Definition
Deformity characterised by
- dorsiflexion of calcaneus
- plantarflexion of forefoot / plantaris / forefoot equinus
Both sides of foot have elevated arch
Aetiology
Weakness of triceps surae
- polio - most common worldwide
- spina bifida
CP
Spinocerebellar degeneration / Friedreich's Ataxia
CMT
Spinal dysraphism
Compartment Syndrome / Deep Posterior
Pathology
Imbalance of T achilles and dorsiflexors
- dorsiflexion of calcaneus
- moves insertions of T achilles anterior
- further weakens the lever arm
Forefoot becomes flexed because of
- gravity
- action of muscles during gait
Symptoms
Difficulty walking
Obvious deformity
Shoe fitting & wear problems
Painful callosities
Signs
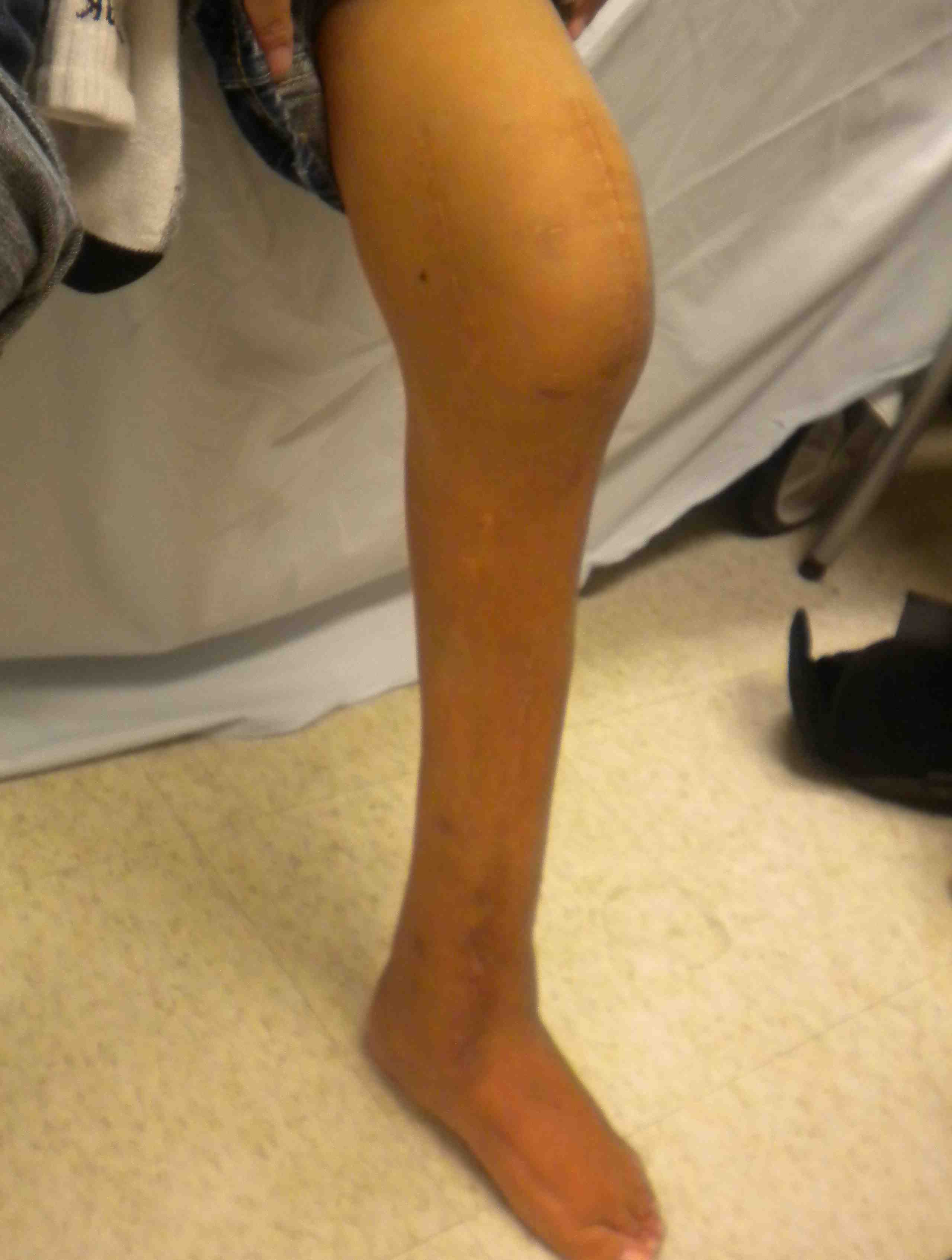
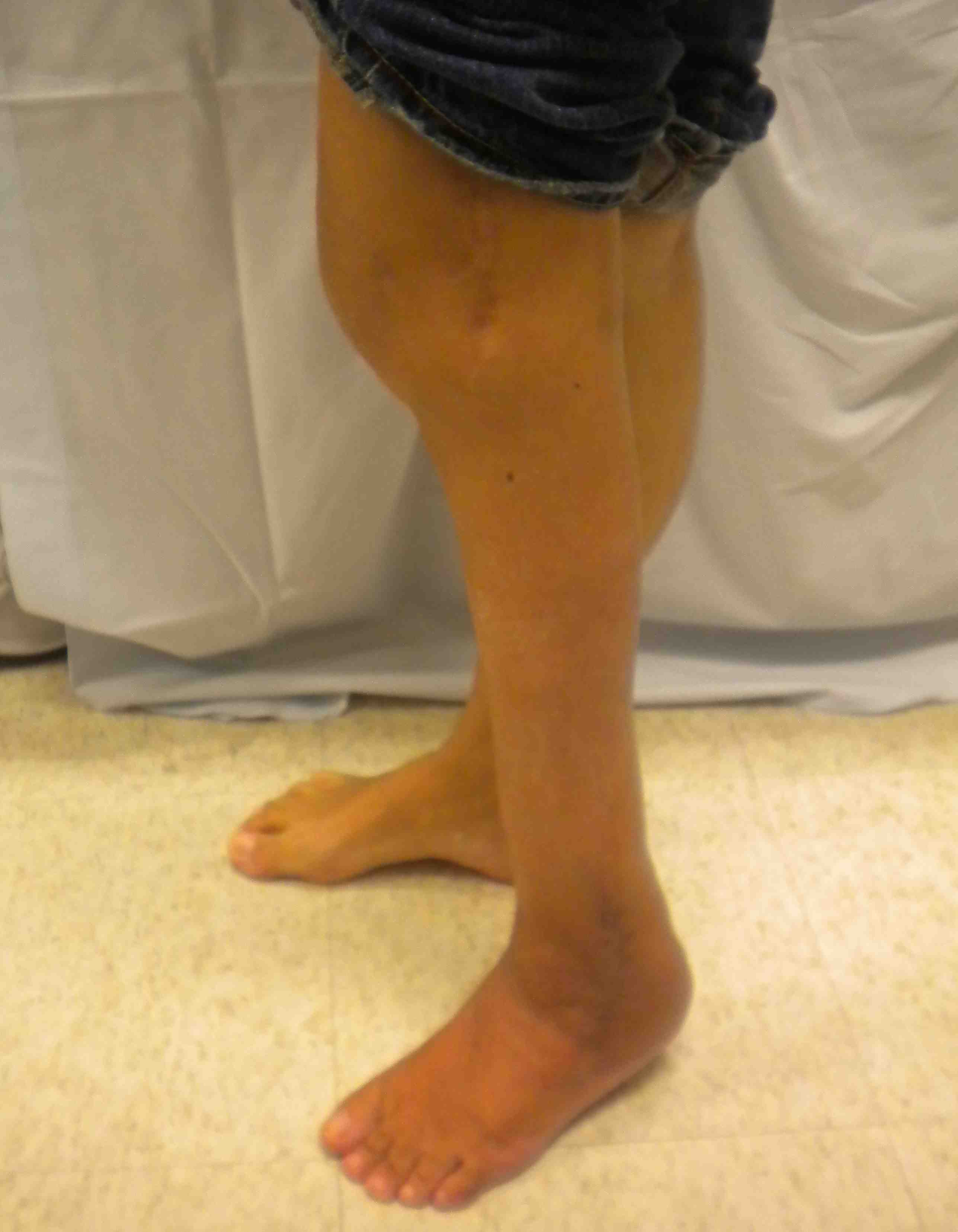
Elevated longitudinal arch
Prominent heel with abundant callus on plantar aspect
- called pistol grip deformity
- usually claw toes
Heel usually in neutral
X-ray
Lateral XR Foot
1. Calcaneal pitch > 30o
- dorsiflexion of calcaneus
- < 20o normal
2. Meary's angle > 10o
- talus - first metatarsal
MRI Spine
Exclude Spinal dysraphism
Management
Non-operative
Modification of shoe wear / orthoses
Operative
Principles
1. Correct deformity by soft tissue releases & osteotomy
2. Tendon transfer to calcaneus
Age 0-5
Indication
- spina bifida
- other conditions cause little disability
- don't operate
Operations
1. T Achilles to fibula
- prevents varus & stimulates fibula growth
2. T Anterior to T Achilles
Age 5-12
Grice arthrodesis STJ + T Achilles transfer to fibula
Age > 12
Triple arthrodesis
Definition
Pure Cavus deformity characterised by
- dorsiflexion of Calcaneus
- plantarflexion of Forefoot
Aetiology
Weakness of Tendoachilles
Usually neuromuscular
- Polio (most common worldwide)
- Spina bifida
- Cerebral palsy
- Spinocerebellar Degen (Friedreich's Ataxia)
- CMT
- Spinal dysraphism
Compartment Syndrome Deep Posterior
Pathology
Imbalance of tendoachilles and dorsiflexors causes dorsiflexion of calcaneus
Forefoot becomes flexed because of
- gravity
- action of muscles during gait
- result is elevated longitudinal arch
History
Difficulty walking
Shoe fitting & wear problems
Painful callosities
Examination
Elevated longitudinal arch
Heel usually in neutral
Usually claw toes
Xray
Lateral xray
- Calcaneal pitch > 30o
- Meary's angle > 30o
MRI
Exclude spinal dysraphism
Management
Nonoperative
Modification of shoe wear / orthoses
Operative
Age 0 - 5
Best avoided
Tibialis anterior to Tendoachilles transfer
Age 5-12
Grice arthrodesis
- extra-articular subtalar arthrodesis
Tendon transfer
- Tibialis anterior
- Tibialis posterior
- peroneals
Age >12
As Above
Triple arthrodesis
