Background
Epidemiology
Much less common than hip and knee OA
Patients tend to be younger


Much less common than hip and knee OA
Patients tend to be younger
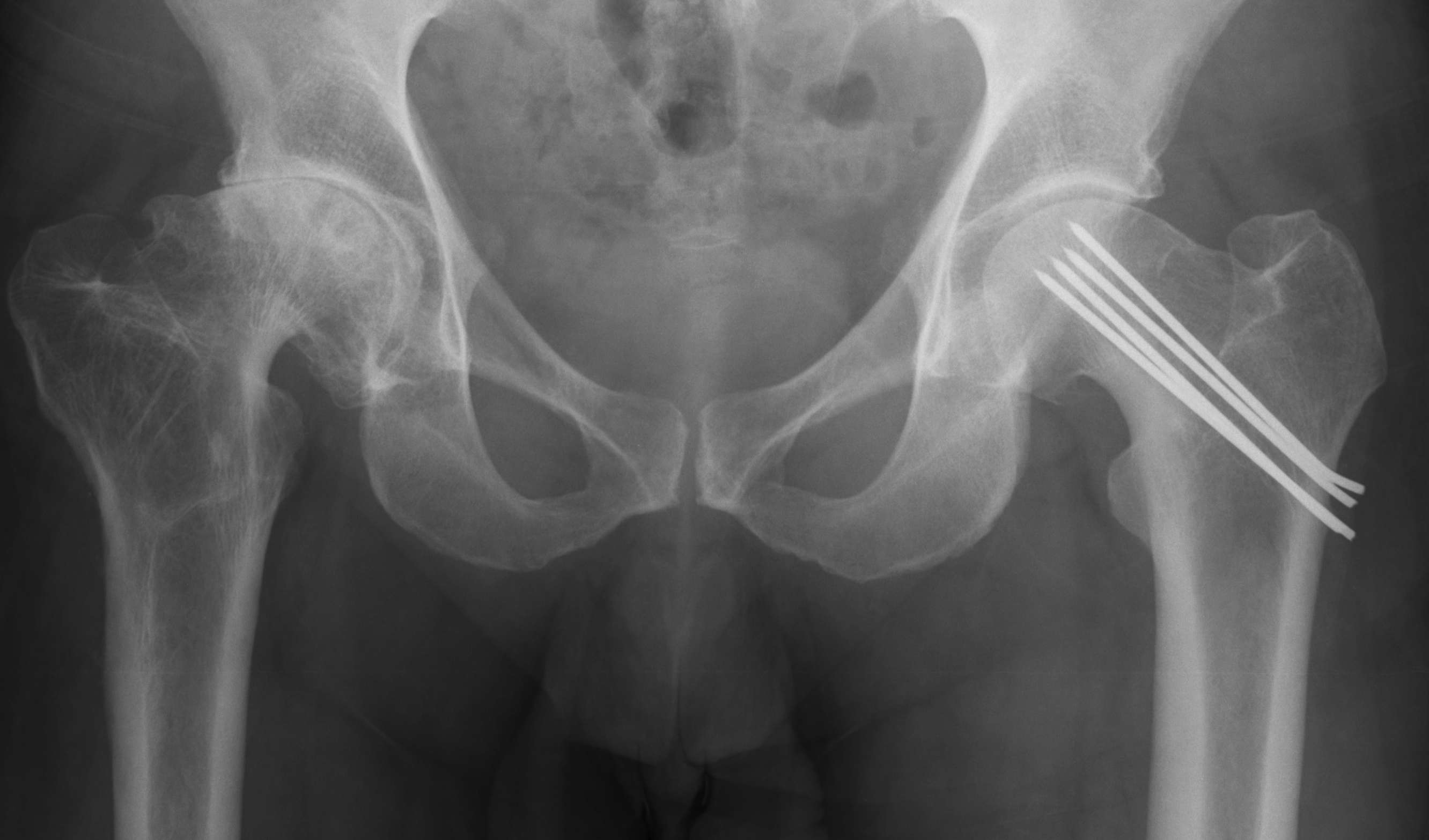
Osteoarthritis
- abnormal morphology
- loss of head neck offset
- bony impingement on acetabulum
AVN
1 - 2 %
Medial Aspect of foot
- proximal to navicular
- part of T posterior tendon
Usually will fuse with navicular (50%)
1. Probably not a cause of flat foot
- excising accessory navicular / rerouting / reattaching tibialis posterior
- will not help pes planus
2. Pain
- may fracture
Tibial facture with break in skin
- open wound communicating with fracture or haematoma
Patient is immediately at higher risk of deep infection
Wound continuously oozes dark red fracture haematoma
Up to 1/4 of tibia fractures open
Grade 1
- wound < 1cm
- usually inside out
10%
70o swing phase
80o climb up stairs
90o climb down stairs + sit down in chair
100o low chair
Stiffness usually subsides at 6-8/52
- generally improves out to 3/12
- slow improvement for up to next 9/12
0.05%
1. Thrombosis
- most common scenario
- tourniquet with atherosclerosis
- indirect damage to vessel
- femoral or popliteal
2. Embolisation
- atherosclerosis again
- blue toes syndrome post operatively
3. Vessel transection
Knee > Hip
- superficial position
- limited cover of well vascularised muscle
- watershed area of skin blood supply anterior to the skin incision
- much increased in fully constrained prosthesis
Ideal < 1%
Increased with
- revision
- prior infection
- RA / Psoriatic arthropathy
- DM
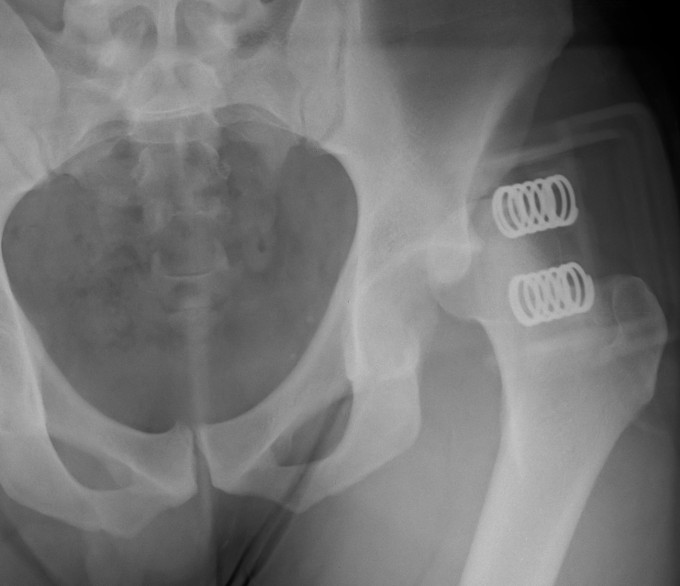
Young men
Posterior / Anterior 9:1
High velocity injury
- head direction at impact decides direction of dislocation
Anterior Dislocation
Externally rotated & abducted leg
- flexion = inferior dislocation