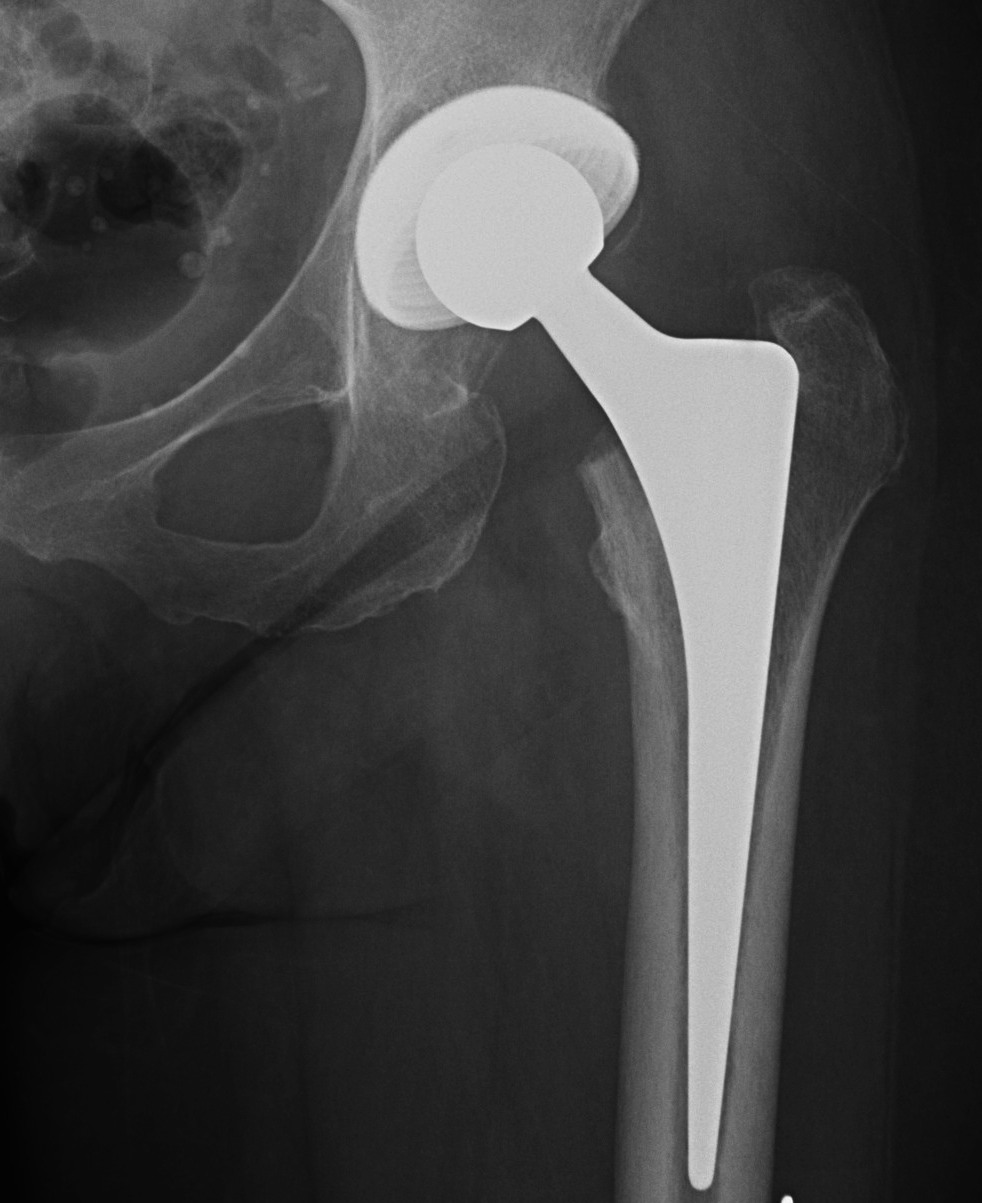
Indications
Disabling hip pain
Severe functional impairment
Failure non operative management
Etiology
Primary OA: 50%
Secondary OA: 50%
Secondary OA
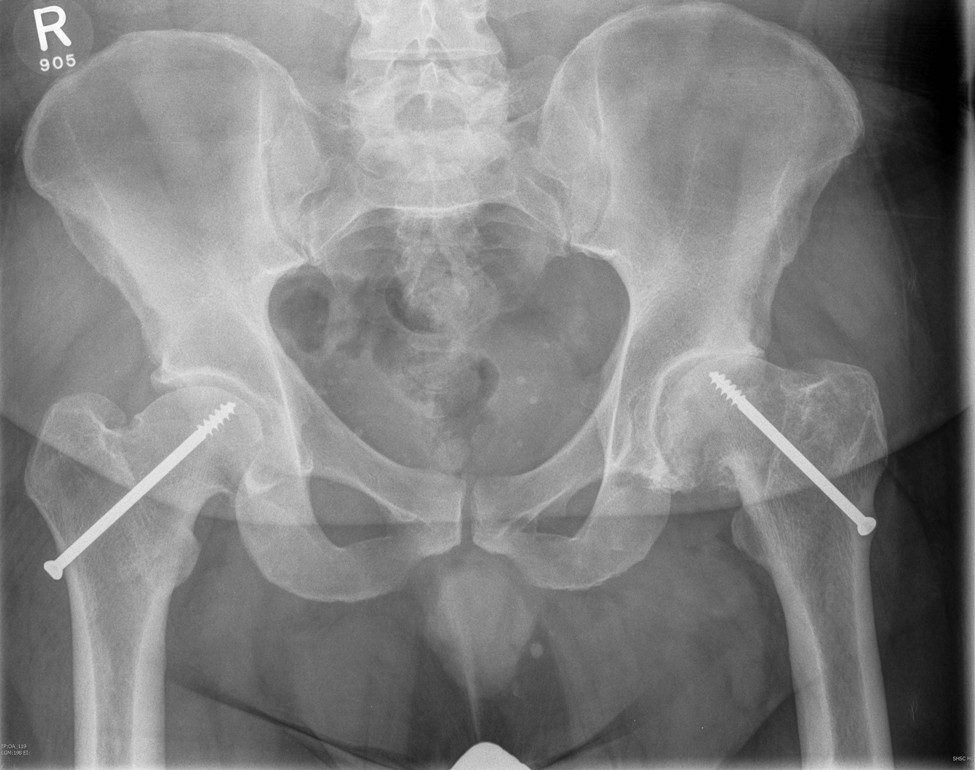
SUFE Perthes
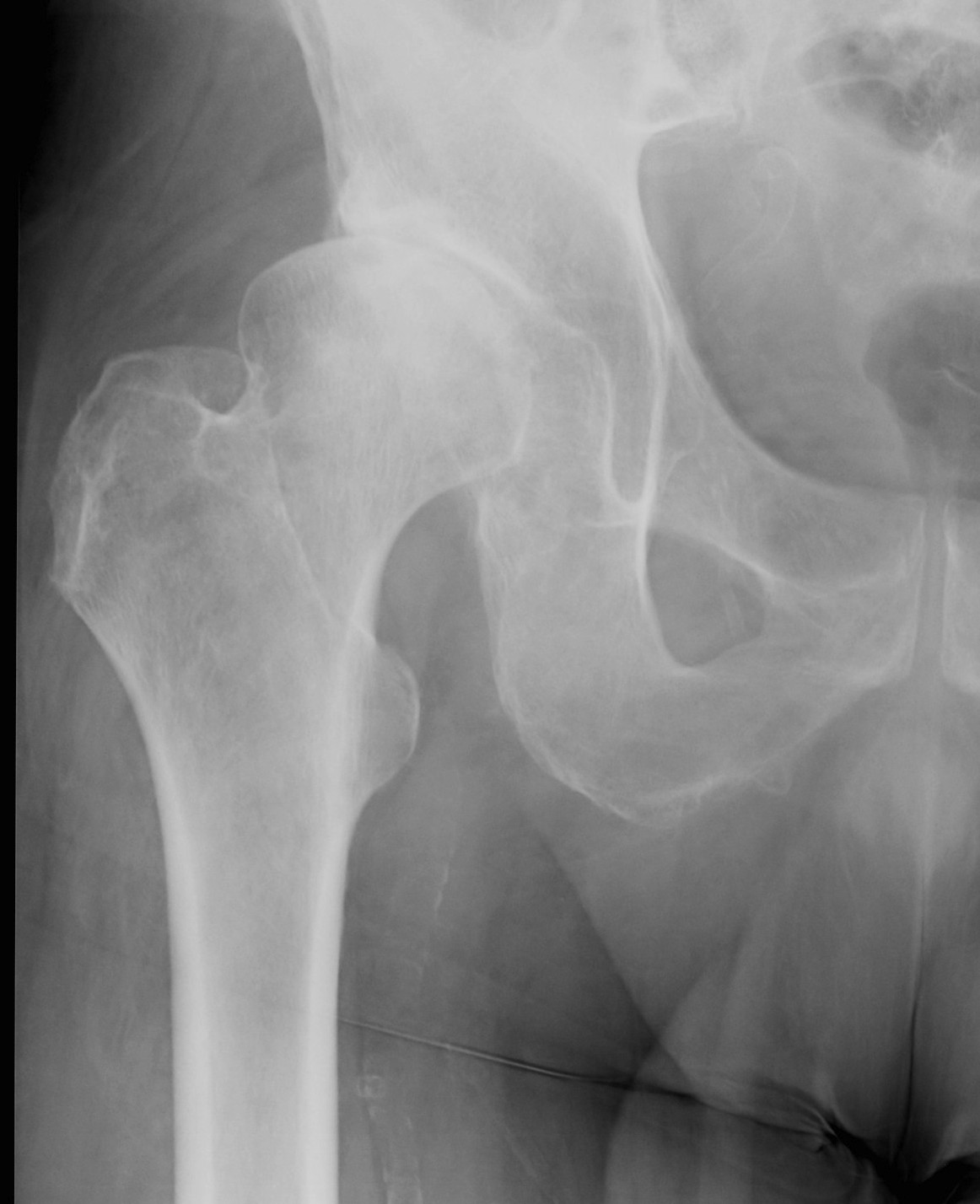
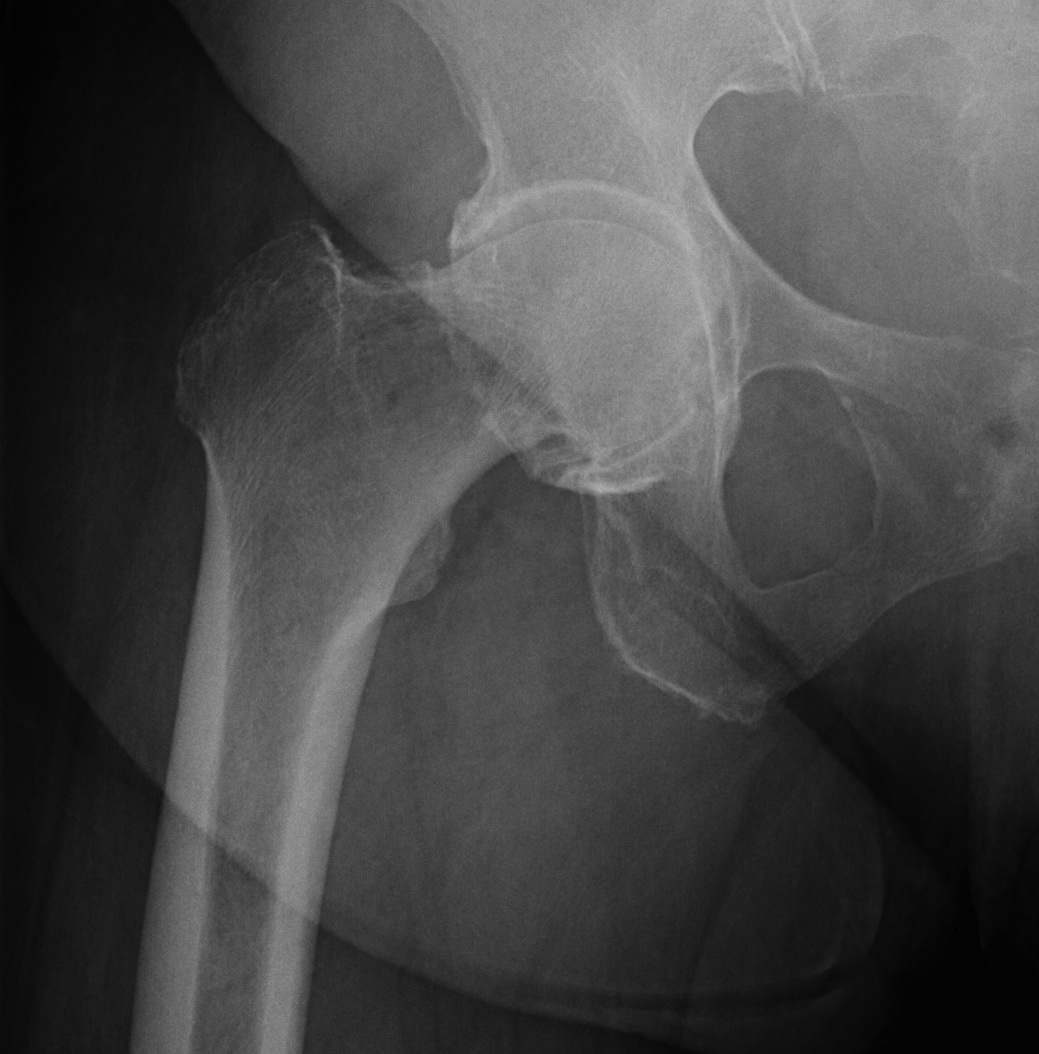
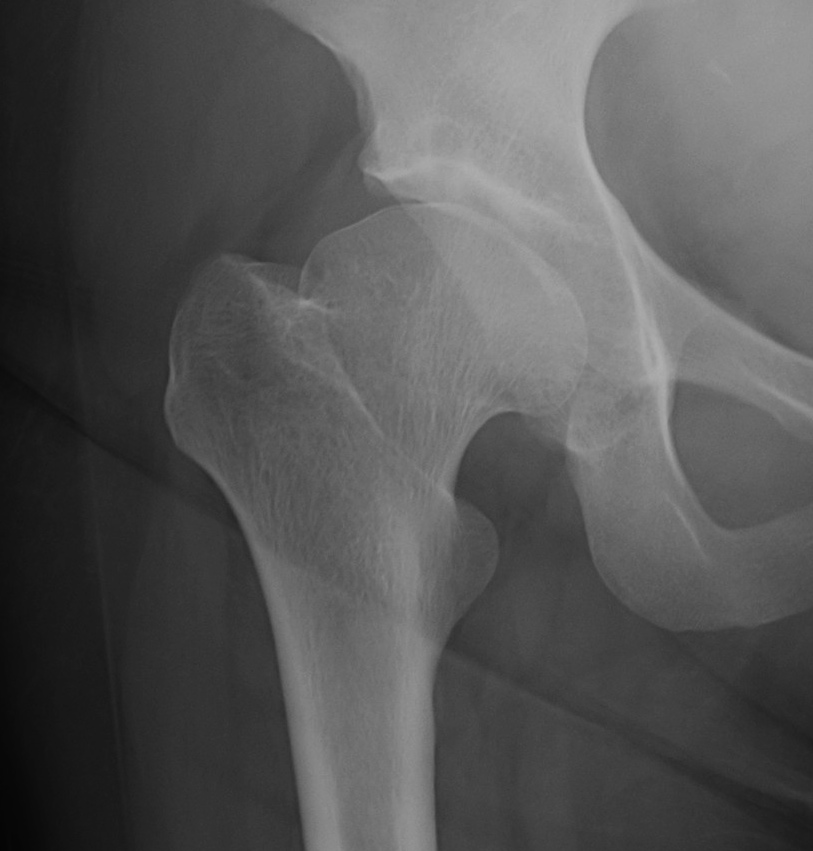
DDH Protrusio
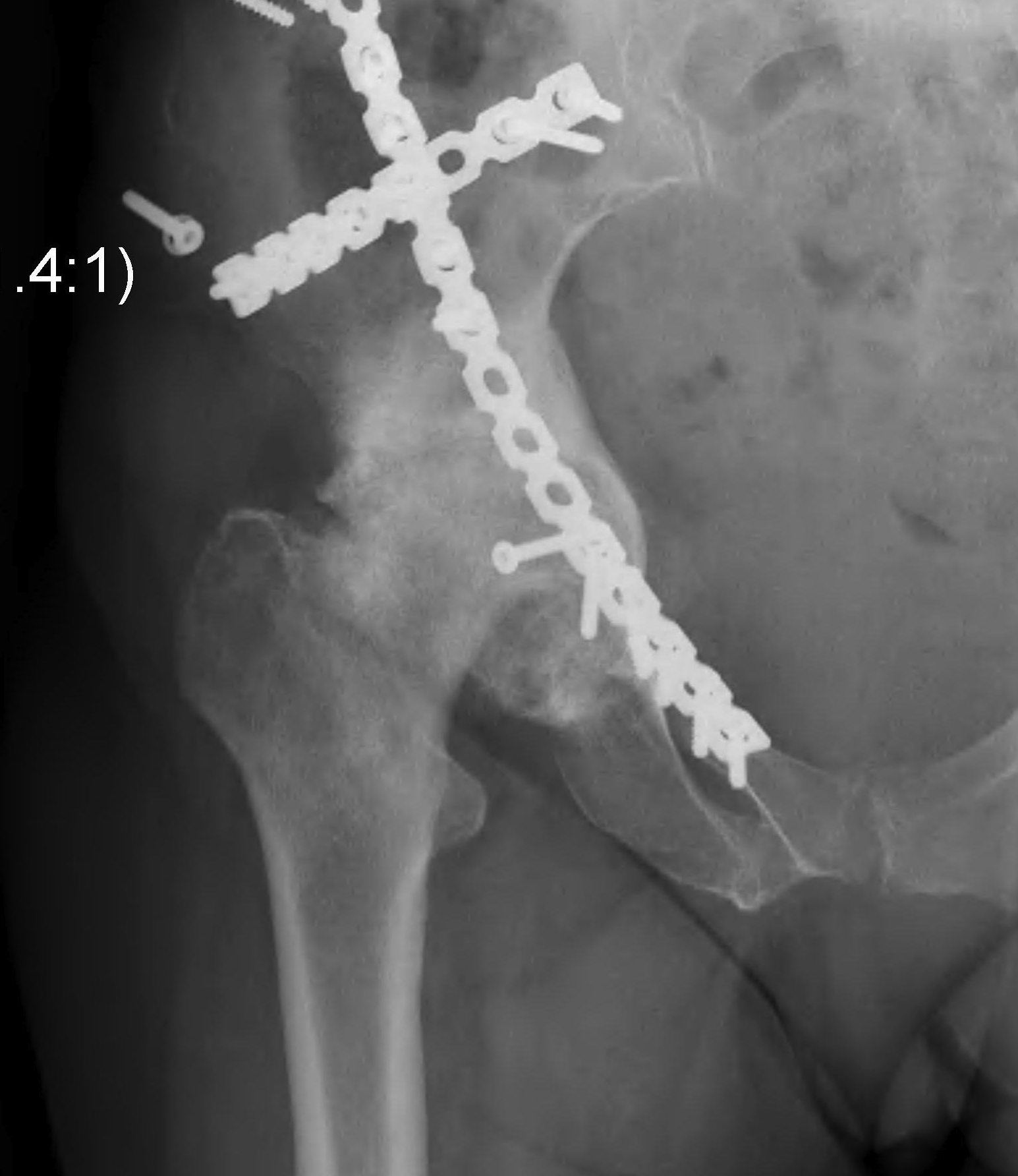
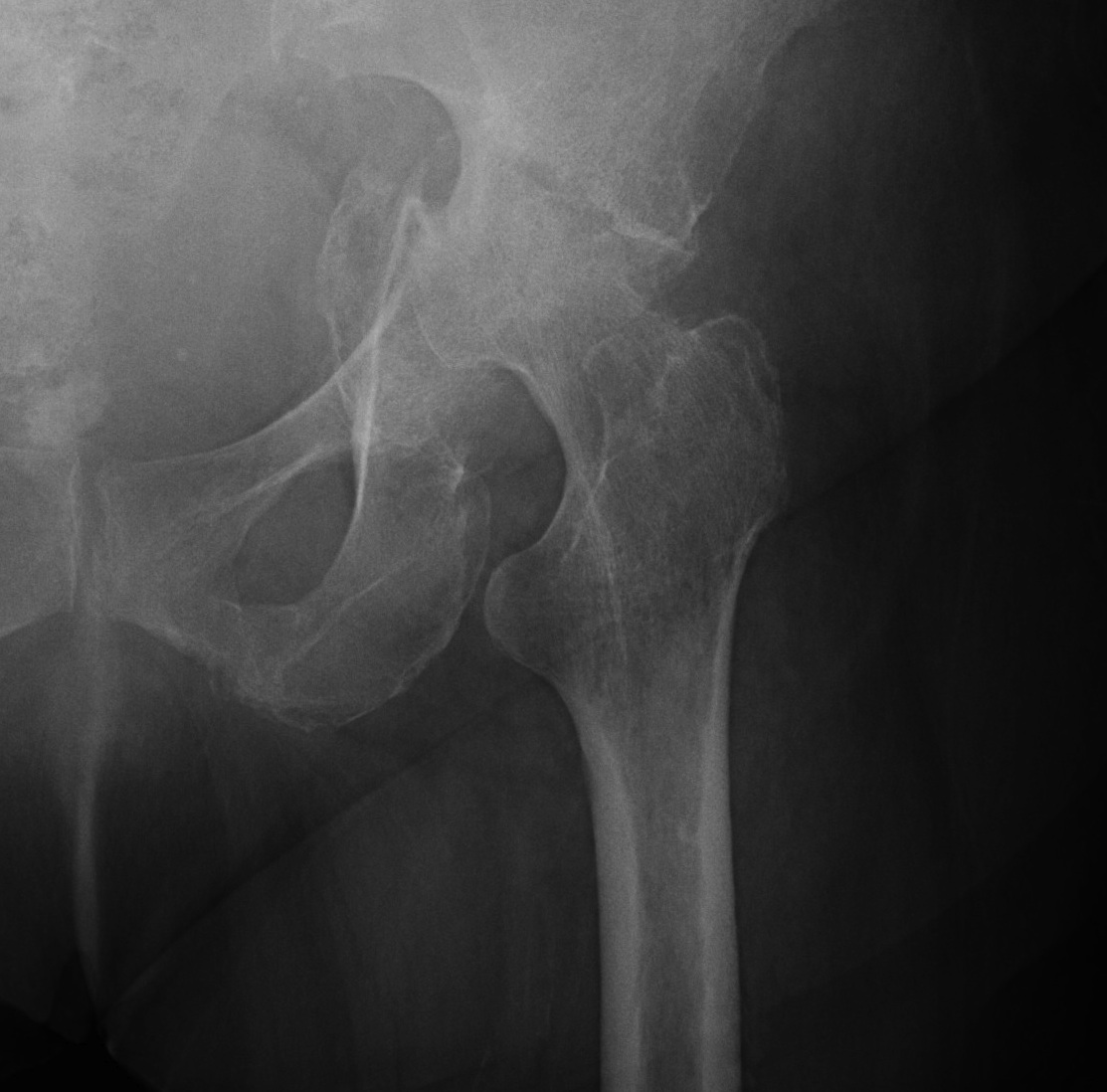
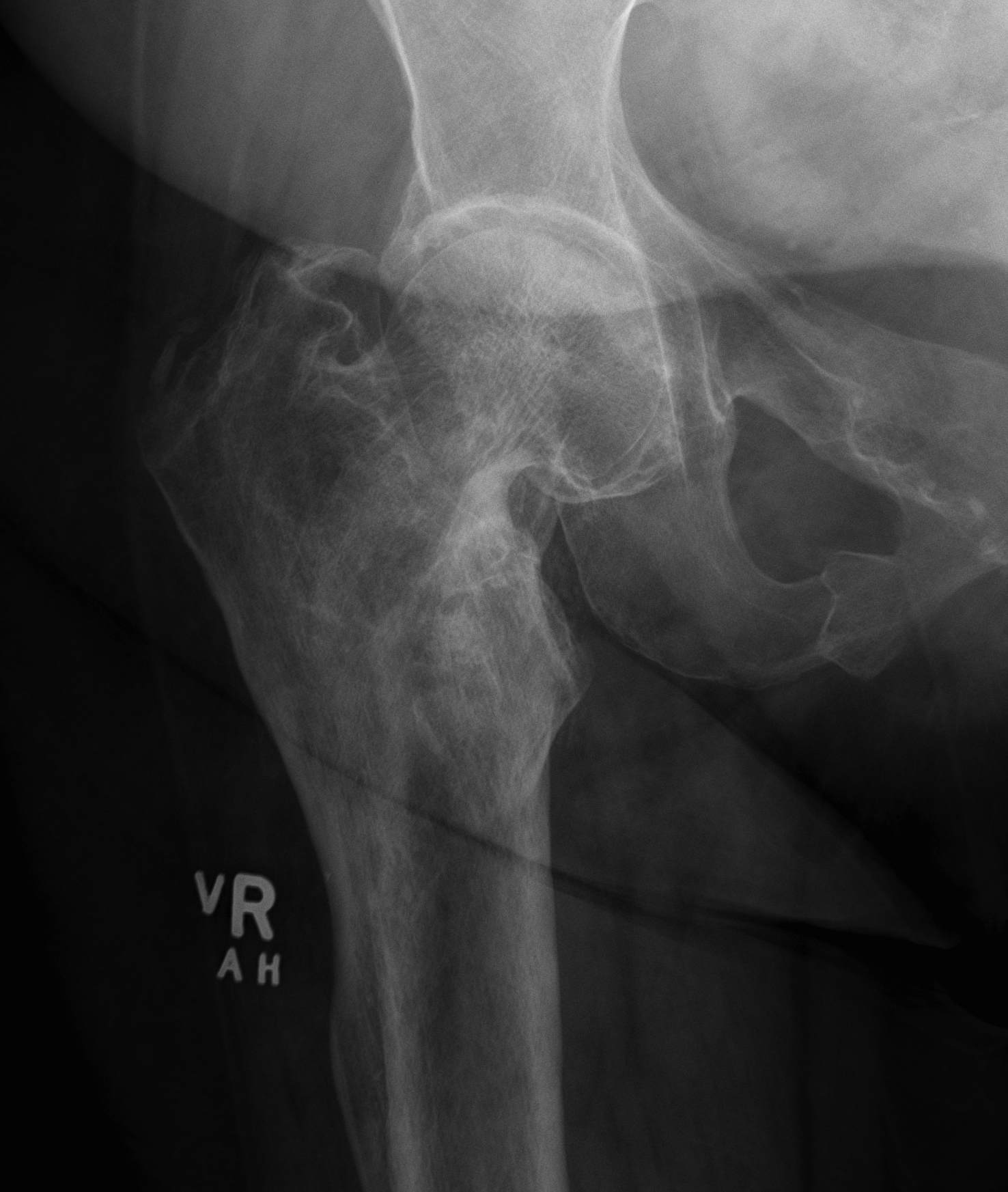
Trauma
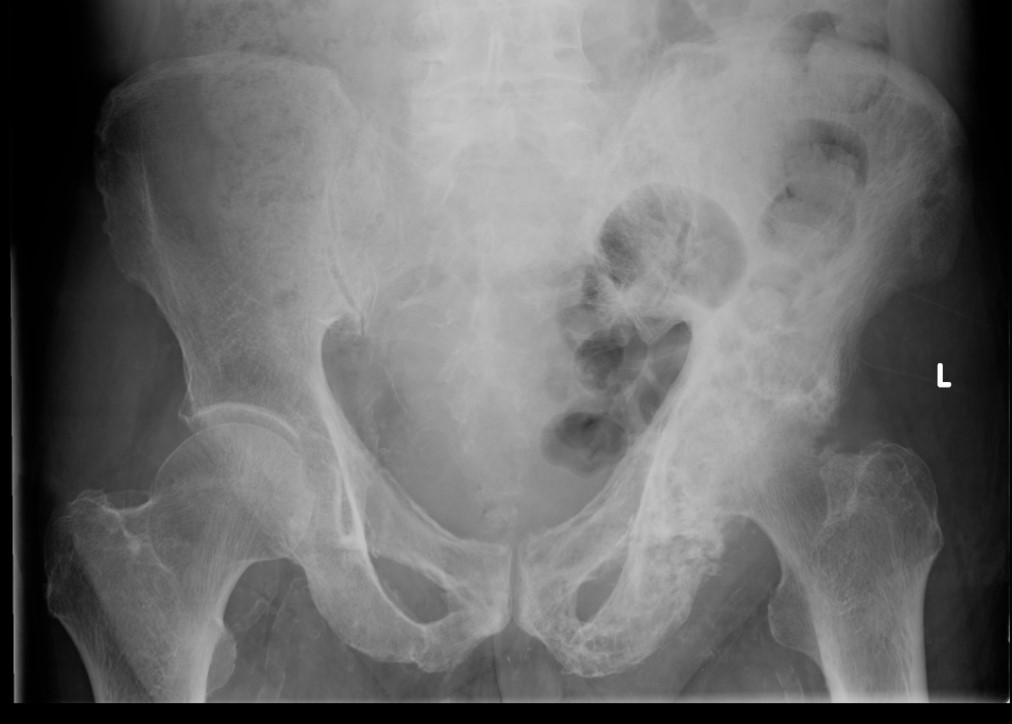
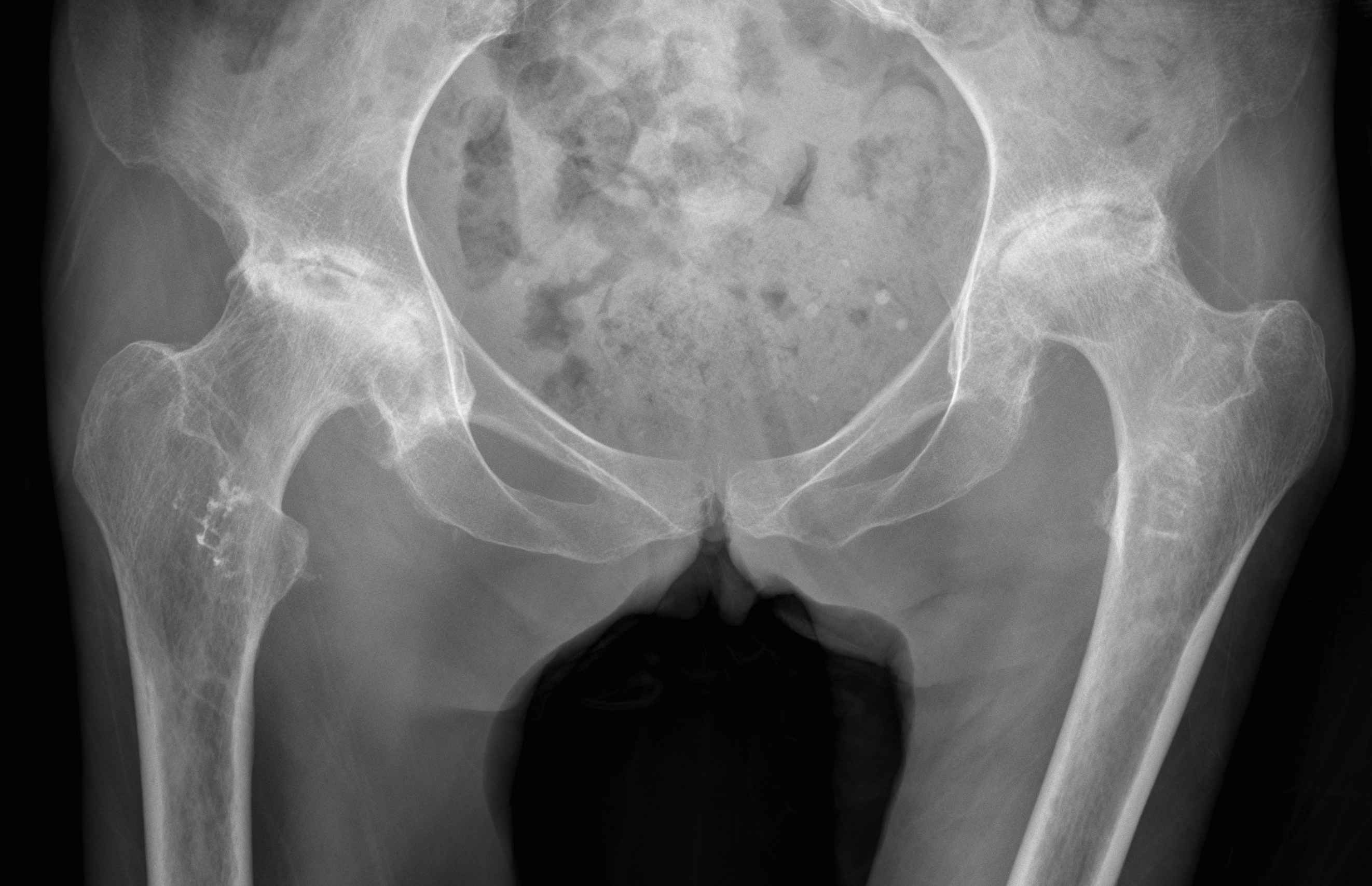
Paget's AVN
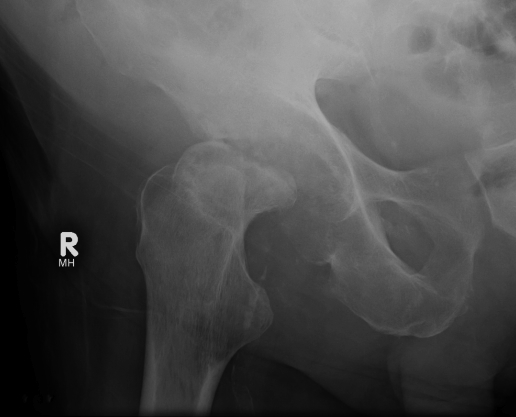
Sepsis
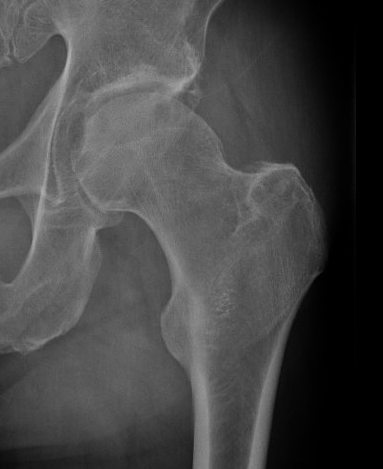
FAI
Contraindications
Absolute
Active infection
Charcot
Flail / Neuromuscular impairment
Inadequate soft tissue cover
Relative
Young patient
Heavy demand
Obese
Poor compliance
Poor mental state
Complications
Informed consent
Infection
Dislocation
Intra-operative fracture
Bleeding / transfusion
Nerve injury
Vascular injury
Leg length discrepancy
DVT / PE
Heterotopic ossification
Loosening / revision
Issues
Simultaneous versus staged bilateral THA
Outpatient surgery
Infection prevention
TXA
Drains
Closure
DVT prophylaxis
Hip precautions
One- versus two-stage bilateral THA
Ramezani et al J Orthop Surg Res 2022
- meta-analysis
- 30,000 one stage bilateral THA
- 75,000 two stage bilateral THA
- one stage had lower DVT, complications, cost, hospital stay
- one stage had higher PE, and periprosthetic fracture
Shao et al J Arthroplasty 2017
- meta-analysis
- one stage bilateral lower major complications, DVT, hospital stay
- no difference in PE or cardiovascular complications
Partridge et al Arthroplasty 2020
- National database of 14,500 patients
- one stage bilateral THA increased PE, MI, renal failure, chest infection, and in-hospital death
- shorter hospital stay for one stage
Outpatient surgery
- RCT of 220 patients
- < 75, no walker, no opioids, BMI < 40
- direct anterior under spinal
- 85/112 (76%) outpatient group discharged same day, 26/27 after 1 day
- 81/108 (75%) inpatient group discharged after overnight stay, 18/108 went home same day
- increased VAS pain scores first day with outpatient group
- no difference in complications, readmissions, emergency visits
Infection prevention
Antibiotics
- prospective study of 2000 patients
- cephalosporin prior to skin incision lowers infection rate
Surgical helmet systems
Rahardja et al J Arthroplasty 2022
- 19,000 TKA
- surgical helmet use reduced risk of infection
Antibiotic impregnated bone cement
- systematic review of 10 studies and 14,000 patients
- antibiotic-impregnated cement decreased deep infection rates
Dilute Povidone-Iodine irrigation
Shohat et al J Arthroplasty 2022
- database of 31,000 cases of total joint arthroplasty
- irrigation with dilute povidone-iodine reduced infection rate compared with saline
Ebrahimzadeh et al BMC Musculoskeletal Disorder 2023
- systematic review of 13 studies and 64,000 total joint arthroplasty
- iodine irrigation reduces infection compared with saline
Vancomycin powder
Peng et al Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2021
- systematic review of 9 studies and 4500 total joint arthroplasty
- vancomycin powder reduced rate of infection
Tranexamic acid (TXA)
TXA
- meta-analysis of 25 RCTs in THA
- TXA reduced blood loss, transfusion, and hospital stay
- no increase in DVT
IV versus topical TXA
- meta-analysis of 7 RCTs
- IV versus topical TXA
- no difference in blood loss, transfusion, and hospital stay
IV TXA versus IV + topical TXA
- meta-analysis of IV TXA versus IV TXA + topical TXA in THA
- IV + topical TXA superior in reducing blood loss and transfusion
Closed suction drains
Chen et al Eur J Orthop Surg Rehab 2014
- meta-analysis of 16 RCTs and 1600 patients undergoing THA
- drain versus no drains
- no difference in hematoma, infections
- increased transfusion with drains
Sutures versus staples
Liu et al J Orthop Surg Res 2021
- systematic review of 5 RCTs
- staples versus sutures
- increased superficial infection and prolonged discharge with staples
- increased time with sutures
DVT prophylaxis
Aspirin versus enoxeparin
- RCT of 100 mg of aspirin or 40 mg enoxeparin after THA / TKA
- 9000 patients
- 35 days in THA, 2 weeks TKA
- symptomatic VTE in aspirin group 3.5%
- symptomatic VTE in enoxeparin group 1.8% (p=0.007)
- subanalysis of CRISTAL study
- no increased wound drainage with enoxeparin (9%) versus aspirin (8%) with staple closure
- ? increased wound drainage with enoxeparin and subcuticular closure
- no increased reoperation rate
Rivaroxaban
Anderson et al N Eng J Med 2018
- RCT of 3500 patients undergoing THA / TKA
- 5 days of xarelto
- either xarelto or aspirin 81mg for 30 days THA / 9 days TKA
- VTE in 0.6% aspirin and 0.7% xarelto
Hip precautions
Korfitsen et al Acta Orthop 2023
- systematic review of 8,800 patients
- no evidence that hip precautions (flexion / adduction / internal rotation) decrease dislocation rates
