Definition
Deficiency of bony elements on lateral side of lower limb
- characterised by hypoplastic or aplastic fibula
Types
Terminal
- abnormal foot
Intercalary
- normal foot
Epidemiology
Most common congenital deformity of long bones
- M:F 2:1
May be associated with PFFD
Sporadic
- tibial hemimelia can be inherited
Presentation
LLD
Femur
- PFFD with type C / severe
- always slightly short femur
Knee
- cruciate deficiency
- hypoplastic LFC / valgus knee
Tibia
- anteromedial bowing
Ankle
- equino-valgus / ball and socket
- tarsal coalition
Foot
- small limb / foot
- absent lateral ray(s)
- lateral tarsal bones fused or absent
UL deficiency
Classification Coventry
Type 1: Short or partial proximal absence unilaterally
1A: Stable ankle joint ± ball & socket joint
1B: Unstable anklejoint / equinovalgus
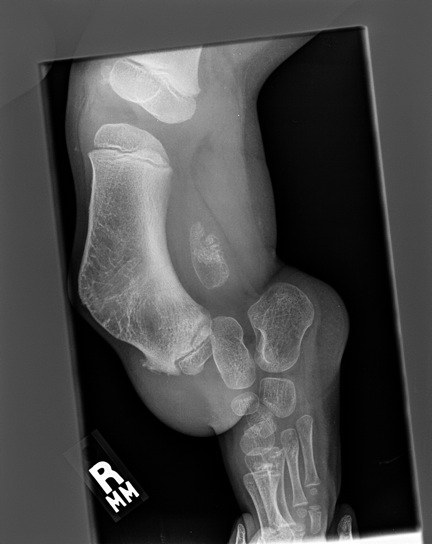
Type 2: Complete absence unilaterally
- tibia short & bowed anteromedially, dimple at apex
- associated with lateral ray deformity & coalitions
Type 3: Bilateral
- severe
- associated with PFFD & upper limb deficiency
DDx
Fibular hemimelia / dysplasia is a spectrum
- child may have only gracile fibular and short leg in tibia and femur
- attributed to fibula hemimelia as no ACL, short femur etc
- can be pseudoarthrosis of tibia
- realise when tibia fractures and then doesn't heal
Management Issues
1. Foot / ankle deformity
Concept
If less than 2 rays or unstable ankle
- cannot salvage
- symes / BKA
Indication for Syme's Amputation
- severe deficient foot that will not serve any useful purpose
- grossly unstable ankle
- associated tibial deficiency such that LLD & unstable AKJ preclude leg lengthening
- associated PFFD
2. LLD
Usually > 5 inches
- can predict based on difference at presentation
- can treat if have normal foot
Usual Options
- < 3cm shoe lift
- 3-5 epiphysiodesis
- 5-10 limb lengthening
- 10-16 limb lengthening + epiphysiodesis
- > 16 amputate
Technique
5cm at a time
Usually start when child 7-8, can understand reason for operations
3. Tibial bowing
Least important
- usually corrects
