Epidemiology
Usually after 50-60 years of age
Aetiology
Primary 90% of cases
Secondary
- AVN
- trauma
- instability
Pathology
Cuff & biceps intact as rule
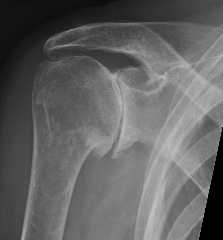
Inferior beard osteophytes
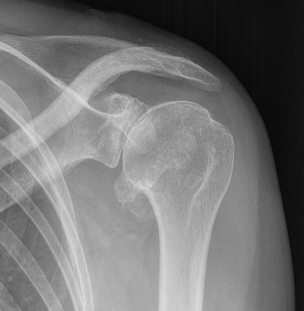
Retroversion of glenoid due to posterior wear
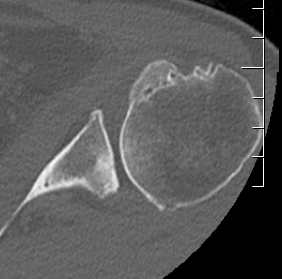
Posterior subluxation not uncommon
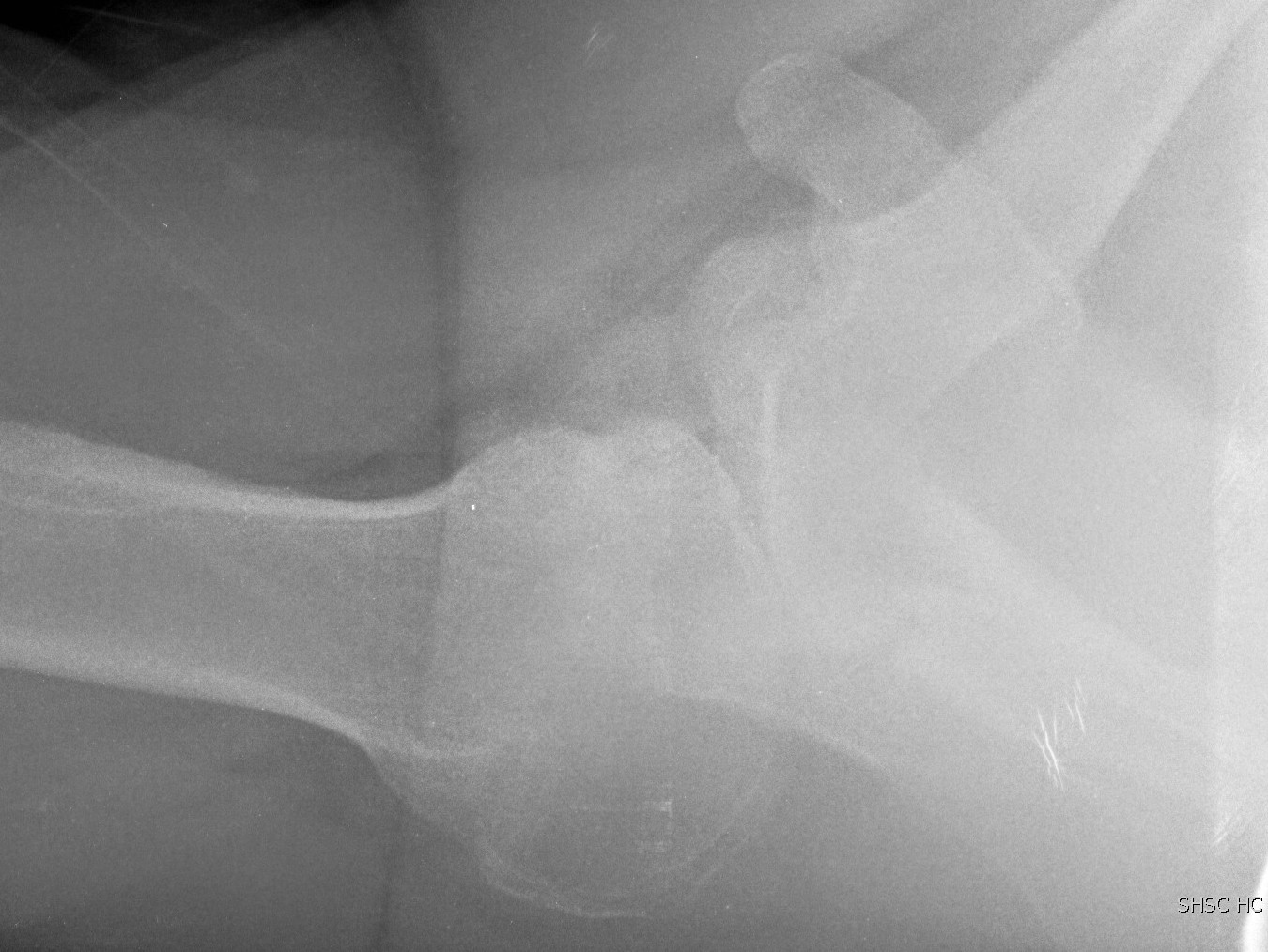
Tight anterior capsule & subscapularis limiting external rotation
Post traumatic
- always soft tissue contracture
- rotator interval contracted
- malunion of tuberosities leads to impingement and offset of normal cuff action
- non-union results in extensive shortening of cuff
- scarring about axillary nerve
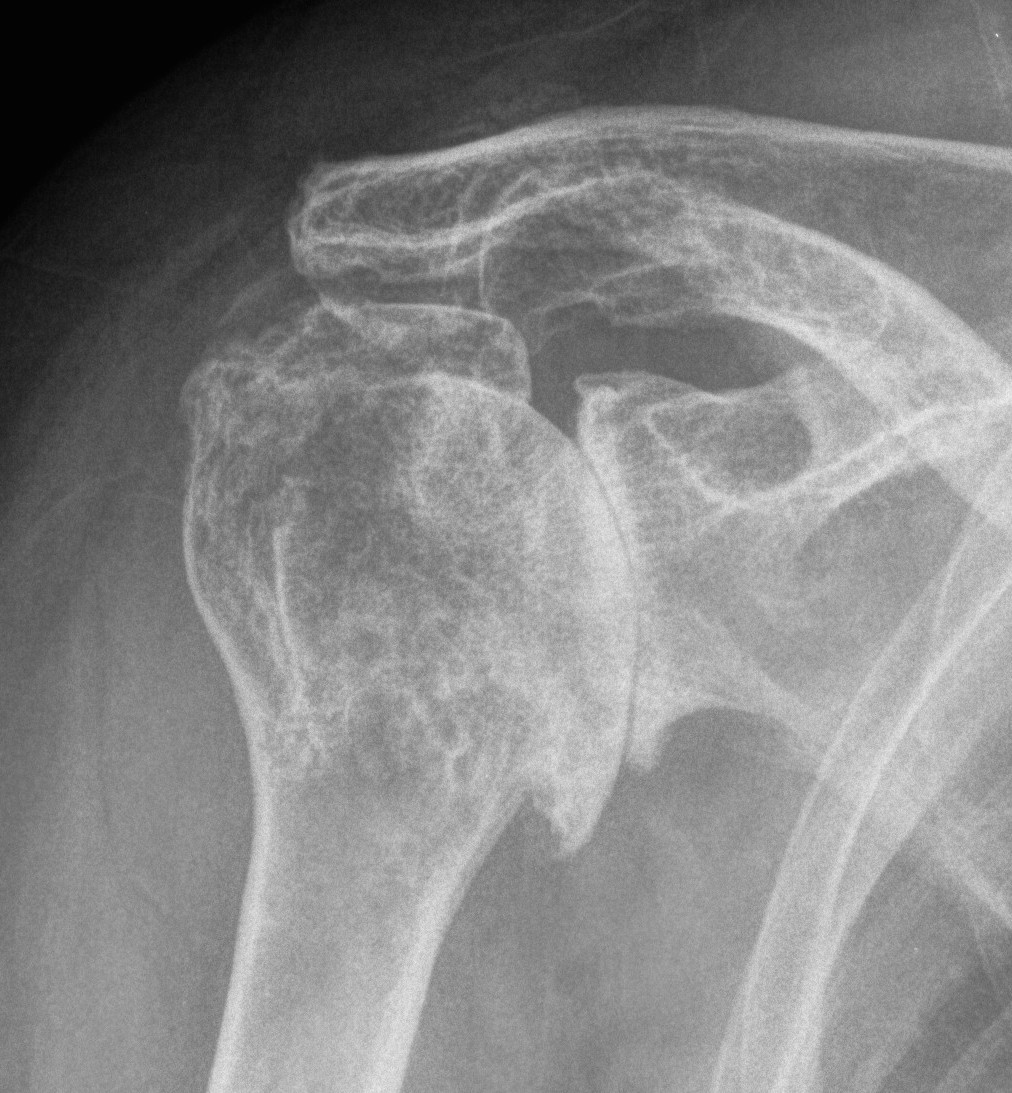
Post-traumatic OA
Signs
Global painful restriction of range of movement
- due to incongruity of joint surfaces
- crepitus
- limitation of ER
DDx Limitation ER
- Frozen Shoulder
- Chronic posterior dislocation
- Arthrodesis
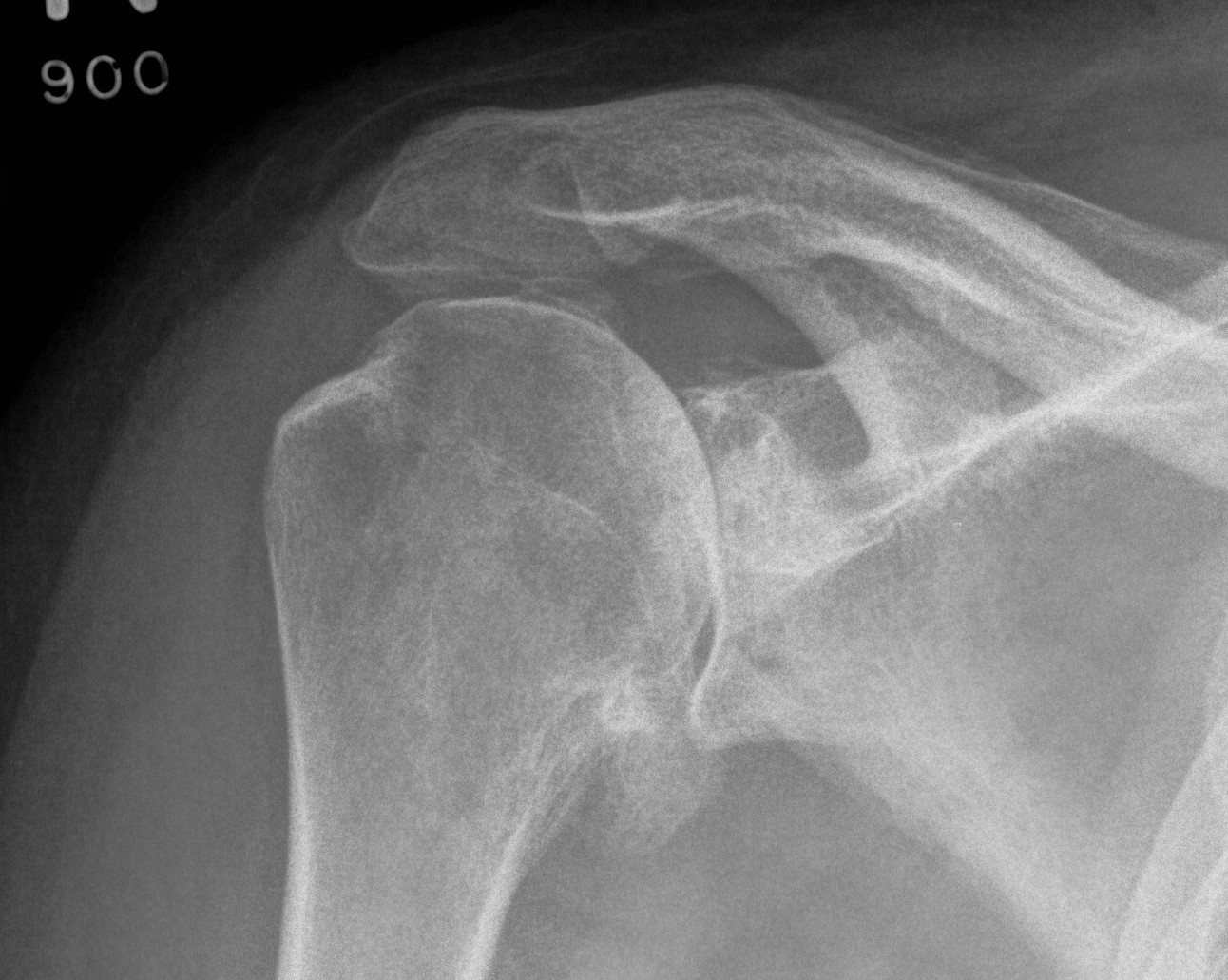
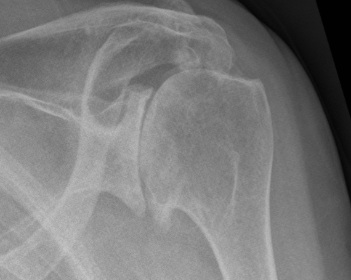
X-ray
Typical changes of OA
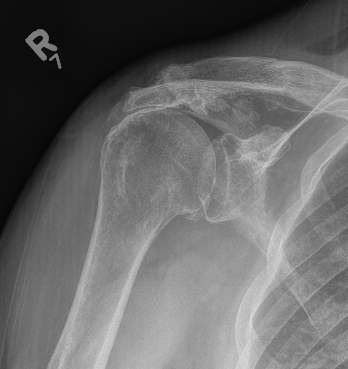
1. Teardrop / beard osteophytes on inferior head & glenoid
2. Osteochondral loose bodies
Beard osteophytes
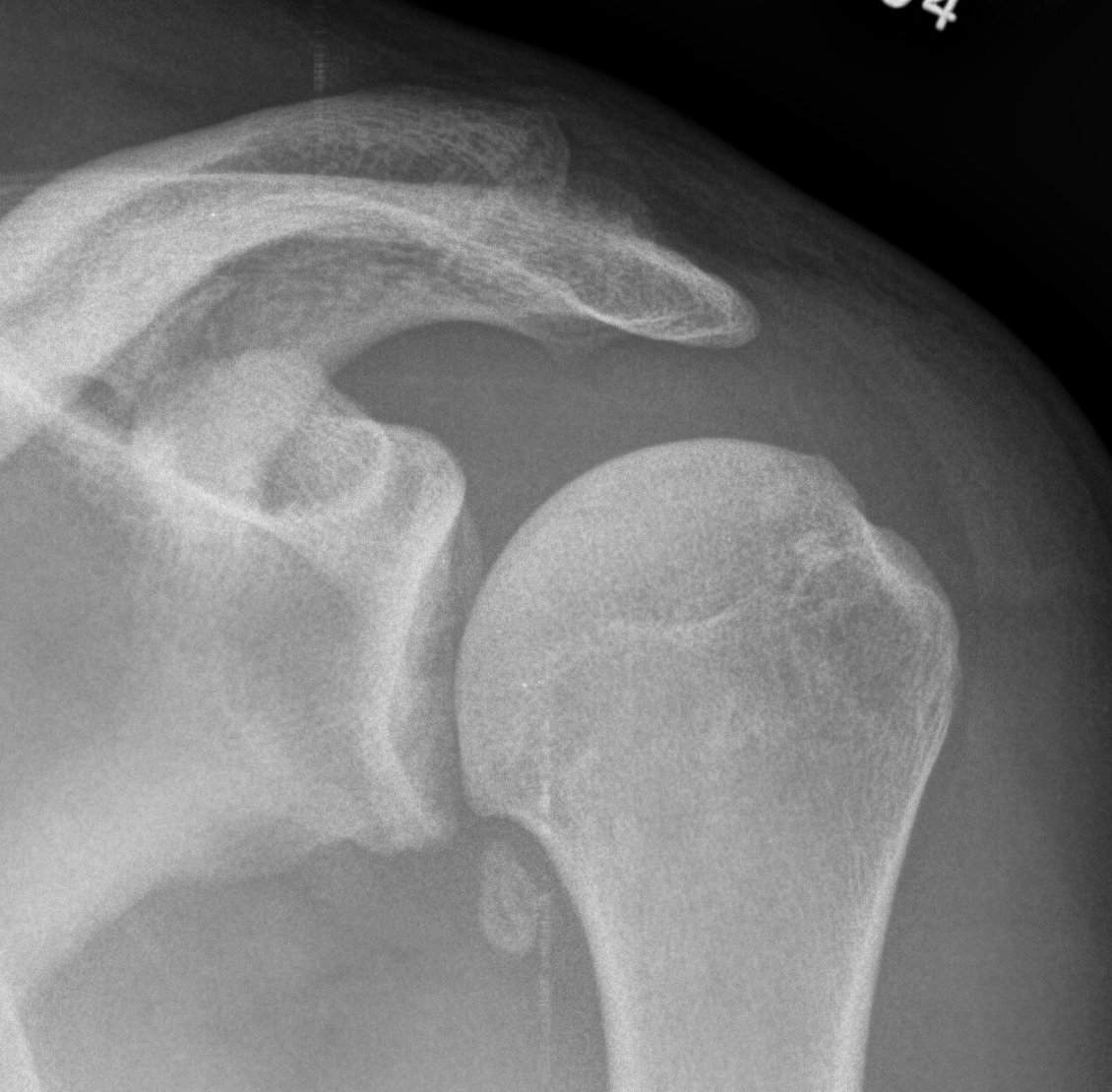
Osteochondral loose body
DDx
Cuff arthopathy
- proximal migration of head
- subacromial sclerosis
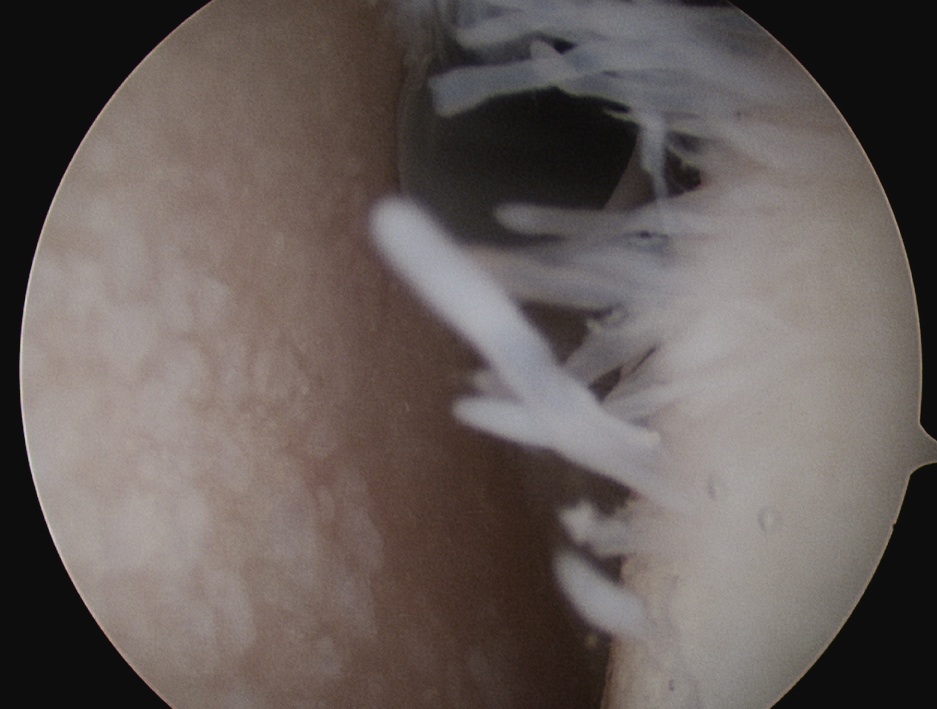
Arthroscopy
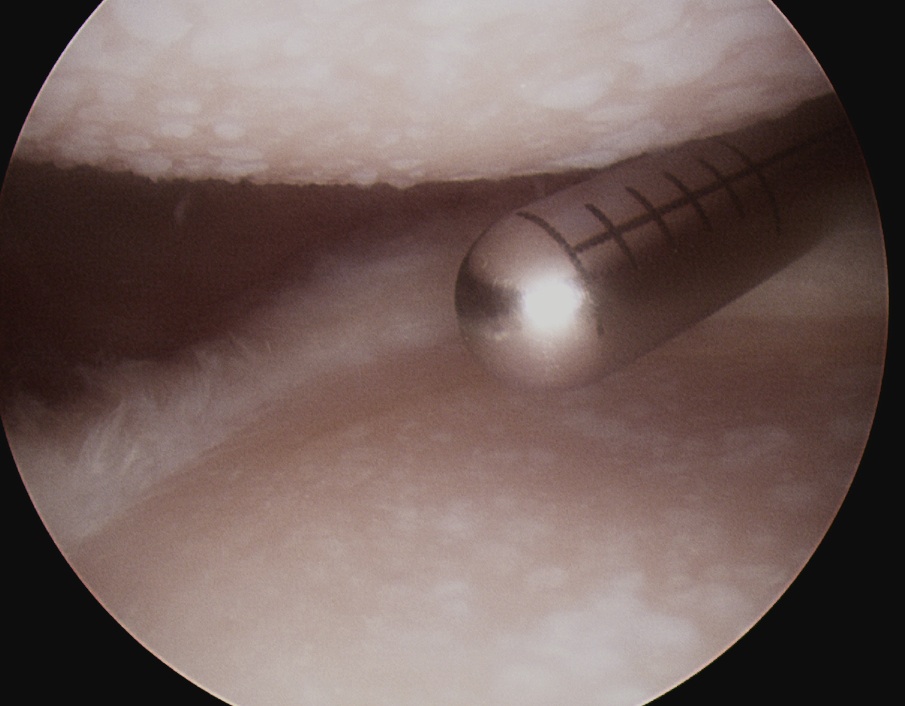
Management
Non-operative
ELMPOPI
Education
Lifestyle modification
Pharmaceuticals - simple analgesia
Physiotherapy
Injections
Injections
Hyaluronic Acid
- systematic review and meta-analysis
- no statistical difference in outcomes between HA and placebo
Bone Marrow Aspirate
Dwyer et al. Arthros Sports Med Rehab 2021
- RCT cortisone versus bone marrow aspirate for shoulder OA
- 25 shoulders
- improved QuickDASH and EQ5D but not WOMAC at 12 months post injection
Platelet rich plasma
Randomized trials on clinicaltrials.gov
None published yet
Operative
Options
Arthroscopic debridement
Glenoid resurfacing with glenoid biological resurfacing
Arthrodesis
Replacement
1. Arthroscopic Debridement
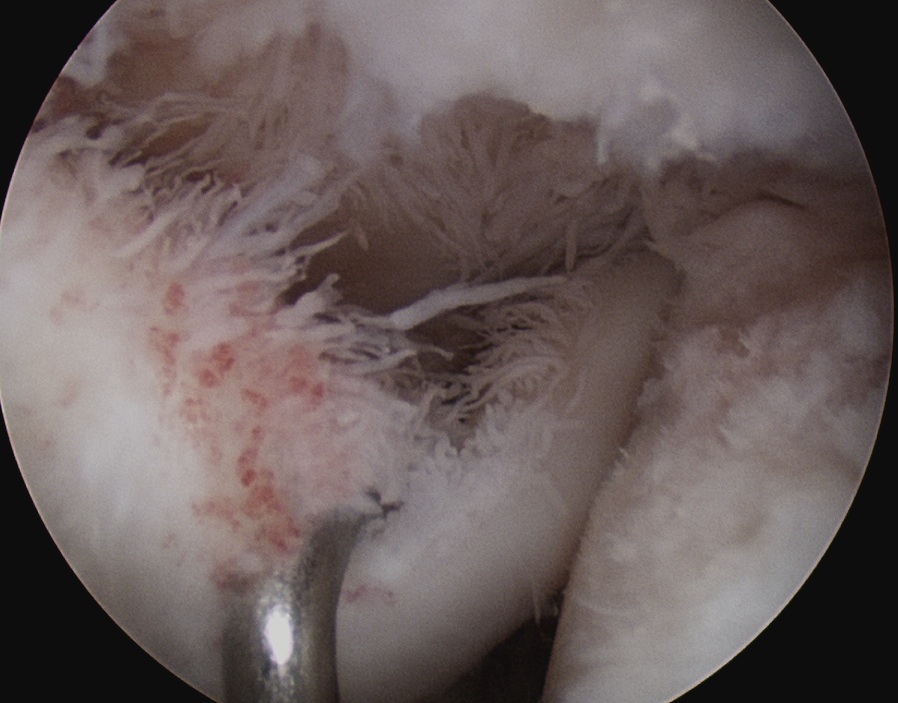
Technique
A. Glenohumeral joint
- deal with biceps tendon pathology if present (tenotomy / tenodesis)
- synovectomy
- capsular release
- chondroplasty
- remove beard osteophyte
B. Subacromial space
- acromioplasty
- CA ligament left intact
- ACJ resection
Results
- 49 shoulders mean age 52 at 5 year follow up
- 26% progressed to total shoulder at mean of 2.6 years
- otherwise significant improvements in clinical outcomes
- 38 shoulders mean age 53 at 10 year follow up
- 63% 10 years survival
- humeral head flattening and severe joint incongruency risk factors for TSA
2. Humeral head replacement with glenoid biological resurfacing
Meaike et al. Should Elbow 2020
- 11 studies, 268 shoulders
- revision rate 34%
- another 10% unsatisfactory
3. Arthrodesis
Indication
May be considered in very young active patient
Issues
Limited movement
Difficult to perform
4. Arthroplasty
Options
Hemiarthroplasty (young patient or insufficient glenoid bone stock)
Anatomical TSA
Reverse TSA
aTSA v revTSA for OA
Australian Joint Registry 2024
| 5 year | 10 years | 14 years | |
|---|---|---|---|
| anatomic TSA stemmed n=7,400 | 8% | 13% | 18% |
| anatomic TSA stemless n=4,415 | 4% | 4% | |
| Reverse stemmed n=24,000 | 4% | 5% | 7% |
Parada et al. J Should Elbow Surg 2021
- 2224 aTSA revision rate 5.6%
- 4158 revTSA revision rate 2.5%