Technique ACL PCL and MCL
Options for MCL
Repair
Reconstruction
Femoral repair of MCL
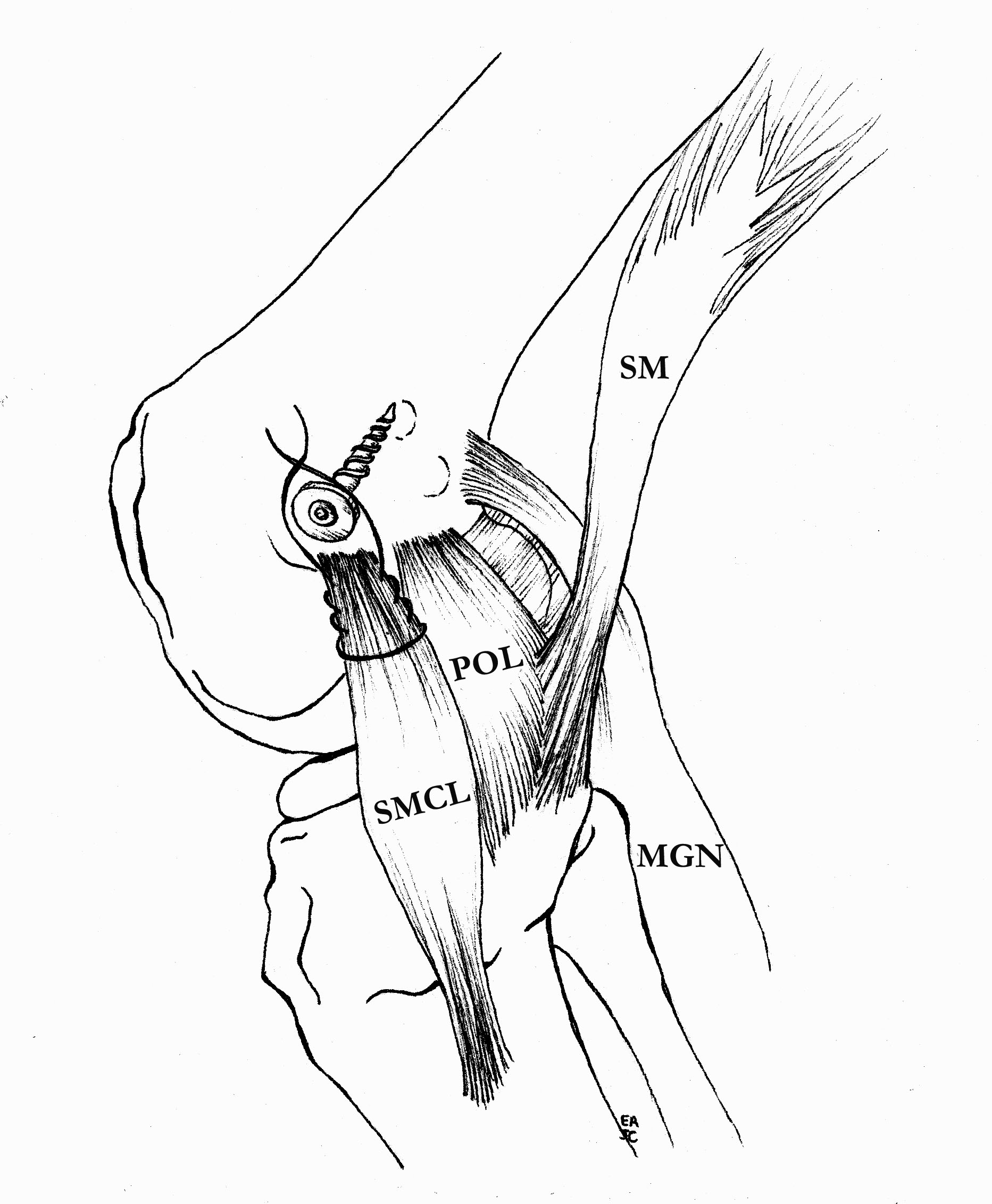
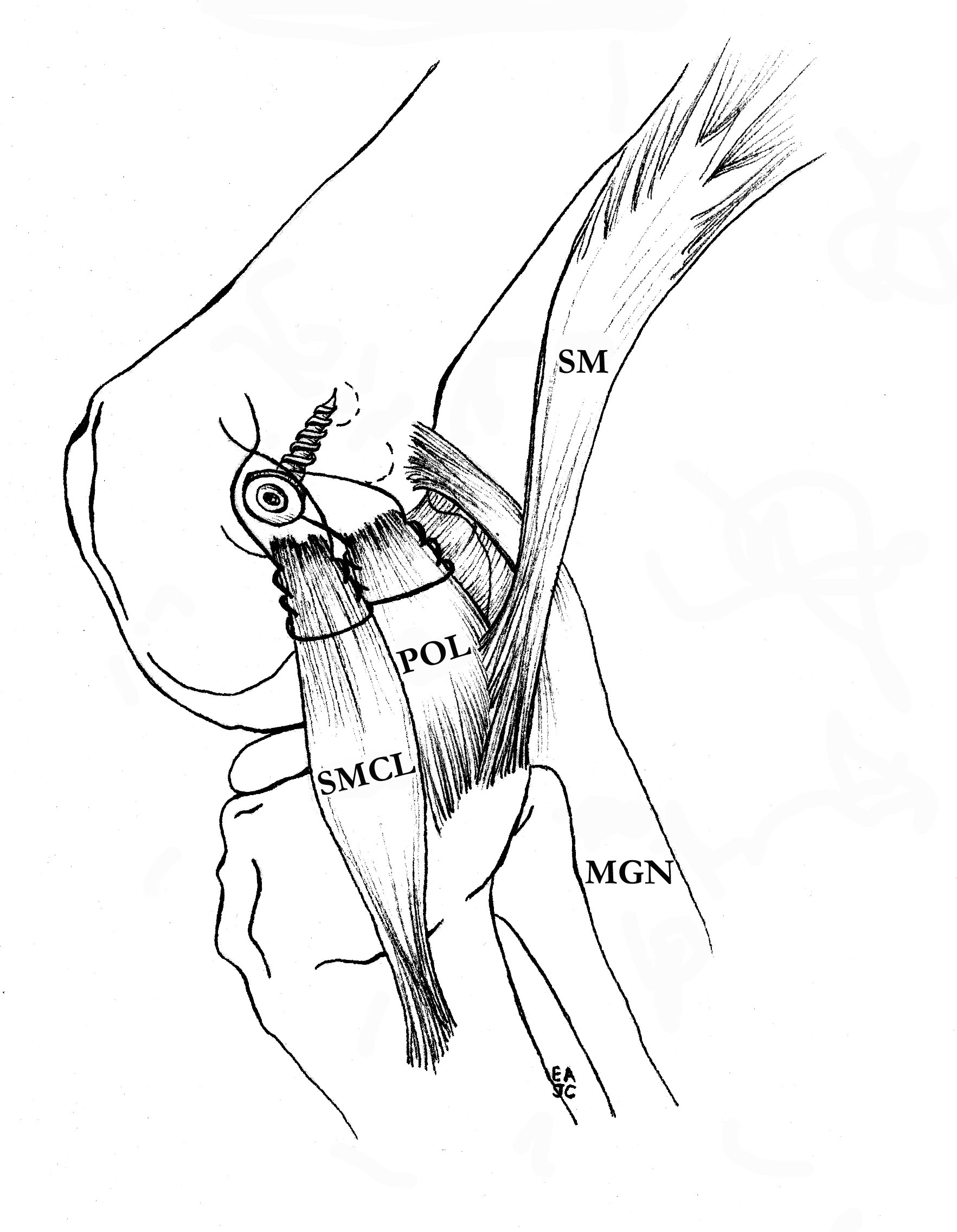
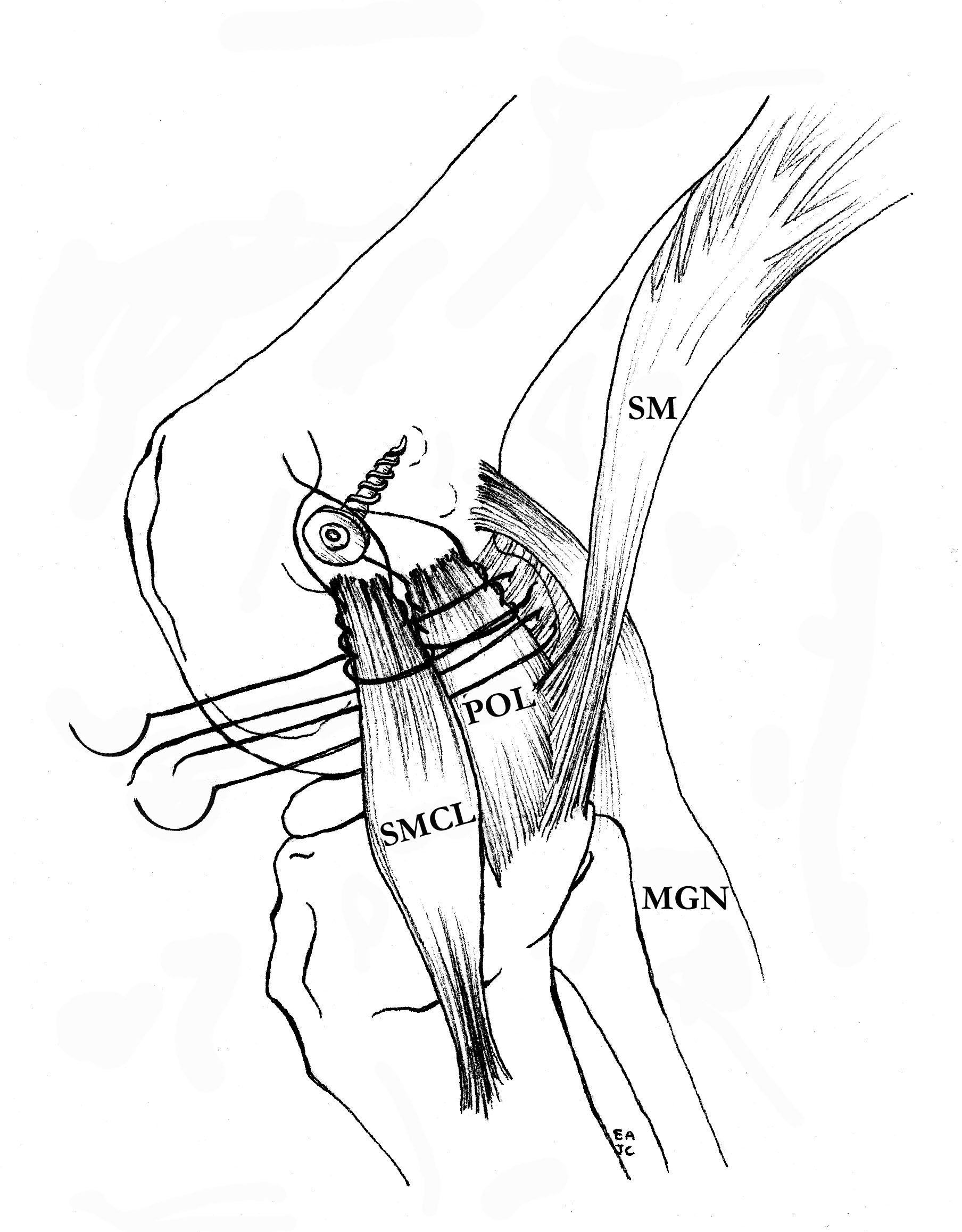
Repair
Reconstruction



Incision
- lateral border femur
- 15 cm proximal to knee joint
- curve anteriorly across patella tendon
Harvest ITB
- expose ITB
- width and length depend on patient size
- usually central 3 cm
- take 25 - 30 cm in length
- tubularise end and leave threads long to pass tendon
Lateral dissection
- expose and elevate LCL
- haemarthrosis
- DVT
- infection
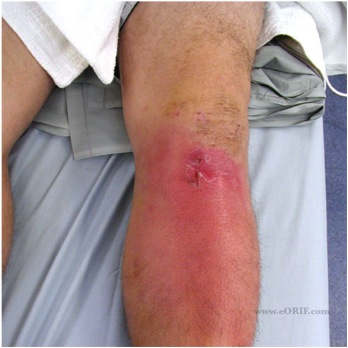
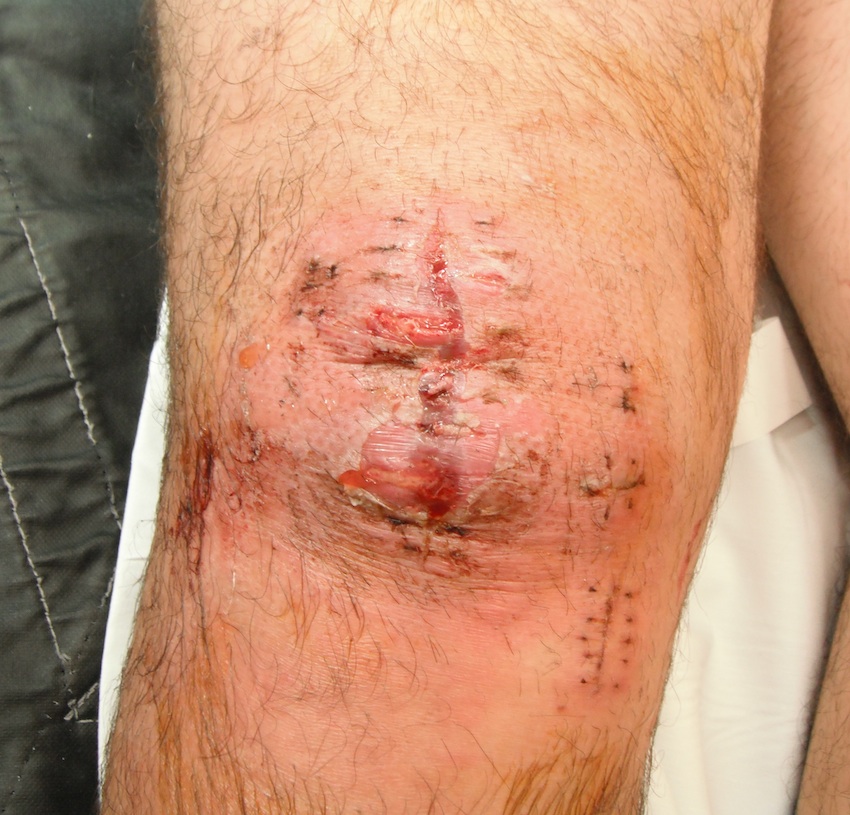
Incidence
Avoiding convergence of ACL tunnel and femoral tunnels of popliteus / LCL
- drill LCL and popliteus femoral tunnels anterior to avoid more posterior ACL tunnel
- avoid drilling LCL femoral tunnel proximal, to avoid more proximal ACL tunnel
Moatshe et al. Am J Sports Med 2017
- avoiding tunnel convergence
- aim LCL and popliteus tunnel anteriorly 35o
Graft Preparation
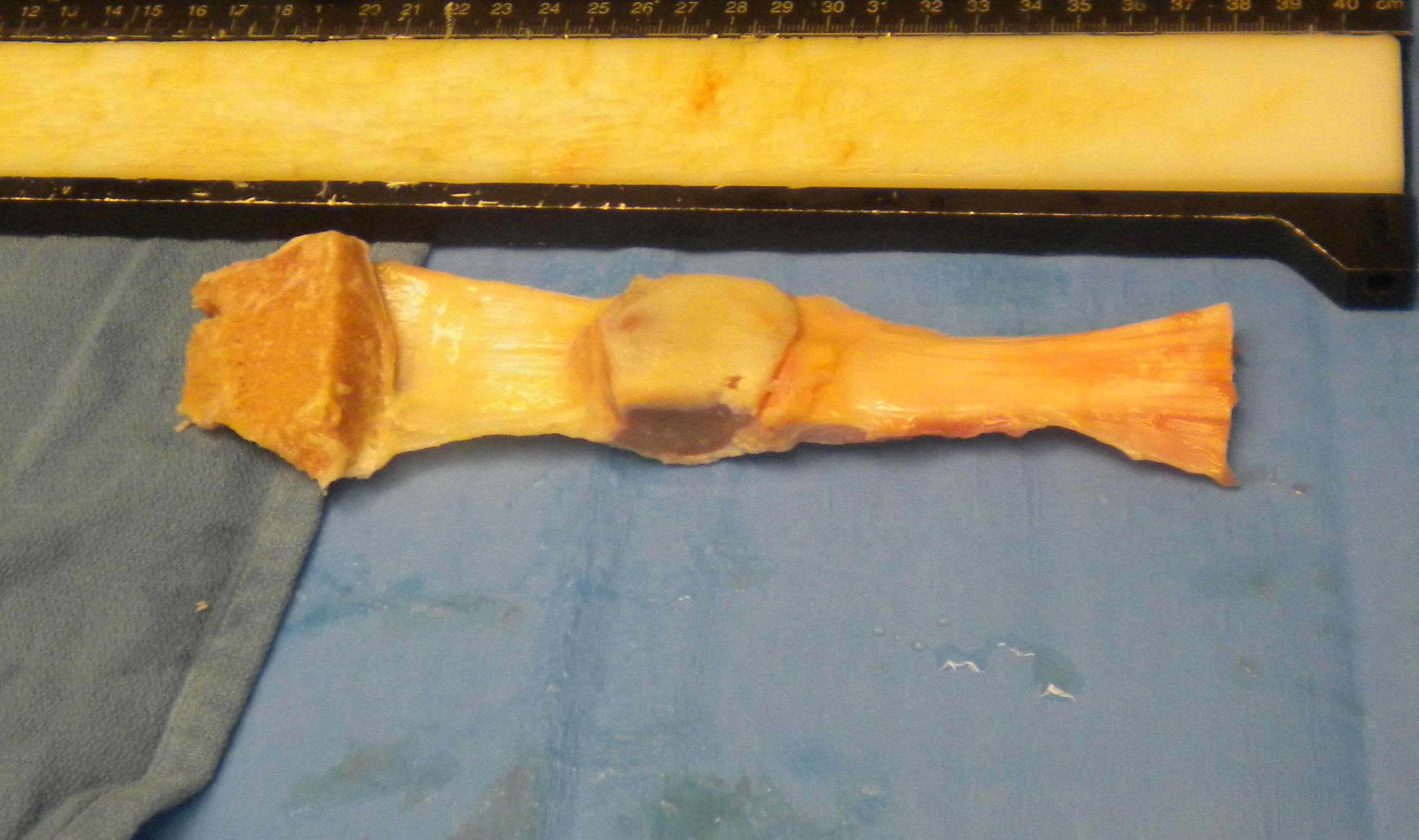
Defrost
- in 2 litres normal saline
- can add vancomycin powder
Choose which part of graft to use
- usually central third
- can take either side
- try to leave sufficient graft in case of disasters
- i.e. dropping or rupturing graft
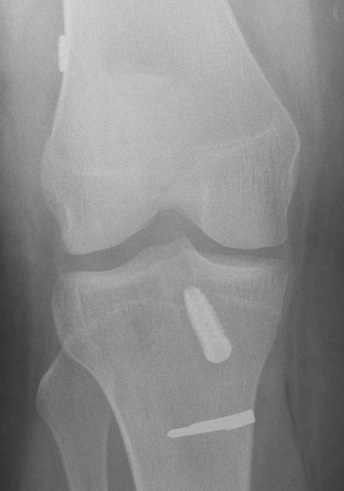
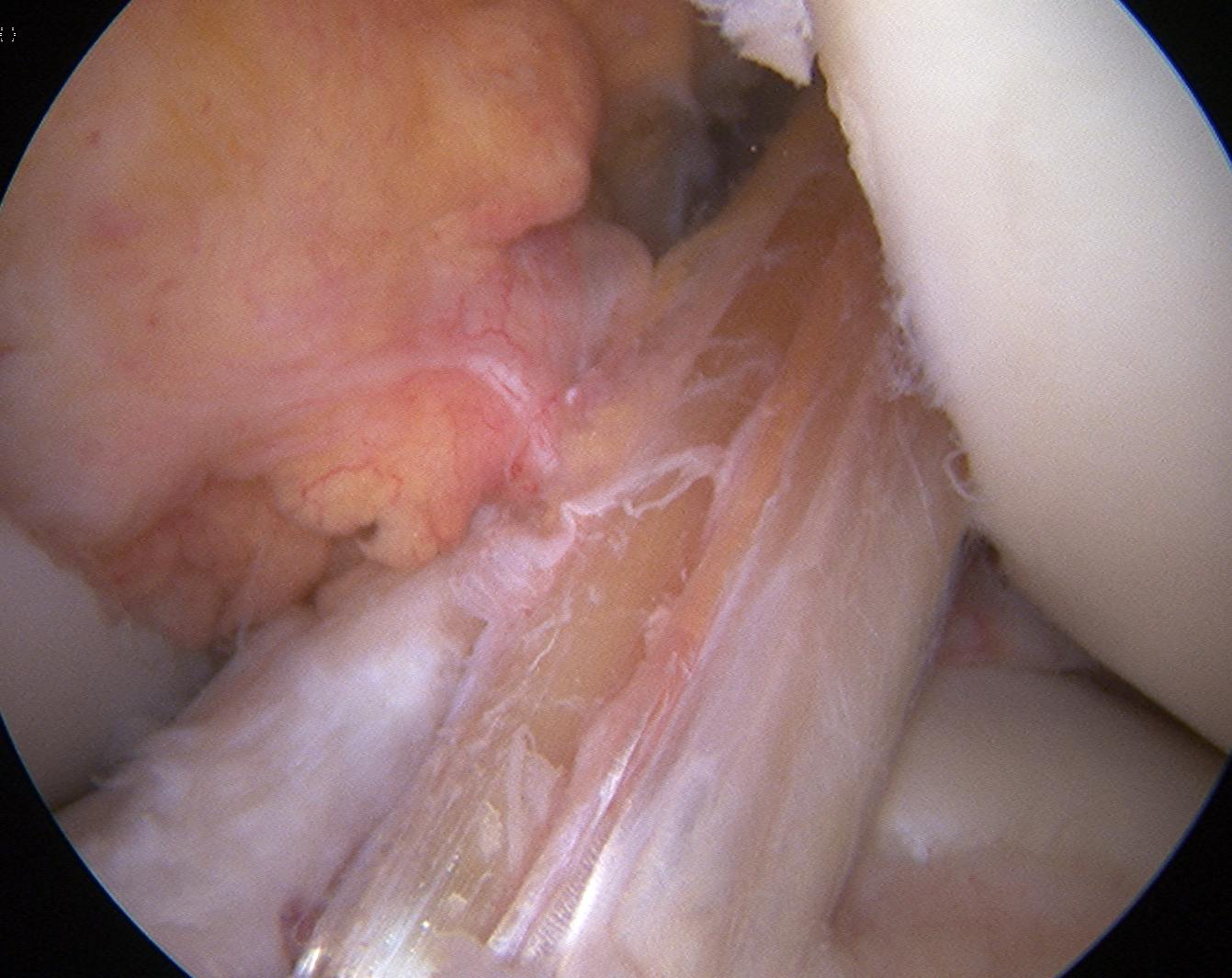
Advantage
- endobutton simple yet strong fixation
- endobutton eliminates problem if blow out back wall
Up to 8% patients with ACL reconstruction will have recurrent instability and graft failure
- increased with surgical inexperience
1. Be inadequate from the start
- inadequate tension
- poor tunnel placement
Shelbourne 1995
- noticed patients noncompliant with their rehab protocol were doing much better
- looked at what noncompliant patients were doing
- what they were doing was advancing activities as tolerated
Reviewed results of accelerated rehabilitation
- fewer ruptures with better ROM
Major recommendations
Natural History of ACL deficient knee is variable
- functional instability 15% - 90%
- progression to OA is variable
Depends on level of patient demands / activity
1. Late meniscal injury in ACL deficient knee
15-25%
2. Function
Daniels Am J Sports Med 1994
- 292 ACL defecients knees
Developmental Anatomy
Knee joint first appears as a mesenchymal cleft at 8 weeks gestation
- ACL and PCL separate entities by week 10