Fusion
Mueller-Weiss disease

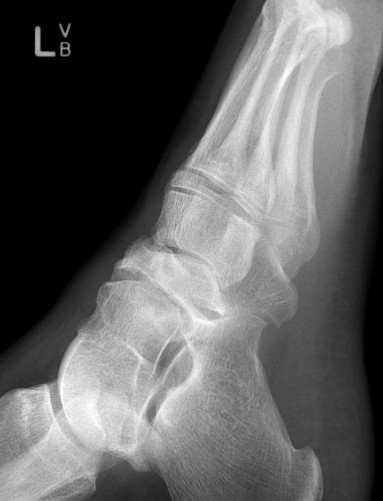
Definition
Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the navicular
Ankle Arthrodesis
Results
90% fusion rates
Lose 70% sagittal plane ROM
70% sagittal plane ROM
Disadvantages of Arthrodesis
Non union rates up to 12%
Decreased gait speed
Poor mobility over uneven surfaces
Subtalar and Triple Arthodesis
Biomechanics
Able to achieve relatively high level of function after STJ fusion
- previously believed that isolated STJ fusion should not be performed
- believed that triple arthrodesis was operation of choice for hindfoot
- STJ fusion has superior result with less stress on AJ
Average loss of DF 30% / PF 10%
Position of hindfoot determines flexibility of transverse tarsal (CCJ & TNJ) joints
- imperative that fusion be positioned in ~ 5o valgus
Rheumatoid Fingers
Conditions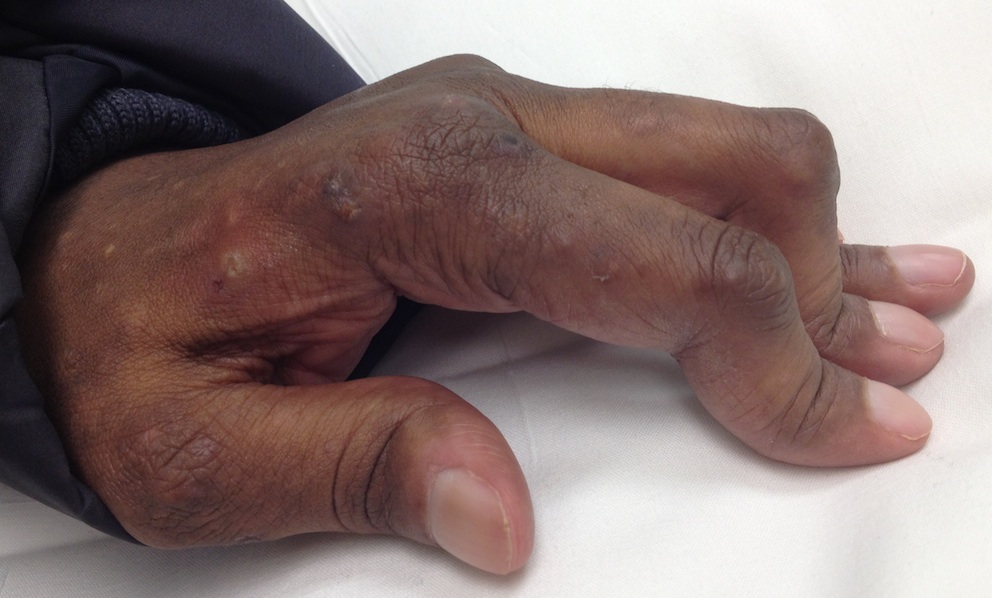
1. PIPJ Synovitis
- synovectomy via dorsomedial approach
2. Flexor tenosynovitis
- may cause trigger finger
- trial HCLA
- remove synovits but don't release A1 pulley
- will worsen ulna drift
3. DIPJ
- rarely affects
Rheumatoid Wrist
Epidemiology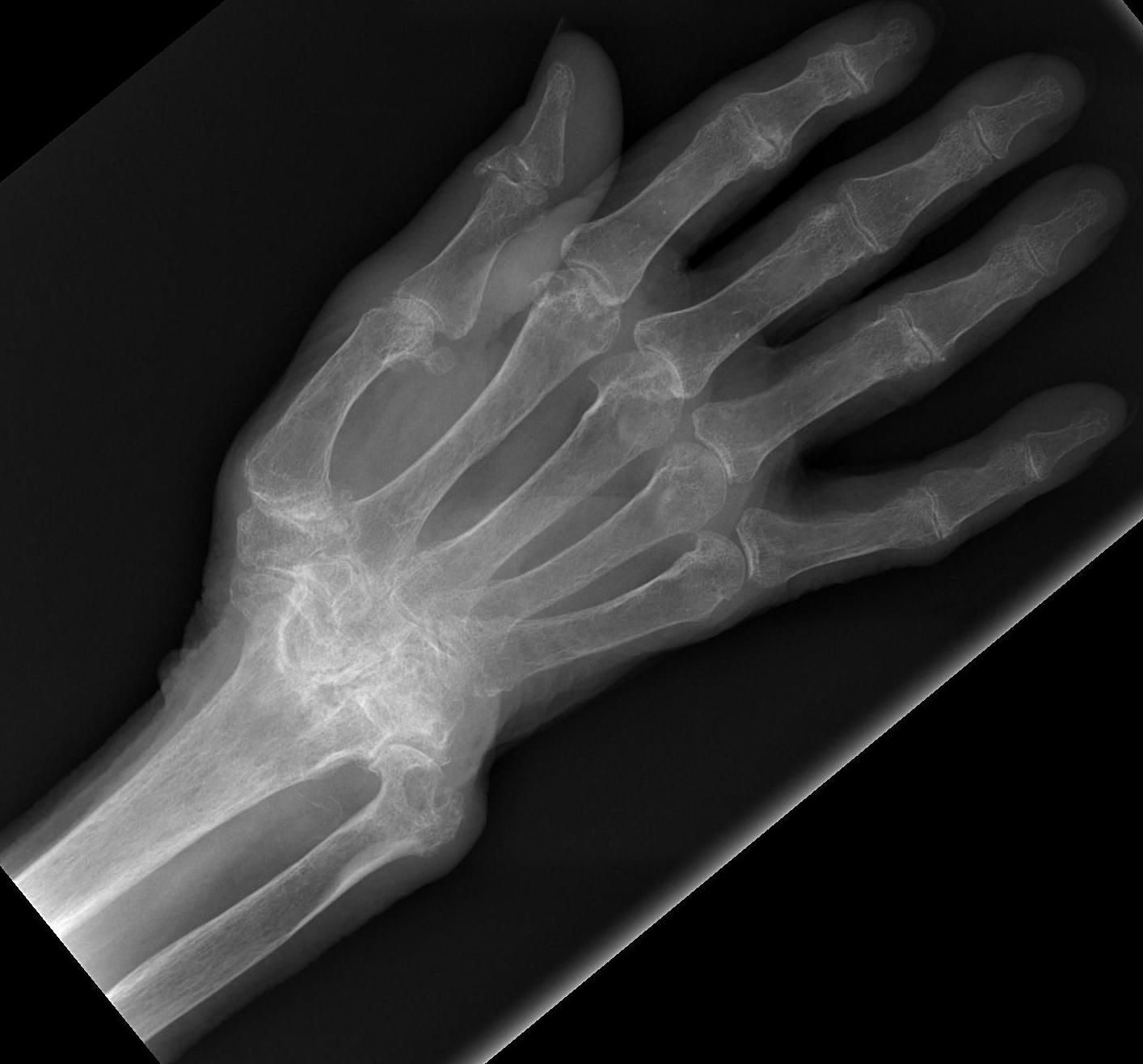
Extremely common
- 90% by 10 years have wrist problems
Principles
Landsmeer 1961
- treat wrist at same time as treat fingers or will recur
Frequently combine procedures
- synovectomy
- tendon transfer
- ulna procedure
Os Acromiale
Definition
Failure of fusion of adjacent ossification centers
Epidemiology
Incidence 3%
Bilateral in 60%
Anatomy
4 ossification centers present in acromion
- pre-acromion
- mesoacromion
- metaacromion
- basiacromion
Osteoarthritis
Epidemiology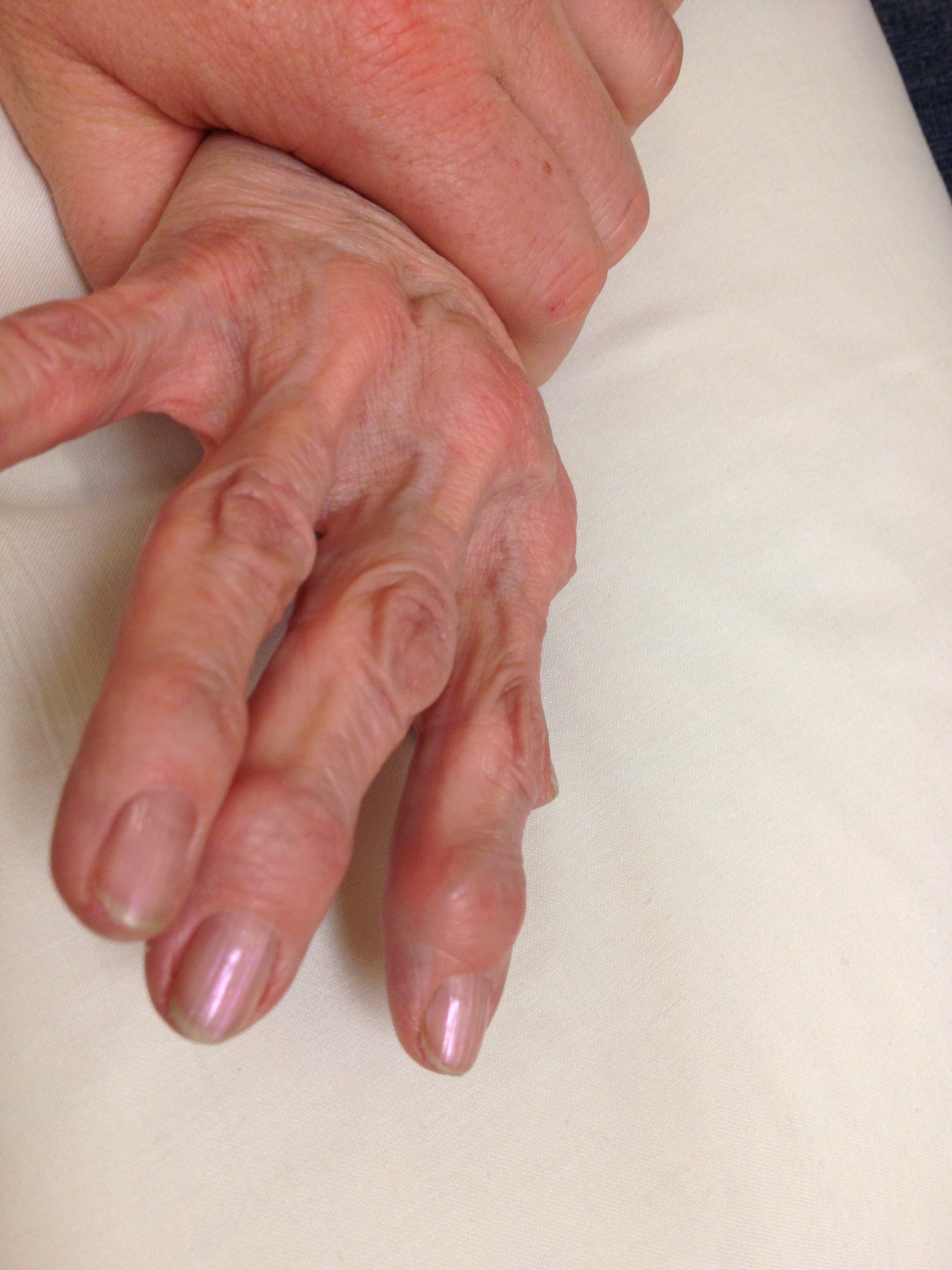
Male & Females > 60 years
- X-ray evidence of OA
Symptomatic
- 25% females
- 15% males
Affected joints
Base thumb
PIPJ / Bouchard's nodes
DIPJ / Heberden's nodes
Tarsal Coalition
Definition
Congenital fibrous, cartilaginous or bony connection of 2 or more tarsal bones
- due to failure of segmentation
Peroneal Spastic Flat Foot
- tarsal coalition
- tarsal pain
- reduced STJ motion
- rigid pes planus
- peroneal muscle spasm / tightness
Epidemiology
Present in 6% of population
- symptomatic in 1% of population
Bilateral in 50%
