not proceed to Secondary Survey until stable
Early monitoring
- PR / BP
- O2 sats
- arterial line
- NGT / IDC - if no CI
Trauma Series
- lateral C spine / CXR / AP pelvis
Blood at meatus / high riding prostate / suspected urethral disruption
- urethrogram / 15 mls contrast via IDC in urethral meatus with balloon minimally inflated
- if urethra intact on xray / advance into bladder
- inflate with 1500mls contrast / saline and leave balloon inflated
- looking for bladder injury
- extraperitoneal - IDC left in situ draining
- intraperitoneal - requires surgery
- if urethra not intact requires urology intervention / surgery
Secondary survey
Meticulous examination from head to toe encompassing all systems looking for occult injury
History
Get ancillary history
- ambulance officers / police / Family / Patient / Witnesses
Allergies
Medications
Past medical history
Last ate
Events related to accident
- MOI / Restraint / Ejection
Head to toe
Scalp - lacerations / open fractures
Eyes - pupils
Face - fractures
Mouth
C spine
- tender
- step / gap / boggy swelling
- ROM if conscious and co-operative / no distracting injuries
Neck
- subcutaneous emphysema
- lacerations
- tracheal deviation
- oesophageal injury
- vessel injury
Chest
- breath Sounds
- heart Sounds
- subcutaneous emphysema
- ribs / sternum / clavicle fracture
Abdomen
- distension
- tenderness
Pelvis
- spring test
- push / pull test
- tenderness / ecchymosis
- blood meatus / scrotal ecchymosis / open injuries (rectum / vagina) / high riding prostate
UL
- shoulder girdle and clavicle / SC jts
- long bones
- dislocations
- neurovascular
- compartments
LL
- long bones
- dislocations
- neurovascular
- compartments
Spine logroll
- step / gap / boggy swelling / tender / ecchymosis
- PR - tone / power / sensation / BCR / anal wink reflex
