DDx
Primary
Benign
Osteoid Osteoma
Osteoblastoma
Osteochondroma
ABC
Hemangioma
Giant Cell tumour
EG
Malignant
Chordoma
Ewings
Osteosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma
Lymphoma
Multiple myeloma
Secondary
Leukaemia
Prostate / Breast / Lung / Thyroid / Kidney
DDx by Site
Posterior elements
- OO, OB, ABC
- chordoma / osteosarcoma
Vertebral body
- giant cell
- hemangioma
Sacrum
- chordoma
- Ewing's
Benign Spinal Tumours
ABC
Patient in teens or twenties
Night pain
Posterior elements
Treatment
Embolisation
Surgical resection
- complete to prevent recurrence
Wong et al Paediatr Radiol 2022
- sclerotherapy in 14 patients with cervical spine ABC
- success in 12 / 14 patients
- one spasm of cerebellar artery, causing infarct
- 2 patients required surgery
Giant cell tumour
30 - 40 years
In sacrum
Present with pain
May have bladder and bowel dysfunction
Treatment
Wide excision
- may get incontinence
Adjunctive radiotherapy
Now using serial embolisation
Hemangiomas
Very common
- usually asymptomatic and incidental finding
- vertebral body or posterior element
- thoracic spine
Xray
- striations
MRI
- High signal on T2
Treatment
Indicated for collapse or neurology
Surgical excision
Embolisation
Radiotherapy
Osteoid Osteoma
Male between 20 - 40
Posterior elements lumbar spine
- < 2 cm
Can cause scoliosis
- in apex of convexity
Treatment
Surgical Removal / High frequency radioablation
Often scoliosis will then resolve if not too long standing
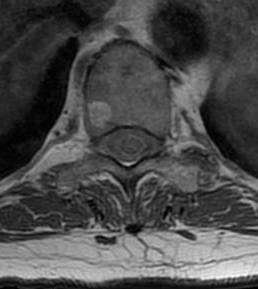
Osteoblastoma
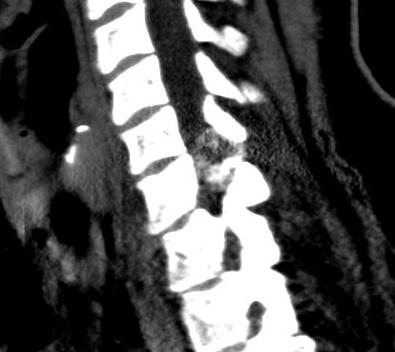
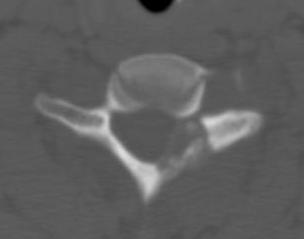
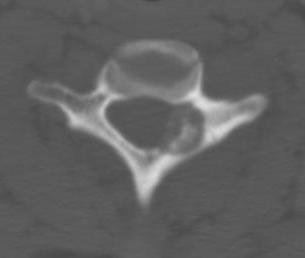
Similar histology to OO
- > 2 cm
Much more aggressive / less common
Found in the posterior elements
- male teens, twenties
Treatment
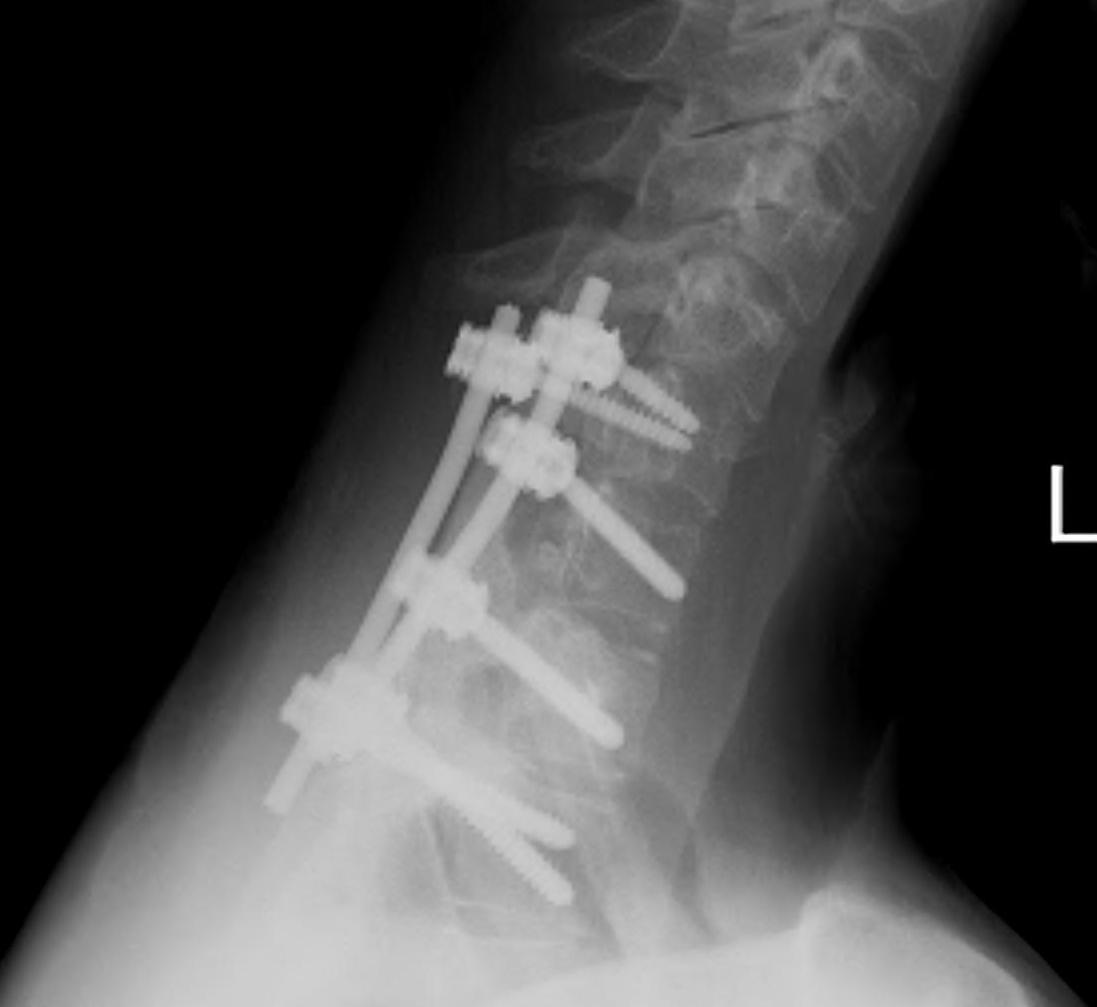
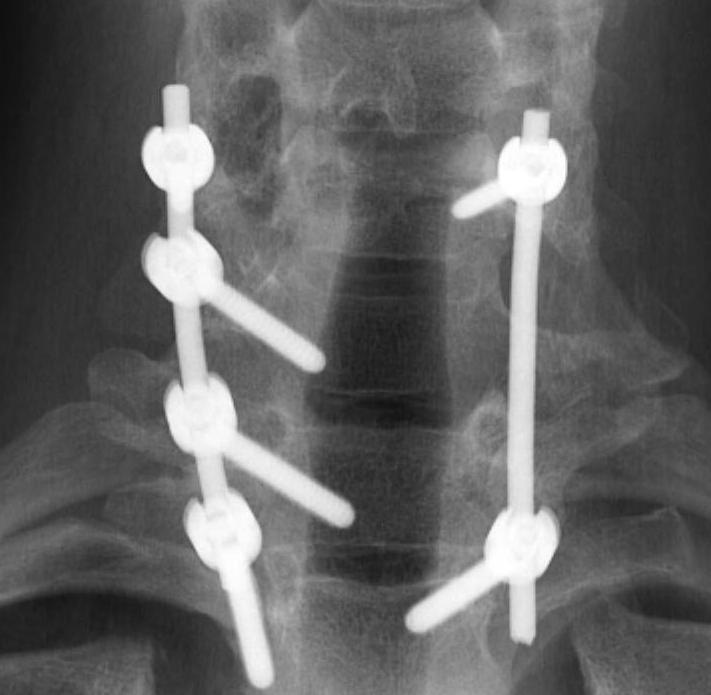
Wide excision +/- posterior fusion
Can recur
- life long follow up
Eosinophilic Granuloma
Vertebroplanar in young child < 10
Treatment
Self limiting
- will reconstitute up to 50% vertebral height
Primary Malignant Tumours
Chordoma
Rare slow growing malignant tumours
- arise from primitive nervous system
- slow to metastasise
50% sacrococcygea
Elderly patients
Treatment
Surgical Resection
- very difficult
Adjunctive Radiotherapy
Life expectancy 10 - 15 years after diagnosis
Osteosarcoma
Uncommon
Vertebral body
Treatment
Radical excision
Adjunctive radiotherapy and chemotherapy
Chondrosarcoma
Middle age or older
Males
Patient with Maffucci / Ollier's
Treatment
Wide surgical resection
Overall prognosis is poor as this is difficult
Lymphoma
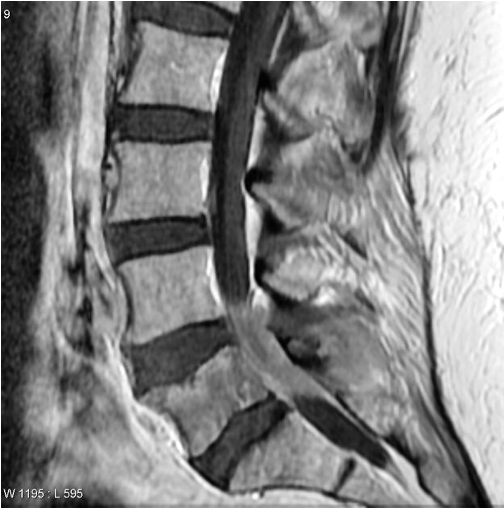
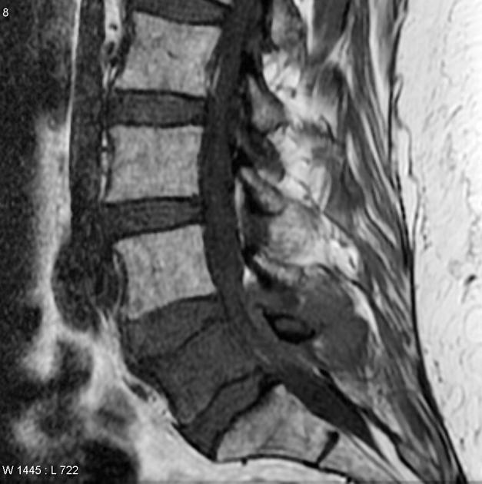
Can be solitary lesion
Anterior element
Treatment
Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
Surgery if unstable / deformity
Ewing's
50% in sacrum
Young male in teens
Treatment
Surgical resection
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy
20% 5 year survival
Multiple Myeloma / Plasmocytoma
50 - 80 years
Treatment
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy
Surgery for instability
Spinal Cord Tumours
DDx by Location
Extramedullary
- neuroblastoma
- ganglioneuroma
- Ewings sarcoma
- leukaemia
- lymphoma
- synovial cysts
Extramedullary Intradural
- dermoid
- epidermoid
- meningioma
- neurofibroma
Intradural
- astrocytoma
- ependymoma
- lipoma
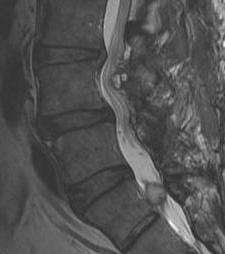
Meningioma
Slow Growing
F:M 9:1
Intra-dural / extramedullary
Management
- intradural resection
- RTX for residual tumour which is growing
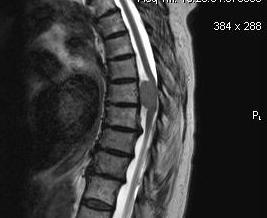
Ependymoma
Primary glial tumour of spinal cord
- intramedullary
- tend to be benign in spinal cord (c.f. intracranial
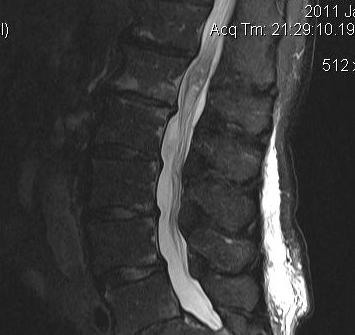
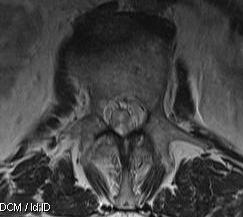
Management
- debulking
- radiotherapy