Non Operative Management
Options / ELM POPI
Education
Lifestyle Management
- weight loss
- reduce sport
Physiotherapy
Orthotics
- walking stick
- braces
Pharmaceuticals
- NSAIDS
- acetominophen
- glucosamine
Injections
- cortisone
- hyaluronic acid
- PRP
- stem cells
Definition OA
Loss of integrity of the articular cartilage
Outerbridge Grading
I Fibrillation
II Fragmentation < 1/2 depth
III Fragmentation > 1/2 depth
IV Erosion to bone
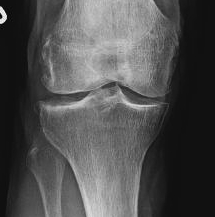
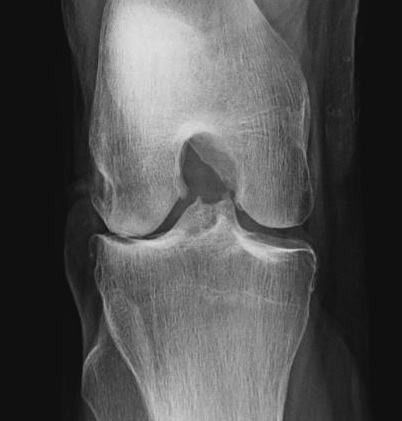
Investigations
Rosenberg view / tunnel view
- 45o flexion weight bearing view
Rationale
- most early cartilage loss is in 30-60o flexion range
- can be missed with view in extension
Glucosamine
Action
- stimulates proteoglycan synthesis by chondrocytes
- has mild anti-inflammatory properties
- however, therapeutics seems to be via PG independent mechanism
Results
Several clinical trials in patients with OA
- superior results with glucosamine sulfate compared to placebo
- reduced incidence of adverse effects
JBJS Am 2000
- meta-analysis
- glucosamine and chondroitin are effective for improving outcomes
- the magnitude of effect is unclear because of inconsistencies in study design
- dependence on industry support for study execution
Advantage
- harmless
Disadvantage
- reasonably expensive
- $30 / month
Reasonable to trial and continue if works
Hylan Injections / Viscosupplementation
Compound
Hylans are cross linked molecules of Hyaluronan
- derived from rooster combs or newer synthetic compounds
80% hydrate Hylan A
- water soluble molecule of approximately 6 million MW
- a marked increase in elastoviscosity compared to hyaluronan
20% hydrated Hylan B
- a solid derivative with continuous cross-linking between all the constituent molecules
- forms a more stable, highly elastic hydrated molecule
Options
Synvisc
- 3 x doses
Durolane
- synthetic
- single dose
Cost
$4 - 500 per treatment
Rationale
In inflamed joint
- decreased concentration and MW of hyaluronan
- stimulates inflammation
OA
- synovial fluid significantly reduced viscoelasticity
- synvisc replaces the pathological synovial fluid
- supplementing elasticity and viscosity thereby reducing pain and improving mobility
In vitro effects
- cell migration and phagocytosis slowed down or inhibited in elastoviscous environment
- nociceptors also sensitive to visco-elastic state
- high MW hyaluronan also decreases concentration of bradykinins etc
Results
Wobig Clin Ther 1998
- 57 knees 3 x 2ml injections each 1 week apart
- vs 60 knees saline injection
- 12 week end point
- X rays grade II-III
- 40% better pain relief in control
- 82% better pain relief in synvisc
Bellamy et al Cochrane Review
- evidence supports use of HA injection in knee OA
Complications
1% risk of acute allergic reaction
- sudden swelling and pain
- treat with cortisone injection
Technique
Patient with Grade 2/3 OA
- trial injection
- no sport / high impact activities for a few days
- takes 2 weeks to work
- needs to get 6 - 9 months of improvment to repear
Weight loss
Wt loss > 5 kg in women halves risk of degenerative OA by 50%
Physiotherapy
Quadriceps rehab shown to improve function without worsening arthritic symptoms
Walking Stick
Cane in the opposite hand decreases weight bearing load by 30 - 60%
Braces
1. Compressive
- neoprene
- provide warmth
2. Supportive
- hinged brace (varus-valgus)
- ACL brace
- PF braces
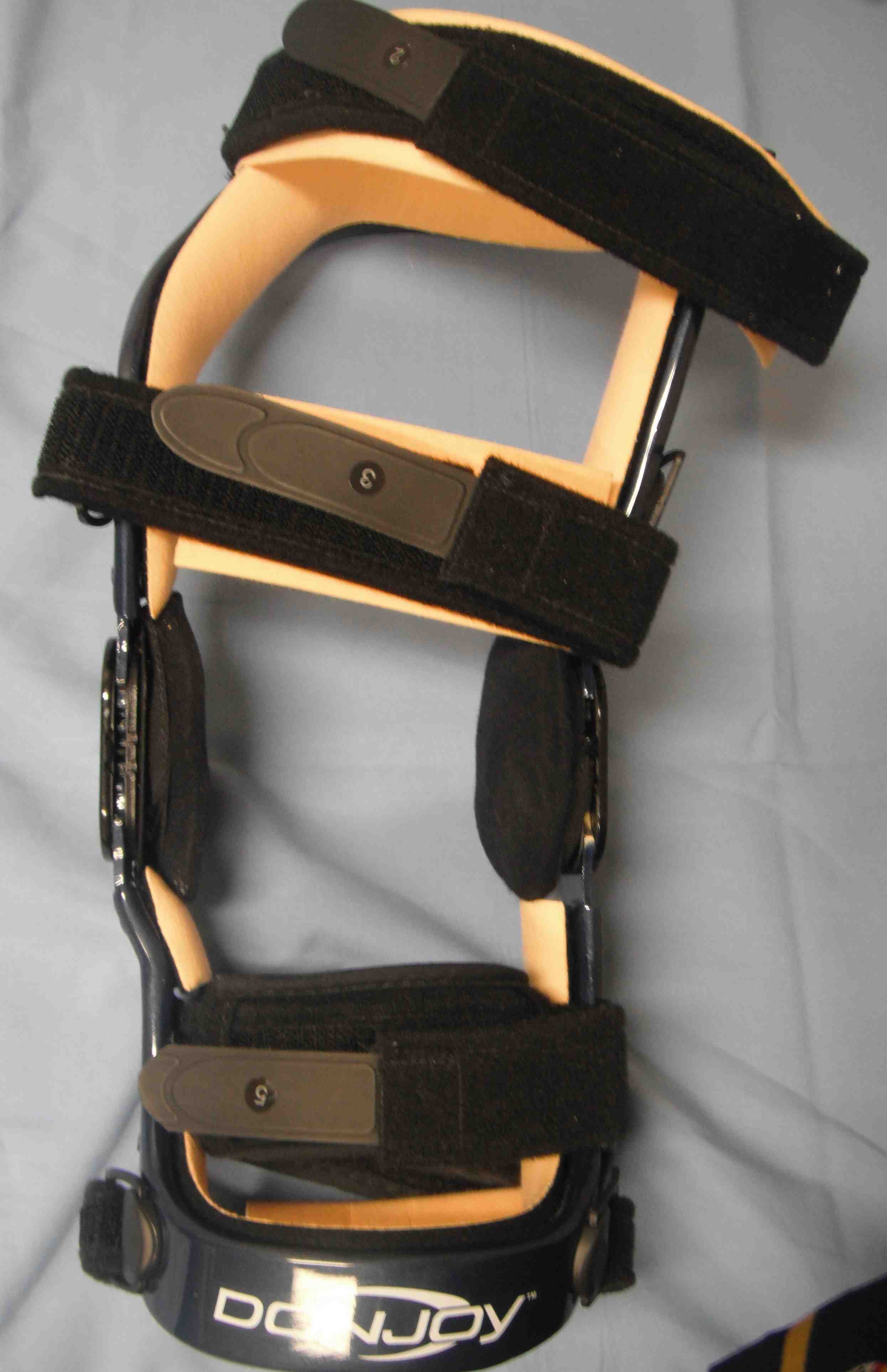
3. Unloading
- unloading varus knees
- 3 or 5o
- expensive / need to be correctly fitted
- doesn't work on large obese knees due to fitting issues
- shown to decrease pain

Orthotics
Lateral heel wedge for varus knee
- shown to decrease pain in 50% patients
Arthroscopic Lavage
Mechanism
Unclear
1. Removal "Chemical Soup"
- cartilage debris
- crystals
- inflammatory factors
2. Able to treat internal derangement at same time
- chondral flaps
- meniscal tears
Indications
A. To postpone TKR
- young, mild OA, no malalignment
- loose bodies
- mechanical symptoms
- recent effusion
B. Want to establish patient has severe enough OA to warrant TKR that you cannot see on X-ray
- staging OA
- HTO v TKR
Results
Kirkley et al N Eng J Med 2008
- RCT of moderate to severe OA
- arthroscopic lavage and debridement v physiotherapy / medical therapy only
- no difference in outcome
Herrlin et al Knee Surg Sports 2007
- randomised patients with degenerative / non traumatic medial meniscal tears
- arthroscopic debridement v exercise program
- no difference in two groups
Stem Cells
- RCT of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells versus placebo
- 261 patients
- improved outcomes at 6 months with MSCs treatment
- RCT of allogenic mesenchymal stem cells versus placebo
- 146 patients
- improved outcomes at 12 months with MSCs
- reduced cartilage deterioration with MSCs on MRI
