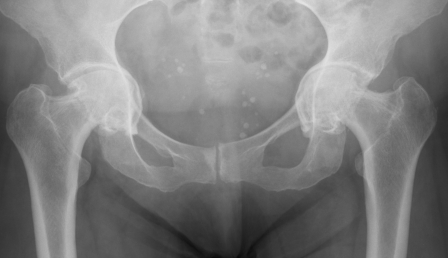
Definition
Abnormal protrusion of the femoral head into the acetabulum
- centre edge angle > 40o
- protrusion of the acetabulum beyond ilioischial line / Kohlers line
Etiology
Primary
Otto's Disease
- middle aged females
- ? related to osteomalacia / coxa vara
Secondary
PROFSHAMN
- Paget's
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteomalacia / Osteogenesis imperfect
- Fracture / central dislocation
- Septic arthritis especially TB
- Hemiarthroplasty
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Marfan's syndrome, malignancy
- Neurofibromatosis
- systematic review
- 783 cases
- most common cause inflammatory arthritis
- RA / psoriatic / SLE / ankylosing spondylitis
Sotelo-Garza / Charnley classification
Medial wall of acetabulum as ilioischial line
Grade I: Mild protrusion 1-5mm
Grade II: Moderate protrusion 6-15 mm
Grade III: Severe protrusion >15 mm
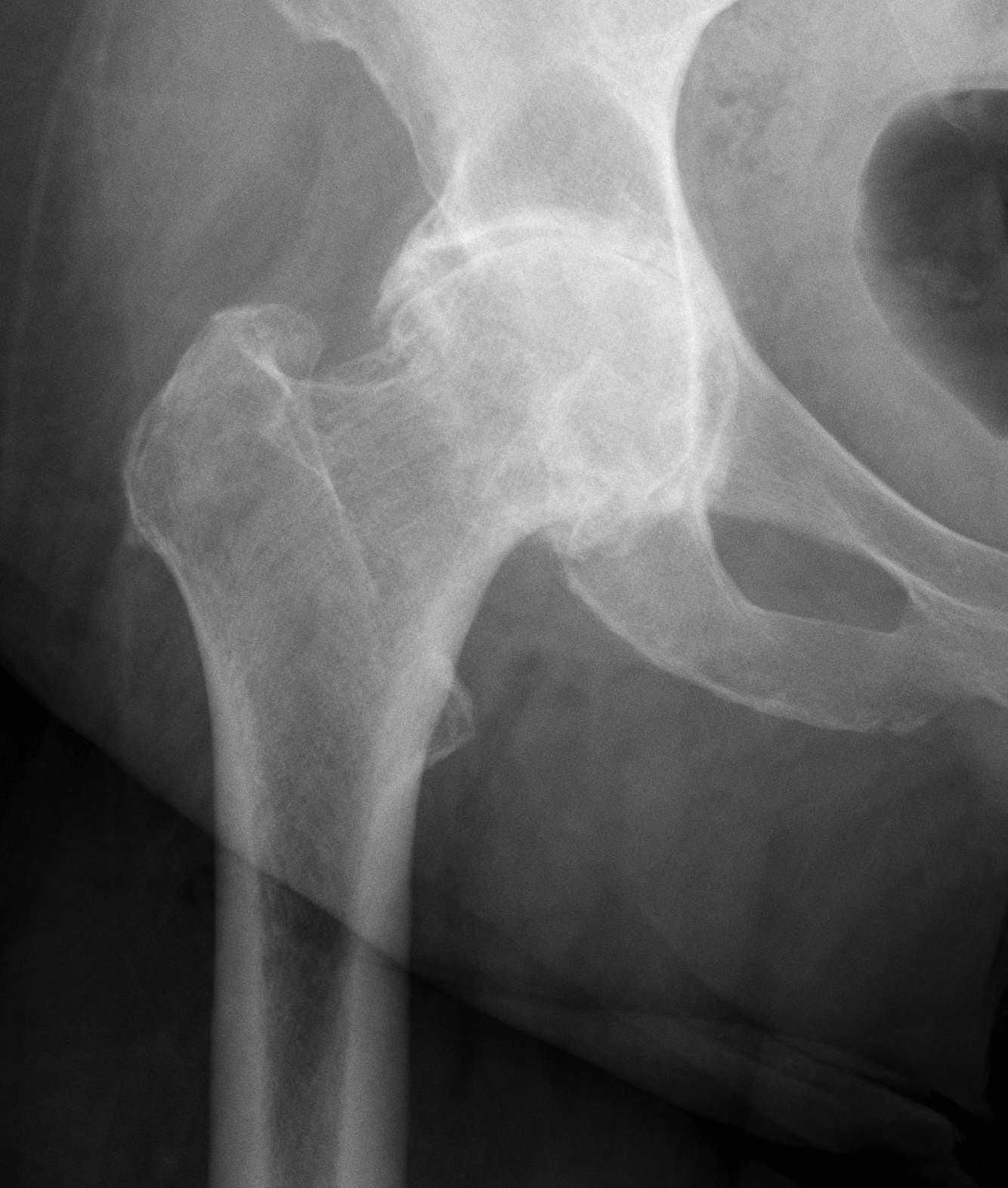
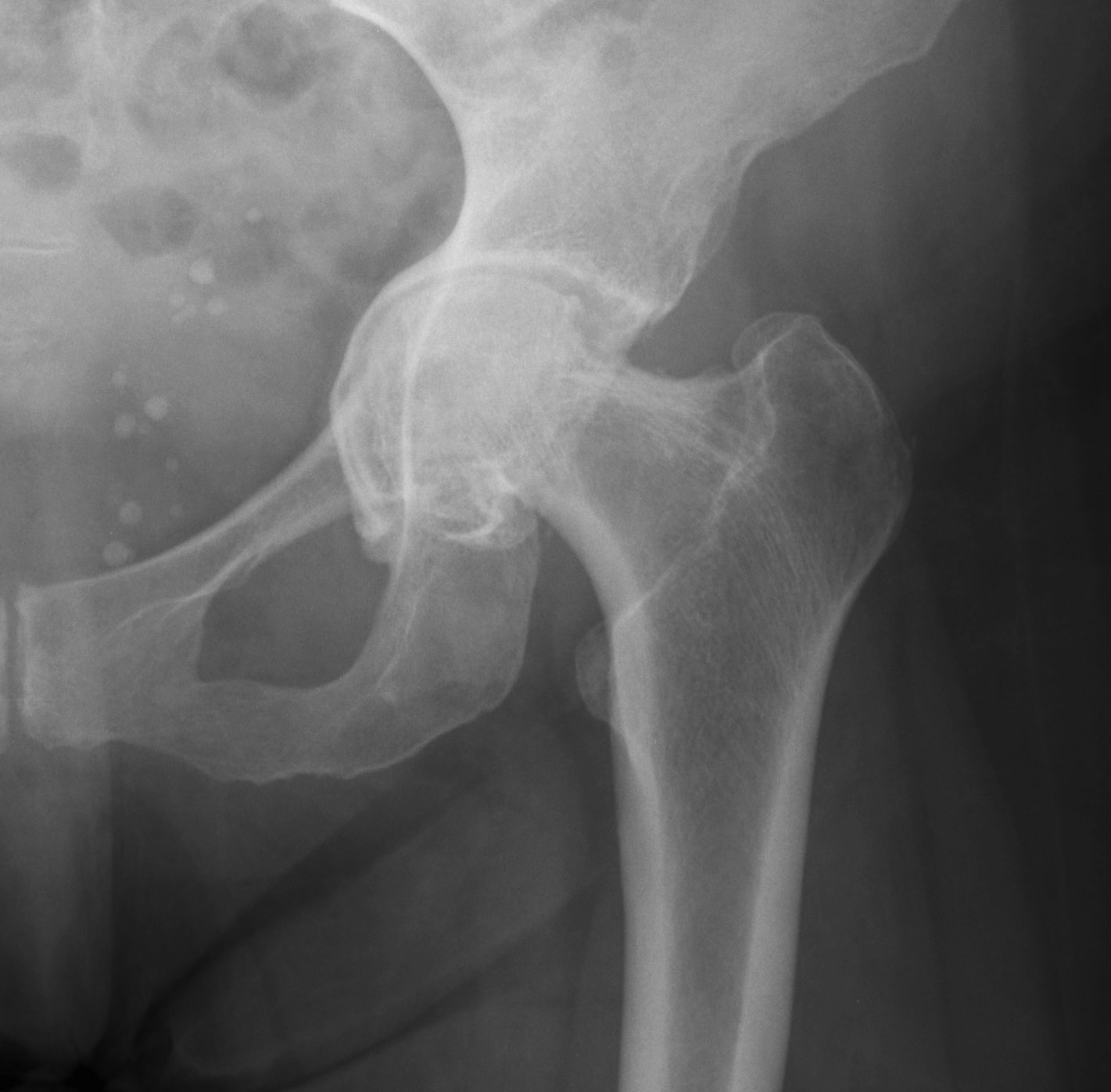
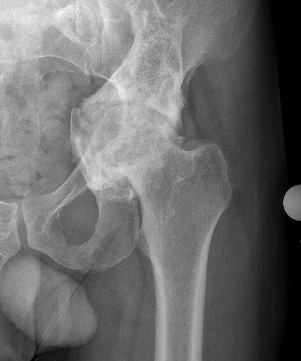 Grade I Grade II Grade III
Grade I Grade II Grade III
Natural history
Can be progressive, especially with inflammatory causes
- chronic steroids
- osteomalacia
Management
A. Skeletally immature
Triradiate fusion +/- valgising osteotomy
- 173 patients with Marfan's syndrome
- incidence protrusio 16%
- all protrusio developed in firths 2 decades of life
Steel et al J Pediatr Orthop 1996
- triradiate fusion in 22 hips with Marfan's syndrome
- 12 of 19 restored to normal
B. Young adult
Valgising intertrochanteric femoral osteotomy (VITO)
- aim for 20-30° valgus correction
- if neck shaft angle is 130° aim for 155°
- trapezoid shortening to minimize LLD
Require soft tissue release especially psoas
C. Middle aged / elderly
THA
THA Protrusio
Principle
1. Place hip center anatomically
- reduces revision rates
- THA in 162 hips with protrusio
- 89% survival at 15 years with uncemented cups
- increased revision risk with non anatomical hip center
2. Manage bone defects
- contained defect - morcellized bone graft
- uncontained defect / deficient medial wall - mesh / cage / reinforcement rings
Assess medial wall integrity with CT
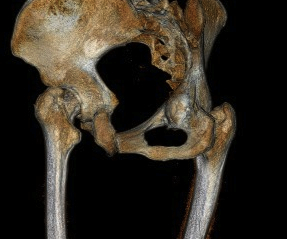
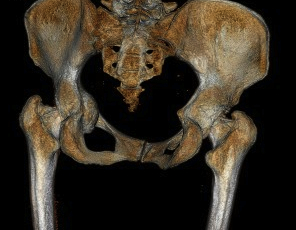
Determine Hip Centre
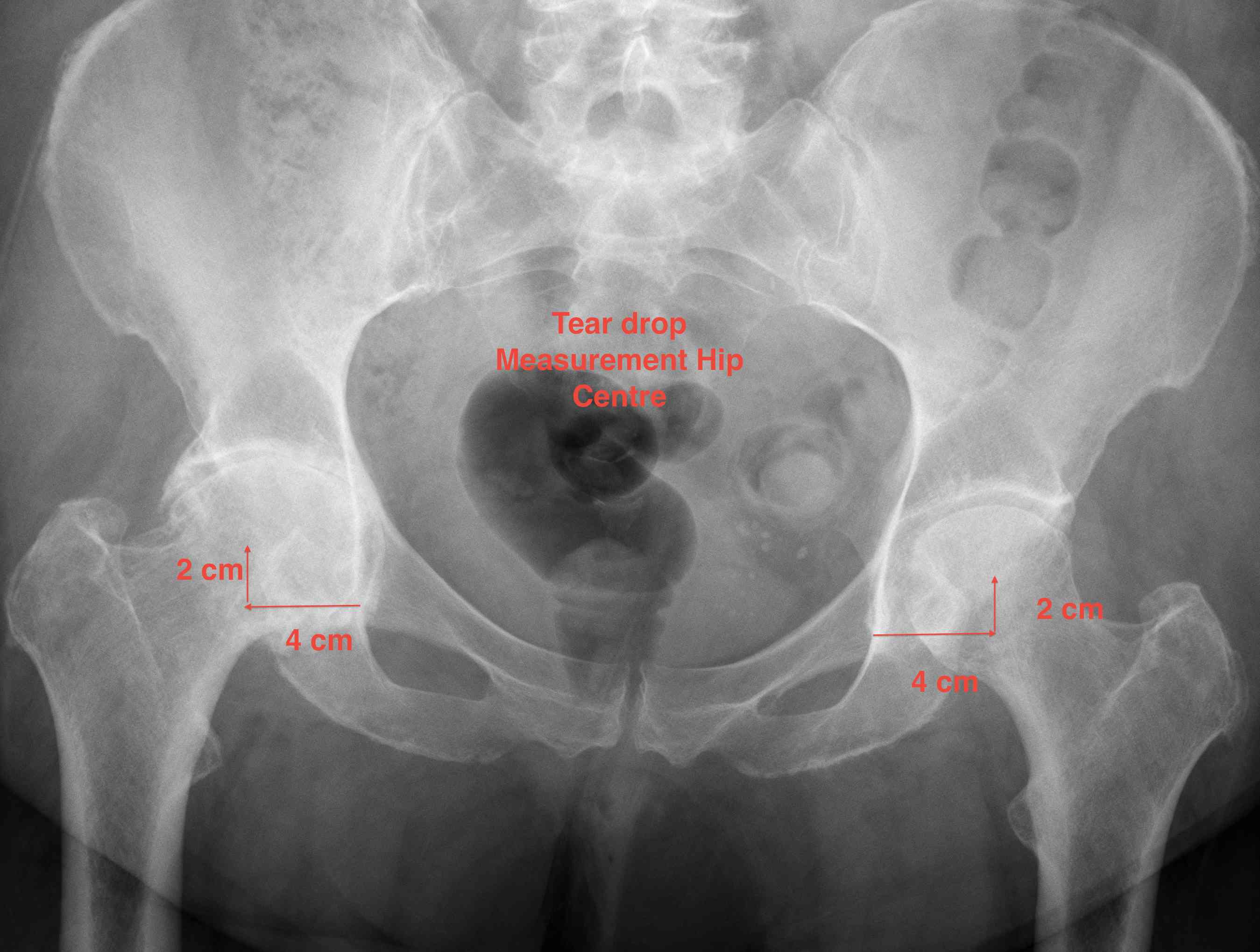
1. Teardrop
- average 2 cm vertical & 4 cm horizontal from teardrop
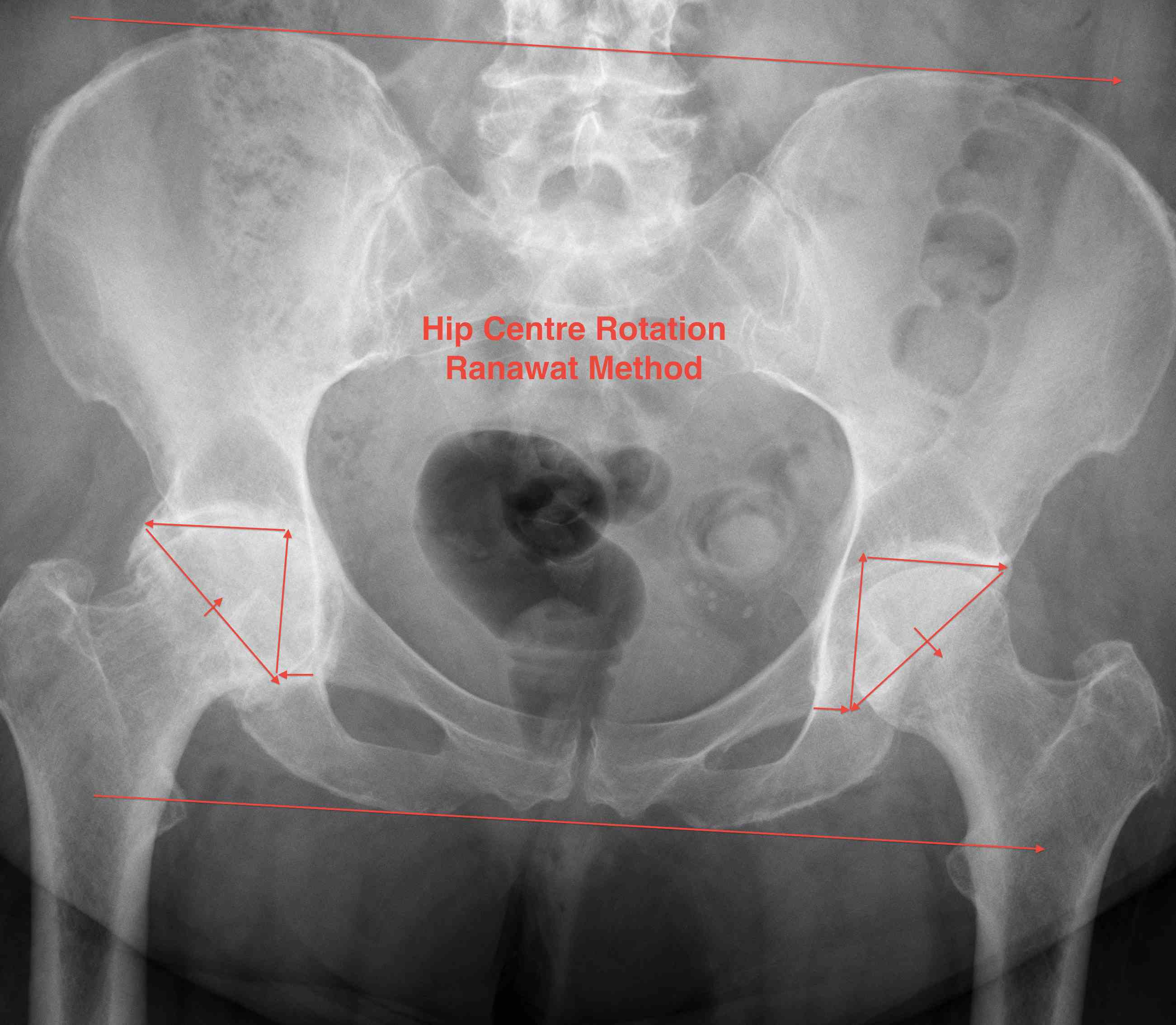
2. Ranawat Method
- draw parallel horizontal lines at the levels of the iliac crests and ischial tuberosity and mark 3 points
- Point 1: 5mm lateral to intersection of Shenton's and Kohler's lines
- Point 2: located superior to point 1 by a distance 1/5 of the pelvic height
- Point 3: similar distance horizontally from vertical line
- Isosceles triangle between 1/2/3 locates the acetabulum: line 2/3 through subchondral bone
Management Bone Defects
Algorithm
A. < 5mm - no graft required
B. > 5mm but medial wall intact - morcellised bone graft
C. No medial wall - mesh / reinforcment ring / cage + morcellised bone graft

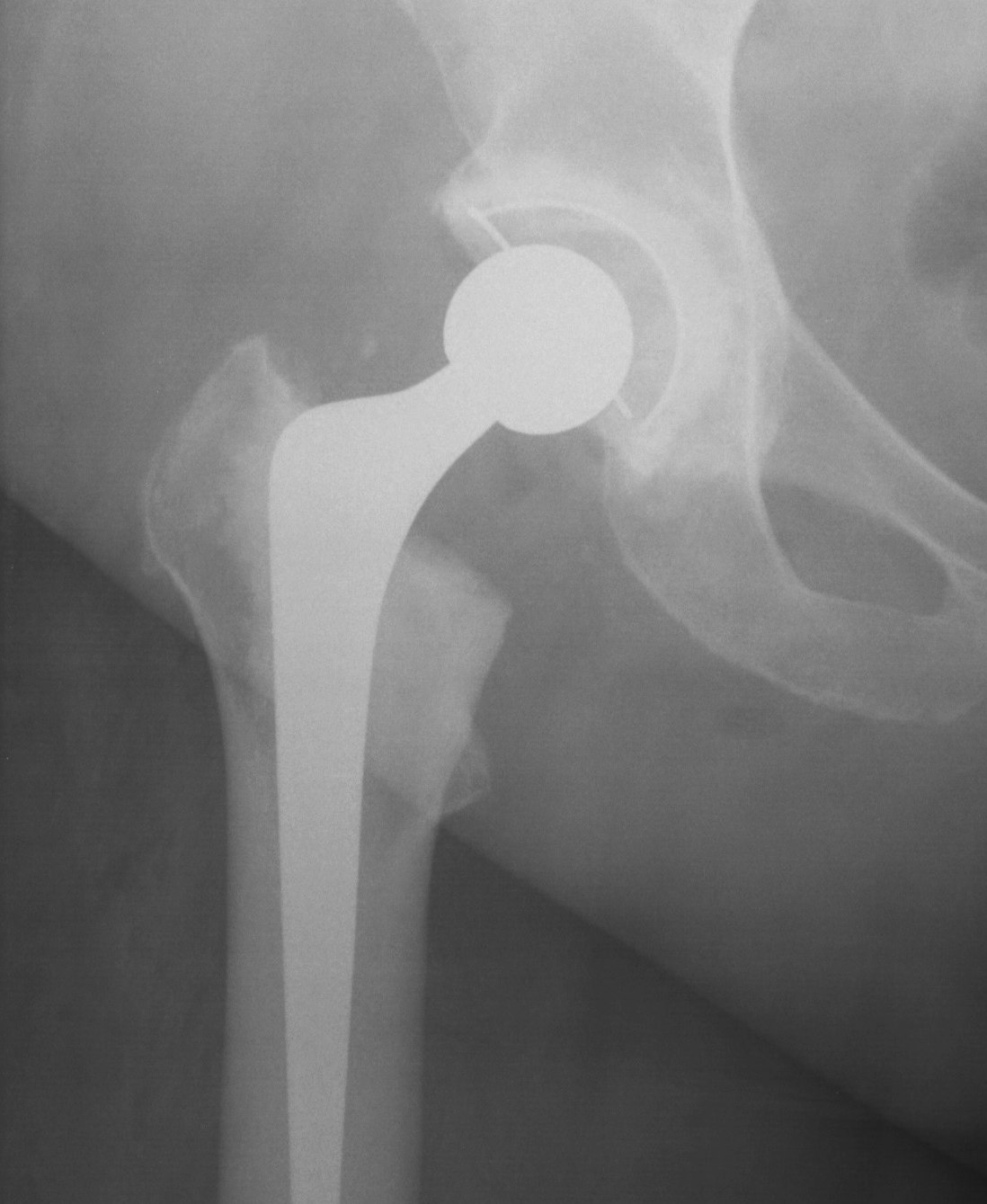
No bone graft required

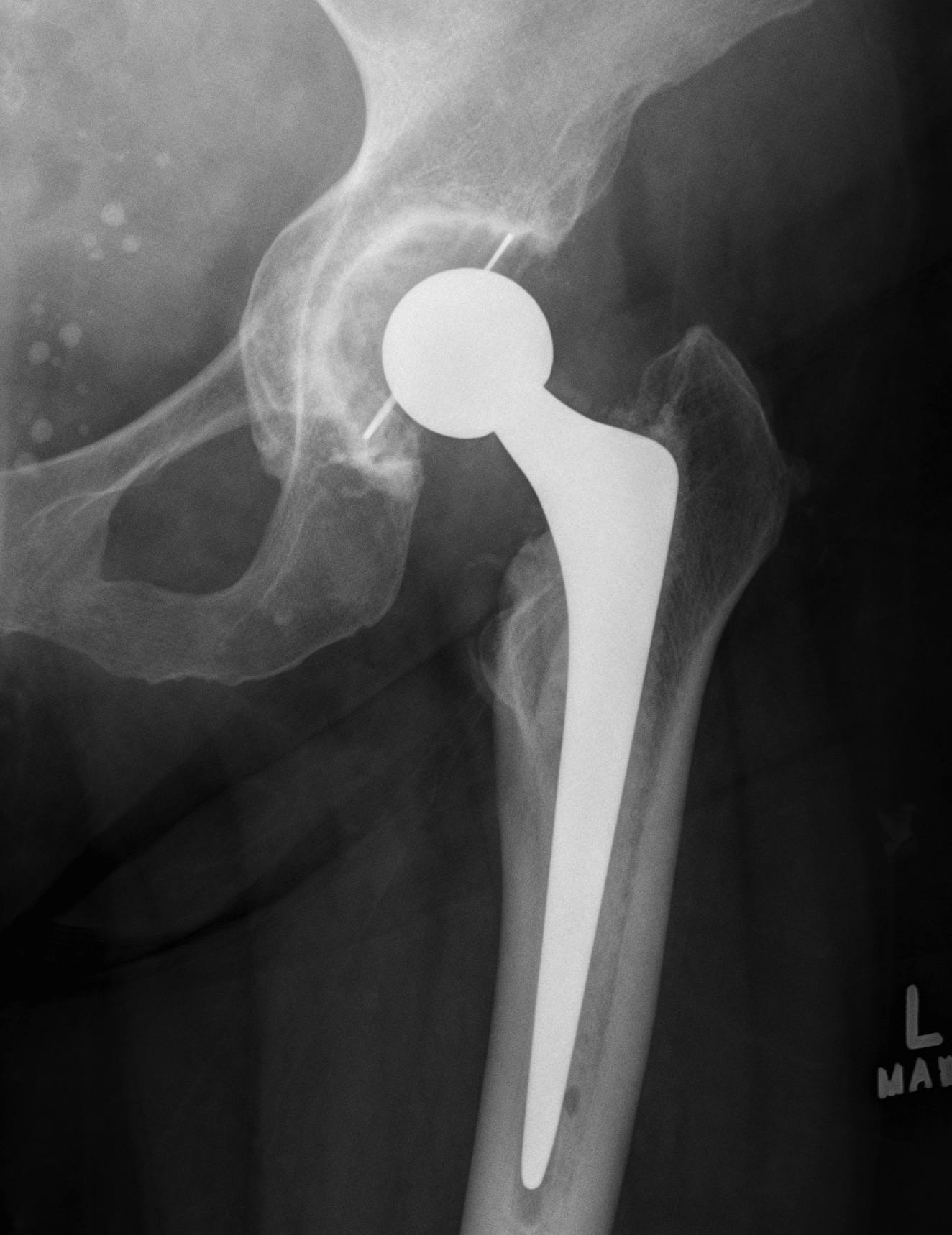
Medial wall intact, morcellized bone graft
Technique
Approach
- sciatic nerve is nearer the joint than normal - identify and protect early
- dislocation of the hip can be difficult - in situ neck cut
Reaming
- enlarge rim only
- avoid creating peripheral defect
Contained acetabular defect
- morcellised bone graft
- rim fit uncemented cup
- cemented cup
Uncontained acetabular defect
- wire mesh / bone graft / cemented cup
- cage
Restore anatomical center
- intra-operative landmarks - acetabular rim
- fluoroscopy
- image less navigation
- CT guided navigation
- Robotic assistance
