Concept
1. Initial press fit with mechanical stability
2. Osteoconductive surface to allow osteointegration
3. Contact viable host bone
Advantage over cemented cups
Liner options
- different thickness for head sizes
- different bearing surfaces
- elevated liners
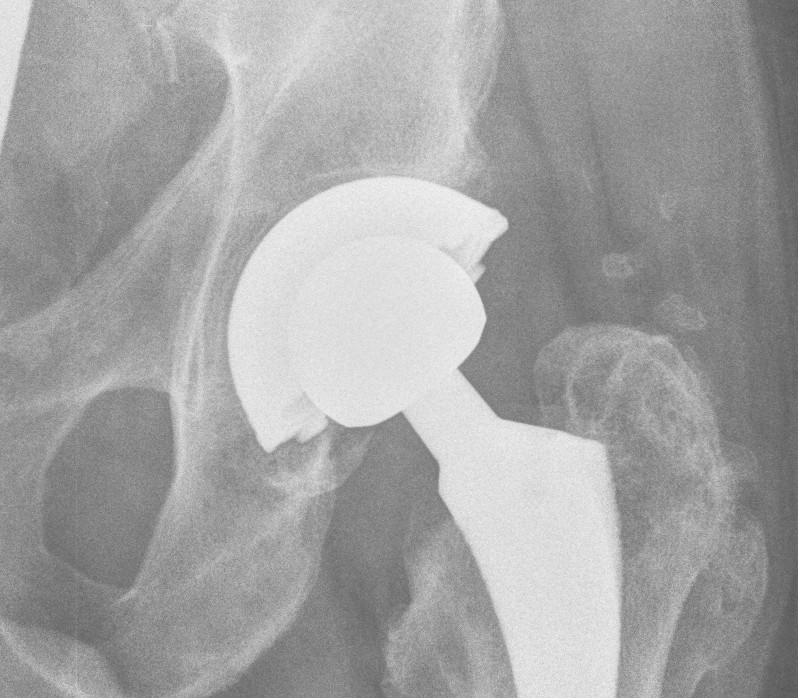
Press fit
Goal
- tight peripheral press fit with complete seating
- < 0.5 mm gaps
- < 150 um of micromotion to limit fibrous ingrowth
Reaming
- underream by 1 mm in normal bone
- underream by 2 - 3 mm in osteoporotic bone
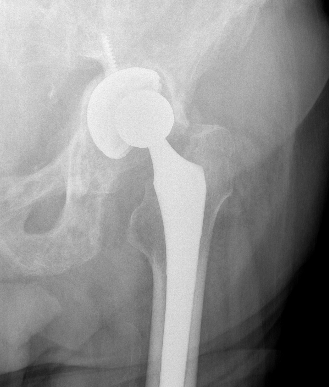
Cup Design
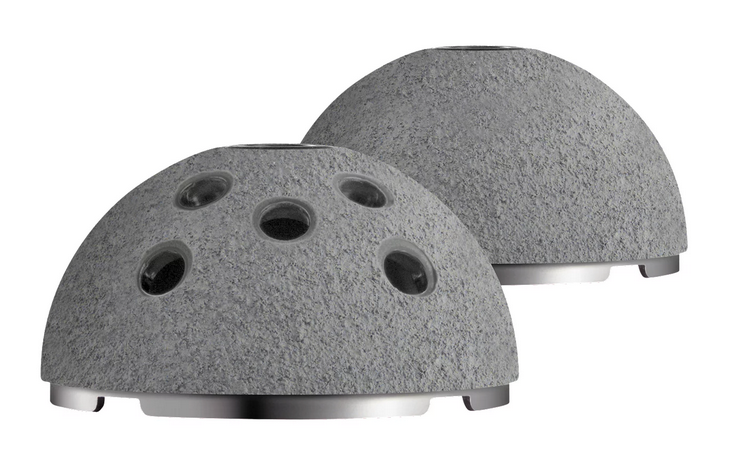


Stryker Trident Titanium and HA coated
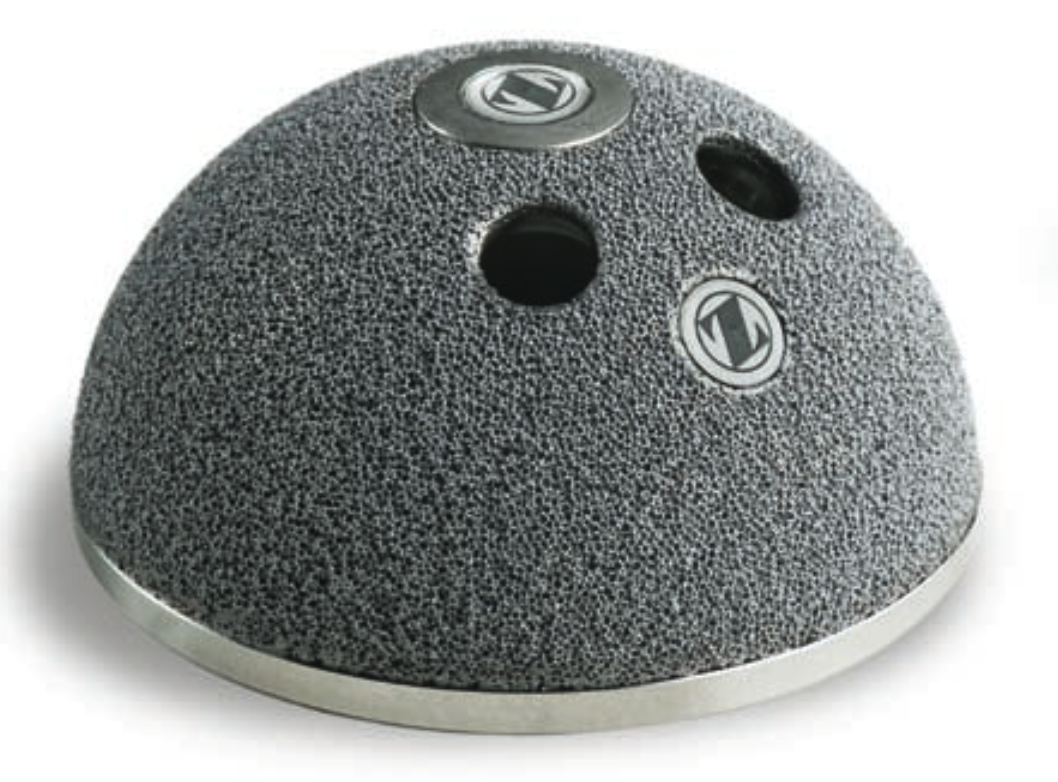

Zimmer Trabecular Metal Tantalum Cup
Material
- titanium - similar modulus of elasticity to bone, most common
- tantalum - ? superior osteointegration, used often in revision
Porous coatings
- titanium / hydroxyapatite coating
- high coefficient of friction for initial rigid fixation
- pores allow bony ingrowth long term
Shape
- designed to engage in the outer periphery of acetabulum
- hemispherical / nonhemispherical / elliptical
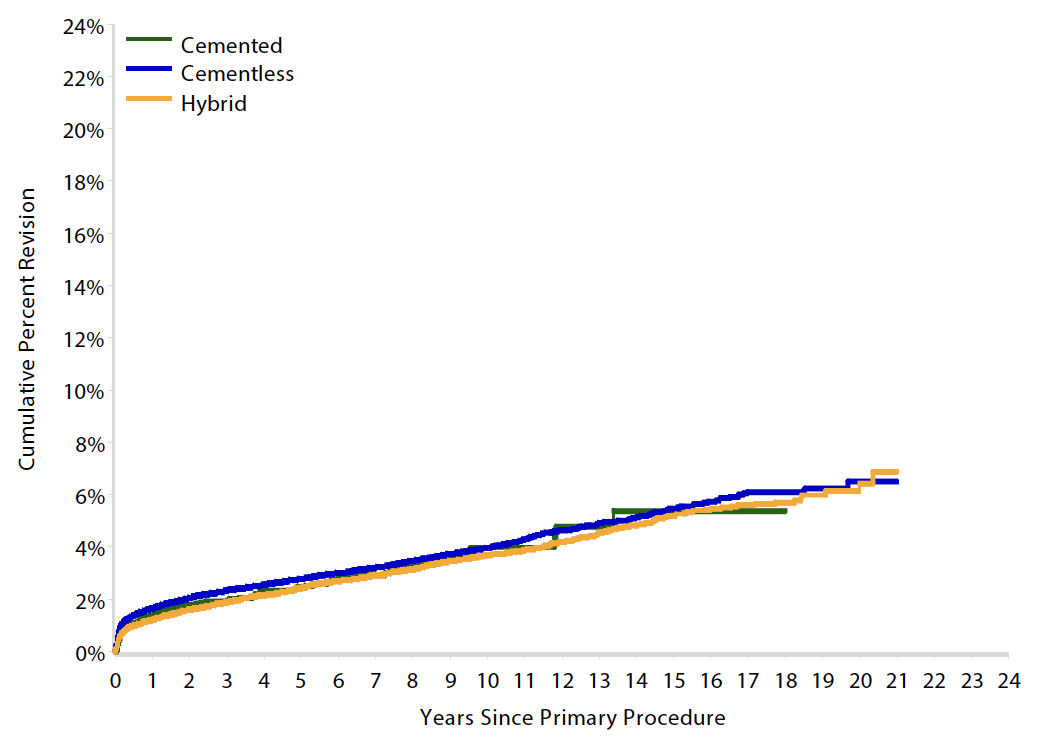
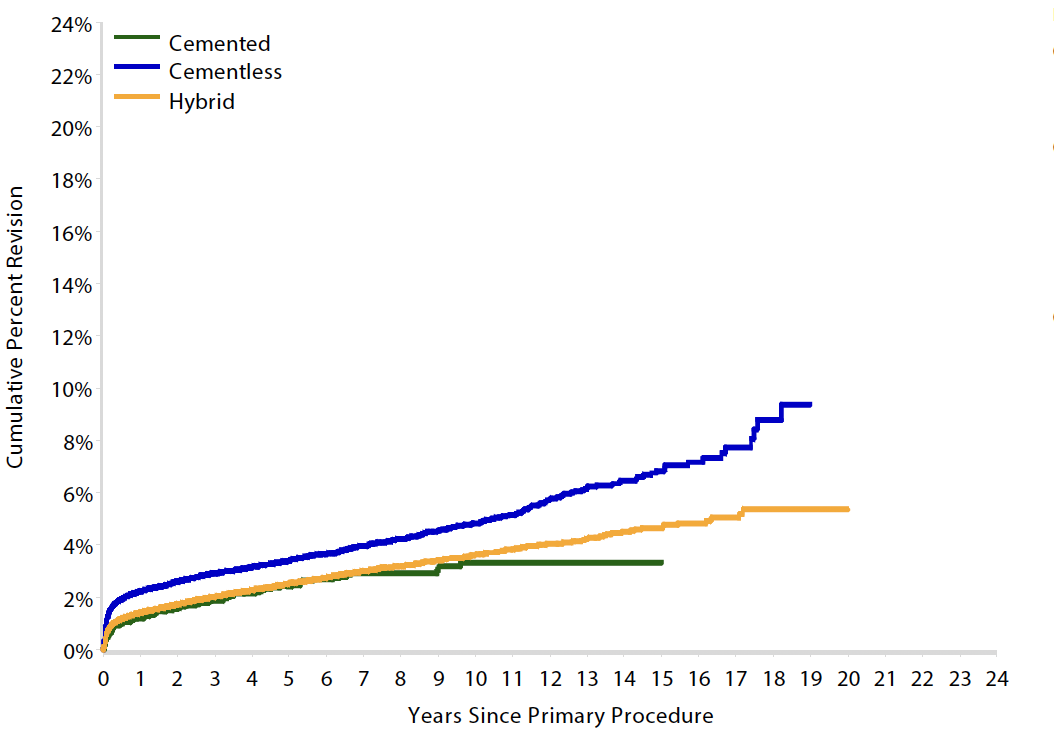
Results
Australian Joint Registry 2023 Revision rates by fixation (400,000 THA)
| Cemented | Uncemented | Hybrid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 year | 2.6 | 3.0 | 2.6 |
| 10 year | 3.8 | 4.3 | 3.9 |
| 15 year | 5.1 | 5.9 | 5.3 |
| 20 year | 7.0 | 6.7 |
15 year revision rate by age
64 - 74 year > 75 years
| Cemented | Uncemented | Hybrid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 55 | 6.4 | 7.2 | |
| 55 - 64 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 6.1 |
| 65 - 74 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 5.2 |
| > 75 | 3.3 | 6.8 | 4.7 |
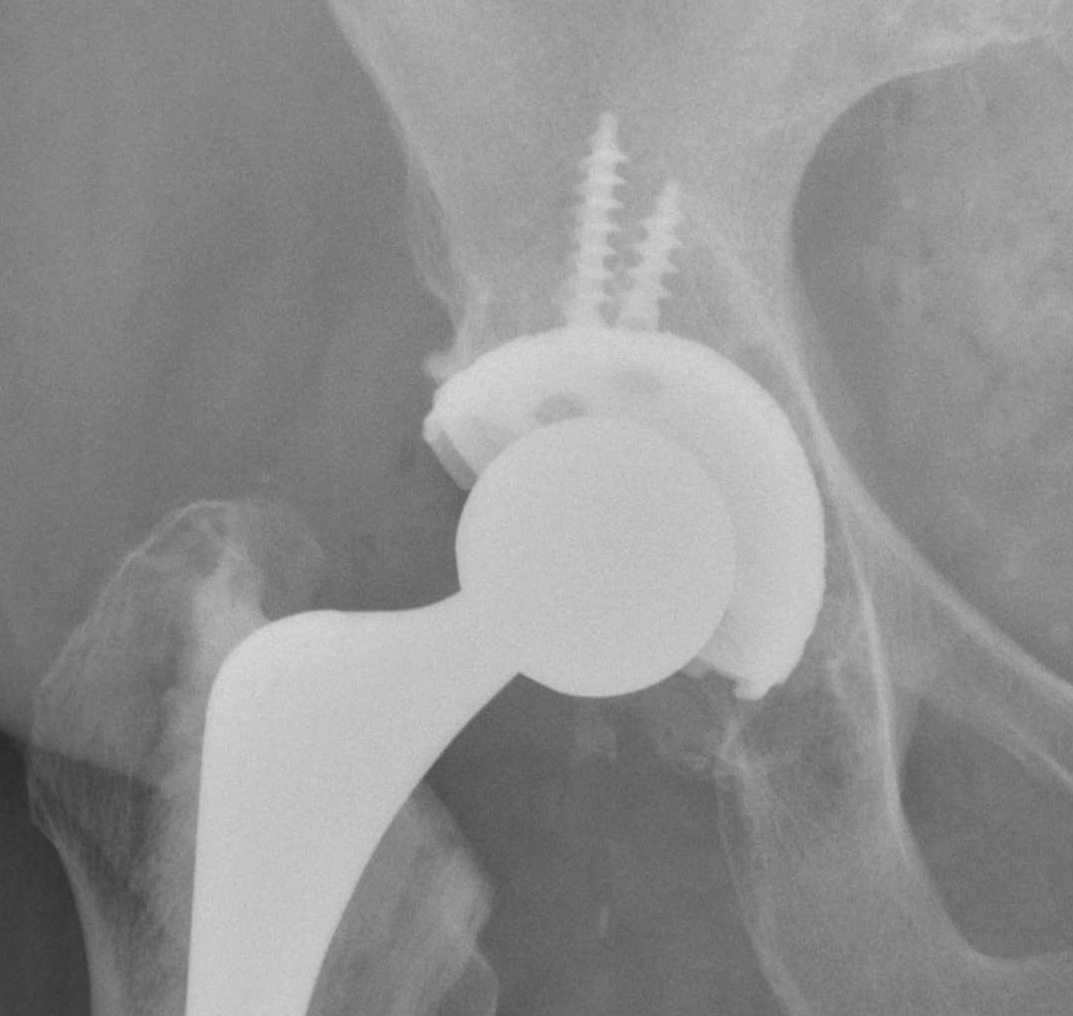
Screw fixation

Goal
Transacetabular screw fixation to augment initial cup stability
Safe zones
- anatomical cadaveric study
- line ASIS to to ischial tuberosity through center of acetabulum
- line perpendicular to this creates four quadrants
- safe quadrants are the posterior quadrants
- anterior screws can emerge within pelvis
Structures at risk
AS quadrant
- external iliac vein and artery
AI quadrant
- obturator nerve and vessels, femoral artery
PI quadrant
- internal pudenal vessels, inferior gluteal nerve & vessels
- screws < 25 mm
PS quadrant
- sciatic nerve / superior gluteal nerve and vessels in danger at greater sciatic notch
- aim screw between 2 cortices of ilium
- direct towards sacro-iliac joint
- can tolerate 85 mm screws
Results
- meta-analysis of 4 RCTs
- no effect of supplementary screw fixation
Shengui et al J Orthop Traumatol 2022
- systematic review of 19 studies and 4000 patients
- screw fixation did not alter migration / revision / wear
Technique Uncemented Cup
Centre reamer in desired hemisphere of acetabulum
- begin 6 - 10 mm below templated size
- medialize initially
- remainder reaming in direction of final component position
- 45o abduction, 20 - 30o anteversion
- increase until contact anterior and posterior
- AP diameter is what determines cup size
- petechial bleeding
- don't take away all subchondral bone
- continually assess posterior / anterior walls - must preserve
Can bone graft base and reverse ream
- especially with flattened hemisphere
Insert component 1 - 2 mm larger
- ensure seating (remove insertion handle and probe base)
- ensure stability
- add screws if any doubt into posteriosuperior quadrant
Complications
Acetabular fracture
Increased risk
- small acetabulum
- under-reaming
- elderly / osteoporotic bone
Management
- screws
- posterior column plating
- cage
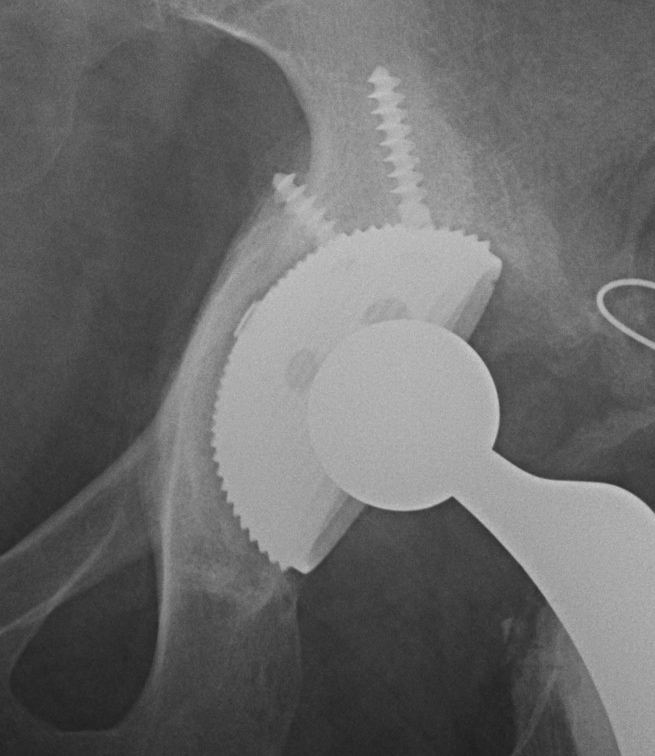
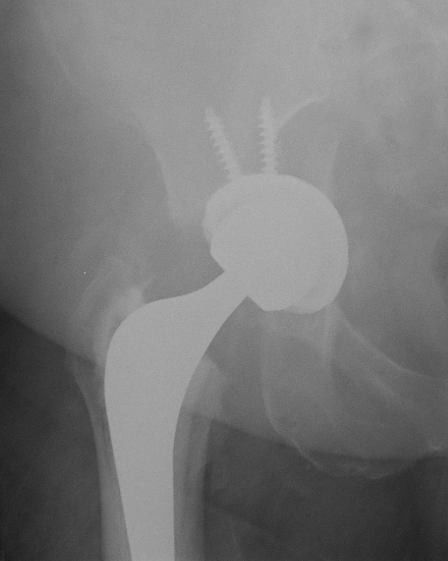
Failure of initial acetabular press fit
Acetabular spin out
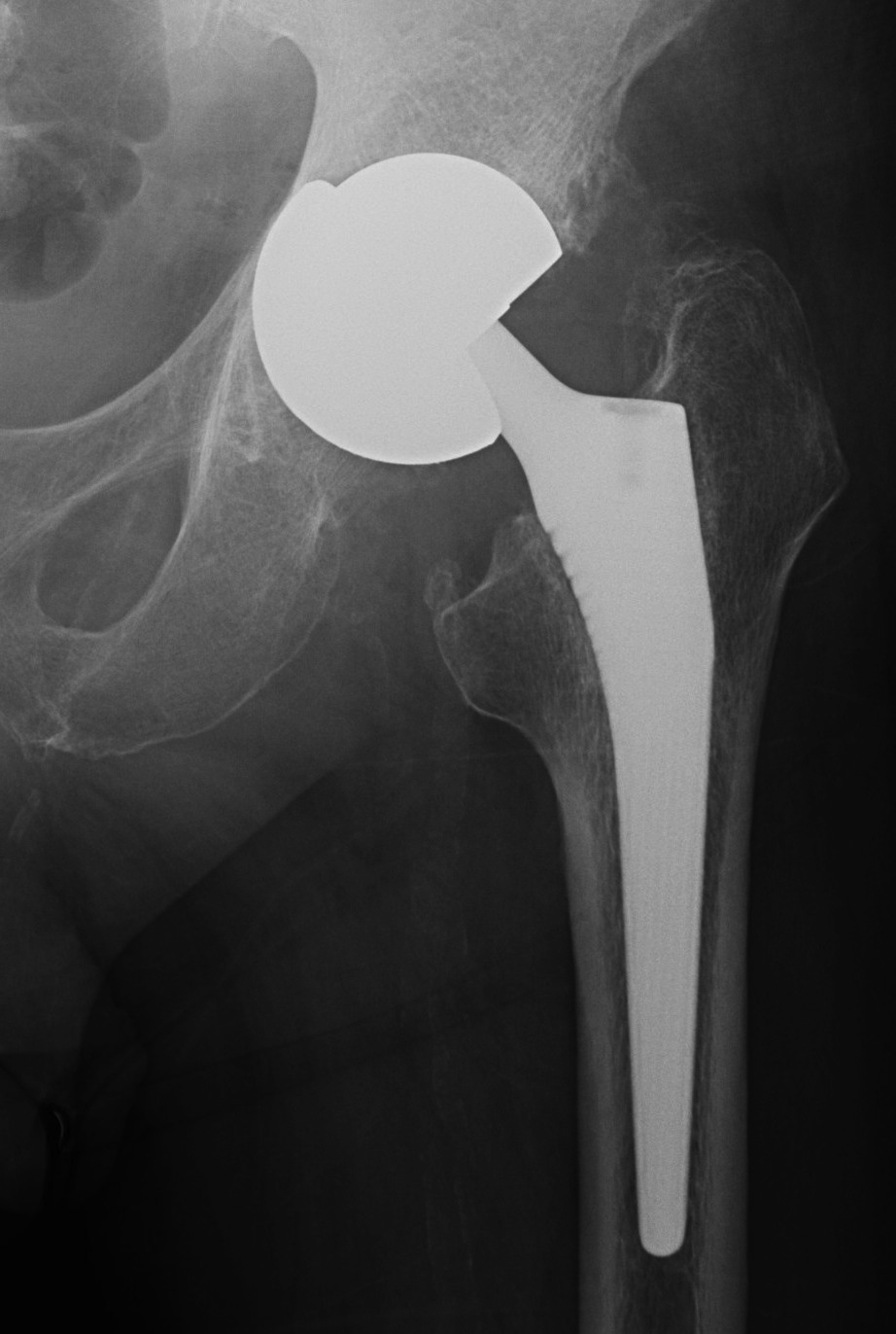
Errant Screw placement
Anterior quadrants
- can cause catastrophic haemorrhage
Management
- angiogram / embolism
- laparotomy / pelvic packing
Malposition
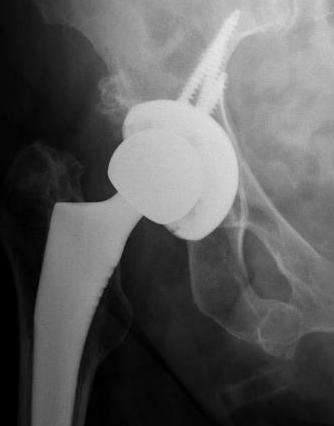
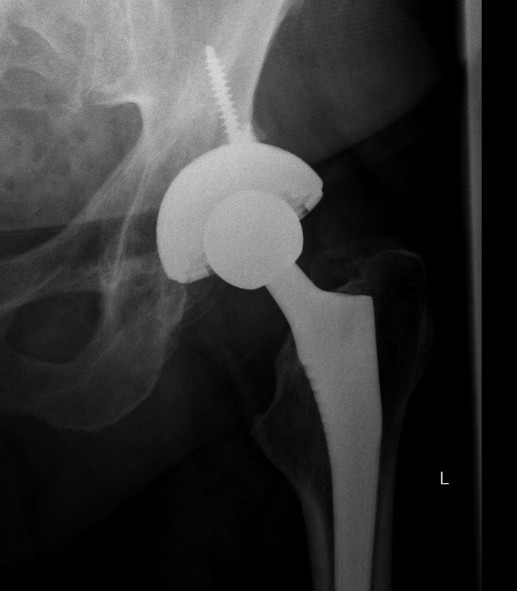
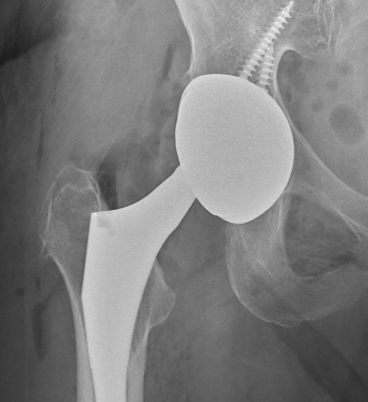
Loosening